
Alcohol and Women ♀ Nioaka N. Campbell, MD University of South Carolina School of Medicine Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 1

Alcohol Use In Women u Significant health concern – 43% current drinkers u Alcohol use disorders (AUDs) – 4. 5 M with abuse – 2. 5 M with dependence Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 2

Alcohol Research u Most in male subjects (14% women) u May not consider gender differences – Body weight – Body fat – Alcohol dehydrogenase Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 3

‘Drink Like A Man’ u Gender gap narrowing: 1975=23% 2001=12% u College women in co-ed dorms adopt pattern of men u Rates are similar age 12 -17, 17% Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 4

Gender Specific Sequelae u Mortality rate: ♀= 2 x ♂ with AUDs u 3 rd leading cause of death, both sexes ages 35 -55 u Other sequelae: – Liver disease, CNS damage, Breast CA Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 5

Diagnosing AUDs In Women u <50% with AUD are identified by their MD u Yet: ♀ more often frequent their MD Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 6

This Lecture Will Cover: u Epidemiology of use and AUDs u Course of alcoholism in women u Consequences, gender specific u Assessment of women with AUDs u Treatment issues in this population Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 7

Epidemiology

Race/Ethnicity Comparisons u Caucasian – Highest prevalence – 55% past month use – 87% lifetime use Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 u African American – Highest abstainers: (46% vs 34% whites) – 37% past month use – 73% lifetime use 9

Race/Ethnicity Comparisons u Hispanic – 62% foreign born abstain – 40% past month use – 73% lifetime use u Native American – 65% abstain – 36% past month use – 81% lifetime use – Highest ‘heavy drinking’ >5 drinks/time, 30% Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 10

Abstinence u Reported in past year, 2004: – 56% women vs. 43% men u Lifetime, 1997: – 22% women vs. 13% men – ↓ with education – ↓ with ↑ salaries Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 11
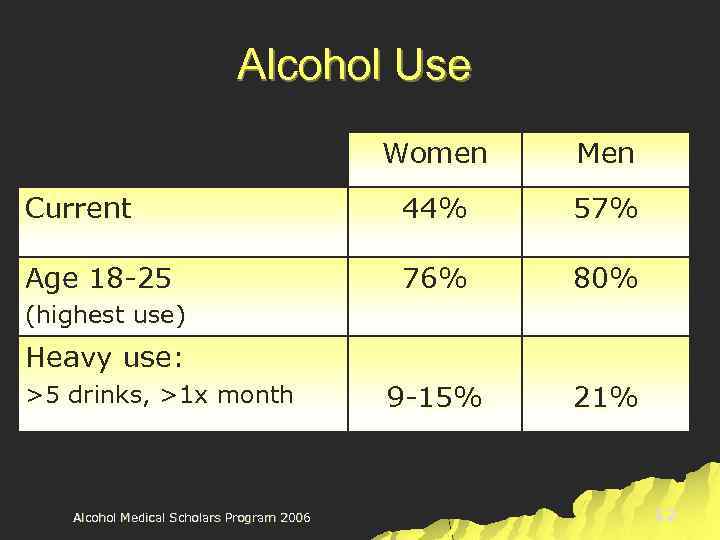
Alcohol Use Women Men Current 44% 57% Age 18 -25 76% 80% 9 -15% 21% (highest use) Heavy use: >5 drinks, >1 x month Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 12

Defining Alcohol Abuse u Clinically significant impairment in ≥ 1 in 12 months: – Failure to fulfill major obligations – Physically hazardous conditions – Legal problems (DUIs, disorderly cond. ) – Social/Interpersonal problems Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 13

Defining Alcohol Dependence u Clinically significant impairment in ≥ 3 in year: – Withdrawal - Tolerance – Larger amt. /longer period than intended – Persistent desire/efforts to cut down – Excessive time with or obtaining alcohol – Activities given up due to alcohol – Continued use despite problems Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 14

Alcohol Use Disorders Women Men Lifetime abuse 6% 13% Lifetime dependence 8% 20% Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 15

Drinking Consequences u Driving fatalities: 9% ♀ vs. 18% ♂ u Victimization: ETOH related rape, assault u Domestic violence: victims 2 X risk of AUD Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 16

Drinking Consequences u Unemployment: 48% ♀ vs. 33% ♂ u Antisocial PD: 15% ♂ vs. 5% ♀ u Health consequences: liver, CNS, hangover Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 17
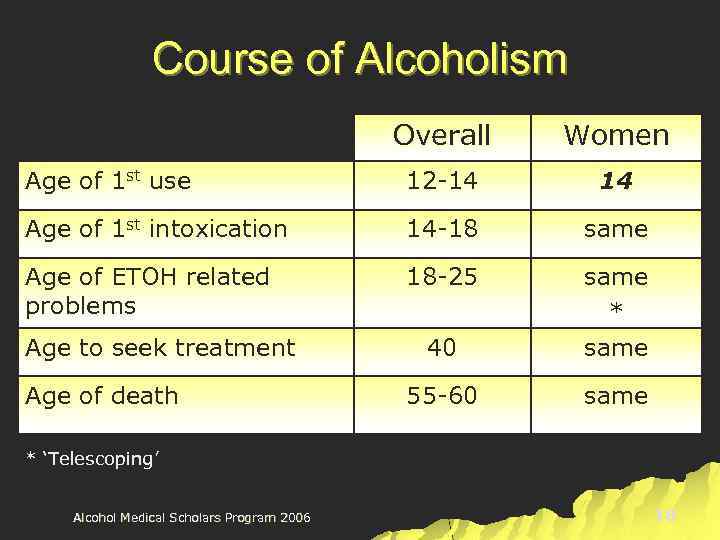
Course of Alcoholism Overall Women Age of 1 st use 12 -14 14 Age of 1 st intoxication 14 -18 same Age of ETOH related problems 18 -25 40 same * same 55 -60 same Age to seek treatment Age of death * ‘Telescoping’ Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 18

Health Problems and AUDs u Axis I D/O: major depression, anxiety, eating, suicide(40%♀ with AUD) u Comorbidity vs. independent disorders u Hormonal disruption, changes u Breast Cancer – 2% cases attributed to alcohol use Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 19

Fetal Alcohol Syndrome u Varying components: – Facial malformations – Pre and post-natal growth retardation – CNS abnormalities – Spontaneous abortions – Mild to moderate MR Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 20

Fetal Alcohol Syndrome u u 1% of US population 15% pregnant age 14 -44 “had a drink” u $200 M/yr for children with FAS u Since 1990 guidelines – abstention Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 21

Assessment of Women with AUDs u Avoid stereotype – Stigma, guilt – Presentation u History – Routine screening – Open vs closed questions – Non-judgmental attitudes – Problem focused assessment Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 22

Psychosocial Assessment Factors u Risk u Protective – Isolation – Multiple roles – Early initiation – Married – Hx of neglect, abuse – Student athletes – Other Axis I D/O – Tobacco Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 23

Genetic Factors u 50 -60% variation of AUD risk u Twin and adoption studies Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 24

Assessment Challenges u Time u Objective Tools – CAGE - MAST - AUDIT (Gender and Racial differences) u Pregnancy – HBQ -TACE Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 25

Treatment u 1 in 4 ♀ with AUD receive tx u♂ with AUD: 2 X likely as ♀ to receive tx u Barriers – Stigma – Legal sanction Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 - Child care Limited resources 26

Treatment Programs u Some currently provide: – Womens’ gp, child care, post partum u Womens’ only: – 2 X completion – Child care options – Minority populations Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 27

DHHS Treatment Guidelines u Child care u Vocational/Legal assistance u Female intake provider u Empower u General medical assessment u Thorough assessments Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 28

Summary u Use/AUDs: significant womens’ issues u Course: varied, unique u Consequences: gender specific u Assessment: routine, thorough u Treatment: comprehensive, individualized Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 29

Questions? ♀ Alcohol Medical Scholars Program 2006 30