 Alaska
Alaska
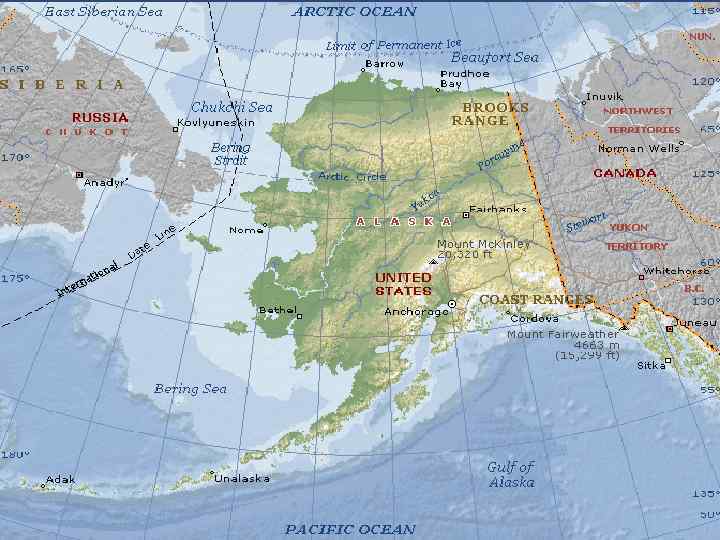
 • • Alaska, northernmost and westernmost state of the United States, and the largest state of the Union. It occupies the extreme northwestern region of the North American continent and is separated from Asia by the 82 -km wide Bering Strait. Alaska has belonged to the United States since 1867, when it was bought from Russia. By 1900 Alaska had become a land of golden opportunity as one gold discovery followed another and prospectors arrived by the tens of thousands. On January 3, 1959, Alaska was admitted to the Union as the 49 th state.
• • Alaska, northernmost and westernmost state of the United States, and the largest state of the Union. It occupies the extreme northwestern region of the North American continent and is separated from Asia by the 82 -km wide Bering Strait. Alaska has belonged to the United States since 1867, when it was bought from Russia. By 1900 Alaska had become a land of golden opportunity as one gold discovery followed another and prospectors arrived by the tens of thousands. On January 3, 1959, Alaska was admitted to the Union as the 49 th state.
 • Alaska is a rugged, wild, beautiful land of majestic mountains and deep, high-walled fjords; of slow-moving glaciers and still-active volcanoes; of dense, coniferous forests and desolate, treeless islands; of hot springs and icy streams. It is a land of contrasts, with extremes of wind and sun, snow and rain, heat and cold. • Alaska is called the Last Frontier, because of its opportunities and many lightly settled regions, and the Land of the Midnight Sun, because the sun shines nearly around the clock during Alaskan summers. Anchorage is Alaska’s largest city, and Juneau is the state capital. • Alaska occupies the northwestern portion of North America. It includes the Aleutian Islands, a chain of about 150 islands that arcs westward across the Pacific Ocean. • Alaska has a total area of 1, 593, 438 sq km , including 45, 327 sq km of inland water and 70, 849 sq km of coastal water. Alaska has more area of lakes and rivers than any other state. • Alaska can be divided into three major natural regions: the Coast Ranges region, the Interior region, and the Arctic region.
• Alaska is a rugged, wild, beautiful land of majestic mountains and deep, high-walled fjords; of slow-moving glaciers and still-active volcanoes; of dense, coniferous forests and desolate, treeless islands; of hot springs and icy streams. It is a land of contrasts, with extremes of wind and sun, snow and rain, heat and cold. • Alaska is called the Last Frontier, because of its opportunities and many lightly settled regions, and the Land of the Midnight Sun, because the sun shines nearly around the clock during Alaskan summers. Anchorage is Alaska’s largest city, and Juneau is the state capital. • Alaska occupies the northwestern portion of North America. It includes the Aleutian Islands, a chain of about 150 islands that arcs westward across the Pacific Ocean. • Alaska has a total area of 1, 593, 438 sq km , including 45, 327 sq km of inland water and 70, 849 sq km of coastal water. Alaska has more area of lakes and rivers than any other state. • Alaska can be divided into three major natural regions: the Coast Ranges region, the Interior region, and the Arctic region.
 Climate • Alaska has four different climatic zones: maritime, continental, transitional, and Arctic. Kodiak, the Aleutians, and southeastern and south central Alaska have a climate primarily influenced by the sea, so that temperatures do not vary greatly throughout the year, but rainfall is quite high and frequent. • Western Alaska, a transitional climate, has much lower temperatures and less rainfall, but, like the Aleutians, frequent periods of extremely high winds and blowing snow. • Arctic Alaska has very little snowfall, cool summer temperatures, and frequent high winds, particularly from the east. The interior has a continental climate characterized by extremely great temperature variations, but only moderate rain and snow.
Climate • Alaska has four different climatic zones: maritime, continental, transitional, and Arctic. Kodiak, the Aleutians, and southeastern and south central Alaska have a climate primarily influenced by the sea, so that temperatures do not vary greatly throughout the year, but rainfall is quite high and frequent. • Western Alaska, a transitional climate, has much lower temperatures and less rainfall, but, like the Aleutians, frequent periods of extremely high winds and blowing snow. • Arctic Alaska has very little snowfall, cool summer temperatures, and frequent high winds, particularly from the east. The interior has a continental climate characterized by extremely great temperature variations, but only moderate rain and snow.
 Rivers and Lakes • The principal river is the Yukon River, which rises in the nearby Yukon Territory. About two-thirds of its 3, 190 km course lies in Alaska. • The Yukon is one of the longest navigable rivers in the world. Shallow-draft riverboats and barges can navigate its whole length during the ice-free summer weeks. Its main tributaries include the Porcupine, the Tanana, the Koyukuk, and the Innoko rivers.
Rivers and Lakes • The principal river is the Yukon River, which rises in the nearby Yukon Territory. About two-thirds of its 3, 190 km course lies in Alaska. • The Yukon is one of the longest navigable rivers in the world. Shallow-draft riverboats and barges can navigate its whole length during the ice-free summer weeks. Its main tributaries include the Porcupine, the Tanana, the Koyukuk, and the Innoko rivers.
 Plant Life • Forests cover 35 percent of Alaska’s land area. The most important commercial species of trees are birch, Sitka spruce (the state tree), western hemlock, black spruce, and white spruce.
Plant Life • Forests cover 35 percent of Alaska’s land area. The most important commercial species of trees are birch, Sitka spruce (the state tree), western hemlock, black spruce, and white spruce.
 Animal life • Bears Fishing in Alaska’s vast wilderness provides a home for a wide range of wildlife, including several species of bears. Here, an Alaska brown bear and her yearling cubs fish for salmon. • The Kodiak, a species of brown bear found on Kodiak Island, can reach a weight of 780 kg (1700 lb) and a height of 3 m (10 ft). Polar bears can be found along Alaska’s Arctic coast, and black bears also inhabit the state. • In southeastern Alaska are found the black bear, grizzly bear, black-tailed deer, moose, mountain goat, marten, red fox, mink, wolf, coyote, otter, and beaver. The sea lion, harbor seal, sea otter, porpoise, and several species of whale are common along the coast. Halibut, herring, cod, crab, and shrimp are also found in abundance in coastal waters.
Animal life • Bears Fishing in Alaska’s vast wilderness provides a home for a wide range of wildlife, including several species of bears. Here, an Alaska brown bear and her yearling cubs fish for salmon. • The Kodiak, a species of brown bear found on Kodiak Island, can reach a weight of 780 kg (1700 lb) and a height of 3 m (10 ft). Polar bears can be found along Alaska’s Arctic coast, and black bears also inhabit the state. • In southeastern Alaska are found the black bear, grizzly bear, black-tailed deer, moose, mountain goat, marten, red fox, mink, wolf, coyote, otter, and beaver. The sea lion, harbor seal, sea otter, porpoise, and several species of whale are common along the coast. Halibut, herring, cod, crab, and shrimp are also found in abundance in coastal waters.
 THE PEOPLE OF ALASKA • Alaska Whites make up 69. 3 percent of the population of Alaska. • The largest other group is composed of descendants of the state’s original inhabitants–the Eskimo, the Aleut, and other indigenous peoples.
THE PEOPLE OF ALASKA • Alaska Whites make up 69. 3 percent of the population of Alaska. • The largest other group is composed of descendants of the state’s original inhabitants–the Eskimo, the Aleut, and other indigenous peoples.
 Principal Cities • Most of the principal cities in Alaska lie along the coast in the southern part of the state. All of them are small by comparison with the chief cities of nearly all other states. • Anchorage, with a population (2000) of 260, 283, is by far the largest city in Alaska. It serves as the chief commercial center of southern Alaska and as the principal transportation center of the entire state. Juneau, with a population of 30, 711, is the state capital and the largest city in the Alaska Panhandle. It is also a port and commercial center. Sitka was the capital of Russian America and the first capital of the territory of Alaska. The port city is now a government and education center.
Principal Cities • Most of the principal cities in Alaska lie along the coast in the southern part of the state. All of them are small by comparison with the chief cities of nearly all other states. • Anchorage, with a population (2000) of 260, 283, is by far the largest city in Alaska. It serves as the chief commercial center of southern Alaska and as the principal transportation center of the entire state. Juneau, with a population of 30, 711, is the state capital and the largest city in the Alaska Panhandle. It is also a port and commercial center. Sitka was the capital of Russian America and the first capital of the territory of Alaska. The port city is now a government and education center.
 National Parks • The 15 national parks in Alaska are home to the United States’ tallest mountains and biggest glaciers and some of its most exotic wildlife. Alaska contains the country’s six largest national parks: Wrangell-Saint Elias, Gates of the Arctic, Denali, Lake Clark, Katmai, and Glacier Bay. • Of the 20 highest mountains in the United States, 17 are in Alaska. Mount Mc. Kinley, North America’s largest mountain at 6, 194 m (20, 320 ft), is a defining highlight in Denali National Park and Preserve.
National Parks • The 15 national parks in Alaska are home to the United States’ tallest mountains and biggest glaciers and some of its most exotic wildlife. Alaska contains the country’s six largest national parks: Wrangell-Saint Elias, Gates of the Arctic, Denali, Lake Clark, Katmai, and Glacier Bay. • Of the 20 highest mountains in the United States, 17 are in Alaska. Mount Mc. Kinley, North America’s largest mountain at 6, 194 m (20, 320 ft), is a defining highlight in Denali National Park and Preserve.
 The end
The end


