871d0760615082bfa5b27aa000af00f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 al ste Sy nic ch Te ms Modeling Do. DAF Compliant Architectures Operational © Telelogic AB
al ste Sy nic ch Te ms Modeling Do. DAF Compliant Architectures Operational © Telelogic AB
 An Architecture Development Process © Telelogic AB
An Architecture Development Process © Telelogic AB
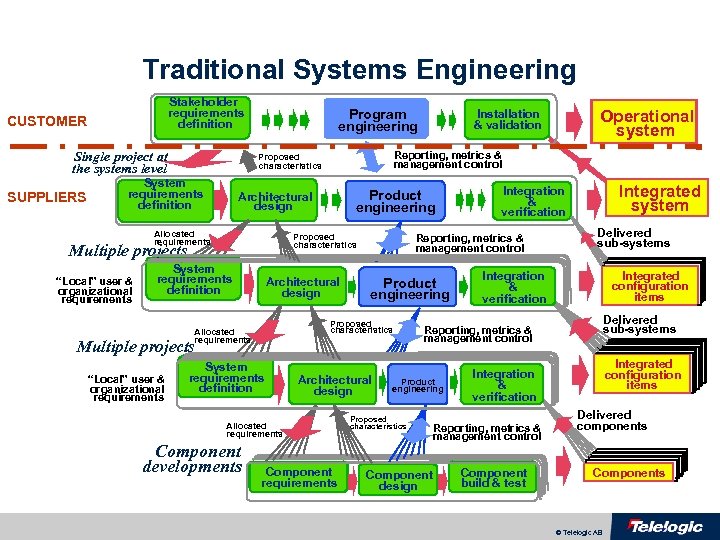 Traditional Systems Engineering Stakeholder requirements definition CUSTOMER Single project at the systems level SUPPLIERS Program engineering Product engineering Architectural design Allocated requirements Proposed characteristics Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics System requirements definition Architectural design Product engineering Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements System requirements definition Architectural design Allocated requirements Component developments Component requirements Integrated system Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics Allocated requirements Operational system Installation & validation Delivered sub-systems Integration & verification Integrated configuration items Delivered sub-systems Reporting, metrics & management control Product engineering Proposed characteristics Component design Integrated configuration items Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Component build & test Delivered components Components © Telelogic AB
Traditional Systems Engineering Stakeholder requirements definition CUSTOMER Single project at the systems level SUPPLIERS Program engineering Product engineering Architectural design Allocated requirements Proposed characteristics Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics System requirements definition Architectural design Product engineering Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements System requirements definition Architectural design Allocated requirements Component developments Component requirements Integrated system Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics Allocated requirements Operational system Installation & validation Delivered sub-systems Integration & verification Integrated configuration items Delivered sub-systems Reporting, metrics & management control Product engineering Proposed characteristics Component design Integrated configuration items Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Component build & test Delivered components Components © Telelogic AB
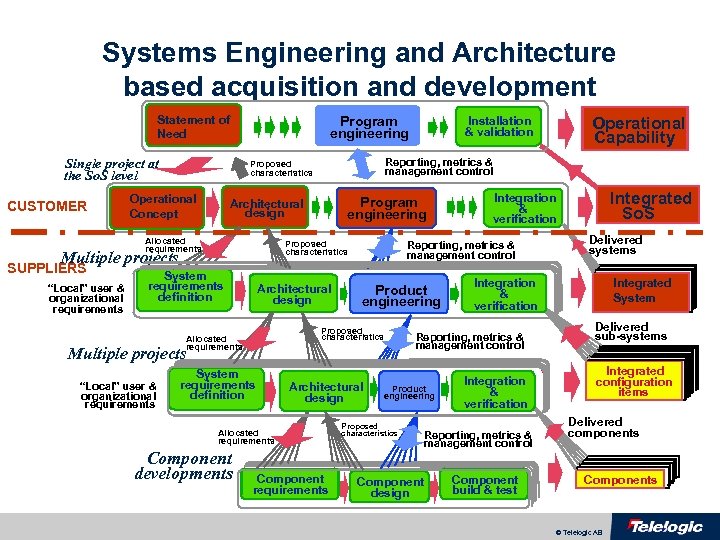 Systems Engineering and Architecture based acquisition and development Statement of Need Single project at the So. S level CUSTOMER Program engineering Proposed characteristics Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements Program engineering Architectural design Allocated requirements SUPPLIERS Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics Operational Concept System requirements definition Architectural design Product engineering Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements System requirements definition Architectural design Allocated requirements Component developments Component requirements Proposed characteristics Component design Delivered systems Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Product engineering Integrated So. S Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics Allocated requirements Operational Capability Installation & validation Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Component build & test Integrated System Delivered sub-systems Integrated configuration items Delivered components Components © Telelogic AB
Systems Engineering and Architecture based acquisition and development Statement of Need Single project at the So. S level CUSTOMER Program engineering Proposed characteristics Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements Program engineering Architectural design Allocated requirements SUPPLIERS Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics Operational Concept System requirements definition Architectural design Product engineering Multiple projects “Local” user & organizational requirements System requirements definition Architectural design Allocated requirements Component developments Component requirements Proposed characteristics Component design Delivered systems Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Product engineering Integrated So. S Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Proposed characteristics Allocated requirements Operational Capability Installation & validation Integration & verification Reporting, metrics & management control Component build & test Integrated System Delivered sub-systems Integrated configuration items Delivered components Components © Telelogic AB
 Systems Engineering is a Club Sandwich Our apologies to Forrest Gump! Requirements layer Modelling layer Requirements layer © Telelogic AB
Systems Engineering is a Club Sandwich Our apologies to Forrest Gump! Requirements layer Modelling layer Requirements layer © Telelogic AB
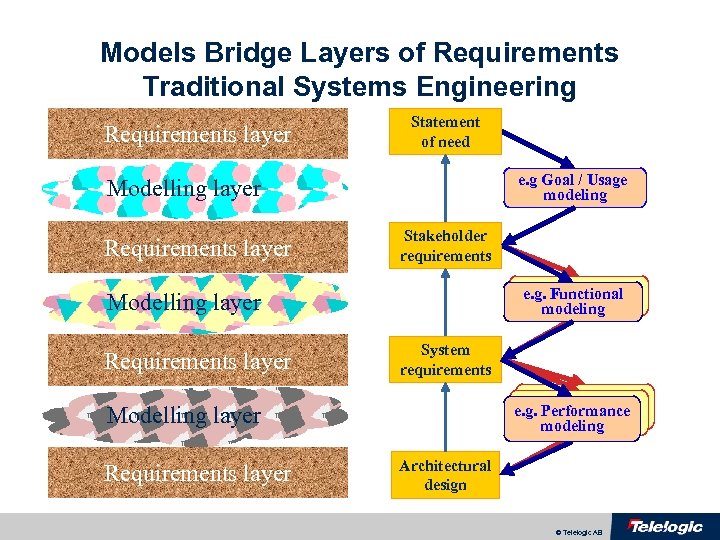 Models Bridge Layers of Requirements Traditional Systems Engineering Requirements layer Statement of need e. g Goal / Usage modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Stakeholder requirements Functional e. g. Functional modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer System requirements Functional e. g. Performance modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Architectural design © Telelogic AB
Models Bridge Layers of Requirements Traditional Systems Engineering Requirements layer Statement of need e. g Goal / Usage modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Stakeholder requirements Functional e. g. Functional modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer System requirements Functional e. g. Performance modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Architectural design © Telelogic AB
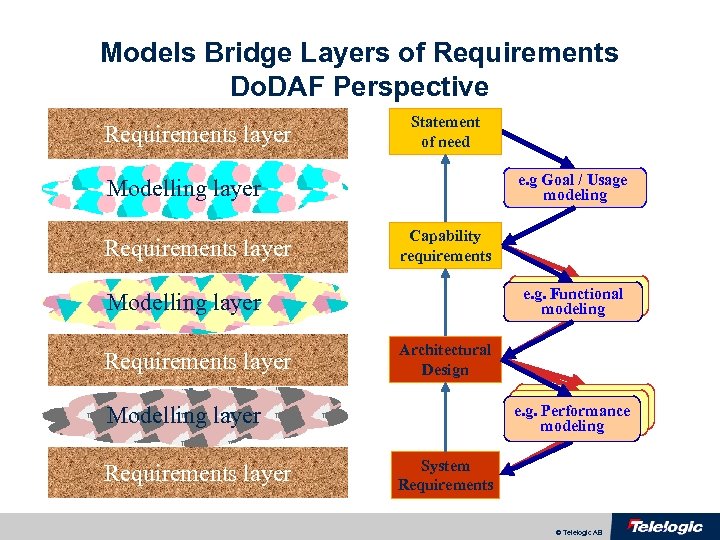 Models Bridge Layers of Requirements Do. DAF Perspective Requirements layer Statement of need e. g Goal / Usage modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Capability requirements Functional e. g. Functional modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Architectural Design Functional e. g. Performance modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer System Requirements © Telelogic AB
Models Bridge Layers of Requirements Do. DAF Perspective Requirements layer Statement of need e. g Goal / Usage modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Capability requirements Functional e. g. Functional modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer Architectural Design Functional e. g. Performance modeling Modelling layer Requirements layer System Requirements © Telelogic AB
 The Role of Models can be used to complement requirements management at each of the different layers and are useful in a number of ways: • Architecture modeling adds formality to the design process that lies between each layer of requirement • The architecture model promotes an active understanding of the details in large requirements documents • The design rationale gathered around the architecture model becomes the rationale for traceability between layers of requirements • The structure of the architecture model can be used to give structure to the requirements document • The architecture model is the basis for: – costing, interoperability analysis, partitioning to different development teams, scheduling (WBS), analysis of alternatives, early validation, and risk management. © Telelogic AB
The Role of Models can be used to complement requirements management at each of the different layers and are useful in a number of ways: • Architecture modeling adds formality to the design process that lies between each layer of requirement • The architecture model promotes an active understanding of the details in large requirements documents • The design rationale gathered around the architecture model becomes the rationale for traceability between layers of requirements • The structure of the architecture model can be used to give structure to the requirements document • The architecture model is the basis for: – costing, interoperability analysis, partitioning to different development teams, scheduling (WBS), analysis of alternatives, early validation, and risk management. © Telelogic AB
 Systems Modeling Techniques • A very wide range of very domain-specific modeling techniques may be used to aid systems design: – Aerodynamic models using wind tunnels – Safety, reliability and maintainability models – Weight distribution models – Network performance models using queuing theory • Although many models are necessarily domain-specific, every system has aspects which can be modeled using a basic approach such as Do. DAF. • A basic architecture model that proves that the architecture provides the desired capabilities (structure and behavior) should be done prior to committing resources to more detailed modeling and simulation. © Telelogic AB
Systems Modeling Techniques • A very wide range of very domain-specific modeling techniques may be used to aid systems design: – Aerodynamic models using wind tunnels – Safety, reliability and maintainability models – Weight distribution models – Network performance models using queuing theory • Although many models are necessarily domain-specific, every system has aspects which can be modeled using a basic approach such as Do. DAF. • A basic architecture model that proves that the architecture provides the desired capabilities (structure and behavior) should be done prior to committing resources to more detailed modeling and simulation. © Telelogic AB
 The Basic Systems Engineering Process © Telelogic AB
The Basic Systems Engineering Process © Telelogic AB
 Activities in the Systems Engineering Process • There are two major activities in the Basic systems engineering process: – To analyze the input requirements and create a model – To derive the output requirements from the model • These steps are applied recursively through the layers. © Telelogic AB
Activities in the Systems Engineering Process • There are two major activities in the Basic systems engineering process: – To analyze the input requirements and create a model – To derive the output requirements from the model • These steps are applied recursively through the layers. © Telelogic AB
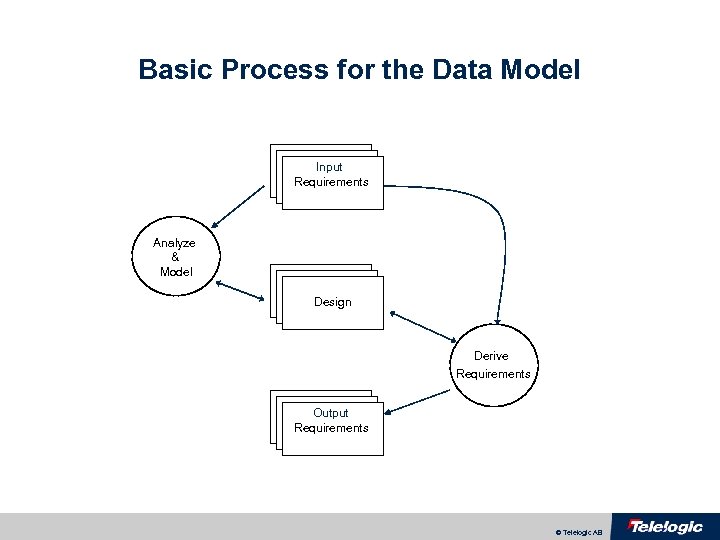 Basic Process for the Data Model Requirements Input Requirements documents Analyze & Model Requirements documents Design documents Derive Requirements Output Requirements documents © Telelogic AB
Basic Process for the Data Model Requirements Input Requirements documents Analyze & Model Requirements documents Design documents Derive Requirements Output Requirements documents © Telelogic AB
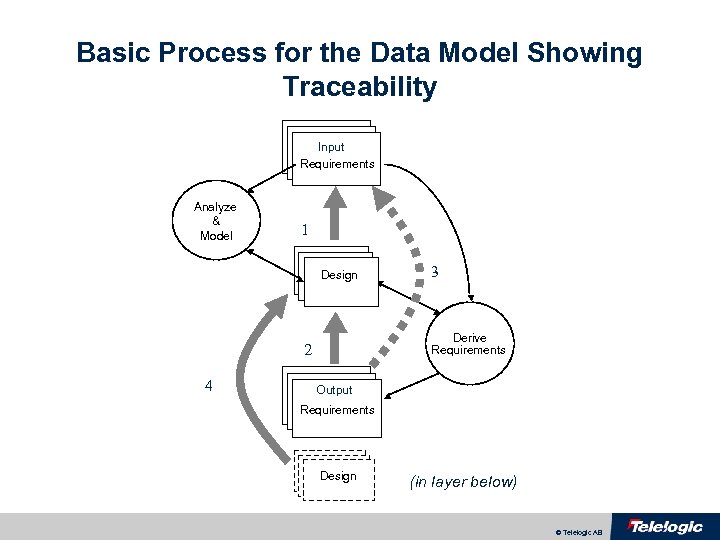 Basic Process for the Data Model Showing Traceability Requirements Input documents Requirements Analyze & Model 1 Design documents 2 4 3 Derive Requirements Output documents Requirements documents Design documents (in layer below) © Telelogic AB
Basic Process for the Data Model Showing Traceability Requirements Input documents Requirements Analyze & Model 1 Design documents 2 4 3 Derive Requirements Output documents Requirements documents Design documents (in layer below) © Telelogic AB
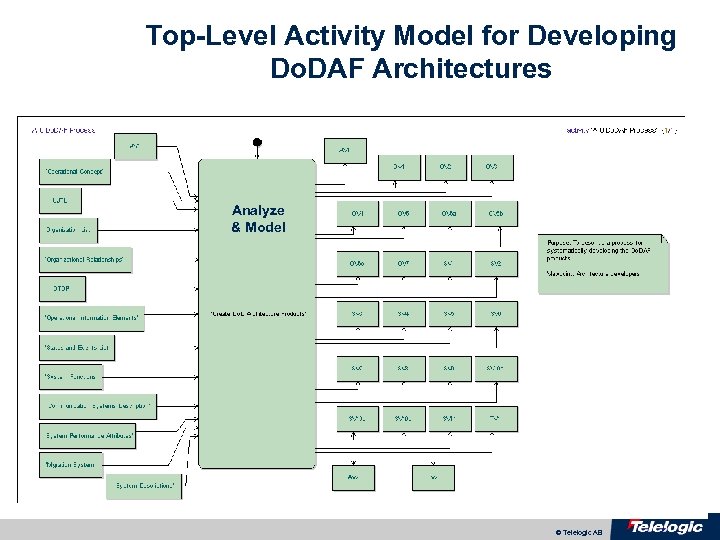 Top-Level Activity Model for Developing Do. DAF Architectures Analyze & Model © Telelogic AB
Top-Level Activity Model for Developing Do. DAF Architectures Analyze & Model © Telelogic AB
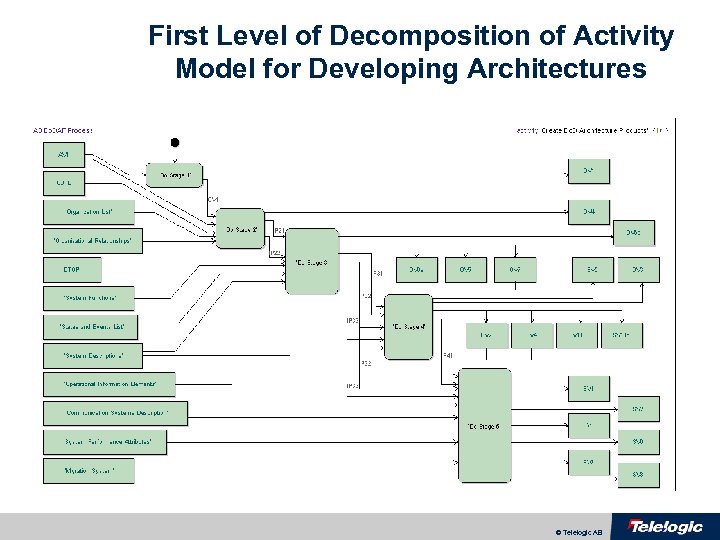 First Level of Decomposition of Activity Model for Developing Architectures © Telelogic AB
First Level of Decomposition of Activity Model for Developing Architectures © Telelogic AB
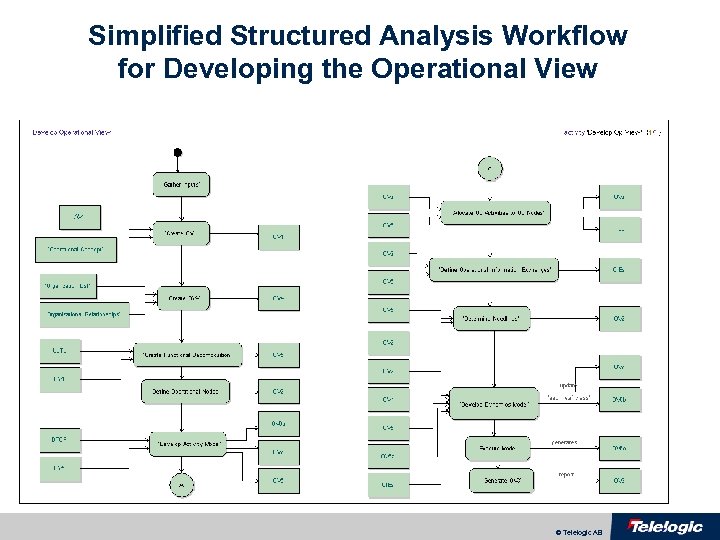 Simplified Structured Analysis Workflow for Developing the Operational View © Telelogic AB
Simplified Structured Analysis Workflow for Developing the Operational View © Telelogic AB
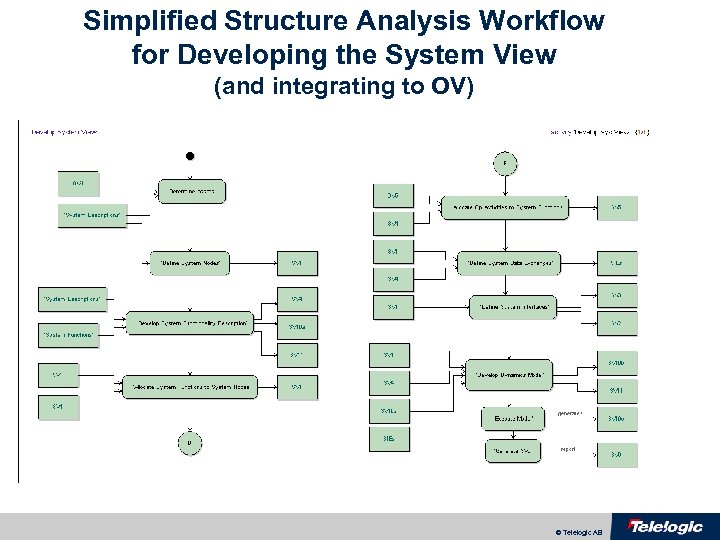 Simplified Structure Analysis Workflow for Developing the System View (and integrating to OV) © Telelogic AB
Simplified Structure Analysis Workflow for Developing the System View (and integrating to OV) © Telelogic AB
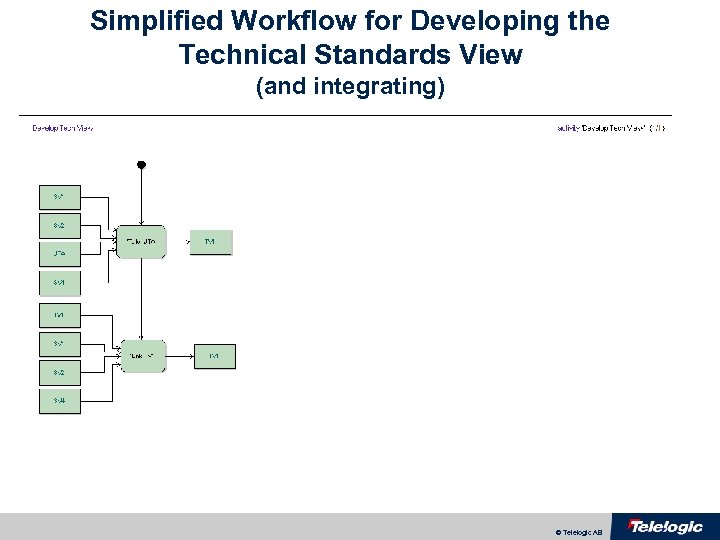 Simplified Workflow for Developing the Technical Standards View (and integrating) © Telelogic AB
Simplified Workflow for Developing the Technical Standards View (and integrating) © Telelogic AB
 Object Oriented Workflow • Structure Analysis decomposes behaviour and structure separately, then does an explicit allocation of behaviour to structure. – Data, Behaviour and Structure are considered independently – Activity model (OV-5) focus • OO Methods focus on objects (the things that possess behaviour and structure) and does implicit allocation of behaviour to structure. – Data, Behaviour and Structure are considered simultaneously – Main goal is to describe re-useable objects that encapsulate behaviour and structure. – Lends itself to iterative development and resilient architectures. – Event Trace (OV-6 c) focus • The Case Study uses a blend of the two methodologies (as does Do. DAF itself). © Telelogic AB
Object Oriented Workflow • Structure Analysis decomposes behaviour and structure separately, then does an explicit allocation of behaviour to structure. – Data, Behaviour and Structure are considered independently – Activity model (OV-5) focus • OO Methods focus on objects (the things that possess behaviour and structure) and does implicit allocation of behaviour to structure. – Data, Behaviour and Structure are considered simultaneously – Main goal is to describe re-useable objects that encapsulate behaviour and structure. – Lends itself to iterative development and resilient architectures. – Event Trace (OV-6 c) focus • The Case Study uses a blend of the two methodologies (as does Do. DAF itself). © Telelogic AB
 The Telelogic Enterprise Architect © Telelogic AB
The Telelogic Enterprise Architect © Telelogic AB
 Telelogic Enterprise Architect - Objective • Use integrated, best of breed tools – Map work products to tool that best supports them • Provide domain-specific menus and help – Make it easy to adopt • Leverage automation – Reports, templates and model execution • Model-based tool repository – Easy model development and update with real-time checking • Standards-based – Proven, standard notation, executable and scalable – Methodology Independent: OO or SADT or a combination – Direct hand-off to systems engineering and software engineering © Telelogic AB
Telelogic Enterprise Architect - Objective • Use integrated, best of breed tools – Map work products to tool that best supports them • Provide domain-specific menus and help – Make it easy to adopt • Leverage automation – Reports, templates and model execution • Model-based tool repository – Easy model development and update with real-time checking • Standards-based – Proven, standard notation, executable and scalable – Methodology Independent: OO or SADT or a combination – Direct hand-off to systems engineering and software engineering © Telelogic AB
 Telelogic Enterprise Architect - What is it? • A TAU G 2 Do. DAF profile and set of templates in DOORS to support and simplify: – Production of architecture descriptions – Analysis of architecture descriptions – Reporting © Telelogic AB
Telelogic Enterprise Architect - What is it? • A TAU G 2 Do. DAF profile and set of templates in DOORS to support and simplify: – Production of architecture descriptions – Analysis of architecture descriptions – Reporting © Telelogic AB
 Telelogic Enterprise Architect - Benefits • Comprehensive support of all views and products – Automated consistency between products – Automatic generation of selected products (e. g. OV-3, OV-6 c, SV-3, SV-5, SV-6, SV-10 c) – Custom icons to enhance communication – Meta-model, based on CADM, drives the tool to speak the language of the domain • Executable Models – Verify behaviour and completeness early • Integration from requirements and standards, through enterprise architecture, to systems designs, development and acquisition – Complete traceability easy to establish and maintain (“Link as you think”) – Impact and gap analysis – Same tool for System Architecture, Software Design, Software Implementation. © Telelogic AB
Telelogic Enterprise Architect - Benefits • Comprehensive support of all views and products – Automated consistency between products – Automatic generation of selected products (e. g. OV-3, OV-6 c, SV-3, SV-5, SV-6, SV-10 c) – Custom icons to enhance communication – Meta-model, based on CADM, drives the tool to speak the language of the domain • Executable Models – Verify behaviour and completeness early • Integration from requirements and standards, through enterprise architecture, to systems designs, development and acquisition – Complete traceability easy to establish and maintain (“Link as you think”) – Impact and gap analysis – Same tool for System Architecture, Software Design, Software Implementation. © Telelogic AB
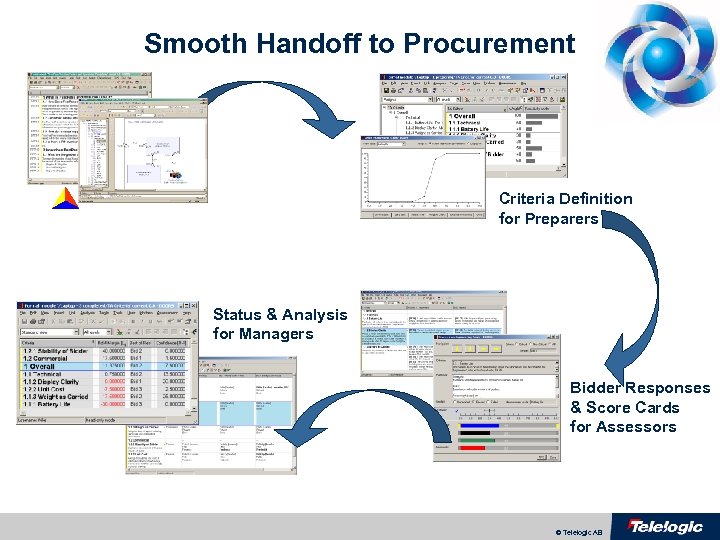 Smooth Handoff to Procurement Criteria Definition for Preparers Status & Analysis for Managers Bidder Responses & Score Cards for Assessors © Telelogic AB
Smooth Handoff to Procurement Criteria Definition for Preparers Status & Analysis for Managers Bidder Responses & Score Cards for Assessors © Telelogic AB
 Smooth Handoff to Engineering Architecture Modeling Reuse Systems Modeling Software Design Application Traceability © Telelogic AB
Smooth Handoff to Engineering Architecture Modeling Reuse Systems Modeling Software Design Application Traceability © Telelogic AB
 Thank You • I hope you found this both educational and enjoyable. • All comments, questions and suggestions welcome. – Greg. Gorman@Telelogic. com © Telelogic AB
Thank You • I hope you found this both educational and enjoyable. • All comments, questions and suggestions welcome. – Greg. Gorman@Telelogic. com © Telelogic AB


