 AJAX AJAX 1
AJAX AJAX 1
 Stands for “Asynchronous JavaScript and XML Development technique for creating interactive web applications AJAX 2 Introduction
Stands for “Asynchronous JavaScript and XML Development technique for creating interactive web applications AJAX 2 Introduction
 Who is using AJAX ? AJAX 3
Who is using AJAX ? AJAX 3
 WebPages can be UPDATED without RELOADING. Single piece of data can be loaded without reloading of entire webpage Multiple HTTP request/response can be processed. AJAX 4
WebPages can be UPDATED without RELOADING. Single piece of data can be loaded without reloading of entire webpage Multiple HTTP request/response can be processed. AJAX 4
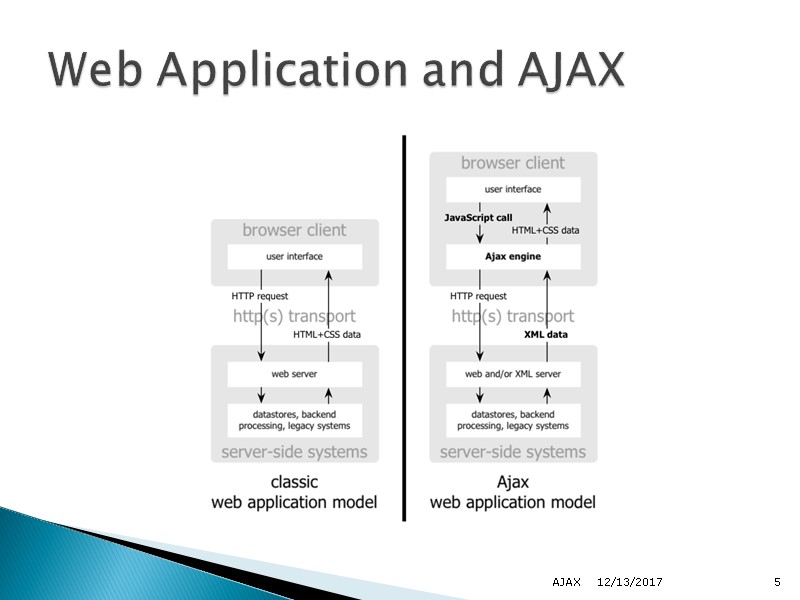 12/13/2017 AJAX 5 Web Application and AJAX
12/13/2017 AJAX 5 Web Application and AJAX
 Real-Time Form Data Validation Form data that require server-side validation can be validated in a form “before” the user submits it. Auto completion A specific portion of form data may be auto-completed as the user types. AJAX 6 Uses of AJAX
Real-Time Form Data Validation Form data that require server-side validation can be validated in a form “before” the user submits it. Auto completion A specific portion of form data may be auto-completed as the user types. AJAX 6 Uses of AJAX
 On Demand Loading Based on a client event, an HTML page can fetch more detailed information on data without refreshing the page. Refreshing data and server push: HTML pages may poll data from a server for up-to-date data such as scores, stock quotes, weather, or application-specific data. 12/13/2017 AJAX 7
On Demand Loading Based on a client event, an HTML page can fetch more detailed information on data without refreshing the page. Refreshing data and server push: HTML pages may poll data from a server for up-to-date data such as scores, stock quotes, weather, or application-specific data. 12/13/2017 AJAX 7
 HTML (or XHTML) and CSS Presenting information Document Object Model Dynamic display and interaction with the information XMLHttpRequest object Retrieving data ASYNCHRONOUSLY from the web server. Javascript Binding everything together 12/13/2017 AJAX 8 Components
HTML (or XHTML) and CSS Presenting information Document Object Model Dynamic display and interaction with the information XMLHttpRequest object Retrieving data ASYNCHRONOUSLY from the web server. Javascript Binding everything together 12/13/2017 AJAX 8 Components
 Create an XMLHttpRequest object Make a HTTP request to the server Handle the response, check for return status Parse the response on success, display result 12/13/2017 AJAX 9 AJAX Architecture
Create an XMLHttpRequest object Make a HTTP request to the server Handle the response, check for return status Parse the response on success, display result 12/13/2017 AJAX 9 AJAX Architecture
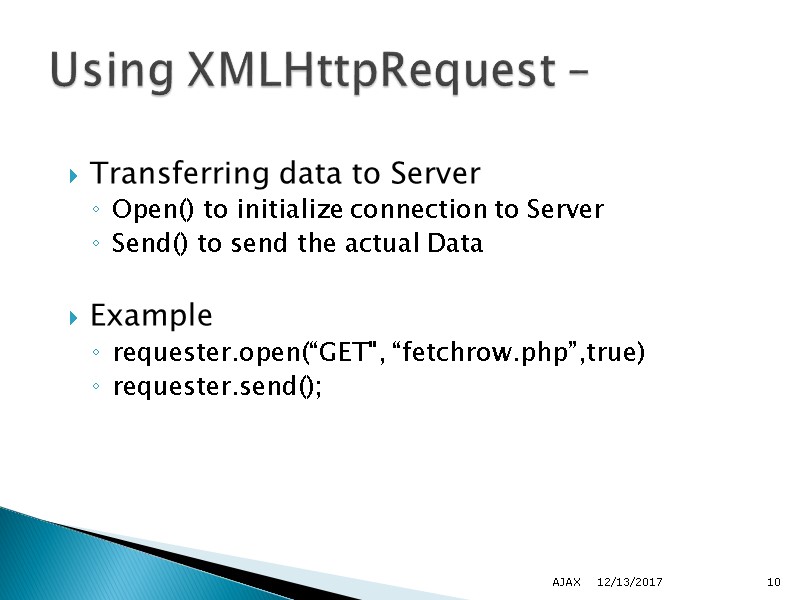 Transferring data to Server Open() to initialize connection to Server Send() to send the actual Data Example requester.open(“GET", “fetchrow.php”,true) requester.send(); 12/13/2017 AJAX 10 Using XMLHttpRequest –
Transferring data to Server Open() to initialize connection to Server Send() to send the actual Data Example requester.open(“GET", “fetchrow.php”,true) requester.send(); 12/13/2017 AJAX 10 Using XMLHttpRequest –
 XMLHttpRequest contacts the server and retrieves the data Can take indeterminate amount of time Event Listener to determine when the object has finished retrieving data Specifically listen for changes in “readyState” variable AJAX 11 What happens after sending data ?
XMLHttpRequest contacts the server and retrieves the data Can take indeterminate amount of time Event Listener to determine when the object has finished retrieving data Specifically listen for changes in “readyState” variable AJAX 11 What happens after sending data ?
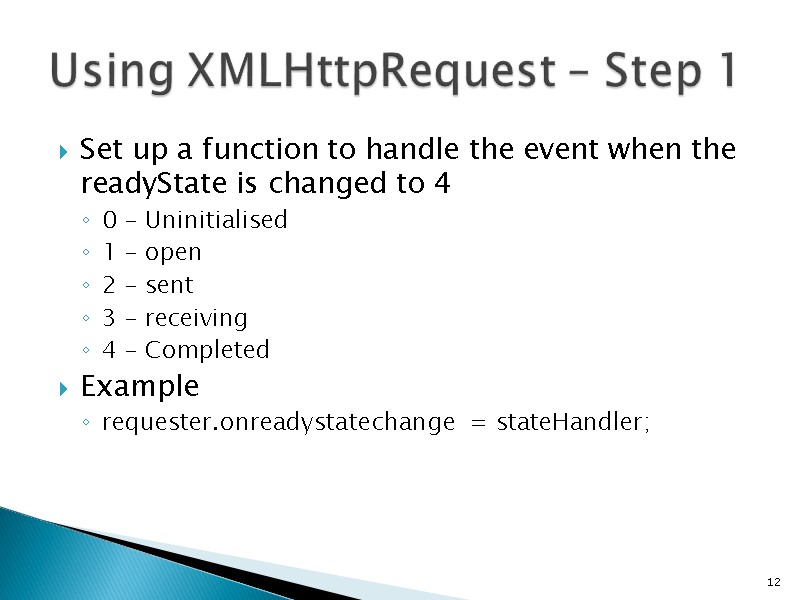 Set up a function to handle the event when the readyState is changed to 4 0 – Uninitialised 1 – open 2 – sent 3 – receiving 4 – Completed Example requester.onreadystatechange = stateHandler; 12 Using XMLHttpRequest – Step 1
Set up a function to handle the event when the readyState is changed to 4 0 – Uninitialised 1 – open 2 – sent 3 – receiving 4 – Completed Example requester.onreadystatechange = stateHandler; 12 Using XMLHttpRequest – Step 1
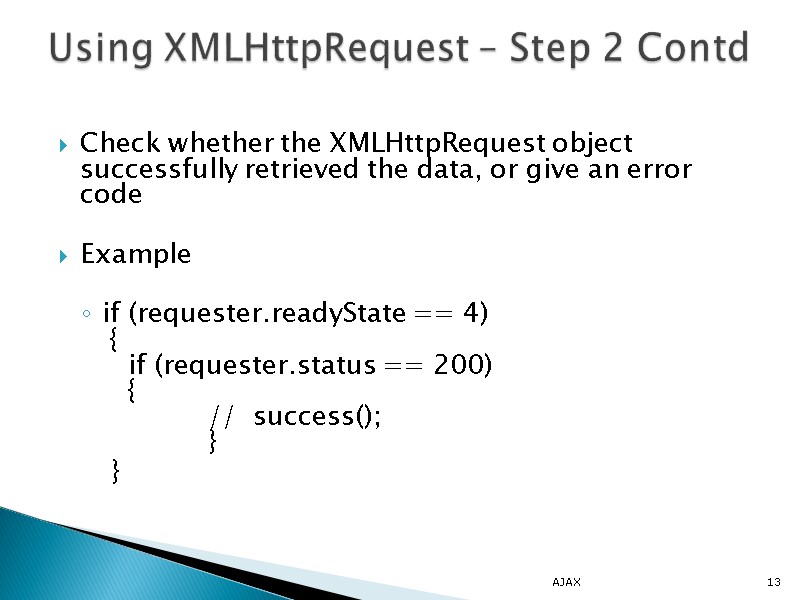 Check whether the XMLHttpRequest object successfully retrieved the data, or give an error code Example if (requester.readyState == 4) { if (requester.status == 200) { // success(); } } AJAX 13 Using XMLHttpRequest – Step 2 Contd
Check whether the XMLHttpRequest object successfully retrieved the data, or give an error code Example if (requester.readyState == 4) { if (requester.status == 200) { // success(); } } AJAX 13 Using XMLHttpRequest – Step 2 Contd
 Rich User Interface Highly Responsive Lower Bandwidth Usage Separation of content, formatting, and behavior AJAX 14 Advantages
Rich User Interface Highly Responsive Lower Bandwidth Usage Separation of content, formatting, and behavior AJAX 14 Advantages





























