fdcb8dad836faa582a51d579652fa7bf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Airline Network Revenue Management with Buy-up Houyuan Jiang Judge Business School University of Cambridge, UK Giovanna Miglionico Dipartimento di Elettronica Informatica e Sistemistica, University of Calabria, Italy 1

Outline § Buy-up § Dynamic program and approximate formulations § Booking policies and their quality § Computational results 2
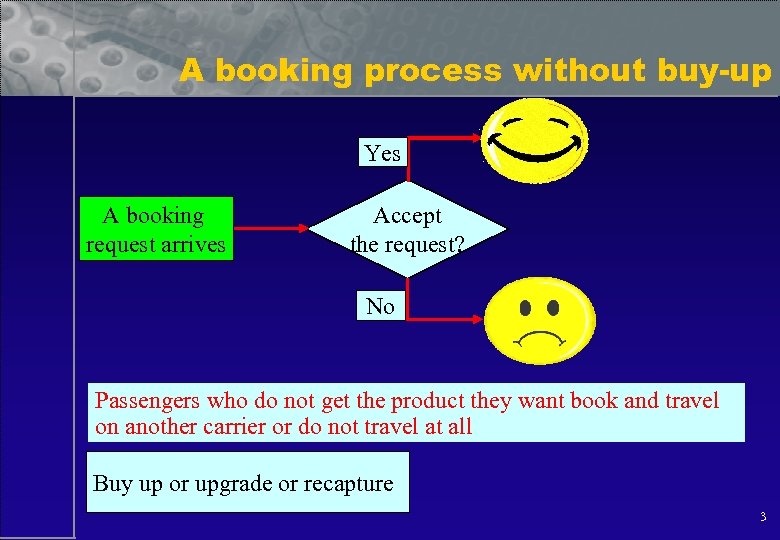
A booking process without buy-up Yes A booking request arrives Accept the request? No Passengers who do not get the product they want book and travel on another carrier or do not travel at all Buy up or upgrade or recapture 3
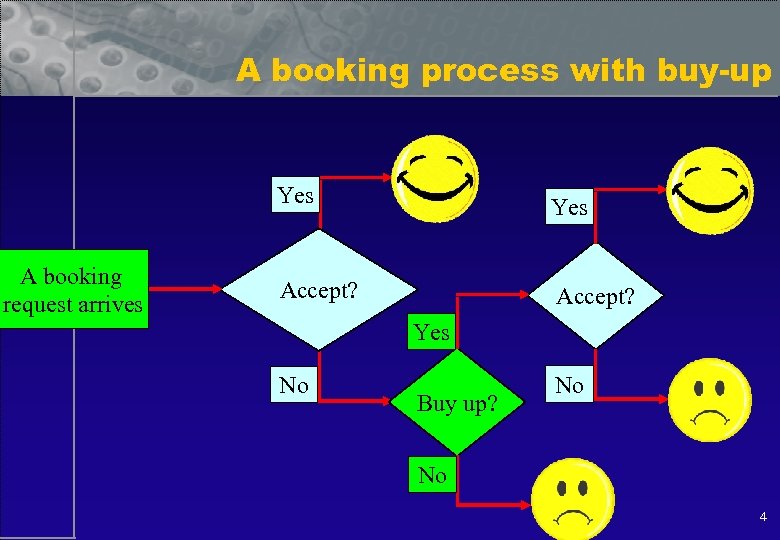
A booking process with buy-up Yes A booking request arrives Yes Accept? Yes No Buy up? No No 4

Literature § § § § Belobaba (OR, 1989) Brumelle, et al (TS, 1990) Buy up You (EJOR, 2003) Talluri and van Ryzin (The Theory and Practice of Revenue Management, 2004) Talluri and van Ryzin (MS, 2004) van Ryzin and Liu (WP, 2004) Gallego et al (WP, 2004) Choice modelling 5

Notation t=T t=0 6

Decision tree at time t Yes A booking request arrives Accept? Yes No No Buy up? No No booking request arrives 7

Dynamic program formulation No arrival First-time accept Second-time reject No buy-up Second-time accept 8

Optimal booking policy 9

Dynamic program formulation without buy-up The airline achieves a higher revenue with buyup than without buy-up if buy-up behaviour is 10

Deterministic LP approximation Revenue Capacity constrs Demand constrs Buy-up constrs Allocation for the first request Allocation for the buy-up requests Buy-up probability Mean demand 11
Randomized LP approximation d is a realization of the random demand Each demand realization results in an RLP 12

Probabilistic NLP approximation 13

Booking Policies of network inventory control Ø Partitioned booking limits: Specify a booking limit for each type of products Ø Bid price control: Calculate the displacement cost of each leg for a product and compare the total displacement cost with the product price Both approximate booking limits and bid prices can be calculated from DLP, PNLP, and RLP, etc 14

Booking policies based on partitioned booking limits First time decision on product j The number of existing bookings of product j that are accepted first time The number of seats allocated to product j Second time decision on product l for buy-ups from product j The number of existing bookings of product l for buy-ups of product j The number of seats allocated to product l for buy-ups of product j 15

Booking policies based on bid price First time decision on product j There are enough seats available on relevant legs Second time decision on product l for buy-ups from product j There are enough seats available on relevant legs 16

Asymptotic optimality § The partitioned booking limits policy for several models are asymptotically optimal when the initial capacity and the total demand are scaled up at the same speed. § The bid-price policy is also shown to be asymptotically optimal provided correct bid prices are used when the initial capacity and the total demand are scaled up at the same speed. 17

Computational results: T 1 E C A D B F G 7 legs : AB, BA, CA, AD, GB, BF, EB, 8 itineraries: AB, BA, CAB, BAD, CABF, EBF, GBAD 2 fares (16 products): Low, High Demand: Truncated normal distributions 18

Computational results: T 1 19

Effect of buy-up probability: T 1 20

Conclusions § Buy-up § Dynamic program and approximate formulations § Booking policies and their quality § Computational results 21

A booking process with buy-up: Another angle Yes A booking request arrives Accept? No Yes Recommend buy up? No 22

Booking policies based on marginal values First time decision Second time decision 23
Effect of buy-up probability: T 1, T 2, T 3, T 4 24
Comparisons with the non-buyup DLP model: T 1, T 2, T 3, T 4 25
fdcb8dad836faa582a51d579652fa7bf.ppt