b4313fa149e04737c3a18c7e6cd1a531.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Airborne Express Group Presentation by: The Braves Spring 2008

Agenda History & Background: Jennifer Smith n Industry Overview: Jennifer Smith n Business Strategy & Analysis: Ryan Mc. Nulty n Competitor Analysis: Pete Marcus n DHL Today!: Ryan Mc. Nulty n Conclusion & Recommendation: Pete Marcus n

Airborne Express-An Overview Headquarters-Originally Seattle, with a hub in Wilmington, OH n Formed by merger of 2 airfreight carriers (in 1968 -Airborne Freight Corp) n 1. The Airborne Flower Traffic Assoc. of California 2. Pacific Air Freight

Airborne Express -An Overview Continued…… n Service Offerings n Letters and Packages • Less than 1 lbs to over 50 lbs. • Overnight, morning, afternoon, and 2 nd day deliveries n Target Customers-(Prior to the 1980’s) n n Business customers-EX: Xerox, IBM, & catalog companies Specifically ignored residential deliveries and infrequent shippers

Airborne Express -An Overview Continued Shipments-900, 000 packages & documents daily n Employees-12, 700 full-time & 8, 000 part-time employees n Fleet n 13, 300 Vans n 175 aircraft (primarily purchase used aircraft and refurbish them) n

Industry-Overview n n n Competitors-mergers and consolidations common (suppliers saturated market) Technology-constantly changing Market n n n Products & Services-dynamic and easily imitable Customer preferences-non-loyal, price consciencious, convenience, habits Growth Opportunities • Domestic markets saturated, global opportunities increasingly important.
Industry Revenues n Trend-Revenues declining n 1985 -Revenue per shipment • Airborne-$19. 37 • Fedex- $19. 19 n 1990 -1991 • Airborne- $11. 43 -10. 78 • Fedex$16. 76 -17. 33 n 1992 -1997 • Airborne- $11. 43 -10. 78 • Fedex$16. 76 -17. 33

Airborne Express. Business Strategies n Corporate n n Business Level Strategies n n Dominant Business diversification Focused Cost Leadership Strategy Analysis n External & Internal Factors • • • Technology Market Share Global Expansion People/Culture Marketing/Sales

Corporate Strategy n Dominant-business diversification n Single Business • Majority of business Shipping-95+% Warehouse Space Rentals-Less than 10%

Business Level Strategy n Owned Airport Hub-Wilmington OH n • Reduced costs in landing fees, rental space • Increased revenues renting & landing fees from other airline business customers Aircraft-filled to 80% capacity vs. Industry • 65 -70% n Focused Cost leadership • Lowest costs-Used airplanes, outsourcing, pickup & delivery rates • Different geographic markets- metro areas only

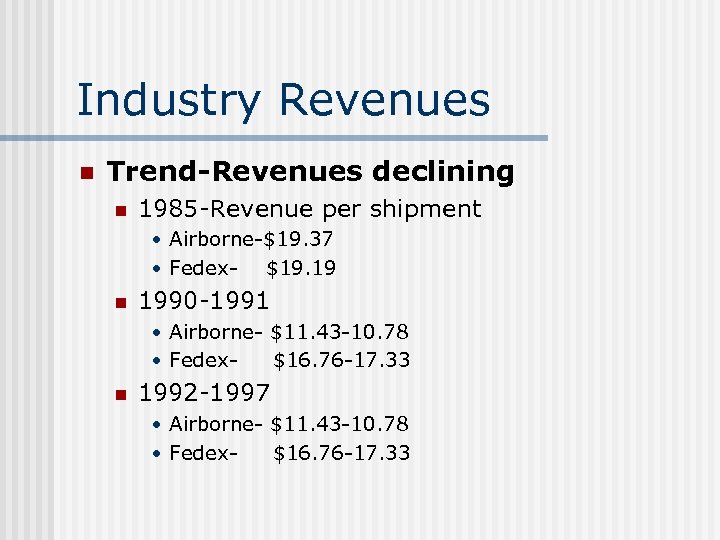
Focused Cost Leadership n Pricing n Overnight, morning delivery rates • Airborne-$10. 95 -80. 70 • Fedex- $13. 86 -86. 86 • UPS$12. 54 -90. 18 n Overnight, afternoon delivery rates • Airborne-$9. 25 -80. 70 • Fedex- $12. 04 -82. 54 • UPS$10. 82 -77. 68* n Second-day delivery rates • Airborne-$6. 25 -58. 00 • Fedex- $8 -54. 89 • UPS$6. 50 -57. 11
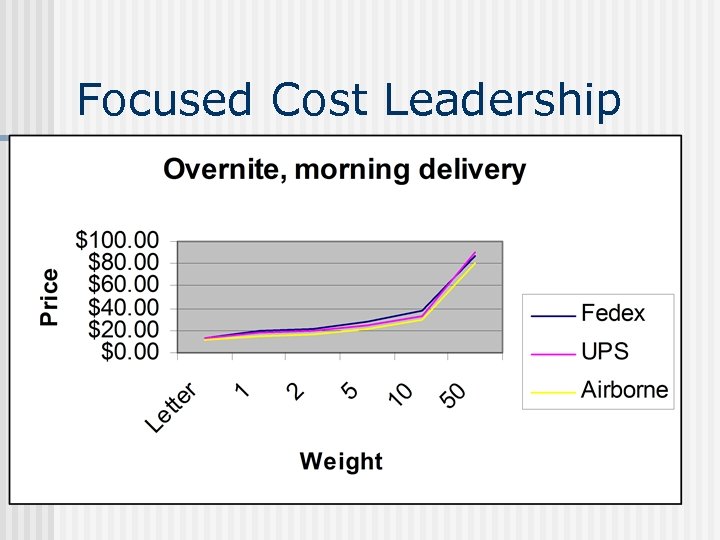
Focused Cost Leadership
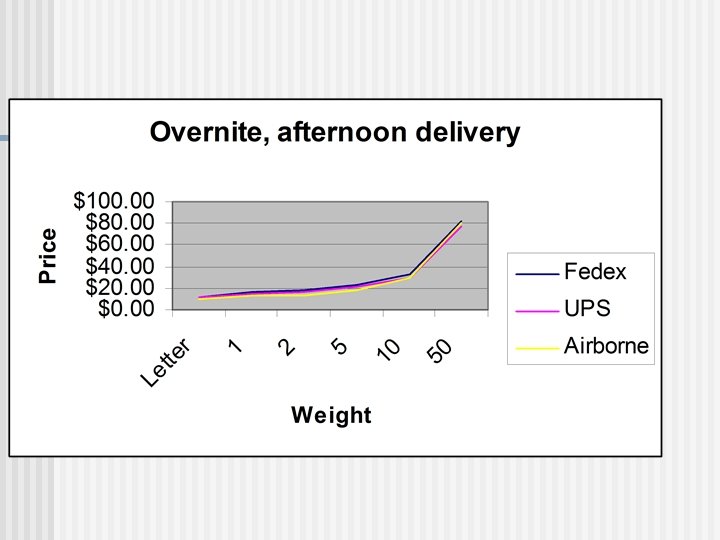

Core Competencies & Resources n External Technology n Market Share n n Internal Factors n People & Culture

Technology n n n Airborne selectively invested in technology, and let its rivals be forerunners Customers could trace packages on their own, utilizing Airborne’s Freight On-Line Control and Update System (FOCUS) Airborne’s website was not as sophisticated as it’s rivals n Customers could only track packages, but not schedule pickup or create shipping paperwork

Market Share n Airborne was often overlooked n n Many people used Fed Ex or UPS By 1997, market share grew faster than Fedex and UPS n Up to 16% of domestic express mail market

People and Culture n n n Employees described Airborne as “Straightlaced, ” “frugal, ” and “very conservative” Top executives answer their own telephones, shield away from interviews, and discourage fringe benefits Company statements reflected modesty
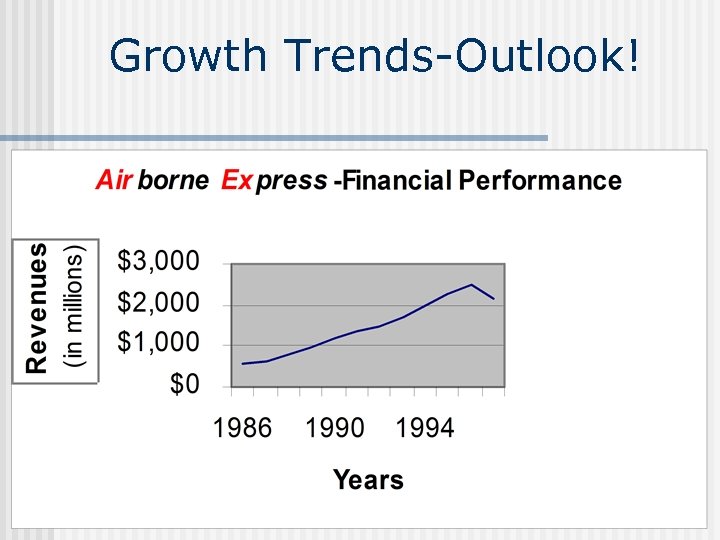
Growth Trends-Outlook!

Growth Trends-1986 -1997 n Airborne Express-Revenues n 1986 -1989: $2573 -5167 • 101% increase n Airborne Express-Revenues n 1990 -1991: $7015 -7688 • 9. 6%* n Airborne Express-Revenues n 1992 -1997: $7550 -11, 520 • 50%

Global Expansion n Only 6% ($78 Million) of Total Assets were invested internationally n n Fed Ex -19% and UPS-12% “There are no significant service advantages which would justify the operation of our own aircraft on international routes” n Airborne used commercial airlines and local partners for international shipping

Today- DHL n DHL acquired Airborne Express August 14, 2003 n n World’s largest international air express network Available to over 220 countries worldwide They own and operate the majority (2/3 rds) of offices worldwide n n Global company-headquartered in London (Deutsche Post World Net) This is far greater than their competitors Faster transit times, smooth customs clearance, simplified billing, and effective shipping tracking are a result of dedicated personnel

Competitor Analysis Strengths Concentration in metropolitan areas n Owns airport n Product Differentiation: 3 Ways n No Retail Service Centers n Used Independent Contractors n Cheaper but later delivery n

OOPS “ When it comes to technology, Airborne doesn’t add on bells and whistles. We use our competitors as guinea pigs. Let them try out the new stuff and see what works”.

Strengths n Concentration in metropolitan areas Exploited Core competencies n Owns airport n n Product Differentiation: 3 Ways No Retail Service Centers n Used Independent Contractors n Cheaper but later delivery n

Weaknesses n Technology n Wages to their Employees n Efficiency and Reliability n Globalization
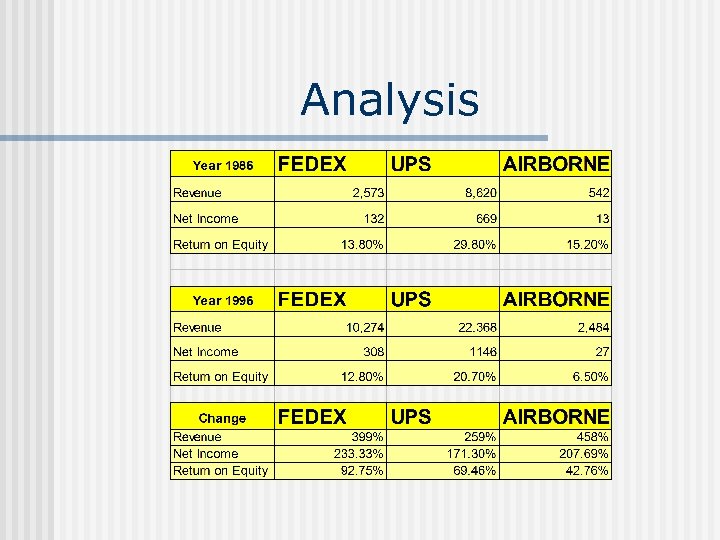
Analysis

Conclusions n Weaknesses counter-acted strengths n Metropolitan areas vs. Efficiency n Owns Airport vs. Globalization n Product Differentiation vs. Efficiency

Recommendations n Be a leader not a follower n n Stay ahead of the competition Know customers and what’s important to them Keep low price differentiation but not at expense of efficiency Continuous Improvement & Growth n n Avoid being comfortable Search for different markets/geographic locations
b4313fa149e04737c3a18c7e6cd1a531.ppt