85bcc7d4156426b0d2d12518eecead2b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Air Pollution & Control
Air Pollution & Control
 Thickness of Atmosphere • The atmosphere is a very thin (relatively) layer of gas over the surface of the Earth • Earth’s radius ~ 6400 km • Atmospheric thickness ~ 100 km • (If you travel 100 km vertically you’d be in space!)
Thickness of Atmosphere • The atmosphere is a very thin (relatively) layer of gas over the surface of the Earth • Earth’s radius ~ 6400 km • Atmospheric thickness ~ 100 km • (If you travel 100 km vertically you’d be in space!)
 Atmospheric Structure and Composition
Atmospheric Structure and Composition
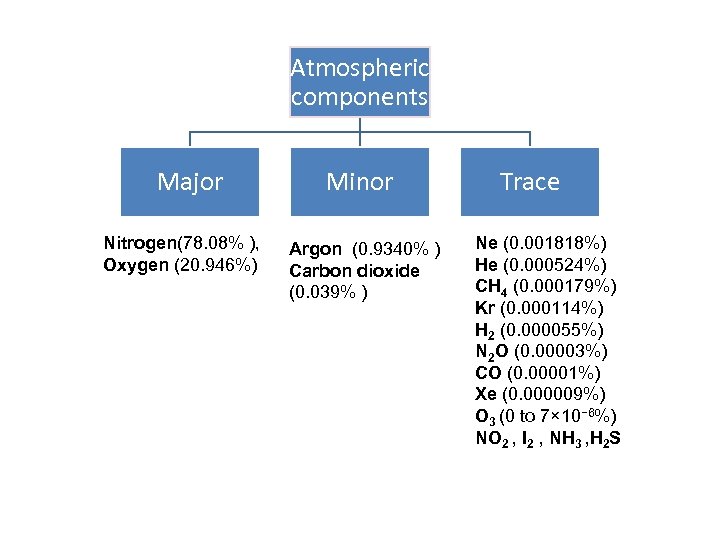 Atmospheric components Major Nitrogen(78. 08% ), Oxygen (20. 946%) Minor Argon (0. 9340% ) Carbon dioxide (0. 039% ) Trace Ne (0. 001818%) He (0. 000524%) CH 4 (0. 000179%) Kr (0. 000114%) H 2 (0. 000055%) N 2 O (0. 00003%) CO (0. 00001%) Xe (0. 000009%) O 3 (0 to 7× 10− 6%) NO 2 , I 2 , NH 3 , H 2 S
Atmospheric components Major Nitrogen(78. 08% ), Oxygen (20. 946%) Minor Argon (0. 9340% ) Carbon dioxide (0. 039% ) Trace Ne (0. 001818%) He (0. 000524%) CH 4 (0. 000179%) Kr (0. 000114%) H 2 (0. 000055%) N 2 O (0. 00003%) CO (0. 00001%) Xe (0. 000009%) O 3 (0 to 7× 10− 6%) NO 2 , I 2 , NH 3 , H 2 S
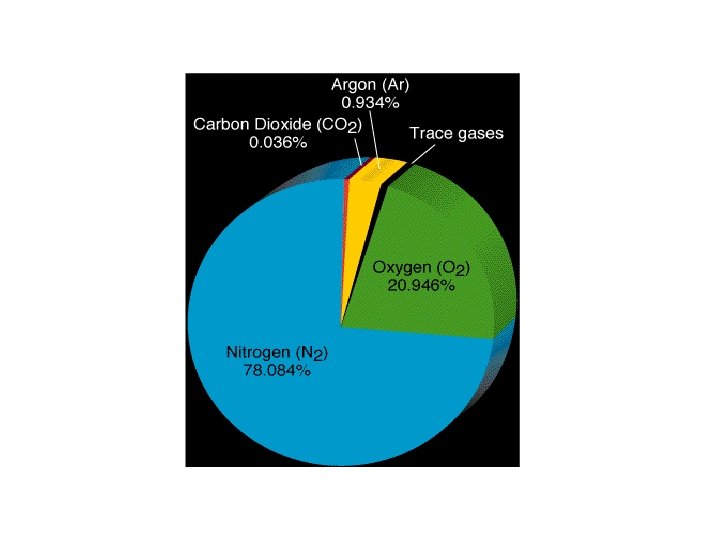
 Composition of the Air v Uniform gases Nitrogen (N 2) , Oxygen (O 2) , Argon (Ar), trace gases (Neon(Ne), Helium (He), Methane (CH 4), etc. ) v Variable gases Water Vapor (H 2 O), O 3, CO 2
Composition of the Air v Uniform gases Nitrogen (N 2) , Oxygen (O 2) , Argon (Ar), trace gases (Neon(Ne), Helium (He), Methane (CH 4), etc. ) v Variable gases Water Vapor (H 2 O), O 3, CO 2
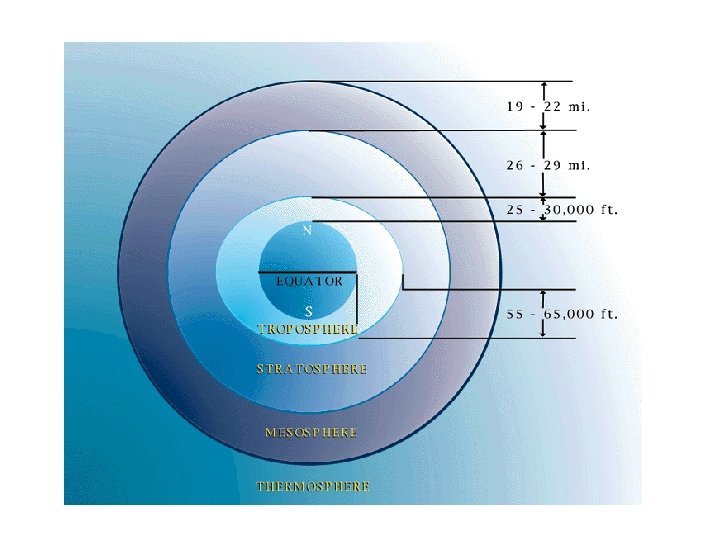
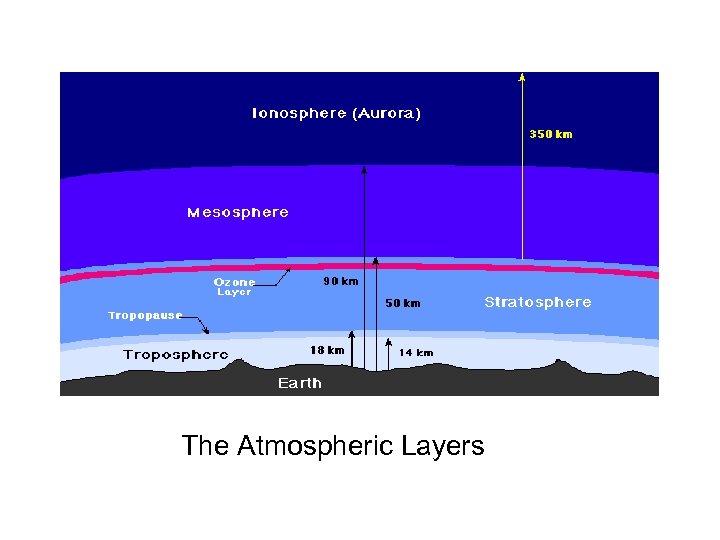 The Atmospheric Layers
The Atmospheric Layers
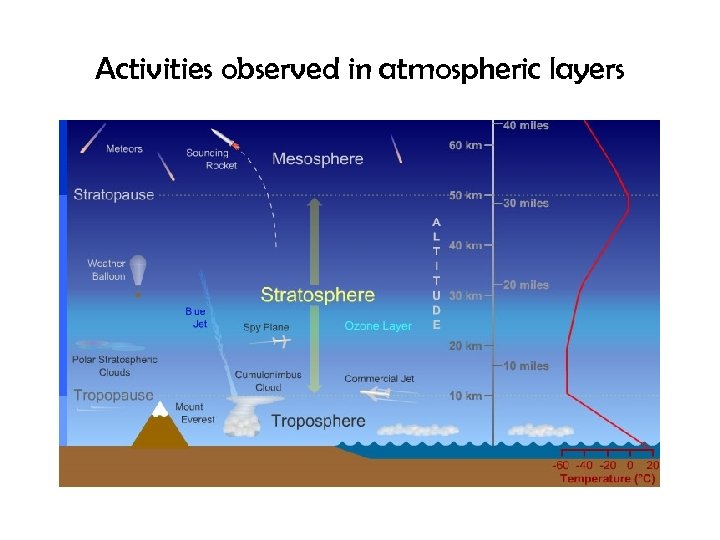 Activities observed in atmospheric layers
Activities observed in atmospheric layers
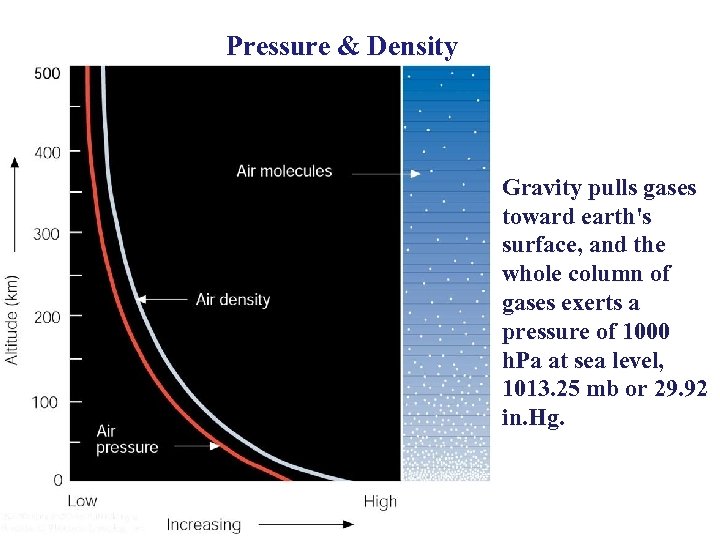 Pressure & Density Gravity pulls gases toward earth's surface, and the whole column of gases exerts a pressure of 1000 h. Pa at sea level, 1013. 25 mb or 29. 92 in. Hg.
Pressure & Density Gravity pulls gases toward earth's surface, and the whole column of gases exerts a pressure of 1000 h. Pa at sea level, 1013. 25 mb or 29. 92 in. Hg.
 Beautiful view of kanchanjangha
Beautiful view of kanchanjangha
 Lapse Rate • The rate at which air temperature decreases with height. • The standard (average) lapse rate in the lower atmosphere is about 6. 5°C per 1 km or 3. 6°F per 1000 ft.
Lapse Rate • The rate at which air temperature decreases with height. • The standard (average) lapse rate in the lower atmosphere is about 6. 5°C per 1 km or 3. 6°F per 1000 ft.
 Lapse Rate • The rate at which air temperature decreases with height. • The standard (average) lapse rate in the lower atmosphere is about 6. 5°C per 1 km or 3. 6°F per 1000 ft. • Positive lapse rate & negative lapse rate
Lapse Rate • The rate at which air temperature decreases with height. • The standard (average) lapse rate in the lower atmosphere is about 6. 5°C per 1 km or 3. 6°F per 1000 ft. • Positive lapse rate & negative lapse rate
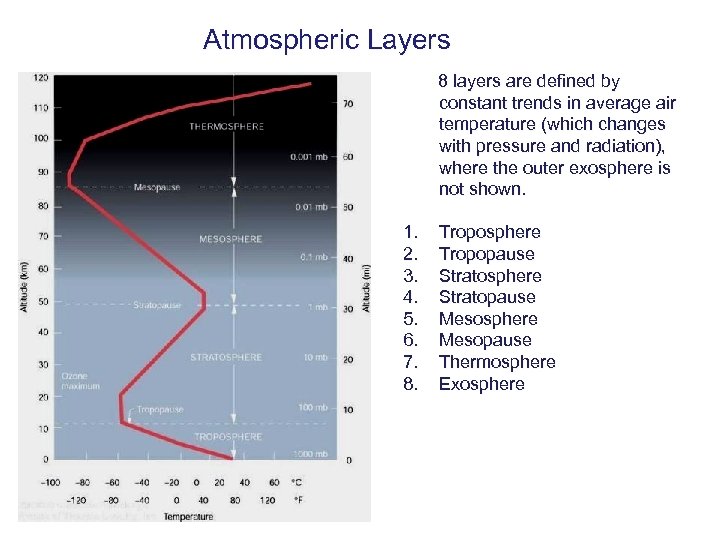 Atmospheric Layers 8 layers are defined by constant trends in average air temperature (which changes with pressure and radiation), where the outer exosphere is not shown. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Troposphere Tropopause Stratosphere Stratopause Mesosphere Mesopause Thermosphere Exosphere
Atmospheric Layers 8 layers are defined by constant trends in average air temperature (which changes with pressure and radiation), where the outer exosphere is not shown. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Troposphere Tropopause Stratosphere Stratopause Mesosphere Mesopause Thermosphere Exosphere
 Vertical Structure of Atmosphere • Troposphere (surface to 10 -18 km) Upper boundary varies from about 10 km (poles in winter) to about 18 km (tropics) Ø Polar latitude: surface to 10 km Ø Moderate latitude: surface to 12 km Ø Equator: surface to 18 km Temperature range: 15 to -56 0 C (30 to -56 0 C ) –ve lapse rate v Weather and climate layer, very turbulent, mixing of air v Most of atmosphere’s mass(80%) ; all of its water
Vertical Structure of Atmosphere • Troposphere (surface to 10 -18 km) Upper boundary varies from about 10 km (poles in winter) to about 18 km (tropics) Ø Polar latitude: surface to 10 km Ø Moderate latitude: surface to 12 km Ø Equator: surface to 18 km Temperature range: 15 to -56 0 C (30 to -56 0 C ) –ve lapse rate v Weather and climate layer, very turbulent, mixing of air v Most of atmosphere’s mass(80%) ; all of its water
 Upper region of troposphere is separated by the lower region of the strtosphere in a narrow range called the Tropopause • Stratosphere (10 -18 km to 50 km) Ø Polar latitude: 10 to 50 km Ø Moderate latitude: 12 to 50 km Ø Equator: 18 to 50 km Very stable in nature Temperature range: -56 to -2 0 C i. e. lapse rate is +ve Why?
Upper region of troposphere is separated by the lower region of the strtosphere in a narrow range called the Tropopause • Stratosphere (10 -18 km to 50 km) Ø Polar latitude: 10 to 50 km Ø Moderate latitude: 12 to 50 km Ø Equator: 18 to 50 km Very stable in nature Temperature range: -56 to -2 0 C i. e. lapse rate is +ve Why?
 Upper region of troposphere is separated by the lower region of the strtosphere in a narrow range called the Tropopause • Stratosphere (10 -18 km to 50 km) Ø Polar latitude: 10 to 50 km Ø Moderate latitude: 12 to 50 km Ø Equator: 18 to 50 km Very stable in nature Temperature range: -56 to -2 0 C i. e. lapse rate is +ve v. Ozone layer ( absorb UV rays 190 nm-380 nm )
Upper region of troposphere is separated by the lower region of the strtosphere in a narrow range called the Tropopause • Stratosphere (10 -18 km to 50 km) Ø Polar latitude: 10 to 50 km Ø Moderate latitude: 12 to 50 km Ø Equator: 18 to 50 km Very stable in nature Temperature range: -56 to -2 0 C i. e. lapse rate is +ve v. Ozone layer ( absorb UV rays 190 nm-380 nm )
 Upper region of stratosphere is separated by the lower region of the mesosphere in a narrow range called the Stratopause • Mesosphere (50 km to 85 km) Temperature range: -2 to -92 0 C Concentration of ozone is very low v Need oxygen to live in this region
Upper region of stratosphere is separated by the lower region of the mesosphere in a narrow range called the Stratopause • Mesosphere (50 km to 85 km) Temperature range: -2 to -92 0 C Concentration of ozone is very low v Need oxygen to live in this region
 Upper region of mesosphere is separated by the lower region of thermosphere in a narrow range called the Mesopause Thermosphere/ Ionosphere (85 km to 500 km) Temperature range: -92 to 1200 0 C “Hot layer” – oxygen molecules absorb energy from solar Rays warming the air. Very few atoms and molecules in this Region.
Upper region of mesosphere is separated by the lower region of thermosphere in a narrow range called the Mesopause Thermosphere/ Ionosphere (85 km to 500 km) Temperature range: -92 to 1200 0 C “Hot layer” – oxygen molecules absorb energy from solar Rays warming the air. Very few atoms and molecules in this Region.
 Magnetoosphere/ Exosphere (500 km to 2000 km) Temperature range: >1200 0 C Air less, probably contains hydrohen gas in ionized state Very little is known about this layer
Magnetoosphere/ Exosphere (500 km to 2000 km) Temperature range: >1200 0 C Air less, probably contains hydrohen gas in ionized state Very little is known about this layer
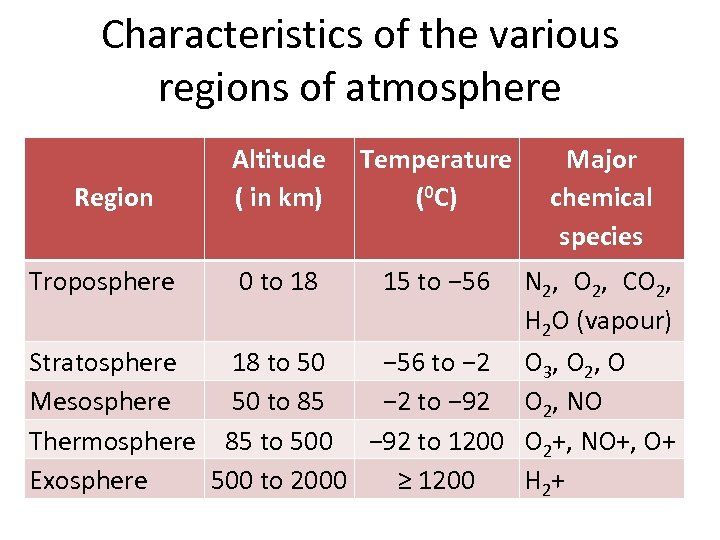 Characteristics of the various regions of atmosphere Region Troposphere Altitude ( in km) Temperature (0 C) Major chemical species 0 to 18 15 to − 56 N 2, O 2, CO 2, H 2 O (vapour) Stratosphere 18 to 50 − 56 to − 2 Mesosphere 50 to 85 − 2 to − 92 Thermosphere 85 to 500 − 92 to 1200 Exosphere 500 to 2000 ≥ 1200 O 3 , O 2 , O O 2, NO O 2+, NO+, O+ H 2 +
Characteristics of the various regions of atmosphere Region Troposphere Altitude ( in km) Temperature (0 C) Major chemical species 0 to 18 15 to − 56 N 2, O 2, CO 2, H 2 O (vapour) Stratosphere 18 to 50 − 56 to − 2 Mesosphere 50 to 85 − 2 to − 92 Thermosphere 85 to 500 − 92 to 1200 Exosphere 500 to 2000 ≥ 1200 O 3 , O 2 , O O 2, NO O 2+, NO+, O+ H 2 +
 Air Pollution and Controll Atmospheric Composition : Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Tropopause and Mesopause. 1 L Energy balance Conductive and Convective heat transfer, radiation heat : transfer, simple global temperature model [Earth as a black body, earth as albedo], Problems. 1 L Green house effects. Definition, impact of greenhouse gases on the global : climate and consequently on sea water level, agriculture and marine food. Global warming and its consequence, Control of Global warming. Earth’s heat budget. 1 L Lapse rate: Ambient lapse rate, adiabatic lapse rate, atmospheric stability, temperature inversion (radiation inversion). 2 L Atmospheric dispersion. Maximum mixing depth, ventilation coefficient, : effective stack height, smokestack plumes and Gaussian plume model. 2 L Definition of pollutants and contaminants , Primary and secondary pollutants: emission standard, criteria pollutant. Sources and effect of different air pollutants- Suspended particulate matter, oxides of carbon, oxides of nitrogen, oxides of sulphur, particulate, PAN. 2 L Smog, Photochemical smog and London smog. Depletion Ozone layer. CFC, : destruction of ozone layer by CFC, impact of other green house gases, effect of ozone modification. 1 L Standards and control measures. Industrial, commercial and residential air : quality standard, control measure (ESP. cyclone separator, bag house, catalytic converter, scrubber (ventury), Statement with brief reference). 1 L
Air Pollution and Controll Atmospheric Composition : Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Tropopause and Mesopause. 1 L Energy balance Conductive and Convective heat transfer, radiation heat : transfer, simple global temperature model [Earth as a black body, earth as albedo], Problems. 1 L Green house effects. Definition, impact of greenhouse gases on the global : climate and consequently on sea water level, agriculture and marine food. Global warming and its consequence, Control of Global warming. Earth’s heat budget. 1 L Lapse rate: Ambient lapse rate, adiabatic lapse rate, atmospheric stability, temperature inversion (radiation inversion). 2 L Atmospheric dispersion. Maximum mixing depth, ventilation coefficient, : effective stack height, smokestack plumes and Gaussian plume model. 2 L Definition of pollutants and contaminants , Primary and secondary pollutants: emission standard, criteria pollutant. Sources and effect of different air pollutants- Suspended particulate matter, oxides of carbon, oxides of nitrogen, oxides of sulphur, particulate, PAN. 2 L Smog, Photochemical smog and London smog. Depletion Ozone layer. CFC, : destruction of ozone layer by CFC, impact of other green house gases, effect of ozone modification. 1 L Standards and control measures. Industrial, commercial and residential air : quality standard, control measure (ESP. cyclone separator, bag house, catalytic converter, scrubber (ventury), Statement with brief reference). 1 L
 References/Books 1. Masters, G. M. , “Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science”, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd. , 1991. 2. De, A. K. , “Environmental Chemistry”, New Age International. 3. Dasmahapatra , Gourkrishna “Environment & Ecology” Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd. 4. Mandal , T “Environment and Ecology” Dhanpat Rai Publishing Company
References/Books 1. Masters, G. M. , “Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science”, Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd. , 1991. 2. De, A. K. , “Environmental Chemistry”, New Age International. 3. Dasmahapatra , Gourkrishna “Environment & Ecology” Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd. 4. Mandal , T “Environment and Ecology” Dhanpat Rai Publishing Company


