9a9f9a5fb517b04f654b79590614e818.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 AIPS tut 1 • The approach: to dip into and out of AIPS several times, each time doing something more complicated. 1. Starting AIPS and exiting. 2. Loading a FITS image and displaying it. 3. Calibration of a continuum observation (an observation of a gravitationally lensed quasar by the MERLIN array in the UK) via a runfile. 4. Some CLEANing. • See chapter 3 of the AIPS Cookbook: – • ftp: //ftp. aoc. nrao. edu/pub/software/aips/TEXT/PUBL /COOK 3. PS. gz There are links to both the cookbook and the AIPS home page off my web site. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • The approach: to dip into and out of AIPS several times, each time doing something more complicated. 1. Starting AIPS and exiting. 2. Loading a FITS image and displaying it. 3. Calibration of a continuum observation (an observation of a gravitationally lensed quasar by the MERLIN array in the UK) via a runfile. 4. Some CLEANing. • See chapter 3 of the AIPS Cookbook: – • ftp: //ftp. aoc. nrao. edu/pub/software/aips/TEXT/PUBL /COOK 3. PS. gz There are links to both the cookbook and the AIPS home page off my web site. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 • AIPS tut 1 Before you start AIPS, there a few things you will need to do. 1. Decide where you want to keep your FITS files. Maybe make a special directory for them. 2. Do export MYAREA=
• AIPS tut 1 Before you start AIPS, there a few things you will need to do. 1. Decide where you want to keep your FITS files. Maybe make a special directory for them. 2. Do export MYAREA=
 AIPS tut 1 – Change the names of your runfiles so they end in.
AIPS tut 1 – Change the names of your runfiles so they end in.
 AIPS tut 1 • At your normal Unix command line, type aips notv® • You will see something like: You have a choice of 5 printers. These are: No. [ type ] Description ------------------------------1. [ PS] n 2. [ PS] Spare 3. [ PS] Main 4. [ PS] n 5. [ PS] n ------------------------------START_AIPS: Enter your choice, or the word QUIT [default is 3]: NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • At your normal Unix command line, type aips notv® • You will see something like: You have a choice of 5 printers. These are: No. [ type ] Description ------------------------------1. [ PS] n 2. [ PS] Spare 3. [ PS] Main 4. [ PS] n 5. [ PS] n ------------------------------START_AIPS: Enter your choice, or the word QUIT [default is 3]: NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
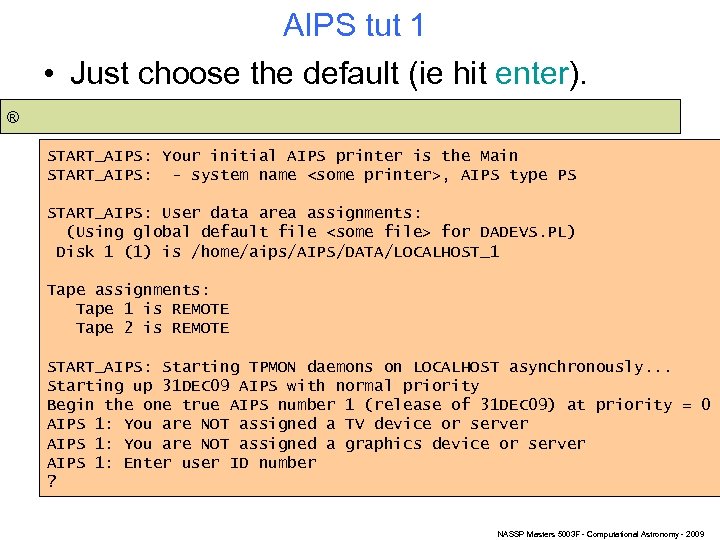 AIPS tut 1 • Just choose the default (ie hit enter). ® START_AIPS: Your initial AIPS printer is the Main START_AIPS: - system name
AIPS tut 1 • Just choose the default (ie hit enter). ® START_AIPS: Your initial AIPS printer is the Main START_AIPS: - system name
 AIPS tut 1
AIPS tut 1
 AIPS tut 1 kleenex® AIPS 1: Begin check for any 'standard' scratch files AIPS 1: Scratch files -- destroyed: 0 still active: 0 AIPS 1: User 2: 4 messages, oldest written 22 -APR-2009 19: 02: 40 AIPS 1: Deleted 0 messages AIPS 1: Saved POPS environment in area named 'LASTEXIT' ► ► AIPS 1: Session command-line history saved. AIPS 1: localhos 31 DEC 09 TST: Cpu= 0. 0 Real= 9 IO= 2
AIPS tut 1 kleenex® AIPS 1: Begin check for any 'standard' scratch files AIPS 1: Scratch files -- destroyed: 0 still active: 0 AIPS 1: User 2: 4 messages, oldest written 22 -APR-2009 19: 02: 40 AIPS 1: Deleted 0 messages AIPS 1: Saved POPS environment in area named 'LASTEXIT' ► ► AIPS 1: Session command-line history saved. AIPS 1: localhos 31 DEC 09 TST: Cpu= 0. 0 Real= 9 IO= 2
 AIPS tut 1 • There are two principal file types in AIPS – lists of visibilities, and images. AIPS denotes these by the letter codes UV and MA respectively. • Before going further, download the file M 82_DIRTY. FITS from my website and put it into your previously selected AIPS data directory. This is a FITS file, an image, which is the product of previous AIPS manipulations. • Now do aips® NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • There are two principal file types in AIPS – lists of visibilities, and images. AIPS denotes these by the letter codes UV and MA respectively. • Before going further, download the file M 82_DIRTY. FITS from my website and put it into your previously selected AIPS data directory. This is a FITS file, an image, which is the product of previous AIPS manipulations. • Now do aips® NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • You will get the same printer prompt as before; just choose the default again. • You’ll be prompted for your user ID same as before, but before you can type it in, AIPS will start up 3 more windows, and print a lot more text at the prompt. – The 3 extra windows are a Tek server, a Message server and a ‘TV’. • Just click back to focus on your original window, and enter your user ID then ®. Don’t worry that the ? prompt has got buried in extra output. • AIPS will give the same messages as before, ending with its POPS > prompt. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • You will get the same printer prompt as before; just choose the default again. • You’ll be prompted for your user ID same as before, but before you can type it in, AIPS will start up 3 more windows, and print a lot more text at the prompt. – The 3 extra windows are a Tek server, a Message server and a ‘TV’. • Just click back to focus on your original window, and enter your user ID then ®. Don’t worry that the ? prompt has got buried in extra output. • AIPS will give the same messages as before, ending with its POPS > prompt. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • Now we’re going to run a task. – AIPS talks about tasks but also things which it calls verbs. The difference is minor: • A task usually takes a while to run. Thus it is run in a ‘forked’ process, in the background, with output to the message server. You can type another command at the prompt in the mean time. • A verb is a quick-running task. There is no fork for these, you have to wait until the verb is finished before entering further commands. • The task we’re going to run is called FITLD. It is one of several AIPS tasks for importing FITS data (typical AIPS overkill). NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • Now we’re going to run a task. – AIPS talks about tasks but also things which it calls verbs. The difference is minor: • A task usually takes a while to run. Thus it is run in a ‘forked’ process, in the background, with output to the message server. You can type another command at the prompt in the mean time. • A verb is a quick-running task. There is no fork for these, you have to wait until the verb is finished before entering further commands. • The task we’re going to run is called FITLD. It is one of several AIPS tasks for importing FITS data (typical AIPS overkill). NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • FITLD also has a lot of parameters to cover all kinds of special cases. Most of these can be left at default values. • (One source of confusion in AIPS is that parameters which have the same name in 2 or more different tasks remember their values from task to task. – The AIPS people claim this is a feature but I think it is a trap for the unwary. ) • AIPS is case insensitive (except for Unix file names). • You can use unambiguous shortening of parameter names. Eg indi instead of indisk. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • FITLD also has a lot of parameters to cover all kinds of special cases. Most of these can be left at default values. • (One source of confusion in AIPS is that parameters which have the same name in 2 or more different tasks remember their values from task to task. – The AIPS people claim this is a feature but I think it is a trap for the unwary. ) • AIPS is case insensitive (except for Unix file names). • You can use unambiguous shortening of parameter names. Eg indi instead of indisk. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • So, at the AIPS prompt, type task ‘fitld’ inp® • The inp requests a list of the FITLD parameters. There are pages of them. See next slide for the first page! – Note that the exact number of lines on the page depends on the size of your terminal window. It may be more or less than I have shown here. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • So, at the AIPS prompt, type task ‘fitld’ inp® • The inp requests a list of the FITLD parameters. There are pages of them. See next slide for the first page! – Note that the exact number of lines on the page depends on the size of your terminal window. It may be more or less than I have shown here. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
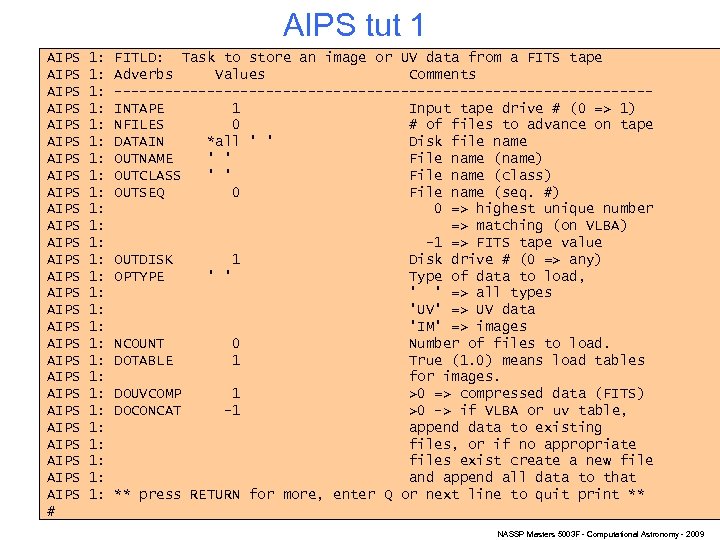 AIPS tut 1 AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS # 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: FITLD: Task to store an image or UV data from a FITS tape Adverbs Values Comments --------------------------------INTAPE 1 Input tape drive # (0 => 1) NFILES 0 # of files to advance on tape DATAIN *all ' ' Disk file name OUTNAME ' ' File name (name) OUTCLASS ' ' File name (class) OUTSEQ 0 File name (seq. #) 0 => highest unique number => matching (on VLBA) -1 => FITS tape value OUTDISK 1 Disk drive # (0 => any) OPTYPE ' ' Type of data to load, ' ' => all types 'UV' => UV data 'IM' => images NCOUNT 0 Number of files to load. DOTABLE 1 True (1. 0) means load tables for images. DOUVCOMP 1 >0 => compressed data (FITS) DOCONCAT -1 >0 -> if VLBA or uv table, append data to existing files, or if no appropriate files exist create a new file and append all data to that ** press RETURN for more, enter Q or next line to quit print ** NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS # 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: FITLD: Task to store an image or UV data from a FITS tape Adverbs Values Comments --------------------------------INTAPE 1 Input tape drive # (0 => 1) NFILES 0 # of files to advance on tape DATAIN *all ' ' Disk file name OUTNAME ' ' File name (name) OUTCLASS ' ' File name (class) OUTSEQ 0 File name (seq. #) 0 => highest unique number => matching (on VLBA) -1 => FITS tape value OUTDISK 1 Disk drive # (0 => any) OPTYPE ' ' Type of data to load, ' ' => all types 'UV' => UV data 'IM' => images NCOUNT 0 Number of files to load. DOTABLE 1 True (1. 0) means load tables for images. DOUVCOMP 1 >0 => compressed data (FITS) DOCONCAT -1 >0 -> if VLBA or uv table, append data to existing files, or if no appropriate files exist create a new file and append all data to that ** press RETURN for more, enter Q or next line to quit print ** NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 • • AIPS tut 1 Don’t worry that it talks about tapes – FITLD can read either from a disk or a tape – and is pretty clever about working out which it has to deal with. Try continued carriage returns until you run out of pages and get back to the > prompt. Now press the up-arrow key. You’ll get the inp back (same as Unix). Now press carriage return to list the params all over again. But test the early exit capability with q® NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
• • AIPS tut 1 Don’t worry that it talks about tapes – FITLD can read either from a disk or a tape – and is pretty clever about working out which it has to deal with. Try continued carriage returns until you run out of pages and get back to the > prompt. Now press the up-arrow key. You’ll get the inp back (same as Unix). Now press carriage return to list the params all over again. But test the early exit capability with q® NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • To get FITLD to load the file you want, you only have to set 3 of the parameters. Do datain ‘MYAREA: M 82_DIRTY. FITS’ outname ‘M 82’ outclass ‘IIM 001’® • Note that AIPS reads the value of your MYAREA envar. It’s possible to type in the full Unix pathname but this parameter only accepts a string of maximum length 48 characters – ie really short. • If you have a file name with some lower case characters, leave off the final ‘ otherwise AIPS will convert whatever you type to upper case. • Do a final inp to check all params are set properly. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • To get FITLD to load the file you want, you only have to set 3 of the parameters. Do datain ‘MYAREA: M 82_DIRTY. FITS’ outname ‘M 82’ outclass ‘IIM 001’® • Note that AIPS reads the value of your MYAREA envar. It’s possible to type in the full Unix pathname but this parameter only accepts a string of maximum length 48 characters – ie really short. • If you have a file name with some lower case characters, leave off the final ‘ otherwise AIPS will convert whatever you type to upper case. • Do a final inp to check all params are set properly. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
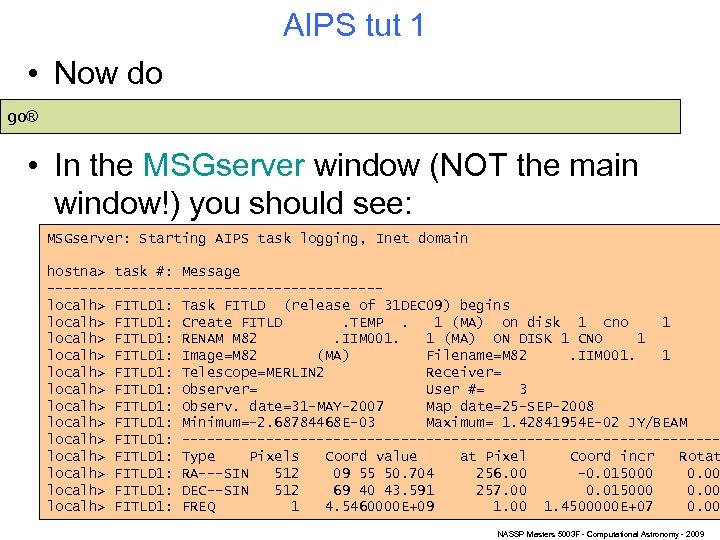 AIPS tut 1 • Now do go® • In the MSGserver window (NOT the main window!) you should see: MSGserver: Starting AIPS task logging, Inet domain hostna> task #: Message --------------------localh> FITLD 1: Task FITLD (release of 31 DEC 09) begins localh> FITLD 1: Create FITLD. TEMP. 1 (MA) on disk 1 cno 1 localh> FITLD 1: RENAM M 82. IIM 001. 1 (MA) ON DISK 1 CNO 1 localh> FITLD 1: Image=M 82 (MA) Filename=M 82. IIM 001. 1 localh> FITLD 1: Telescope=MERLIN 2 Receiver= localh> FITLD 1: Observer= User #= 3 localh> FITLD 1: Observ. date=31 -MAY-2007 Map date=25 -SEP-2008 localh> FITLD 1: Minimum=-2. 68784468 E-03 Maximum= 1. 42841954 E-02 JY/BEAM localh> FITLD 1: --------------------------------localh> FITLD 1: Type Pixels Coord value at Pixel Coord incr Rotat localh> FITLD 1: RA---SIN 512 09 55 50. 704 256. 00 -0. 015000 0. 00 localh> FITLD 1: DEC--SIN 512 69 40 43. 591 257. 00 0. 015000 0. 00 localh> FITLD 1: FREQ 1 4. 5460000 E+09 1. 00 1. 4500000 E+07 0. 00 NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • Now do go® • In the MSGserver window (NOT the main window!) you should see: MSGserver: Starting AIPS task logging, Inet domain hostna> task #: Message --------------------localh> FITLD 1: Task FITLD (release of 31 DEC 09) begins localh> FITLD 1: Create FITLD. TEMP. 1 (MA) on disk 1 cno 1 localh> FITLD 1: RENAM M 82. IIM 001. 1 (MA) ON DISK 1 CNO 1 localh> FITLD 1: Image=M 82 (MA) Filename=M 82. IIM 001. 1 localh> FITLD 1: Telescope=MERLIN 2 Receiver= localh> FITLD 1: Observer= User #= 3 localh> FITLD 1: Observ. date=31 -MAY-2007 Map date=25 -SEP-2008 localh> FITLD 1: Minimum=-2. 68784468 E-03 Maximum= 1. 42841954 E-02 JY/BEAM localh> FITLD 1: --------------------------------localh> FITLD 1: Type Pixels Coord value at Pixel Coord incr Rotat localh> FITLD 1: RA---SIN 512 09 55 50. 704 256. 00 -0. 015000 0. 00 localh> FITLD 1: DEC--SIN 512 69 40 43. 591 257. 00 0. 015000 0. 00 localh> FITLD 1: FREQ 1 4. 5460000 E+09 1. 00 1. 4500000 E+07 0. 00 NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
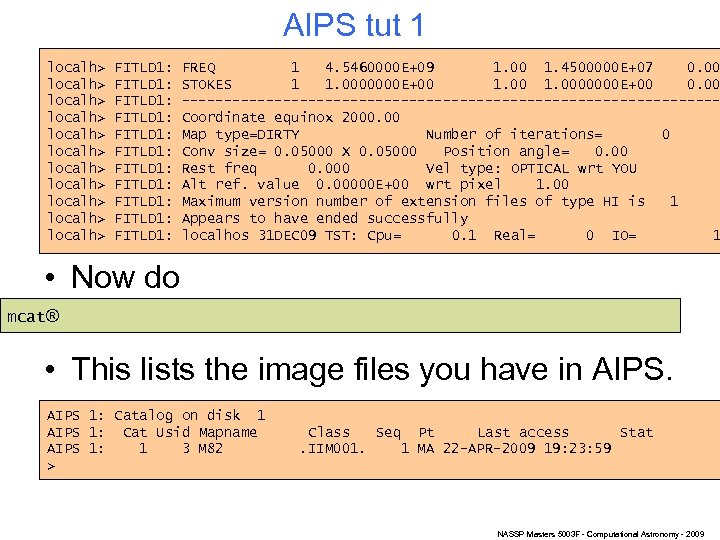 AIPS tut 1 localh> localh> localh> FITLD 1: FITLD 1: FITLD 1: FREQ 1 4. 5460000 E+09 1. 00 1. 4500000 E+07 0. 00 STOKES 1 1. 0000000 E+00 0. 00 --------------------------------Coordinate equinox 2000. 00 Map type=DIRTY Number of iterations= 0 Conv size= 0. 05000 X 0. 05000 Position angle= 0. 00 Rest freq 0. 000 Vel type: OPTICAL wrt YOU Alt ref. value 0. 00000 E+00 wrt pixel 1. 00 Maximum version number of extension files of type HI is 1 Appears to have ended successfully localhos 31 DEC 09 TST: Cpu= 0. 1 Real= 0 IO= 1 • Now do mcat® • This lists the image files you have in AIPS 1: Catalog on disk 1 AIPS 1: Cat Usid Mapname AIPS 1: 1 3 M 82 > Class Seq Pt Last access Stat. IIM 001. 1 MA 22 -APR-2009 19: 23: 59 NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 localh> localh> localh> FITLD 1: FITLD 1: FITLD 1: FREQ 1 4. 5460000 E+09 1. 00 1. 4500000 E+07 0. 00 STOKES 1 1. 0000000 E+00 0. 00 --------------------------------Coordinate equinox 2000. 00 Map type=DIRTY Number of iterations= 0 Conv size= 0. 05000 X 0. 05000 Position angle= 0. 00 Rest freq 0. 000 Vel type: OPTICAL wrt YOU Alt ref. value 0. 00000 E+00 wrt pixel 1. 00 Maximum version number of extension files of type HI is 1 Appears to have ended successfully localhos 31 DEC 09 TST: Cpu= 0. 1 Real= 0 IO= 1 • Now do mcat® • This lists the image files you have in AIPS 1: Catalog on disk 1 AIPS 1: Cat Usid Mapname AIPS 1: 1 3 M 82 > Class Seq Pt Last access Stat. IIM 001. 1 MA 22 -APR-2009 19: 23: 59 NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • Explanation of the various fields: – Cat: each file that AIPS stores has a unique catalog integer. As we’ll see in a minute, this can be a convenient way to grab a particular file. – Usid: should be your user ID integer. You can only see those files corresponding to that ID. – Mapname: should be what you supplied to the outname parameter of FITLD. – Class: should be what you supplied to the outclass parameter of FITLD. Note that all class names are 6 characters between two dots. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • Explanation of the various fields: – Cat: each file that AIPS stores has a unique catalog integer. As we’ll see in a minute, this can be a convenient way to grab a particular file. – Usid: should be your user ID integer. You can only see those files corresponding to that ID. – Mapname: should be what you supplied to the outname parameter of FITLD. – Class: should be what you supplied to the outclass parameter of FITLD. Note that all class names are 6 characters between two dots. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 – Seq: each file with a given combination of name and class has a unique sequence integer. Note that AIPS policy is never to throw anything away. If you modify a file, you usually won’t overwrite the old file: it will just store it with an incremented sequence number. – Pt: either MA for image or UV for visibilities. – Last access: obvious. – Stat: if a task is busy in the background reading from or writing to a file, this ‘busy’ state will be indicated by the status. • Note that ucat will list UV files and pcat will list everything. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 – Seq: each file with a given combination of name and class has a unique sequence integer. Note that AIPS policy is never to throw anything away. If you modify a file, you usually won’t overwrite the old file: it will just store it with an incremented sequence number. – Pt: either MA for image or UV for visibilities. – Last access: obvious. – Stat: if a task is busy in the background reading from or writing to a file, this ‘busy’ state will be indicated by the status. • Note that ucat will list UV files and pcat will list everything. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
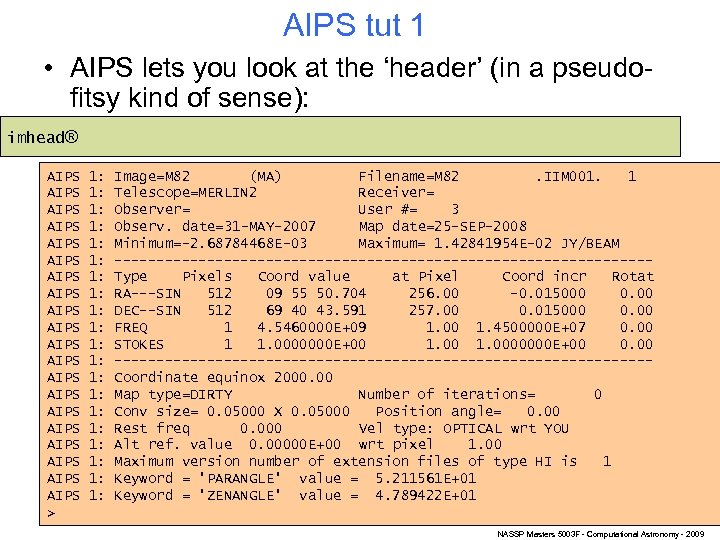 AIPS tut 1 • AIPS lets you look at the ‘header’ (in a pseudofitsy kind of sense): imhead® AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS > 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: Image=M 82 (MA) Filename=M 82. IIM 001. 1 Telescope=MERLIN 2 Receiver= Observer= User #= 3 Observ. date=31 -MAY-2007 Map date=25 -SEP-2008 Minimum=-2. 68784468 E-03 Maximum= 1. 42841954 E-02 JY/BEAM --------------------------------Type Pixels Coord value at Pixel Coord incr Rotat RA---SIN 512 09 55 50. 704 256. 00 -0. 015000 0. 00 DEC--SIN 512 69 40 43. 591 257. 00 0. 015000 0. 00 FREQ 1 4. 5460000 E+09 1. 00 1. 4500000 E+07 0. 00 STOKES 1 1. 0000000 E+00 0. 00 --------------------------------Coordinate equinox 2000. 00 Map type=DIRTY Number of iterations= 0 Conv size= 0. 05000 X 0. 05000 Position angle= 0. 00 Rest freq 0. 000 Vel type: OPTICAL wrt YOU Alt ref. value 0. 00000 E+00 wrt pixel 1. 00 Maximum version number of extension files of type HI is 1 Keyword = 'PARANGLE' value = 5. 211561 E+01 Keyword = 'ZENANGLE' value = 4. 789422 E+01 NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • AIPS lets you look at the ‘header’ (in a pseudofitsy kind of sense): imhead® AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS AIPS > 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: Image=M 82 (MA) Filename=M 82. IIM 001. 1 Telescope=MERLIN 2 Receiver= Observer= User #= 3 Observ. date=31 -MAY-2007 Map date=25 -SEP-2008 Minimum=-2. 68784468 E-03 Maximum= 1. 42841954 E-02 JY/BEAM --------------------------------Type Pixels Coord value at Pixel Coord incr Rotat RA---SIN 512 09 55 50. 704 256. 00 -0. 015000 0. 00 DEC--SIN 512 69 40 43. 591 257. 00 0. 015000 0. 00 FREQ 1 4. 5460000 E+09 1. 00 1. 4500000 E+07 0. 00 STOKES 1 1. 0000000 E+00 0. 00 --------------------------------Coordinate equinox 2000. 00 Map type=DIRTY Number of iterations= 0 Conv size= 0. 05000 X 0. 05000 Position angle= 0. 00 Rest freq 0. 000 Vel type: OPTICAL wrt YOU Alt ref. value 0. 00000 E+00 wrt pixel 1. 00 Maximum version number of extension files of type HI is 1 Keyword = 'PARANGLE' value = 5. 211561 E+01 Keyword = 'ZENANGLE' value = 4. 789422 E+01 NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • Now the fun begins. Do getn 1 tvall® • Note: getn 1 grabs the file with cat no 1. AIPS 1: 1: Hit Hit button A B C D to to enhance B/W or color alternately increment zoom & set zoom center decrement zoom & set zoom center exit • Note that you don’t get the AIPS > cursor back. The TV is in control now. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • Now the fun begins. Do getn 1 tvall® • Note: getn 1 grabs the file with cat no 1. AIPS 1: 1: Hit Hit button A B C D to to enhance B/W or color alternately increment zoom & set zoom center decrement zoom & set zoom center exit • Note that you don’t get the AIPS > cursor back. The TV is in control now. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • The TV window should light up and display what is in the image. • You should see what looks like a single point source centred in a fairly cruddy field. Comments: – The field is cruddy because it is a dirty image. – The point source is actually a supernova remnant which may have gone off as recently as 1980. Observations spaced a few years apart show it expanding rapidly. • You’ll also note that the cursor becomes a purple cross when it crosses the TV. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • The TV window should light up and display what is in the image. • You should see what looks like a single point source centred in a fairly cruddy field. Comments: – The field is cruddy because it is a dirty image. – The point source is actually a supernova remnant which may have gone off as recently as 1980. Observations spaced a few years apart show it expanding rapidly. • You’ll also note that the cursor becomes a purple cross when it crosses the TV. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
 AIPS tut 1 • Click in the TV window to capture focus on it. Then press keyboard key b a couple of times. The display should zoom in. • Now click with left mouse button somewhere in the image: the image should recentre to where you clicked. • Press key a then drag the mouse over the image. You should be able to change the contrast and brightness. • Pressing a again gives you a false-colour map, with the same mouse drag capability. • There's lots more you can do with the TV. See the Cookbook chapter 6. 4. But for now we'll get out of the TV and then AIPS. Press the d key to get out of ‘TV mode'. This should get you back your AIPS > cursor. Then kleenex out to unix. – All the windows disappear eventually although it can take a few seconds. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009
AIPS tut 1 • Click in the TV window to capture focus on it. Then press keyboard key b a couple of times. The display should zoom in. • Now click with left mouse button somewhere in the image: the image should recentre to where you clicked. • Press key a then drag the mouse over the image. You should be able to change the contrast and brightness. • Pressing a again gives you a false-colour map, with the same mouse drag capability. • There's lots more you can do with the TV. See the Cookbook chapter 6. 4. But for now we'll get out of the TV and then AIPS. Press the d key to get out of ‘TV mode'. This should get you back your AIPS > cursor. Then kleenex out to unix. – All the windows disappear eventually although it can take a few seconds. NASSP Masters 5003 F - Computational Astronomy - 2009


