bd6f94daa0699b293f95eaddc03ae00b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 • Aim: What role does Congress play in our government? • Do Now: When do you hear about Congress in the news?
• Aim: What role does Congress play in our government? • Do Now: When do you hear about Congress in the news?
 Congress US CAPITOL BUILDING Legislative Branch – “makes laws”
Congress US CAPITOL BUILDING Legislative Branch – “makes laws”
 If progress is the advancement of society, what is congress?
If progress is the advancement of society, what is congress?
 Facts About Congress: Senate: • Serve a 6 year term • Considered an “exclusive club” • 100 members • Based on equal representation House of Representatives: • Serve 2 year terms • Not as prestigious • 435 members • Based on population
Facts About Congress: Senate: • Serve a 6 year term • Considered an “exclusive club” • 100 members • Based on equal representation House of Representatives: • Serve 2 year terms • Not as prestigious • 435 members • Based on population
 Founders’ Intentions 1. Strongest branch 2. Separation of lawmaking power from executive 3. Bicameralism balances large/small states • House – more connected to people (2 yr term) • Senate – allows for independent thinking (6 yr term)
Founders’ Intentions 1. Strongest branch 2. Separation of lawmaking power from executive 3. Bicameralism balances large/small states • House – more connected to people (2 yr term) • Senate – allows for independent thinking (6 yr term)
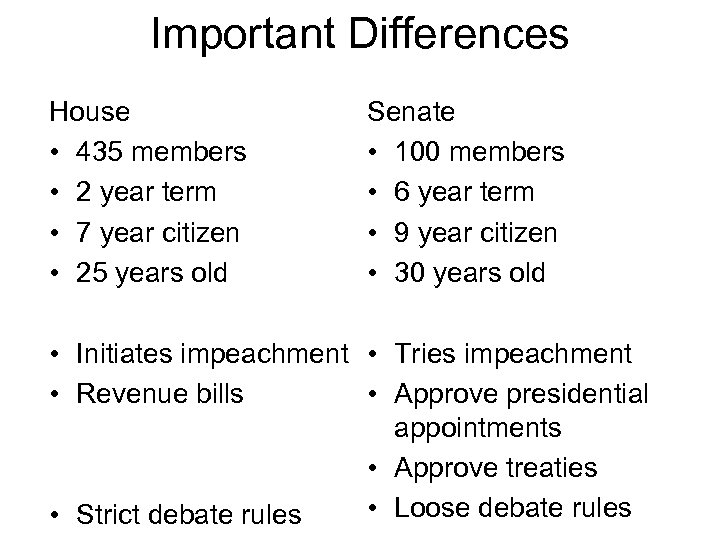 Important Differences House • 435 members • 2 year term • 7 year citizen • 25 years old Senate • 100 members • 6 year term • 9 year citizen • 30 years old • Initiates impeachment • Tries impeachment • Revenue bills • Approve presidential appointments • Approve treaties • Loose debate rules • Strict debate rules
Important Differences House • 435 members • 2 year term • 7 year citizen • 25 years old Senate • 100 members • 6 year term • 9 year citizen • 30 years old • Initiates impeachment • Tries impeachment • Revenue bills • Approve presidential appointments • Approve treaties • Loose debate rules • Strict debate rules
 Constitutional Powers Article I, Section 8 • To lay and collect taxes, duties, imports • To borrow money • To regulate commerce (states and foreign) • To establish rules for naturalization • To coin money • To create courts (except Supreme Court) • To declare war • To raise and support an army and navy
Constitutional Powers Article I, Section 8 • To lay and collect taxes, duties, imports • To borrow money • To regulate commerce (states and foreign) • To establish rules for naturalization • To coin money • To create courts (except Supreme Court) • To declare war • To raise and support an army and navy
 Evolution of Powers Elastic clause has extended Congress powers • Oversight of budget – can restrict the fed. budget prepared by executive branch • Appropriations – set amount of money made available for various activity in a fiscal year • Investigation – Congress can launch investigations (Watergate, Clinton-Lewinski hearings, Steroids in baseball)
Evolution of Powers Elastic clause has extended Congress powers • Oversight of budget – can restrict the fed. budget prepared by executive branch • Appropriations – set amount of money made available for various activity in a fiscal year • Investigation – Congress can launch investigations (Watergate, Clinton-Lewinski hearings, Steroids in baseball)
 Who’s in Congress? 110 th Congress (2007 -2008) • 85% male • 85% White • 40% Lawyers 109 th Congress (2005 -2006) • 29 accused of spousal abuse • 7 have been arrested for fraud • 19 arrested for writing bad checks • 117 have bankrupted at least 2 businesses • 8 have been arrested for shoplifting • In 1998 alone, 84 were stopped for drunk driving
Who’s in Congress? 110 th Congress (2007 -2008) • 85% male • 85% White • 40% Lawyers 109 th Congress (2005 -2006) • 29 accused of spousal abuse • 7 have been arrested for fraud • 19 arrested for writing bad checks • 117 have bankrupted at least 2 businesses • 8 have been arrested for shoplifting • In 1998 alone, 84 were stopped for drunk driving
 Elections • House members directly elected • Senators directly elected after 17 th Amend • House Incumbent advantage – Why? – Name recognition – Proven track record – Franking privileges – free mailing
Elections • House members directly elected • Senators directly elected after 17 th Amend • House Incumbent advantage – Why? – Name recognition – Proven track record – Franking privileges – free mailing
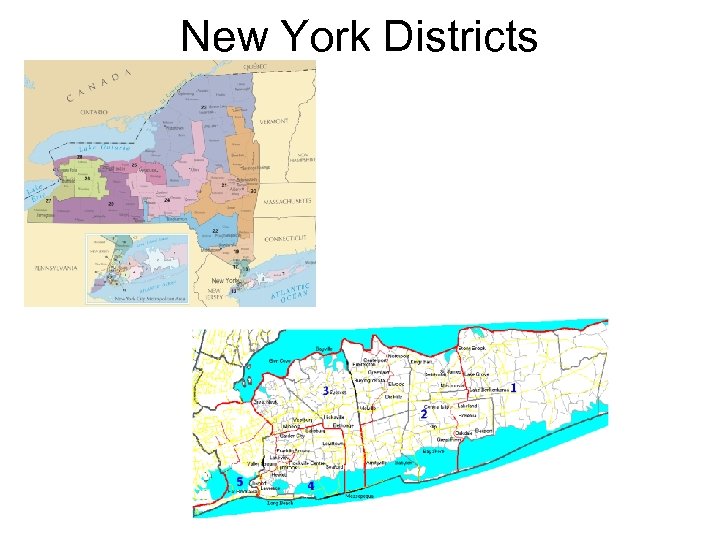 New York Districts
New York Districts
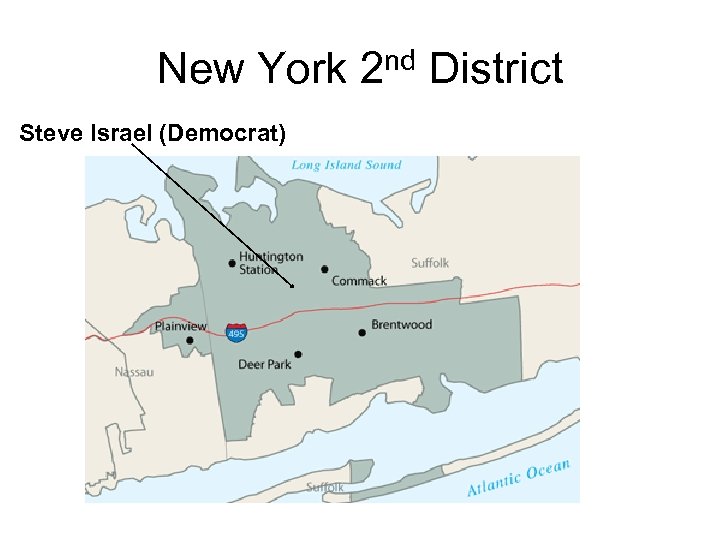 New York 2 nd District Steve Israel (Democrat)
New York 2 nd District Steve Israel (Democrat)
 House Size • 435 Members • Constitution requires reapportionment every ten years based on the census • States can gain or lose representatives
House Size • 435 Members • Constitution requires reapportionment every ten years based on the census • States can gain or lose representatives
 Problems to Solve in Determining Congressional Districts: 1. Determine total size of the House 2. Allocating seats in the House among the states 3. Determining the size of Congressional districts within the states 4. Determining the shape of those districts.
Problems to Solve in Determining Congressional Districts: 1. Determine total size of the House 2. Allocating seats in the House among the states 3. Determining the size of Congressional districts within the states 4. Determining the shape of those districts.
 What issues are related to Congressional redistricting? Malapportionment: drawing the boundaries of legislative districts so they are unequal in population Gerrymandering: drawing the boundaries of legislative districts in bizarre or unusual shapes to favor one party.
What issues are related to Congressional redistricting? Malapportionment: drawing the boundaries of legislative districts so they are unequal in population Gerrymandering: drawing the boundaries of legislative districts in bizarre or unusual shapes to favor one party.
 Landmark Cases • Baker v. Carr (1962): The Supreme Court has jurisdiction over legislative apportionment • Gray v. Sanders (1963): “One person, One vote” • Wesberry v. Sanders (1964): found unequal district pop. unconstitutional – 14 th amend • “One person, One vote” • Reynolds v. Sims (1964): State legislature districts had to be roughly equal in population • Easley v. Cromartie (2001) – redistricting for political ideology was constitutional, led to increase in minority reps
Landmark Cases • Baker v. Carr (1962): The Supreme Court has jurisdiction over legislative apportionment • Gray v. Sanders (1963): “One person, One vote” • Wesberry v. Sanders (1964): found unequal district pop. unconstitutional – 14 th amend • “One person, One vote” • Reynolds v. Sims (1964): State legislature districts had to be roughly equal in population • Easley v. Cromartie (2001) – redistricting for political ideology was constitutional, led to increase in minority reps
 Wesberry v. Sanders – some further information • Malapportionment was a major problem throughout the South where rural areas, populated mostly by whites, had more political power than urban areas, populated mostly by minorities. • Supreme court case of Wesberry v Sanders created the concept of “one person, one vote” • The result of Wesberry was that urban areas were now more evenly represented - and notice how after 1964 public policies suddenly started to change
Wesberry v. Sanders – some further information • Malapportionment was a major problem throughout the South where rural areas, populated mostly by whites, had more political power than urban areas, populated mostly by minorities. • Supreme court case of Wesberry v Sanders created the concept of “one person, one vote” • The result of Wesberry was that urban areas were now more evenly represented - and notice how after 1964 public policies suddenly started to change
 Powers of Congress: • Represent Constituents, Make Laws • Unique Powers of each house: – House of Reps: Initiate tax laws and spending bills, impeachment • House Ways and Means Committee: Oversees taxing and spending – Senate: Confirmation of Presidential appointments: federal court, ambassadorships, cabinet positions, ratify treaties, impeachment trial – Neither House may: Pass Bills of Attainder, Ex Post Facto Laws, Grant titles of nobility, tax exports
Powers of Congress: • Represent Constituents, Make Laws • Unique Powers of each house: – House of Reps: Initiate tax laws and spending bills, impeachment • House Ways and Means Committee: Oversees taxing and spending – Senate: Confirmation of Presidential appointments: federal court, ambassadorships, cabinet positions, ratify treaties, impeachment trial – Neither House may: Pass Bills of Attainder, Ex Post Facto Laws, Grant titles of nobility, tax exports
 Non Legislative (non-lawmaking) Tasks: • Oversight: investigate charges of corruption and waste • Public Education: bring national attention to important issues • Impeachment of Officials • Amending the Constitution (w. State Legislatures) – 2/3 Vote by Members of Congress – 3/4 Approved by State Legislatures • Advice and Consent (confirmations)
Non Legislative (non-lawmaking) Tasks: • Oversight: investigate charges of corruption and waste • Public Education: bring national attention to important issues • Impeachment of Officials • Amending the Constitution (w. State Legislatures) – 2/3 Vote by Members of Congress – 3/4 Approved by State Legislatures • Advice and Consent (confirmations)
 Leadership • Majority party controls the most significant leadership positions • House - Speaker of the House • • Allows people to speak on floor Assigns bills to committees Influences which bills are brought to a vote Appoints members of special and select committees • Senate – Majority Leader • Schedules Senate business • Prioritizes bills
Leadership • Majority party controls the most significant leadership positions • House - Speaker of the House • • Allows people to speak on floor Assigns bills to committees Influences which bills are brought to a vote Appoints members of special and select committees • Senate – Majority Leader • Schedules Senate business • Prioritizes bills
 The Senate • Vice Pres. is the President of the Senate (tie breaker) • The majority party picks a senior member to be the President Pro Tempore in the VP’s absence (honorific title) • Majority Leader: elected by majority party – Is recognized first in any debate • Minority Leader: elected by minority party
The Senate • Vice Pres. is the President of the Senate (tie breaker) • The majority party picks a senior member to be the President Pro Tempore in the VP’s absence (honorific title) • Majority Leader: elected by majority party – Is recognized first in any debate • Minority Leader: elected by minority party
 What’s the whip? Whips, deputy whips: Senator or Representative who 1. ensures members are present to vote 2. keeps track of how party members will vote on bills 3. persuades party members to vote a certain way
What’s the whip? Whips, deputy whips: Senator or Representative who 1. ensures members are present to vote 2. keeps track of how party members will vote on bills 3. persuades party members to vote a certain way
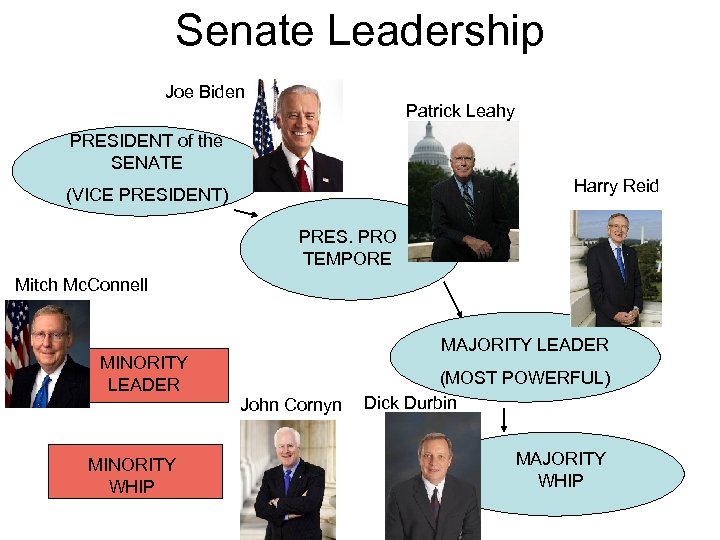 Senate Leadership Joe Biden Patrick Leahy PRESIDENT of the SENATE Harry Reid (VICE PRESIDENT) PRES. PRO TEMPORE Mitch Mc. Connell MAJORITY LEADER MINORITY LEADER John Cornyn MINORITY WHIP (MOST POWERFUL) Dick Durbin MAJORITY WHIP
Senate Leadership Joe Biden Patrick Leahy PRESIDENT of the SENATE Harry Reid (VICE PRESIDENT) PRES. PRO TEMPORE Mitch Mc. Connell MAJORITY LEADER MINORITY LEADER John Cornyn MINORITY WHIP (MOST POWERFUL) Dick Durbin MAJORITY WHIP
 House of Representatives • Speaker of the House: elected by majority party – Powerful position – 3 rd in line to become president (after VP) – Decides who will be recognized to speak – Rules on which topics are relevant – Influences committee assignments – Names members to select committees and conference committees – Influences which bills get to the floor for debate – Sets the calendar for when bills will be addressed
House of Representatives • Speaker of the House: elected by majority party – Powerful position – 3 rd in line to become president (after VP) – Decides who will be recognized to speak – Rules on which topics are relevant – Influences committee assignments – Names members to select committees and conference committees – Influences which bills get to the floor for debate – Sets the calendar for when bills will be addressed
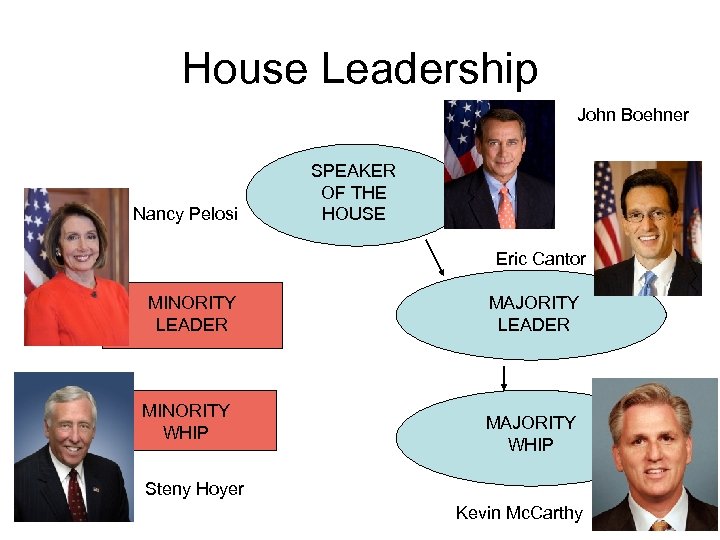 House Leadership John Boehner Nancy Pelosi SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE Eric Cantor MINORITY LEADER MINORITY WHIP MAJORITY LEADER MAJORITY WHIP Steny Hoyer Kevin Mc. Carthy
House Leadership John Boehner Nancy Pelosi SPEAKER OF THE HOUSE Eric Cantor MINORITY LEADER MINORITY WHIP MAJORITY LEADER MAJORITY WHIP Steny Hoyer Kevin Mc. Carthy
 Caucuses • Association of Congress members created to advance a political ideology, or a regional, economic, or ethnic interest • Approves committee assignments • Elects committee leaders • Helps build consensus on legislative agenda of the party Congressional Black Caucus is one notable caucus of democrats
Caucuses • Association of Congress members created to advance a political ideology, or a regional, economic, or ethnic interest • Approves committee assignments • Elects committee leaders • Helps build consensus on legislative agenda of the party Congressional Black Caucus is one notable caucus of democrats
 Types of Committees: • Standing Committee: Permanently established legislative committee that consider and are responsible for legislation within a certain subject area – Can propose legislation by reporting a bill out to the full House or Senate • Select Committees: Appointed for a limited time and purpose • Joint Committees: Committees on which both Senators and Representatives serve – an important joint committee is a Conference Committee – appointed to resolve differences in the Senate and House versions of the same bill
Types of Committees: • Standing Committee: Permanently established legislative committee that consider and are responsible for legislation within a certain subject area – Can propose legislation by reporting a bill out to the full House or Senate • Select Committees: Appointed for a limited time and purpose • Joint Committees: Committees on which both Senators and Representatives serve – an important joint committee is a Conference Committee – appointed to resolve differences in the Senate and House versions of the same bill
 Committee Composition: • The Committee Chair is a powerful position • The majority party makes up a majority of each committee and names the chairperson – Each House member serves on two Standing Committees (one if they are on an “exclusive committee” – i. e. Ways and Means, Appropriations) – Each Senator may serve on two “major” committees and one “minor” committee
Committee Composition: • The Committee Chair is a powerful position • The majority party makes up a majority of each committee and names the chairperson – Each House member serves on two Standing Committees (one if they are on an “exclusive committee” – i. e. Ways and Means, Appropriations) – Each Senator may serve on two “major” committees and one “minor” committee
 Decentralization of Congress • Today, power is more decentralized than in the past – members must work for their constituents and not always for the party • Chairmen cannot always block legislation or discourage junior members • Process of lawmaking is slower for this reason – more amendments to bills are proposed
Decentralization of Congress • Today, power is more decentralized than in the past – members must work for their constituents and not always for the party • Chairmen cannot always block legislation or discourage junior members • Process of lawmaking is slower for this reason – more amendments to bills are proposed
 Important Committees: House of Representatives: House Rules Committee: determines rules under which bills will be considered (time limits, amendments) House Appropriations Committee: funding for contracts and agencies House Ways and Means Committee: taxation, tariffs, and entitlement programs (welfare, social security, unemployment, Medicare)
Important Committees: House of Representatives: House Rules Committee: determines rules under which bills will be considered (time limits, amendments) House Appropriations Committee: funding for contracts and agencies House Ways and Means Committee: taxation, tariffs, and entitlement programs (welfare, social security, unemployment, Medicare)
 Senate: Senate Appropriations Committee: Funding for government agencies Senate Foreign Relations Committee: Foreign aid and policy
Senate: Senate Appropriations Committee: Funding for government agencies Senate Foreign Relations Committee: Foreign aid and policy
 Congressional member behavior • Members may be devoted to constituents, their own views, pressure groups, or party leaders… • Representational view: members vote to please their constituents, often to win reelection • Organizational view: if not voting for their constituents, vote along party lines, committees • Attitudinal view: members ideology determines members vote. Members of House more along lines of average voter, Senators less so… • Either way, member behavior is not usually obvious
Congressional member behavior • Members may be devoted to constituents, their own views, pressure groups, or party leaders… • Representational view: members vote to please their constituents, often to win reelection • Organizational view: if not voting for their constituents, vote along party lines, committees • Attitudinal view: members ideology determines members vote. Members of House more along lines of average voter, Senators less so… • Either way, member behavior is not usually obvious
 Reforming Congress: Areas which could be reformed: • Franking Privilege: the ability of members to mail letters to their constituents free of charge • Pork Barrel Legislation: Legislation that gives tangible benefits to constituents in several districts or states in the hope of winning their votes in return (highways, dams, post offices) • Party Polarization: A vote in which a majority of Democratic Legislators oppose a majority of Republican legislators • Term Limits: should members of Congress have term limits?
Reforming Congress: Areas which could be reformed: • Franking Privilege: the ability of members to mail letters to their constituents free of charge • Pork Barrel Legislation: Legislation that gives tangible benefits to constituents in several districts or states in the hope of winning their votes in return (highways, dams, post offices) • Party Polarization: A vote in which a majority of Democratic Legislators oppose a majority of Republican legislators • Term Limits: should members of Congress have term limits?
 Ethics: Senate: House: • Gifts: no more than $100 except from spouse or personal friend • Lobbyists may not pay for gifts, • Lobbyists may not pay for gifts or travel, or charitable contributions travel, even if lobbyists is spouse to groups controlled by senators or personal friend • Fees: No fees for lectures or • Travel: House members may writings (“honoraria”) except for travel at the expense of others if charity in certain circumstances travel is for officially connected meetings • Outside income may not exceed 15 percent of Senators salary • No honoraria • Ex Senators may not try to • Ex members may not lobby influence members of Congress for one year after leaving Senate leaving office
Ethics: Senate: House: • Gifts: no more than $100 except from spouse or personal friend • Lobbyists may not pay for gifts, • Lobbyists may not pay for gifts or travel, or charitable contributions travel, even if lobbyists is spouse to groups controlled by senators or personal friend • Fees: No fees for lectures or • Travel: House members may writings (“honoraria”) except for travel at the expense of others if charity in certain circumstances travel is for officially connected meetings • Outside income may not exceed 15 percent of Senators salary • No honoraria • Ex Senators may not try to • Ex members may not lobby influence members of Congress for one year after leaving Senate leaving office
 • Why are members of the House more concerned about their committee membership than senators? • What factors might influence the decisions of a committee when considering legislation? • Why might a member of Congress try to get on certain committees? • To what extent do the opinions of committee members reflect public opinion?
• Why are members of the House more concerned about their committee membership than senators? • What factors might influence the decisions of a committee when considering legislation? • Why might a member of Congress try to get on certain committees? • To what extent do the opinions of committee members reflect public opinion?


