7d4e90e56b3a44bba7c357d891b73200.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
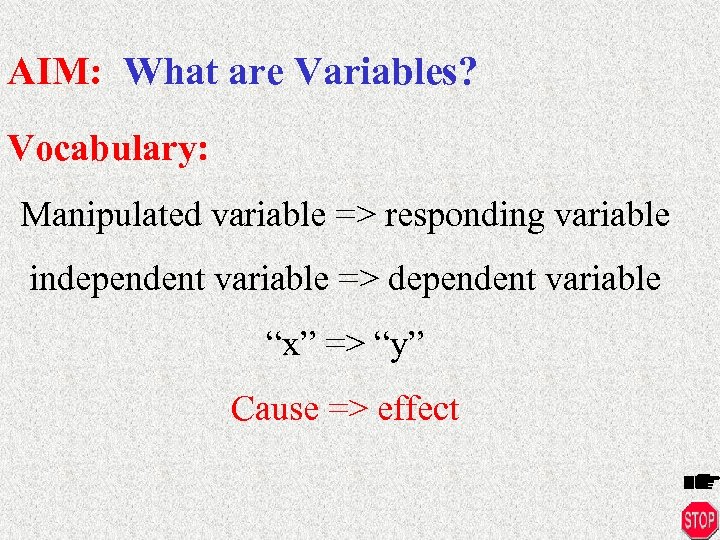
AIM: What are Variables? Vocabulary: Manipulated variable => responding variable independent variable => dependent variable “x” => “y” Cause => effect

VARIABLES WHAT IS A MANIPULATED VARIABLE? Thing that you “change” in an Experiment Manipulated Variable Independent Variable “x”

VARIABLES WHEN YOU CHANGE THE MANIPULATED VARIABLE THE RESPONDING VARIABLE IT CHANGES ALSO!

VARIABLES AS an example: How would you devise an experiment which would test whether a fertilizer actually helped plants grow? What is the independent variable? What is the dependent variable

VARIABLES AS an example: How would you devise an experiment which would test whether sunlight actually helped plants grow? What is the independent variable? What is the dependent variable

VARIABLES AS an example: How would you devise an experiment which would test whether Mr. Z’s fish could live in salt water? What is the independent variable? What is the dependent variable
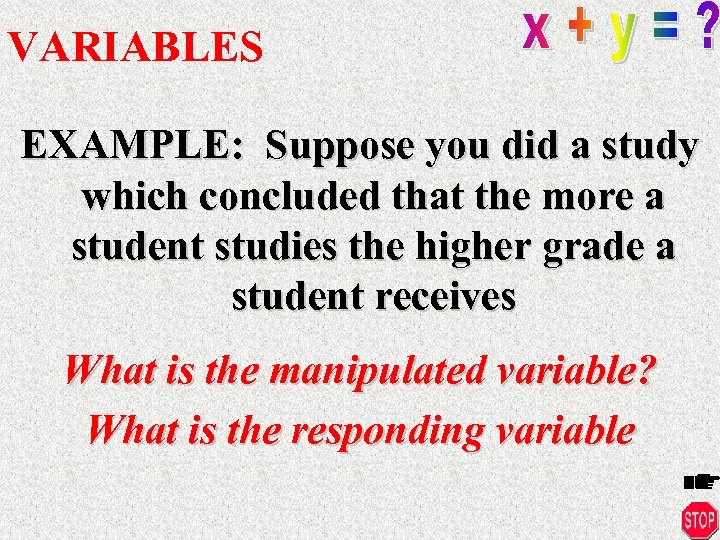
VARIABLES EXAMPLE: Suppose you did a study which concluded that the more a student studies the higher grade a student receives What is the manipulated variable? What is the responding variable

VARIABLES EXAMPLE: Suppose you did a study which concluded that the older people become, then the higher becomes their IQ What is the manipulated variable? What is the responding variable

VARIABLES EXAMPLE: Suppose you did a study which concluded that the more children watch TV, then the lower their SAT scores What is the manipulated variable? What is the responding variable

VARIABLES EXAMPLE: Suppose you did a study which concluded that the more fertilizer a plant receives, then the more flowers it produces What is the manipulated variable? What is the responding variable

VARIABLES EXAMPLE: Suppose you did a study which concluded that oceans which have a higher “salt” content will have less fish What is the manipulated variable? What is the responding variable

VARIABLES EXAMPLE: Suppose you did a study which concluded that the faster a car travels, the less its fuel economy will be What is the manipulated variable? What is the responding variable

VARIABLES üEXAMPLE: Suppose you did a study which concluded that as the average temperature in a pond increases, then the average number of frog “croaks” (per minute) increases üWhat is the manipulated variable? üWhat is the responding variable

Those we try to Change (Cause) The result of the Change (effect) • Independent Variable • Manipulated Variable • X variable • dependent variable • responding variable • Y variable

VARIABLES Consider This: Will a house plant grow better in a warm room or a colder room What is going to be the manipulated variable? The Temperature of the Room

VARIABLES Consider This: Will a house plant grow better in a warm room or a colder room What is going to be the responding variable? Plant Growth

VARIABLES EXAMPLE: Lava from a Hawaiian volcano travels a 20 feet every minute What is the manipulated variable? What is the responding variable Time => distance

VARIABLES TIPS FOR IDENTIFYING VARIABLES 1. Identify the problem being investigated 2. Identify the manipulated variable and the responding variable 3. Identify which one CAUSES the other one to change
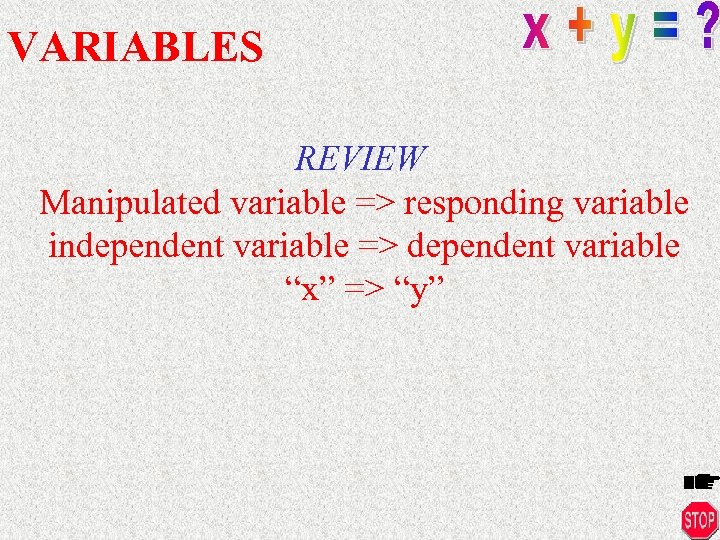
VARIABLES REVIEW Manipulated variable => responding variable independent variable => dependent variable “x” => “y”

VARIABLES ØClass Handout Activity pg. 46: Controlling Variables ØGraph Data Table

VARIABLES Homework: Internet Questions Finish a Graph of the Data Table
7d4e90e56b3a44bba7c357d891b73200.ppt