a9f41a8695950bf2b566c43cbcdc7d23.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Aim: Do the middle Ages deserve to be called the “Dark Ages”? Do Now: What do you think would happen to American society if the entire United States government collapsed? Would things go on as usual? If not, what would change?

I What were the middle Ages? A) In 476 CE the Roman Empire fell in Western Europe. Without a centralized government, people fled from the cities to the country. Literacy and trade fell. B) Historians refer to the years between 476 CE and the Renaissance (the rebirth of Western Europe) as the middle Ages. C) However, at the same time that Western Europe was in the middle ages, the eastern half of the Roman Empire continued as the Byzantine Empire, and the Islamic world was experiencing a Golden Age. 476 CE Rome in Western Europe fell 476 - 1450 Western Europe was in the middle Ages 15 -16 th centuries Western Europe “woke up” to the Renaissance

II Charlemagne and the Holy Roman Empire A) Charlemagne was a leader of the Franks, a barbarian tribe. He tried to rebuild the Roman Empire. B) He was crowned Holy Roman Emperor by the Pope in 800 CE. C) He created the strongest government since Rome; he built schools and conquered what is today France and Germany. After he died in 814, his empire began to decline. In 843, his grandsons signed the Treaty of Verdun that divided up his empire. 1. Why do you think Charlemagne’s empire was called the Holy Roman Empire if the western Roman Empire had fallen over 300 years before? 2. Why do you think it was significant that the Pope crowned Charlemagne?
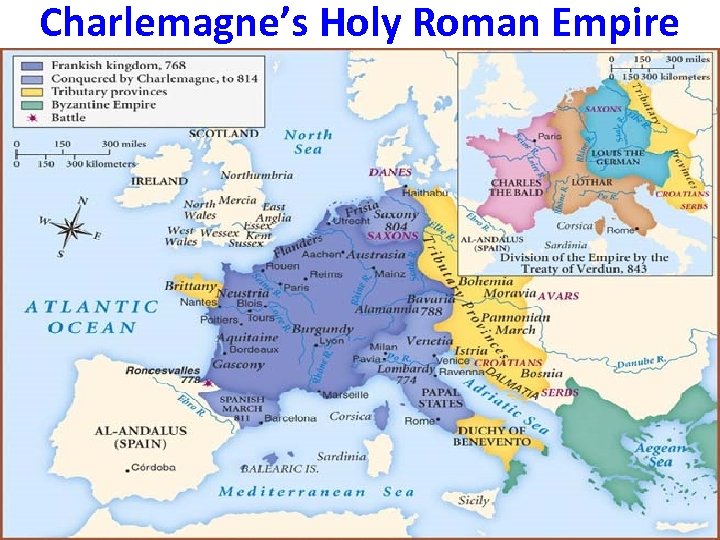
Charlemagne’s Holy Roman Empire
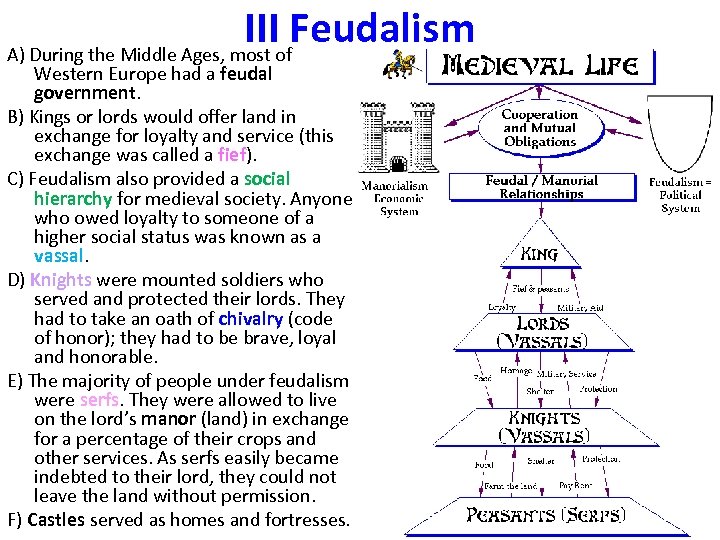
IIIof. Feudalism A) During the Middle Ages, most Western Europe had a feudal government. B) Kings or lords would offer land in exchange for loyalty and service (this exchange was called a fief). C) Feudalism also provided a social hierarchy for medieval society. Anyone who owed loyalty to someone of a higher social status was known as a vassal. D) Knights were mounted soldiers who served and protected their lords. They had to take an oath of chivalry (code of honor); they had to be brave, loyal and honorable. E) The majority of people under feudalism were serfs. They were allowed to live on the lord’s manor (land) in exchange for a percentage of their crops and other services. As serfs easily became indebted to their lord, they could not leave the land without permission. F) Castles served as homes and fortresses.

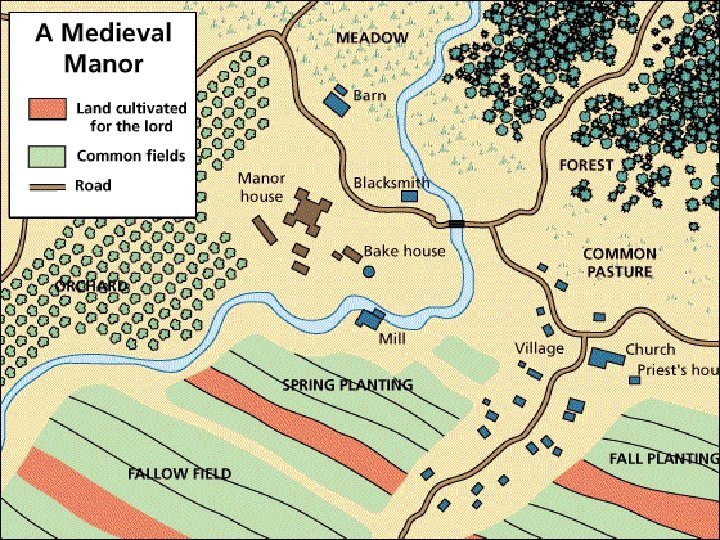
IV Manorialism A) Manorialism was a medieval economic system. B) It was based around the manor (a large farm estate). Serfs (peasant farmers) worked the land in exchange for the lord’s protection and permission to live on the land. C) In order to maximize the amount of crops produced, serfs used crop rotation. In the two field system, the serfs would plant one field and leave the other fallow (unplanted) so the soil could regain its nutrients. By the later middle ages, many were using the three field system. The serfs would plant two fields, and leave third fallow. (This produced more crops than the two field system).

V The Medieval Church A) In Western Medieval Europe, the Church (based in the Vatican in Rome) owned the most land, and had the most power. B) Everyone had to pay a tithe, or 10% of their income to the Church. C) Almost no one except for the clergy (people who worked in the Church) were educated. D) Monks and nuns were Christians who took a vow of chastity and served god for life. They often lived in monasteries (isolated communities), or helped the poor. Some monks created illuminated manuscripts (illustrated texts); they would hand write and illustrate the Bible. **Monks also hand copied ancient Greek and Roman texts, preserving them!

The Medieval Church Continued… E) Early Medieval Churches were built in the Romanesque style. They had Roman style arches, vaulted ceilings, and thick walls.

The Medieval Church Continued… F) Later Medieval Churches were built in the Gothic style; they were taller and lighter with more detail.

The Medieval Church Continued… G) The Church began the inquisition to find and stop heresy (actions that went against the Church), as well as blasphemy (speech or writing that went against the Church). H) In the 15 th century the Church began the Inquisition. Officials would ask questions to prove if you were truly Catholic. If they believed you not to be a true Catholic and you did not confess, they would torture you, often until death.

VI The Crusades A) In 638 CE the Umayyad Muslims conquered Jerusalem and built the Dome of the Rock. They allowed Jews and Christians to pray at their holy sites if they paid a tax. B) In the 1050 s, the Seljuk Turks (Muslims) took control of Jerusalem. Unlike the Umayyads, they often were intolerant of Jews and Christians. The situation got worse and in 1095 the Byzantine emperor asked the Pope for help. D) 1095 Pope Urban II called for Christian Knights to travel to the Holy Land rescue it from the Turks. He promised those who went forgiveness of their sins, though many also went for wealth and adventure.
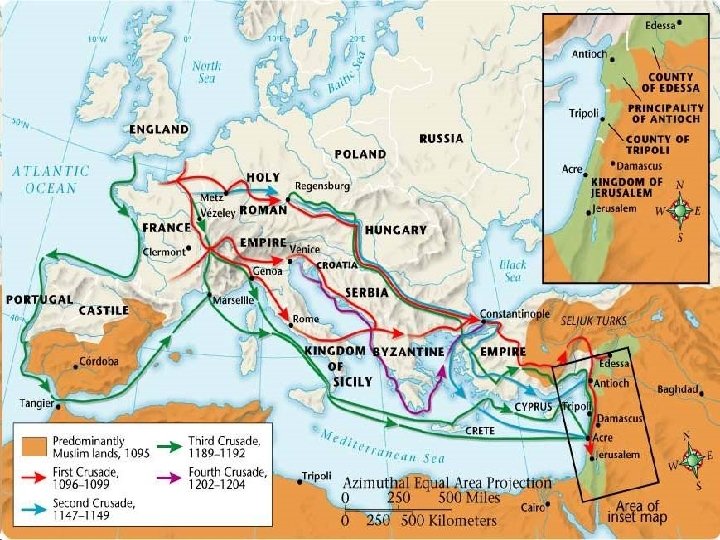

The Crusades Continued… E) During the First Crusade, in 1099 the Christians conquered Jerusalem and established a Christian feudal kingdom. F) However, the Muslims were able to gain back some of the land they lost. This led to more crusades. “Entering the city, our pilgrims pursued and killed the Saracens up to the temple of Solomon. [The Wailing or Western Wall] There the Saracens [Muslims] assembled and resisted fiercely all day, so that the whole temple flowed with their blood. At last the pagans were overcome and our men seized many men and women in the temple, killing them or keeping them alive as they saw fit…Afterwards our men went rejoicing and weeping for joy to adore the sepulcher of our Savior Jesus [a Church built where Jesus was believed to have died]…” -1099, an anonymous eye witness Do you think this is an accurate eyewitness account? How do you know? During the 12 th century, Saladin was a very strong Muslim leader. He recaptured Jerusalem but allowed the crusaders to leave safely.
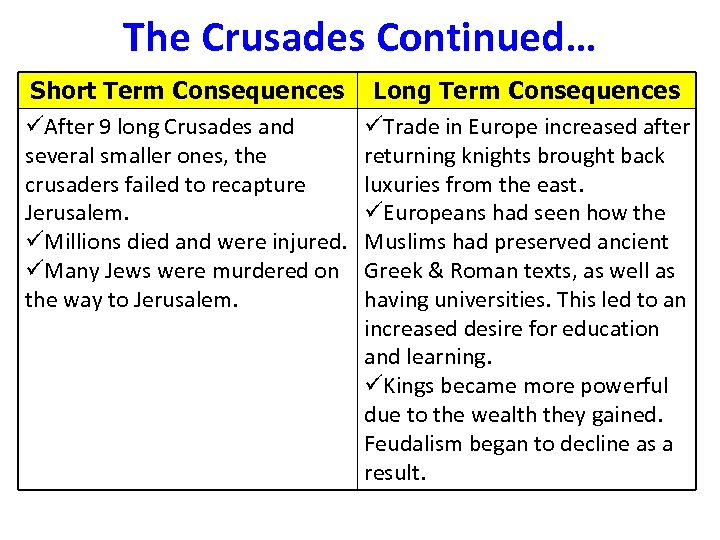
The Crusades Continued… Short Term Consequences üAfter 9 long Crusades and several smaller ones, the crusaders failed to recapture Jerusalem. üMillions died and were injured. üMany Jews were murdered on the way to Jerusalem. Long Term Consequences üTrade in Europe increased after returning knights brought back luxuries from the east. üEuropeans had seen how the Muslims had preserved ancient Greek & Roman texts, as well as having universities. This led to an increased desire for education and learning. üKings became more powerful due to the wealth they gained. Feudalism began to decline as a result.

VII The Black Death A) CAUSES: The Black Death was a deadly disease spread by fleas on rats. It began in Asia in the 1340 s and spread along trade routes to Africa, the Middle East and Europe. B) Symptoms included black swellings, pain and death within days. Medieval doctors often wore masks to protect themselves. They would bleed their patients (often making it worse). C) Flagellants travelled town to town, whipping themselves. They believed G-d was punishing them. Many Europeans also blamed the Jews; it led to increased anti-Semitism. D) CONSEQUENCES: 1/3 of Europeans died. Approximately 75 million died worldwide. Due to less serfs, many lords switched from farming to raising sheep. Serfs began to move to towns and cities.
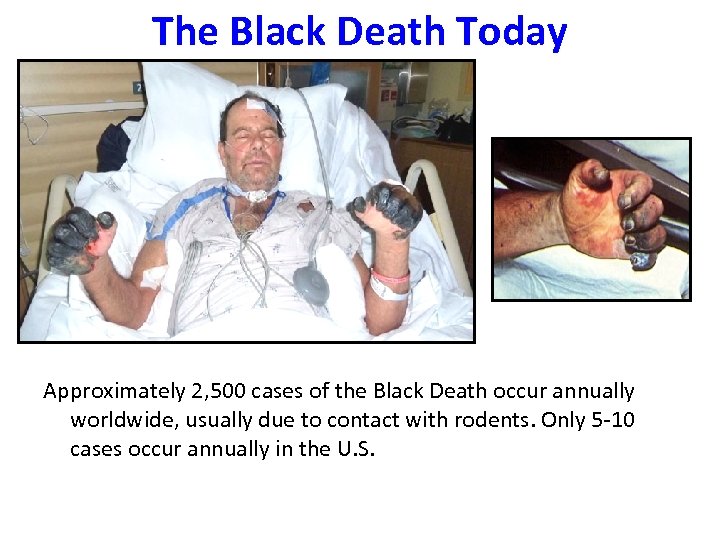
The Black Death Today Approximately 2, 500 cases of the Black Death occur annually worldwide, usually due to contact with rodents. Only 5 -10 cases occur annually in the U. S.

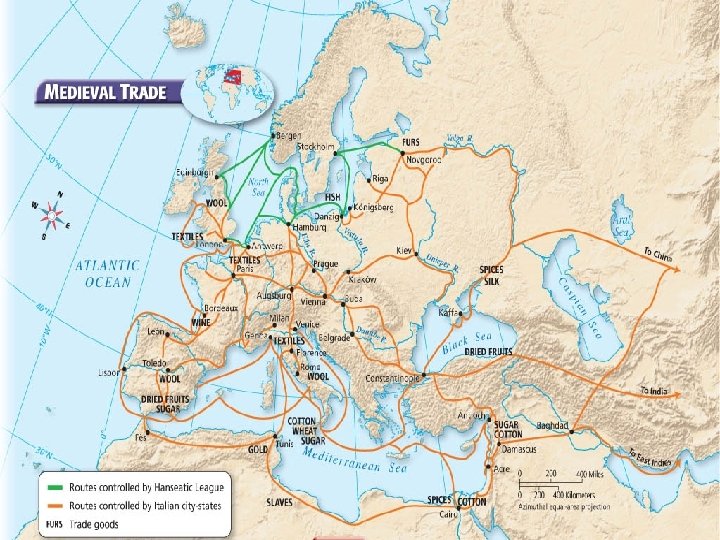
VIII Medieval Towns and Trade A) The agricultural revolution (switch from a wooden to an iron plow, switch from the 2 field to the 3 field system) increased crops, leading to an increase in Europe’s population. This helped lead to the growth of towns and cities. B) The commercial revolution allowed people to go to banks for loans, insurance, and to buy stocks in businesses. Merchants would set up temporary shops along busy trade routes. Over time, these became trade fairs, and eventually towns. C) Many lords made town charters, allowing a town to be built on the lord’s land. Bruges, a medieval town in Belgium

Medieval Towns and Trade Continued… D) After the Crusades, trade in medieval Europe increased. It became dominated by the Hanseatic League in northern Europe and Venice in southern Europe. Both built lighthouses, policed piracy and controlled the trade routes. Venice, Italy Bergen, Norway

Medieval Towns and Trade Continued… E) In medieval towns, merchants and craftspeople formed guilds so they could regulate themselves. Guilds: 1. Made sure the quality of the goods/service stayed high 2. Provided social services for its members, such as hospitals 3. Controlled hours of work and prices of goods To join a craft guild (such as the bakers or iron smiths), you had to become an apprentice to a master. After years of training you became a journeyman, and possibly if the guild accepted you, a master.
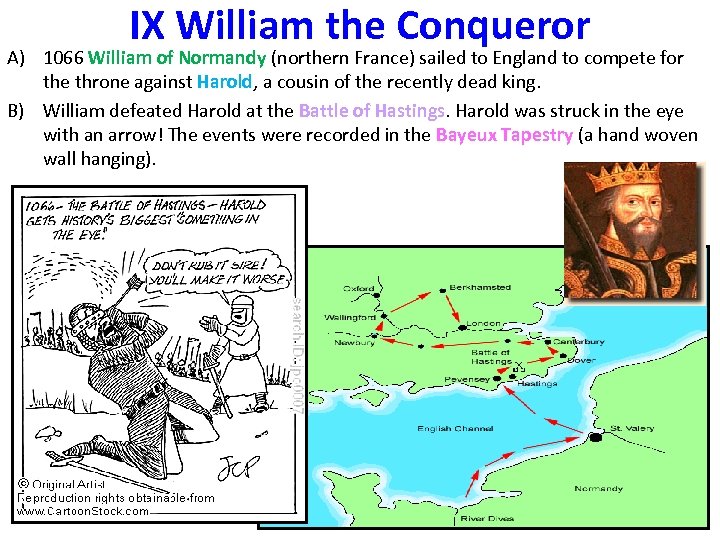
IX William the Conqueror A) 1066 William of Normandy (northern France) sailed to England to compete for the throne against Harold, a cousin of the recently dead king. B) William defeated Harold at the Battle of Hastings. Harold was struck in the eye with an arrow! The events were recorded in the Bayeux Tapestry (a hand woven wall hanging).

William the Conqueror Continued… The Bayeux Tapestry consists of 72 scenes, all hand embroidered. The entire tapestry is 250 feet long!
William the Conqueror Continued… C) After conquering England, William the Conqueror sent government officials to count people and their animals. This information was recorded in the Domesday Book, and was used for tax purposes. (Similar to our census) D) In 1297, King John of England was forced by his nobles to sign the Magna Carta (Great Charter). This document limited the power of the king, and guaranteed certain rights to the nobility. E) By 1400, England’s parliament had 2 houses (Lords & Commons). Parliament checked the power of the king. Magna Carta Excerpts: 1. “No freeman shall be taken, imprisoned, or in any other way destroyed, except by the lawful judgment of his peers. ” 2. “To no one will we sell, to no one will we refuse or delay right or justice. ” How did the Domesday Book get its name? It was believed the only thing more accurate than the Domesday Book would be the Last Judgment or “Doomsday”. “There was no single hide nor a yard of land, nor indeed one ox nor one cow nor one pig which was left out. ”
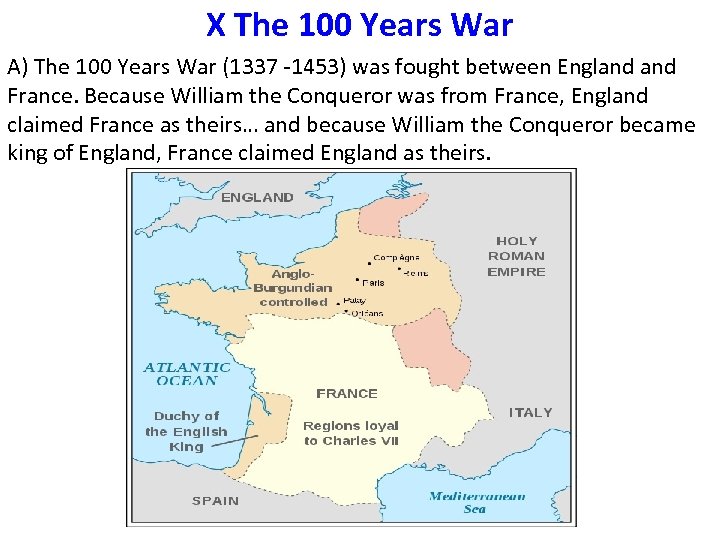
X The 100 Years War A) The 100 Years War (1337 -1453) was fought between England France. Because William the Conqueror was from France, England claimed France as theirs… and because William the Conqueror became king of England, France claimed England as theirs.

The 100 Years War Continued… B) In the beginning of the war, England was winning due to their new weapon, the long bow. (It shot arrows at a longer range and more accurately than the French’s cross bow). B) Joan of Arc was a young peasant girl. She heard a heavenly voice that told her to lead the French to victory in 1429. The French King allowed her to do so. *She rode into battle with a banner, but she never used a weapon. C) Joan did turn the tide of the war; the French were now winning. However, Joan was captured by the Burgundians. The French King refused to pay her ransom and she was sold to the British, put on trial for witchcraft, and burned at the stake in 1431. D) France won the war and kicked the English out, increasing nationalism. Feudalism was ending and being replaced by nation states! The long bow shoots up to 400 yards! An archer could shoot 12 -15 arrows per minute! BUT it took a lot of training to master.

The 100 Years War Continued… Excerpt From a Letter Written by Joan of Arc to the King of England, 1429 “King of England, render account to the King of Heaven of your royal blood. Return the keys of all the good cities which you have seized, to the Maid. She is sent by God to reclaim the royal blood, and is fully prepared to make peace, if you will give her satisfaction; that is, you must render justice, and pay back all that you have taken…” 1. If you were the King of England, how would you react to this letter? 2. Based on this letter, do you think that Joan of Arc seem more sane or crazy?

XI Medieval Achievements A) Architecture: Romanesque and Gothic Cathedrals, castles B) Art: Bayeux Tapestry, Romanesque and Gothic Cathedrals C) Literature: By the late Middle Ages, books began to be written in the vernacular (every day language). 1. Chaucer: Canterbury Tales 2. Dante: The Divine Comedy D) Philosophy: Peter Abelard and Thomas Aquinas, educated in ancient Greek philosophy, used logic and reason to prove Christianity. E) Commerce and trade: Creation of guilds, banks F) Science and technology: three field system, iron plow, wind mills In The Divine Comedy Dante is guided by Virgil (an ancient Roman poet) through the different levels of hell, purgatory (in-between heaven and hell), and finally heaven. It was written as a warning to a corrupt society to steer itself to the path of righteousness: "to remove those living in this life from the state of misery, and lead them to the state of felicity. "

Key Vocabulary 100 Years War 2 and 3 Field Systems Agricultural Revolution Battle of Hastings Bayeux Tapestry Black Death Charlemagne Chivalry Commercial Revolution Crusades Domesday Book Feudalism Flagellants Guilds Hanseatic League Holy Roman Empire Joan of Arc Knights Manorialism Middle Ages Monastery Monks Pope Urban II Renaissance Saladin Seljuk Turks Serfs Treaty of Verdun Vassal Venice William the Conqueror

Summary Questions 1. What events led to the middle ages? 2. Describe medieval society, government, and economy. How was it different from ancient Rome? 3. List and describe at least 4 key events in the middle ages. Why were they key events? 4. List and describe at least 4 achievements of the middle ages. Why were they achievements? 5. Do you think the middle Ages deserve to be called the “Dark Ages”? Explain.
a9f41a8695950bf2b566c43cbcdc7d23.ppt