40774201ed57a523d33eeb74bdc8bbbf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

AGROCHEMICALS Population: Crop Yields: 1 B in 1830; 5 B in 1986; > 6. 76 B today (Jan 09) ~ 25 bushels/acre (1800) to >110 b/a today ~ 1. 68 tonnes/hectare (1800); 7. 39 tonnes/hecate today

FERTILIZERS NITROGEN: plants require N as NO 3 -, either from natural sources or by symbiotic N 2 fixing bacteria Legume crops have root nodules that contain bacteria capable of converting N≡N to nitrate (via Mo, V based nitrogenase enzymes) egs. alfalfa, lover, most beans and peas ALL others need nitrate – add as fertilizer BUT water soluble so much washes into lakes and streams causing algal blooms

PHOSPHORUS Phosphate rock (and bone meal) is mostly Ca 3(PO 4)2 very insoluble Treatment with sulfuric acid gives more soluble SUPERPHOSPHATE Ca(H 2 PO 4)2 + 2 Ca. SO 4 more easily absorbed by plants BUT more easily washed in to lakes TRIPLE SUPERPHOSPHATE uses phosphoric acid to give Ca(H 2 PO 4)2 POTASSIUM Potash: technically this is K 2 CO 3 from wood ashes but the term now applied to any potassium deposit such as KCl Global ~ 36 M tonnes/y (as K 2 O equivalents) Canada 32% (Saskatchewan and Alberta) NB: Saskatchewan led Canada in jobs, economic growth in 2008 due largely to potash, uranium and oil industries

MIXED BAG FERTILIZERS N-P-K 13 -10 - 6 13% N, as elemental N 10% P, as P 2 O 5 (‘real’ %P = P number x 0. 44) 6% K, K 2 O (‘real’ %K = K number x 0. 83) so 13 -10 -6 is really 13 -4. 4 -5. 0 ! ASIDE: THE ENERGY PROBLEM Corn uses ~ 950 L fuel per hectare so to get 4 kg of corn uses about 1 kg of fuel ENERGY IN: 45 MJ for fuel ENERGY OUT: 10 -60 MJ (depending on efficiency of processes) Diverting corn to fuel use may not make energy sense!

What is alternative to more fertilizers? Plant Growth Hormones (>100 M$) Auxins cause enlargement of cells Gibberellins stimulate division and enlargement Cytokinins stimulate division Gibberellic acid Treatment of sugar cane with 100 g gibberellin per hectare, increases yield ~ 12 tonnes/hectare Good on grapes - larger No good on cabbage - makes it flower

Monsanto’s Polaris HOOCCH 2 N(CH 2 PO 3 H 2)2 = Glyphosphine is an aminoacid derivative which increases sugar content 10 -20% at harvest (introduced in sugar shortage of 1974, enormous profits) – very similar to structure to their herbicide Roundup: LD 50 = 4 g / kg body mass! Very low toxicity to mammals (inhibits plant protein synthesis, specifically of aromatic amino acids) Cyanamid’s Cycocel (Me 3 NCH 2 Cl)+Clalso ripens sugarcane, but reduces the stem length of cereal crops like wheat - reduces fall over in heavy wind/rain Ethephon Cl. CH 2 PO 3 H 2 stimulates latex flow in rubber trees, stimulates flowering in pineapples. . .

HERBICIDES (> 15 B $ World, > 7 B US alone) ~ ½ B kg /y Weeds compete for fertilizer and water; reduce crop yields 90% corn, soya-beans, cotton, pea-nuts, rice treated; 75% of herbicides go on farm crops 2, 4 -D (1946) and 2, 4, 5 -T (late 50’s) (mixture = Agent Orange): 2, 4 -D 2, 4, 5 -T ‘Dioxin’

2, 4 -D (1946) kills broadleaf plants at 200 g – 2. 5 kg per hectare (much less than the inorganic defoliants used to that point) Cheap (use >100 M kg/y); Low mammalian toxicity ~0. 5 g / kg orally, 1. 5 g / kg dermally; degrades quickly in soil, does not concentrate Can use on wheat, barley, corn, sugar, rice, GRASS (home use) then the relative 2, 4, 5 -T was found to be more effective on brush, blackberries: used around power lines AND THE VIETNAM JUNGLE

US used ~70 M L of 50: 50 2, 4 -D/2, 4, 5 -T (AGENT ORANGE) Vietnam sprayed neat, not diluted as used commercially in NA Causes puss oozing acne and birth defects due to the Dioxin impurity in 2, 4, 5 -T - stopped use in 1970 EPA permitted use on rice, rights of way, home use till 1985 (later in Canada) Viktor Yushchenko, Ukrainian Presidential Candidate 2004, Poisoned by ‘dioxin’ (? ) Shows the classic disfigurement Caused by severe chloracne

ATRAZINE (Ciba-Geigy, Shell, Syngenta) Used at 2 -5 kg / hectare LD 50 ~5 g / kg Corn is able to remove -Cl and deactivate so atrazine is widely used Disrupts photosynthesis Controversy: It was one of the more widely used, but Banned in EU in 2004 because detected in ground waters. Some associate the feminization of frogs to atrazine; US disagrees: http: //www. syngentacropprotection-us. com/prod/herbicide/Atrazine/ http: //www. epa. gov/safewater/contaminants/dw_contamfs/atrazine. html http: //www. pan-uk. org/pestnews/Actives/atrazine. htm

Major herbicides in use today • Imazapyr, is a non-selective herbicide used for the control of a broad range of weeds including terrestrial annual and perennial grasses and broadleaved herbs, woody species, and riparian and emergent aquatic species. • Imazapic, is a selective herbicide for both the pre- and post-emergent control of some annual and perennial grasses and some broadleaf weeds. Imazapic kills plants by inhibiting the production of branched chain amino acids, which are necessary for protein synthesis and cell growth. • Glyphosate, a systemic nonselective (it kills any type of plant) herbicide used in no-till burndown and for weed control in crops that are genetically modified to resist its effects. It is an example of an EPSPs inhibitor. • Paraquat, a nonselective contact herbicide used for no-till burndown and in aerial destruction of marijuana and coca plantings. More acutely toxic to people than any other herbicide in widespread commercial use. • 2, 4 -D, a broadleaf herbicide in the phenoxy group used in turf and in no-till field crop production. Now mainly used in a blend with other herbicides that act as synergists, it is the most widely used herbicide in the world, third most commonly used in the United States. It is an example of synthetic auxin. • clopyralid, is a broadleaf herbicide in the pyridine group, used mainly in turf, rangeland, and for control of noxious thistles. Notorious for its ability to persist in compost. It is another example of synthetic auxin. • metoalachlor, a pre-emergent herbicide widely used for control of annual grasses in corn and sorghum; it has largely replaced atrazine for these uses. • dicamba, a persistent broadleaf herbicide active in the soil, used on turf and field corn. It is another example of synthetic auxin. • picloram, a pyridine herbicide mainly used to control unwanted trees in pastures and edges of fields. It is another synthetic auxin. • atrazine, a triazine herbicide used in corn and sorghum for control of broadleaf weeds and grasses. Still used because of its low cost and because it works as a synergist when used with other herbicides, it is a photosystem II inhibitor.

Pesticides and Insecticides Pesticide residues on fruit and vegetables are very small Natural carcinogens, eg. aflatoxin in the mould on peanuts and corn is much more dangerous Risk from carcinogens: 1/3000 motor cycle 1/300 smoking 1/25 car driving 25 x strike by lightening!

Daminozide (ALAR) Uniroyal (1963) Before 1989, BC and Washington apples were sprayed with ALAR to stops premature falling and bruising Feb 1989: ‘ 60 Minutes’ aired a report that ALAR was found in apple juice and caused tumors in rats – at the equivalent to 20, 000 L of apple juice per day per rat! Uniroyal took ALAR off market voluntarily (Apple growers filed a libel suit against CBS, dismissed in ‘ 94) Now apples can develop a natural fungus in bruises that produces the mycotoxin patulin: An antibiotic but also a carcinogen that may be more potent than ALAR!

INSECTICIDES 500 BC 1500 1800 1900’s Burning Sulfur; Arsenic Nicotine (Sulfate) Lead Arsenate 1900 Extract of dried chrysanthemum = PYRETHRUM Have to hit insect Decomposes in sunlight (no good for crops) Low mammalian toxicity

By 1949 had developed more stable synthetic ones: Allethrin could be used in sunlight but needs a synergist, piperonyl butoxide, to prevent insect recovery - used in RAID and expensive Since 1970, for agricultural use, Permethrin (Ambush, Pounce) is better, need only 100 g/hectare – more stable, cheaper, BUT still relatively expensive LD 50 = 2 g/kg - low – known as PYRETHROIDS

THE CHLORINATED PESTICIDES DDT first made in 1873 in Germany (Baeyer) but insecticidal properties not recognized until 1939 (Geigy labs in Switzerland) ALL CHEAP < 50 c/kg in 1940 dichlorodiphenyltrichlorethane Wartime: pyrethrum supply cut off by Japan (troops were lice/tick infested) Tried DDT as 10% powder mixed with talc directly on millions of troops: 3 M people treated in Naples in 1943 alone!

DDT THE GOOD Cheap Effective against all insects Extremely persistent Low toxicity to non-insects DDT THE BAD Cheap - used indiscriminately Kills ‘good’insects Stays around for >20 years Estrogenic effect on birds [LD 50 300 -500 mg/kg, 2 -3 g/kg dermally, but about 10 mg/kg to insects] Insects do not need to eat - absorbed through cuticles: allows Na + to leak into nerve channels, continuous transmission of nerve impulses, overload, death Crop yields went up Stopped Gypsy Moth in East, Spruce Budworm in West Reduced malaria in tropics (1 g/m 2 on house walls), also kills louse (Typhoid), Flea (Plague), Tetse Fly (Sleeping sickness)

Peak production in 1961 ~ 400 Mkg/y; World total production >3 B kg, i. e. > 3 M tons or about ½ kg person alive today! Insect Resistance – overrated! Some insects have developed DDTase which dehydrochlorinates DDT to DDE; however that is easy to overcome by blocking the enzyme, eg. with chlorofenthol

Non-selectivity is bad – most insects not pests! SOLUBLE IN FAT: passes up food chain ALSO VERY PERSISTENT: half life ~ 20 years! UVIC students 1970: ~12 ppm in tissues NOW: ~2 -3 ppm even though use in NA was stopped in 1972! BIRDS: DDE and DDT metabolites mimic diethylstilbestrol and have weakly estrogenic activity: affect Ca transport – thin egg shells See: ‘Silent Spring’ by Rachel Carson (1962) for one view of DDT

In Canada, Methoxychlor is widely used – degrades more quickly But many much more toxic ones were also made: Lindane Dieldrin LD 50 100 mg/kg 50 mg/kg highly toxic to fish and mammals Most have been phased out now but residues remain buried in soils, ocean muds, lake bottoms, etc.
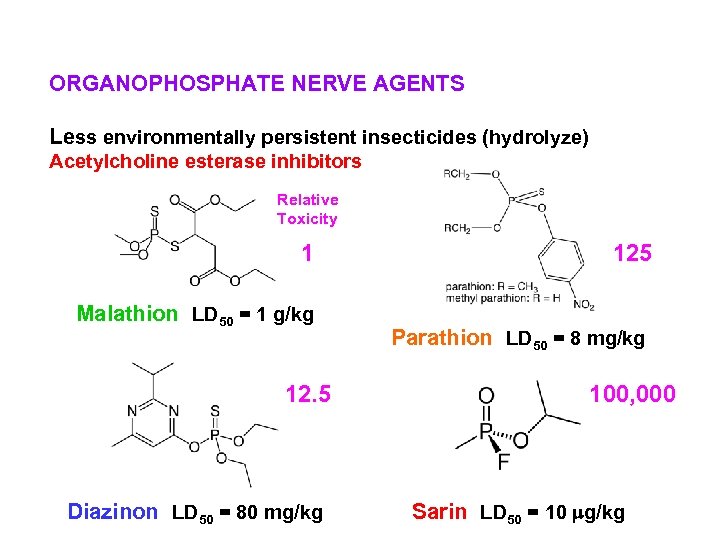
ORGANOPHOSPHATE NERVE AGENTS Less environmentally persistent insecticides (hydrolyze) Acetylcholine esterase inhibitors Relative Toxicity 1 Malathion LD 50 = 1 g/kg 12. 5 Diazinon LD 50 = 80 mg/kg 125 Parathion LD 50 = 8 mg/kg 100, 000 Sarin LD 50 = 10 mg/kg

All species use acetylcholine as a nerve transmitter: Botulinus toxin prevents synthesis of acetylcholine - no impulses paralysis of muscles, etc. Organophosphates block acetylcholine esterase: prevents break down of acetylcholine - nerve impulses continuously sent, overload, convulsions, death ~300, 000 farm workers per year suffer from pesticide poisoning!!

Other important strategies not covered here: Insect biology strategies: pheromones interfere with sexual development interfere with maturation Genetic engineering of crops: disease resistance insect resistance (kill insects when feed on plant) herbicide resistance (to kill weeds but not plant) better climate tolerance (drought, heat, cold)
40774201ed57a523d33eeb74bdc8bbbf.ppt