9f37cd8ec8f59a23ae0a7d714e07eac2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

AGRICULTURAL/AGRIBUSINESS FINANCE By Mrs. Abigail A. Adaku Dept. of Agric. Econs & Agribusiness 1

Order of Presentation Objective Agricultural Finance Financial management decisions Investment decision Goals of financial management Financial assets and markets Financial statements (Income and Balance sheet) • Credit • • 2

Objective • The purpose is to expose students to basic concepts in agricultural finance, financial management and issues of credit to the smallholders in the agricultural sector (production and agribusiness). 3

What is agribusiness? • Agribusiness has been defined as involving those individuals and institutions engaged in the production, processing, transport, storage, financing, marketing, and regulation of the world's food and fiber products. • The agribusiness system is composed of operators, supporters, and coordinators. • The operating organizations are the farmers, transporters, warehousers, processors, and distributors who handle the physical commodity as it flows from the farm to the marketplace. • The supporting institutions are the farm suppliers, financial entities, and research centers that contribute to the system's operators. • The coordinators are governments, contractors, futures markets, and industrial associations that integrate the various stages of the food-andfiber system.

Finance • Finance as a noun is the science of monetary affairs • As a verb, it means to supply money for • Finance professionals think of it as managing money. • For academic purposes we define finance as the study of the flow of funds in an economy or firm 5

Agricultural Finance • It deals with the economics of using financial resources in the agribusiness • It sets out the principles of analysis so the farmer can make a decision with full awareness of the implications. 6

Domestic Trends in Agribusiness Finance • Agricultural share of bank credit portfolio is between 4 -5% • Funds available for lending to agriculture are mainly short term funds • Long term funds are not readily available from bank sources. • Emerging financing include contract farming, guarantee schemes, inventory credit schemes, trader credit and government credit schemes. 7

Importance of Agribusiness Finance • Funding needed for agricultural activities include both investment and operating capital. • Investment capital (medium to long term funds) is needed for irrigation, warehouse, tree crops, pack houses, equipment, • Operating (working) capital is needed for paying labour, utilities, fuel, seed, fertilizer, agrochemicals, etc 8

FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT • FM means planning and control of money and money-related operations within a business. • Concerns acquisition, use of financial resources and protection of equity capital from various sources of risk. • Financial manager’s decisions are drawn from three types of question – What long-term assets should the firm invest in? – What sort of building, machinery and equipment? 9

Financial Management – How will the firm finance the investment? Debt, equity or mix? – How should the firm manage its everyday financial activities such as collecting payment from customers and paying suppliers, etc? – Financial management is broken into three major areas: – investment (capital budgeting), – financing (capital structure) and – working capital (operating fund) management decisions. 10

Financial Management • These decision are interrelated. • Decision to invest in a new capital necessitates financing the investment: consider appropriate balance between short term and long term finance and appropriate debt to equity ratio. • The financial decisions in turn influences and is influenced by the retained earnings used in internal financing. 11

Financial Management • The retained earnings are generally dependent on the dividend policy. • It is a major source of funds for the company. • It contributes to decisions on investment in current assets; including cash, inventories and debtors to ensure that the firm has sufficient cash for the payment of its obligation as they become due. 12

INVESTMENT DECISIONS • Involves the process of planning and controlling long-term investment to generate profit. • FM is concerned not only with how much they expect to receive (magnitude), but also with when they expect to receive it (timing) and how likely they are to receive the returns (risks). • Evaluating the size, timing and risk of future cash flows is the essence of capital budgeting. 13

Financing Decisions (Capital Structure) • The firm’s financial structure is the specific mixture of long-term debt and equity the firm uses to finance its operations. • Two concerns: how much should the firm borrow? What mixture of debt and equity is best? 14

Working Capital Mgt. Decisions • What is the least expensive sources of funds for the firm? • Working capital refers to a firms short-term assets: cash, inventory, and short-term liabilities (loans and accounts payable) • Managing WC is day-to-day activity that ensures that the firm has sufficient resources to continue its operations. 15

FINANCIAL MANAGMENT • Financial manager makes decisions for the stockholders of the firm. To increase the value of the stock. • The goal of financial management is to maximize the current value per share of existing stock, or to maximize the shareholder’s wealth. Reduce risk, provide liquidity? • Goal: Profit maximization. 16

FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT • Assumed overriding goal of management profit maximization has two shortcomings: – It fails to account for the timing of earning. Maximizing profits leave open the question, which year’s profit? – Shareholders might not want to increase next year’s profit at the expense of profit in later year. – It fails to account for risk and uncertainty. 17

FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGER – Obtain the best mix of financing alternatives – Raise funds through sale of stocks and bonds – Allocate funds to current and fixed assets – Take day-to-day decisions on working capital management involving credit management, inventory control and cash management – Develop an appropriate dividend policy within the context of the firm’s objective of maximizing shareholders’ wealth. – Functions are carried out while balancing the profitability and risk components of the firm. 18

FINANCIAL ASSETS • Financial assets are legal documents (or pieces of security paper) which give their owners claim to future cash flows. • It is different from real assets such as cars, houses, factories, or machines (capital assets). • Financial assets are either stocks or bonds and their claim to future income is based on ownership or debt. 19

Financial Assets • Other financial assets include: bank loans, treasury bills, treasury notes, certificates of deposit, debentures, treasury bonds, etc. • Stock ownership means that the holder of a share owns a piece of the company that issued the stock. • Owners of a stock certificate can look for two sources of cash in the future: dividends and the eventual selling price of the share. 20

Financial Assets • A bond signifies a debt relationship • Purchase of bond imply lending money to the firm issuing the bond. Bond holders earn interest on amount lent over the specified period. • Companies issues financial assets to raise money. 21

FINANCIAL MARKETS • Financial markets are mechanisms or transactions in which the firms’ financial assets are traded. • There are three ways in which the market operated: – Direct financing – Indirect financing – Pass through financing 22

Types of Financial Markets • There are different types of financial markets based on the types of securities that are traded, how trading is conducted and who the buyers and sellers are: – Money market: treasury bills, certificate of deposit – Capital market: shares, bonds, long-term loans, – Primary market: deals in newly issued securities (IPO) – Secondary market: deals in already existing shares – Foreign exchange market: forex bureau, Euro-dollar M – Mortgage market: a market where assets are used as collateral securities. 23

Types of Financial Markets – Consumer credit market: a market where assets are given to consumers at cost price plus interest, and payment made at future date. – Over-the counter market: a market where securities are traded in an unorganized manner ( no intermediaries involve, no brokers) – Global: multinationals, national: Local companies, local: suppliers and users of capital and intermediaries: – Public market: financial transaction involving sourcing for funds from the public by users of capital – Private market: financial transactions involving sourcing for funds from specific individuals, groups of individuals or companies 24

FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS • Banks: Central bank, Commercial banks, Merchant banks, Development banks, Rural banks. • Non-Bank financial Institutions – Insurance companies: – Discount houses – Financial houses – Leasing and hire companies – Venture capital funding companies – Ghana Stock Exchange – Micro-finance institutions (savings and loans) – Informal financial sector (susu, money lenders, ) 25
CREDIT • Credit is a sum of money in favour of the person to whom control is transferred. • Provision of credit involve two parties: a lender and a borrower. It involves a price (interest charge)in favour of the lender. • In neoclassical economics, market for credit is like any other market which contains a demand schedule and supply schedule and a price (interest rate). 26

• The price adjusts to bring demand supply into balance. • The lender can be an individual or institution called financial intermediary that provides a supply of credit to potential borrowers. • Once a loan is made the borrower has control over its use, but incurs a debt obligation to repay the principal and interest to the lender. 27

• The borrower in credit transaction is a person or enterprise who has a demand for credit. • Credit should not be confused with capital or farm inputs. Credit is not capital but can be used for investment in a capital asset such as tractor or irrigation facility. • Credit is not a farm input such as seed, fertilizer or labour time. It is used, among others to finance the purchase of variable inputs (working capital) 28

• Credit is fungible. That is interchangeability in the use to which credit can be put. Fungibility makes it easy for borrowers to divert credit from one use to another. • Savers are the other main actors in the rural finance system. They can be individuals, households or institutions ready to supply funds to be held by a financial institution in return for an interest payment (income flows) 29

• This process of saving, lending and borrowing is termed Financial Intermediation. • Institutions that enable this to take place by bringing together savers and borrowers with differing needs in space and time are called Financial Intermediaries. 30

Role of Credit • Alleviate critical constraint hampering growth in agricultural output and productivity • Allow farmers to acquire modern technology and improve productivity • Helps farmers adopt better production and marketing strategies • Helps increase value through processing and better packaging. 31

Problems with Agricultural Credit High levels of default in loan repayment Lack of collateral acceptable to banks High interest cost relative to profit levels Poor release of funds (timing) for agricultural activities • Long gestation period for agric production compared with non-agric activities. (bank preference) • Short payback periods • • 32

Reasons Bank’s Don’t Lend to Smallholders • • High monitoring cost High administrative cost on small loans Lack of adequate collateral, i. e. value, location High risks associated with agric production Poor record keeping for loan decision making Previous bad Bank experiences with farmers Government interventions in agric credit market 33

Why Smallholders Shy Away from Bank Loans • • • Lack of access to bank facilities in rural areas Cumbersome loan processing procedures Poor timing of loan released by Banks Loans may include hidden costs Lack of understanding of formal loan processes 34

Financial Statements • Financial statement are needed to assess and monitor the financial position and progress of the farm business. • Balance sheet • Income statement • Statement of owner equity • Statement of cash flow 35

Balance Sheet • A balance sheet is a systematic listing of all that the business owns (assets) and all that it owes (liabilities) at a specific point in time. • It is a static picture of the firms financial position as of that date • Also known as, net worth statement, the statement of financial condition and statement of financial position. • The balancing factor is the net worth 36

Net Worth • Also known as owner equity. • Calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets 37
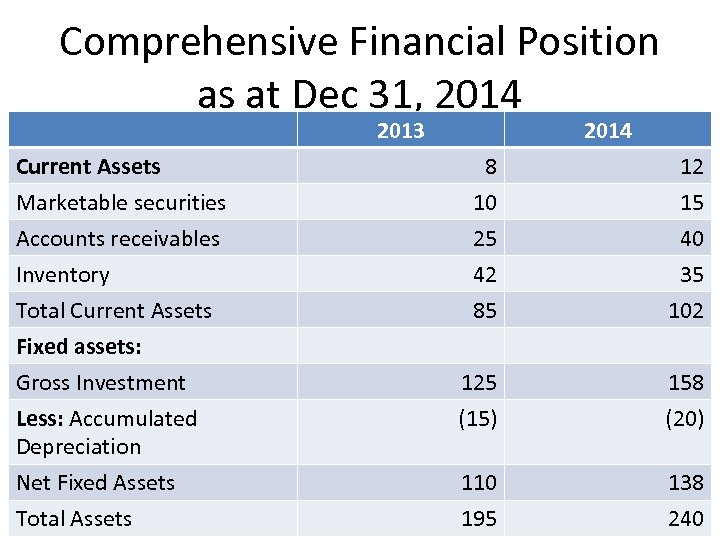
Comprehensive Financial Position as at Dec 31, 2014 2013 Current Assets Marketable securities Accounts receivables Inventory Total Current Assets Fixed assets: Gross Investment Less: Accumulated Depreciation Net Fixed Assets Total Assets 2014 8 10 25 42 85 12 15 40 35 102 125 (15) 158 (20) 110 138 195 38 240
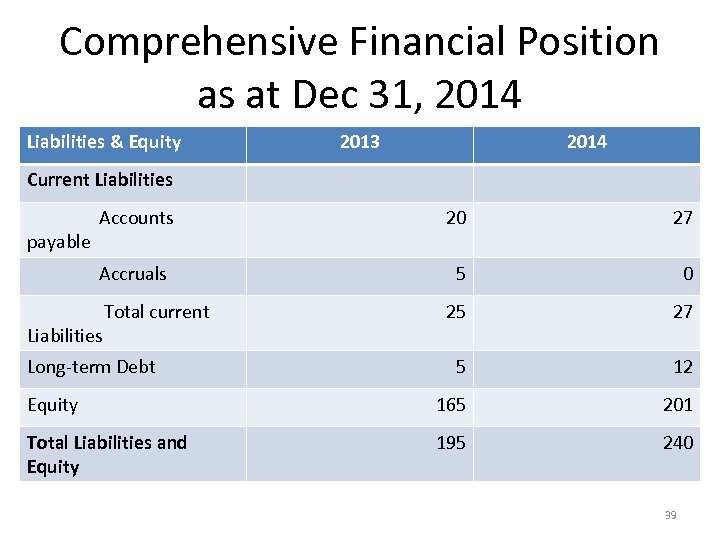
Comprehensive Financial Position as at Dec 31, 2014 Liabilities & Equity 2013 2014 Current Liabilities Accounts 20 27 Accruals 5 0 25 27 5 12 Equity 165 201 Total Liabilities and Equity 195 240 payable Liabilities Total current Long-term Debt 39

Prepare a balance sheet for this farm with the ff. entries • • Land – 665, 600 Growing crop – 41, 888 Operation debt – 33, 511 Equipment – 1, 028, 510 Machinery debt – 162, 630 Depreciation for equip. – 607, 232 Real Estate mortgage – 376, 750 Cash – 15, 517 40

The Income Statement • This is a summary of the revenue (receipts or income) and expenditures (costs) of the business over a specified period of time • Also know as the operating statement or the profit and loss statement • Contrary to the balance sheet, which is a static picture, the income statement covers the business actions of the firm over a specified period of time 41
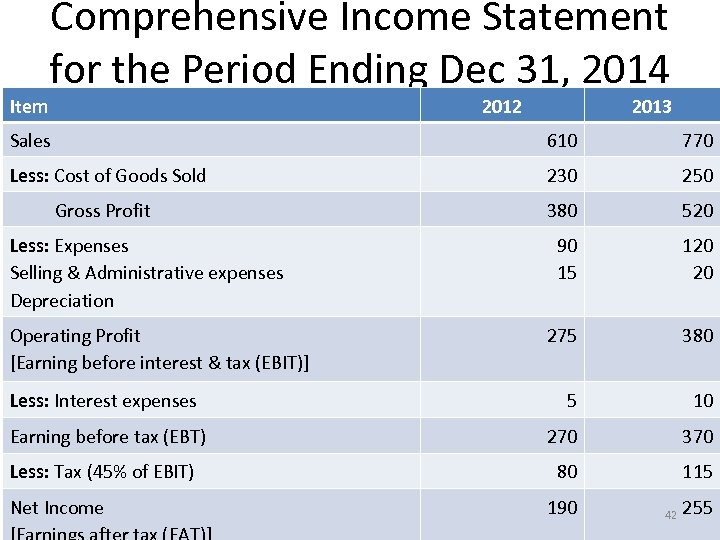
Item Comprehensive Income Statement for the Period Ending Dec 31, 2014 2012 2013 Sales 610 770 Less: Cost of Goods Sold 230 250 Gross Profit 380 520 90 15 120 20 275 380 5 10 Earning before tax (EBT) 270 370 Less: Tax (45% of EBIT) 80 115 Less: Expenses Selling & Administrative expenses Depreciation Operating Profit [Earning before interest & tax (EBIT)] Less: Interest expenses Net Income 190 42 255

THANK YOU QUESTIONS 43

QUESTIONS • What do you understand by the term agricultural finance? • What are involved in financial management? • Does the Comprehensive Financial Position give a complete picture of agriculture? Explain • Discuss the reason financial institutions shy away from extending credit to smallholder farmers. • What are the main sources of finance for agriculture? 44
9f37cd8ec8f59a23ae0a7d714e07eac2.ppt