fc8a7c0db67d58cf8f83e1c71717571e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 KOe. L For All June 4, 2007 Myung-sook PANG, Ph. D. , KERIS jean@keris. or. kr
AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 KOe. L For All June 4, 2007 Myung-sook PANG, Ph. D. , KERIS jean@keris. or. kr
 Contents 1. Korea at a glance 2. UNESCO Prize & CHLS 3. KOe. L is…
Contents 1. Korea at a glance 2. UNESCO Prize & CHLS 3. KOe. L is…
 AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 1. Korea at a Glance
AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 1. Korea at a Glance
 1. Korea and Education n n 48. 8 million people in 99, 000 KM 2 Schools, grade 1 -12 th : 10, 876, 7. 8 M students Colleges & universities : 349, 2. 7 M students Became an OECD member economy in 1996 12 th largest GDP economy 2 nd highest broadband diffusion (2005) 3 rd highest home PC diffusion (2005) n Outstanding achievement in OECD PISA(2003) 1 st in problem solving 2 nd in reading 3 rd in math
1. Korea and Education n n 48. 8 million people in 99, 000 KM 2 Schools, grade 1 -12 th : 10, 876, 7. 8 M students Colleges & universities : 349, 2. 7 M students Became an OECD member economy in 1996 12 th largest GDP economy 2 nd highest broadband diffusion (2005) 3 rd highest home PC diffusion (2005) n Outstanding achievement in OECD PISA(2003) 1 st in problem solving 2 nd in reading 3 rd in math
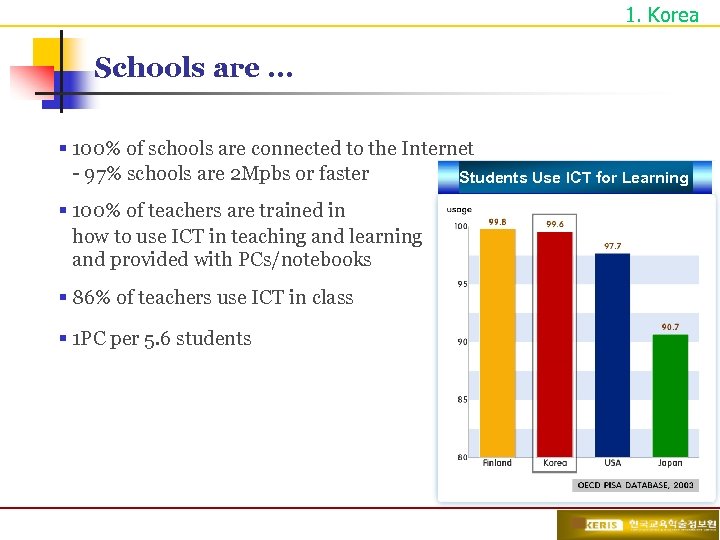 1. Korea Schools are … § 100% of schools are connected to the Internet - 97% schools are 2 Mpbs or faster Students Use ICT for Learning § 100% of teachers are trained in how to use ICT in teaching and learning and provided with PCs/notebooks § 86% of teachers use ICT in class § 1 PC per 5. 6 students
1. Korea Schools are … § 100% of schools are connected to the Internet - 97% schools are 2 Mpbs or faster Students Use ICT for Learning § 100% of teachers are trained in how to use ICT in teaching and learning and provided with PCs/notebooks § 86% of teachers use ICT in class § 1 PC per 5. 6 students
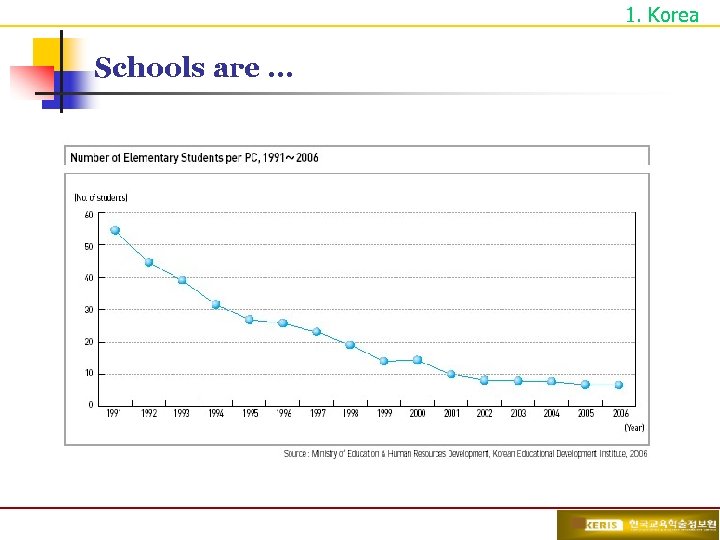 1. Korea Schools are …
1. Korea Schools are …
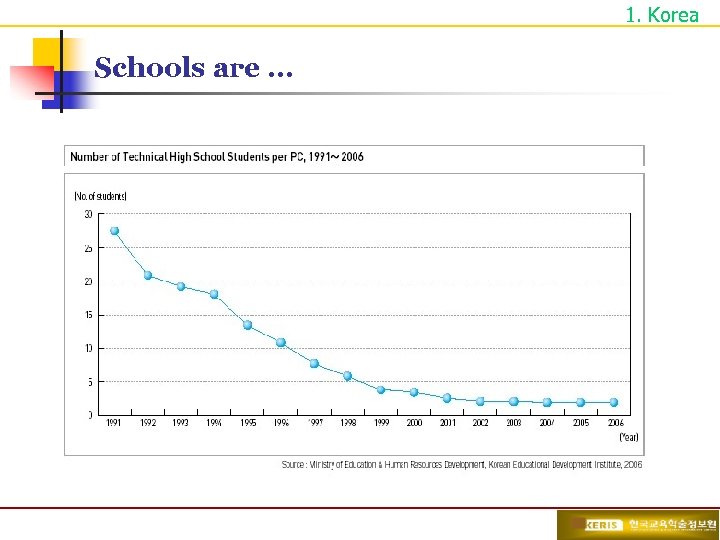 1. Korea Schools are …
1. Korea Schools are …
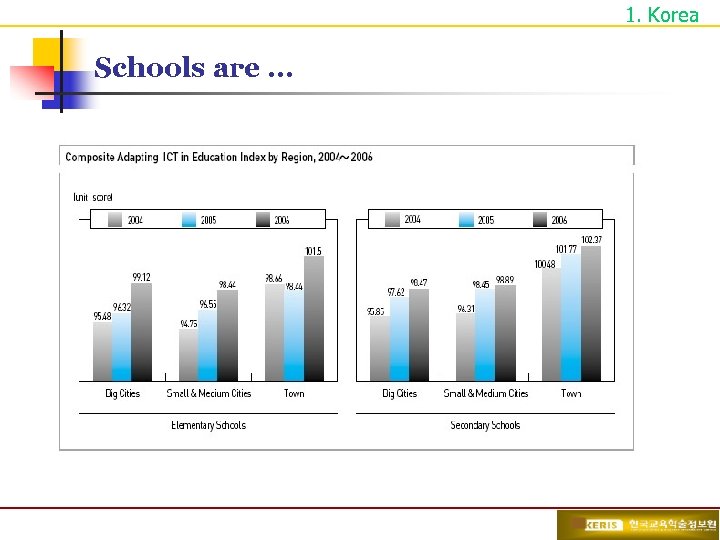 1. Korea Schools are …
1. Korea Schools are …
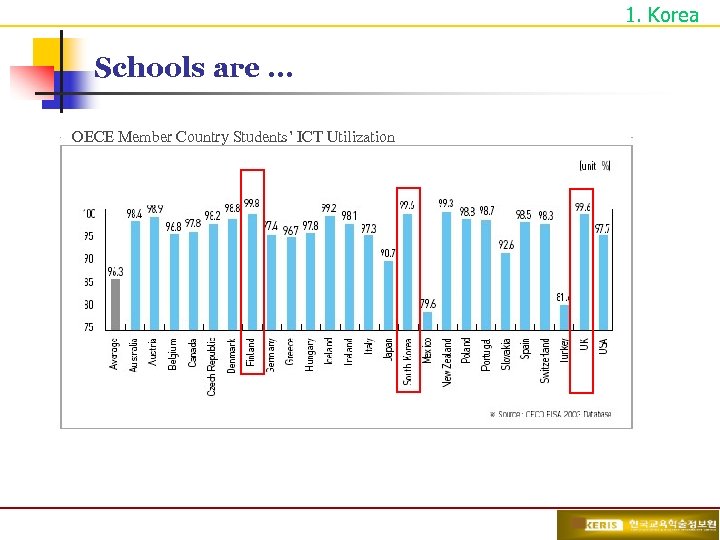 1. Korea Schools are … OECE Member Country Students’ ICT Utilization
1. Korea Schools are … OECE Member Country Students’ ICT Utilization
 1. Korea Universities are … § Research Information Service System (RISS) Users § 60% of faculty § 62% of graduate students § 88. 3% of universities have adopted e-Learning § 17 cyber universities § 40, 000 enrollments
1. Korea Universities are … § Research Information Service System (RISS) Users § 60% of faculty § 62% of graduate students § 88. 3% of universities have adopted e-Learning § 17 cyber universities § 40, 000 enrollments
 1. Korea Sustainable Development Strategies § Firm support and involvement of top administrator in education § Build core competence of organizations (regional information center for ICT teachers in schools § Implement a user-oriented policy § Apply a monitoring and evaluation system § Inter-government, inter-institutions, inter-schools collaboration § Allocate a sustainable block budget
1. Korea Sustainable Development Strategies § Firm support and involvement of top administrator in education § Build core competence of organizations (regional information center for ICT teachers in schools § Implement a user-oriented policy § Apply a monitoring and evaluation system § Inter-government, inter-institutions, inter-schools collaboration § Allocate a sustainable block budget
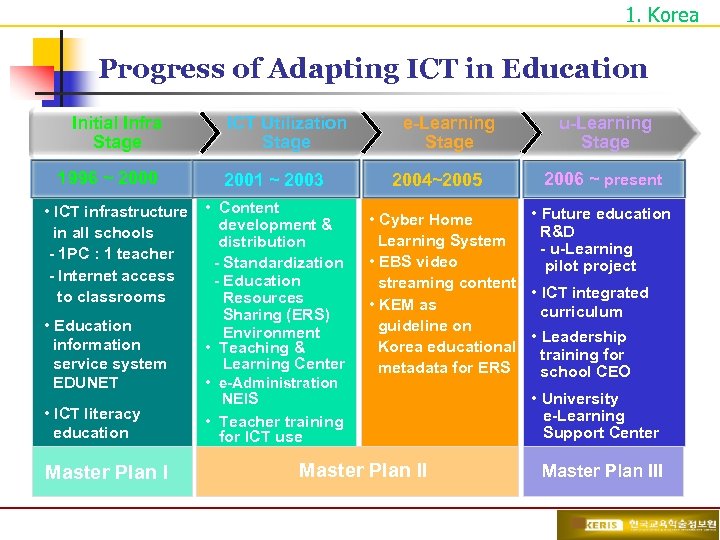 1. Korea Progress of Adapting ICT in Education Initial Infra Stage 1996 ~ 2000 ICT Utilization Stage 2001 ~ 2003 • ICT infrastructure • Content development & in all schools distribution - 1 PC : 1 teacher - Standardization - Internet access - Education to classrooms Resources Sharing (ERS) • Education Environment information • Teaching & Learning Center service system • e-Administration EDUNET NEIS • ICT literacy • Teacher training education for ICT use Master Plan I e-Learning Stage 2004~2005 u-Learning Stage 2006 ~ present • Future education • Cyber Home R&D Learning System - u-Learning • EBS video pilot project streaming content • ICT integrated • KEM as curriculum guideline on • Leadership Korea educational training for metadata for ERS school CEO Master Plan II • University e-Learning Support Center Master Plan III
1. Korea Progress of Adapting ICT in Education Initial Infra Stage 1996 ~ 2000 ICT Utilization Stage 2001 ~ 2003 • ICT infrastructure • Content development & in all schools distribution - 1 PC : 1 teacher - Standardization - Internet access - Education to classrooms Resources Sharing (ERS) • Education Environment information • Teaching & Learning Center service system • e-Administration EDUNET NEIS • ICT literacy • Teacher training education for ICT use Master Plan I e-Learning Stage 2004~2005 u-Learning Stage 2006 ~ present • Future education • Cyber Home R&D Learning System - u-Learning • EBS video pilot project streaming content • ICT integrated • KEM as curriculum guideline on • Leadership Korea educational training for metadata for ERS school CEO Master Plan II • University e-Learning Support Center Master Plan III
 AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 2. ICT Use in Education Policy: Awarded the UNESCO Prize
AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 2. ICT Use in Education Policy: Awarded the UNESCO Prize
 Global Partnership for EFA
Global Partnership for EFA
 4. KERIS Global Partnership for EFA UNESCO King Kamad Bin Isa Al-Khalifa Prize for the Use of ICTs in Education, 2007 at UNESCO HQ, Paris
4. KERIS Global Partnership for EFA UNESCO King Kamad Bin Isa Al-Khalifa Prize for the Use of ICTs in Education, 2007 at UNESCO HQ, Paris
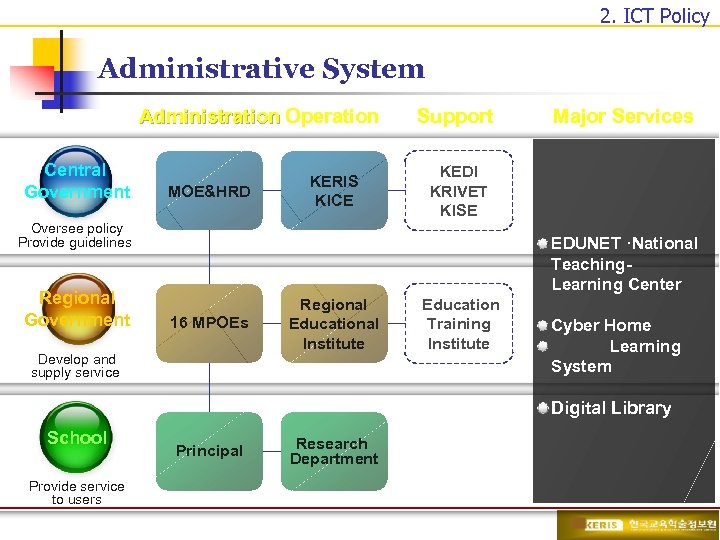 2. ICT Policy Administrative System Administration Operation Central Government MOE&HRD KERIS KICE Support KEDI KRIVET KISE Oversee policy Provide guidelines Regional Government Major Services EDUNET ·National Teaching. Learning Center 16 MPOEs Develop and supply service Regional Educational Institute Education Training Institute Cyber Home Learning System Digital Library School Provide service to users Principal Research Department
2. ICT Policy Administrative System Administration Operation Central Government MOE&HRD KERIS KICE Support KEDI KRIVET KISE Oversee policy Provide guidelines Regional Government Major Services EDUNET ·National Teaching. Learning Center 16 MPOEs Develop and supply service Regional Educational Institute Education Training Institute Cyber Home Learning System Digital Library School Provide service to users Principal Research Department
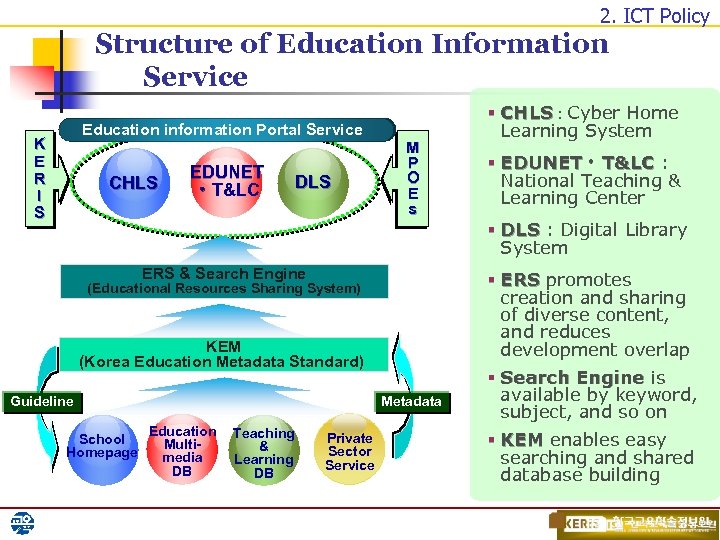 2. ICT Policy Structure of Education Information Service Education information Portal Service K E R I S CHLS EDUNET ㆍT&LC DLS M P O E s § CHLS : Cyber Home Learning System § EDUNETㆍ T&LC : National Teaching & Learning Center § DLS : Digital Library System ERS & Search Engine § ERS promotes creation and sharing of diverse content, and reduces development overlap (Educational Resources Sharing System) KEM (Korea Education Metadata Standard) Guideline School Homepage Metadata Education Multimedia DB Ministry of Education & Human Resources Development Teaching & Learning DB Private Sector Service § Search Engine is available by keyword, subject, and so on § KEM enables easy searching and shared database building
2. ICT Policy Structure of Education Information Service Education information Portal Service K E R I S CHLS EDUNET ㆍT&LC DLS M P O E s § CHLS : Cyber Home Learning System § EDUNETㆍ T&LC : National Teaching & Learning Center § DLS : Digital Library System ERS & Search Engine § ERS promotes creation and sharing of diverse content, and reduces development overlap (Educational Resources Sharing System) KEM (Korea Education Metadata Standard) Guideline School Homepage Metadata Education Multimedia DB Ministry of Education & Human Resources Development Teaching & Learning DB Private Sector Service § Search Engine is available by keyword, subject, and so on § KEM enables easy searching and shared database building
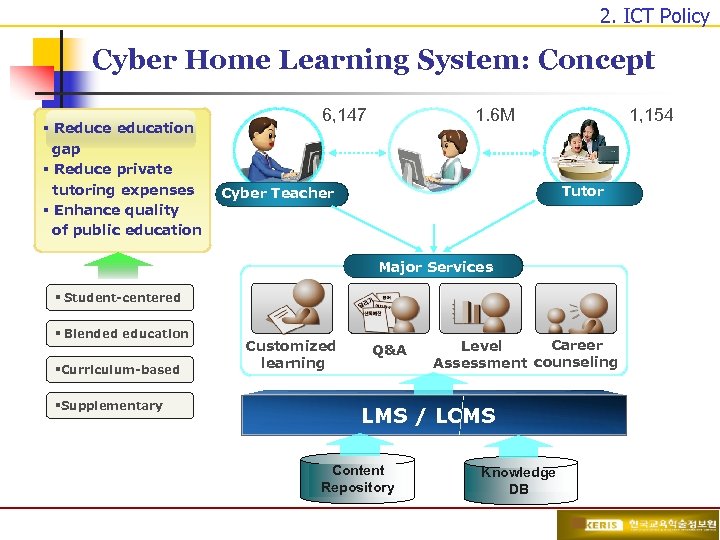 2. ICT Policy Cyber Home Learning System: Concept § Reduce education gap § Reduce private tutoring expenses § Enhance quality of public education 6, 147 Cyber Teacher 1. 6 M 1, 154 Tutor 1: 1 Learning Management Major Services § Student-centered § Blended education §Curriculum-based §Supplementary Customized learning Q&A Career Level Assessment counseling LMS / LCMS Content Repository Knowledge DB
2. ICT Policy Cyber Home Learning System: Concept § Reduce education gap § Reduce private tutoring expenses § Enhance quality of public education 6, 147 Cyber Teacher 1. 6 M 1, 154 Tutor 1: 1 Learning Management Major Services § Student-centered § Blended education §Curriculum-based §Supplementary Customized learning Q&A Career Level Assessment counseling LMS / LCMS Content Repository Knowledge DB
 2. ICT Policy Cyber Home Learning System: Outcomes § Decreased education divide for economically and geographically disadvantaged students § Decreased private tutoring costs in lower income households § Improved achievement of low achieving students § Enhanced positive attitude of students § Enhanced parental understanding of students’ learning capability and attitude through counseling by teachers § Improved achievement § Changes in students’ attitude (49. 73 → 78. 60 in score) Lee, I. S. (2006). Gokran Elementary School KERIS(2006). Analysis of CHLS Effectiveness 2006 (multiple response)
2. ICT Policy Cyber Home Learning System: Outcomes § Decreased education divide for economically and geographically disadvantaged students § Decreased private tutoring costs in lower income households § Improved achievement of low achieving students § Enhanced positive attitude of students § Enhanced parental understanding of students’ learning capability and attitude through counseling by teachers § Improved achievement § Changes in students’ attitude (49. 73 → 78. 60 in score) Lee, I. S. (2006). Gokran Elementary School KERIS(2006). Analysis of CHLS Effectiveness 2006 (multiple response)
 2. ICT Policy Cyber Home Learning System: Exemplary case § Number of registered users 540, 000, cyber teachers 619, and tutors 230 § Seoul Metropolitan Office of Education, www. kkulmat. com
2. ICT Policy Cyber Home Learning System: Exemplary case § Number of registered users 540, 000, cyber teachers 619, and tutors 230 § Seoul Metropolitan Office of Education, www. kkulmat. com
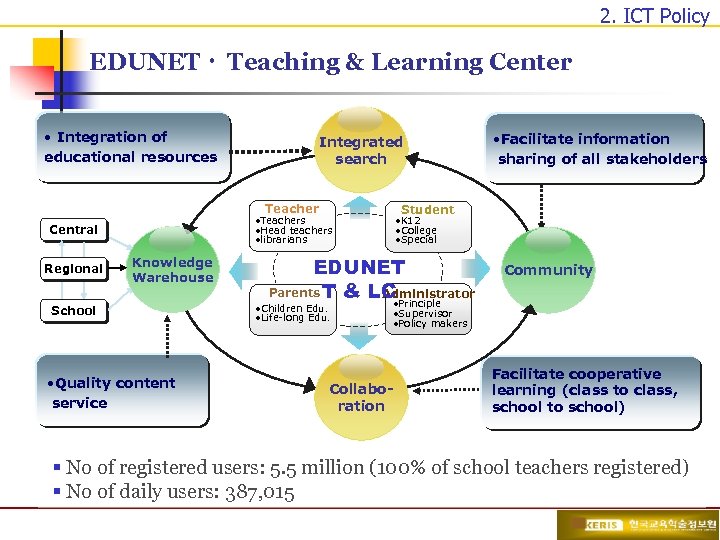 2. ICT Policy EDUNETㆍ Teaching & Learning Center • Integration of educational resources Integrated search Teacher Regional Student • Teachers • Head teachers • librarians Central Knowledge Warehouse School • Quality content service • K 12 • College • Special EDUNET Parents T & LC Administrator • Principle • Children Edu. • Life-long Edu. • Facilitate information sharing of all stakeholders Community • Supervisor • Policy makers Collaboration Facilitate cooperative learning (class to class, school to school) § No of registered users: 5. 5 million (100% of school teachers registered) § No of daily users: 387, 015
2. ICT Policy EDUNETㆍ Teaching & Learning Center • Integration of educational resources Integrated search Teacher Regional Student • Teachers • Head teachers • librarians Central Knowledge Warehouse School • Quality content service • K 12 • College • Special EDUNET Parents T & LC Administrator • Principle • Children Edu. • Life-long Edu. • Facilitate information sharing of all stakeholders Community • Supervisor • Policy makers Collaboration Facilitate cooperative learning (class to class, school to school) § No of registered users: 5. 5 million (100% of school teachers registered) § No of daily users: 387, 015
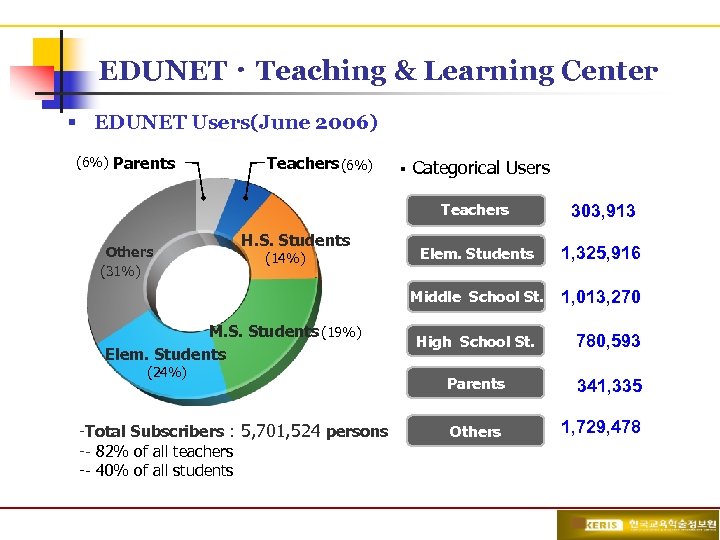 EDUNETㆍTeaching & Learning Center § EDUNET Users(June 2006) (6%) Parents Teachers (6%) § Categorical Users Teachers H. S. Students (14%) M. S. Students (19%) Elem. Students (24%) -Total Subscribers : 5, 701, 524 persons -- 82% of all teachers -- 40% of all students Elem. Students 1, 325, 916 Middle School St. Others (31%) 303, 913 1, 013, 270 High School H. S. Students St. 780, 593 Parents 341, 335 Parents Others 1, 729, 478
EDUNETㆍTeaching & Learning Center § EDUNET Users(June 2006) (6%) Parents Teachers (6%) § Categorical Users Teachers H. S. Students (14%) M. S. Students (19%) Elem. Students (24%) -Total Subscribers : 5, 701, 524 persons -- 82% of all teachers -- 40% of all students Elem. Students 1, 325, 916 Middle School St. Others (31%) 303, 913 1, 013, 270 High School H. S. Students St. 780, 593 Parents 341, 335 Parents Others 1, 729, 478
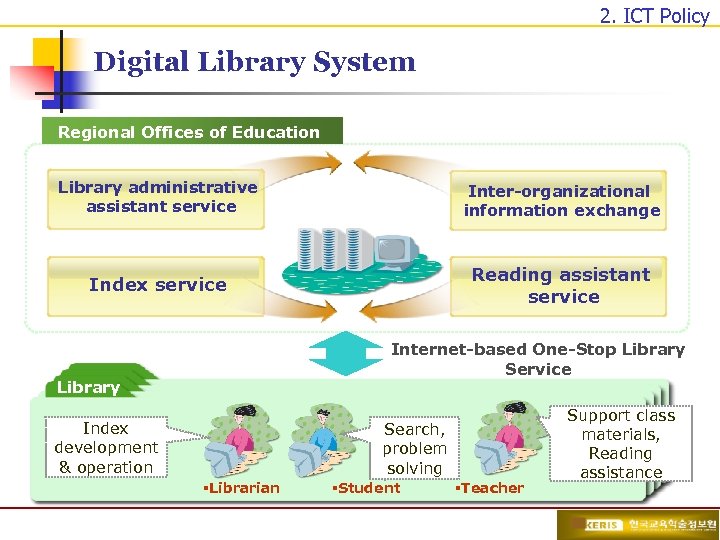 2. ICT Policy Digital Library System Regional Offices of Education Library administrative assistant service Digital Library System Inter-organizational information exchange Reading assistant service Index service Internet-based One-Stop Library Service Library Index development & operation Search, problem solving §Librarian §Student §Teacher Support class materials, Reading assistance
2. ICT Policy Digital Library System Regional Offices of Education Library administrative assistant service Digital Library System Inter-organizational information exchange Reading assistant service Index service Internet-based One-Stop Library Service Library Index development & operation Search, problem solving §Librarian §Student §Teacher Support class materials, Reading assistance
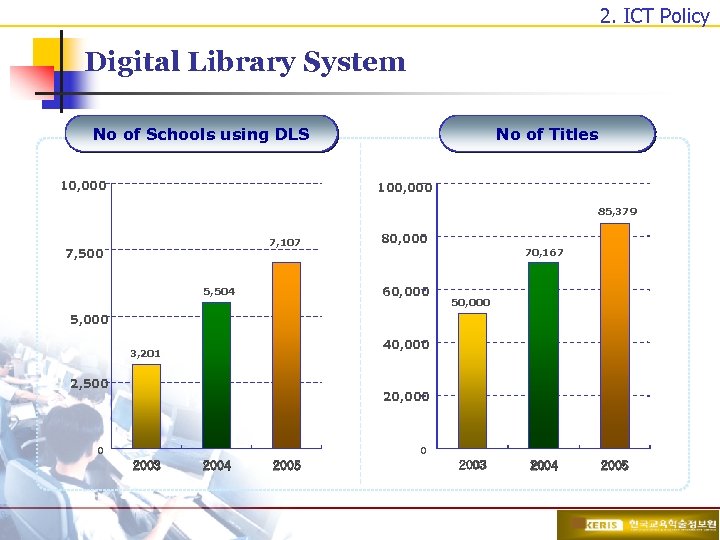 2. ICT Policy Digital Library System No of Titles No of Schools using DLS 10, 000 100, 000 85, 379 7, 107 7, 500 80, 000 70, 167 60, 000 5, 504 50, 000 5, 000 40, 000 3, 201 2, 500 20, 000 0 0 2003 2004 2005
2. ICT Policy Digital Library System No of Titles No of Schools using DLS 10, 000 100, 000 85, 379 7, 107 7, 500 80, 000 70, 167 60, 000 5, 504 50, 000 5, 000 40, 000 3, 201 2, 500 20, 000 0 0 2003 2004 2005
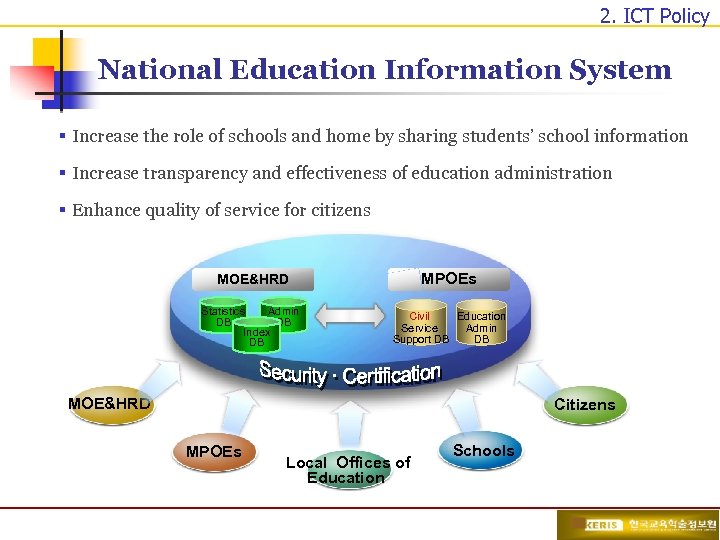 2. ICT Policy National Education Information System § Increase the role of schools and home by sharing students’ school information § Increase transparency and effectiveness of education administration § Enhance quality of service for citizens MOE&HRD MPOEs Statistics Admin DB DB Index DB Civil Education Service Admin Support DB DB MOE&HRD Citizens MPOEs Local Offices of Education Schools
2. ICT Policy National Education Information System § Increase the role of schools and home by sharing students’ school information § Increase transparency and effectiveness of education administration § Enhance quality of service for citizens MOE&HRD MPOEs Statistics Admin DB DB Index DB Civil Education Service Admin Support DB DB MOE&HRD Citizens MPOEs Local Offices of Education Schools
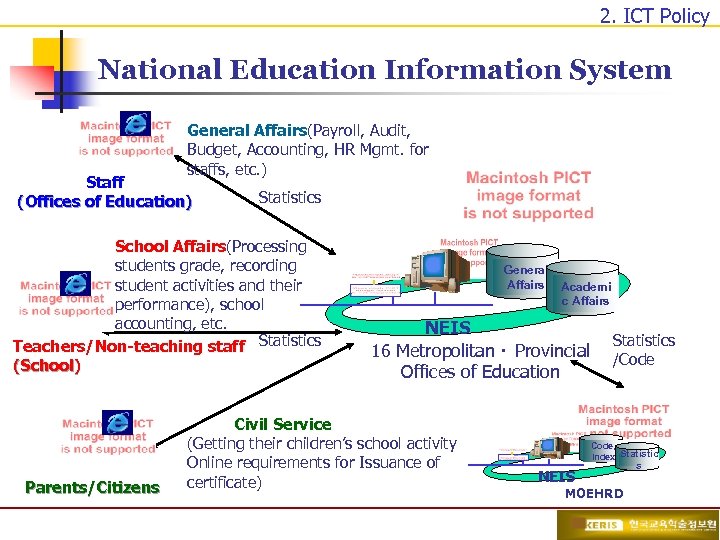 2. ICT Policy National Education Information System General Affairs(Payroll, Audit, Budget, Accounting, HR Mgmt. for staffs, etc. ) Staff (Offices of Education) Statistics School Affairs(Processing students grade, recording student activities and their performance), school accounting, etc. Teachers/Non-teaching staff Statistics (School) Parents/Citizens General Affairs Academi c Affairs NEIS 16 Metropolitanㆍ Provincial Offices of Education Civil Service (Getting their children’s school activity Online requirements for Issuance of certificate) Statistics /Code, Index Statistic NEIS MOEHRD s
2. ICT Policy National Education Information System General Affairs(Payroll, Audit, Budget, Accounting, HR Mgmt. for staffs, etc. ) Staff (Offices of Education) Statistics School Affairs(Processing students grade, recording student activities and their performance), school accounting, etc. Teachers/Non-teaching staff Statistics (School) Parents/Citizens General Affairs Academi c Affairs NEIS 16 Metropolitanㆍ Provincial Offices of Education Civil Service (Getting their children’s school activity Online requirements for Issuance of certificate) Statistics /Code, Index Statistic NEIS MOEHRD s
 AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 3. KOe. L is …
AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 3. KOe. L is …
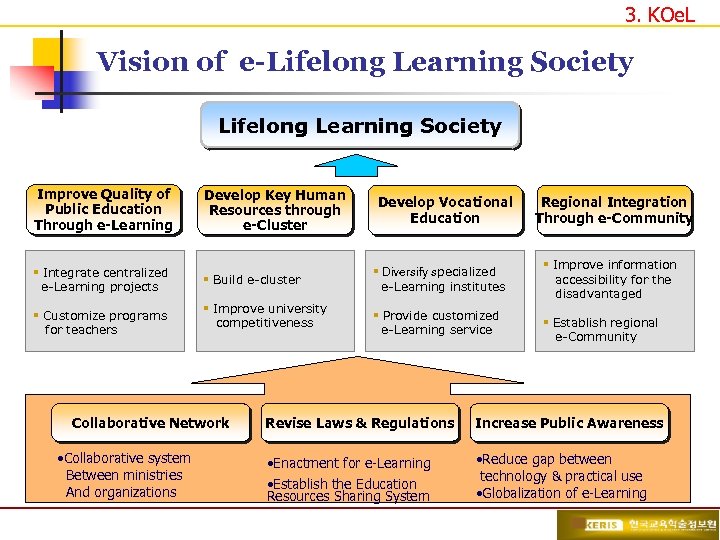 3. KOe. L Vision of e-Lifelong Learning Society Improve Quality of Public Education Through e-Learning Develop Key Human Resources through e-Cluster § Integrate centralized e-Learning projects § Build e-cluster § Customize programs for teachers § Improve university competitiveness Collaborative Network • Collaborative system Between ministries And organizations Develop Vocational Education § Diversify specialized e-Learning institutes § Provide customized e-Learning service Regional Integration Through e-Community § Improve information accessibility for the disadvantaged § Establish regional e-Community Revise Laws & Regulations Increase Public Awareness • Enactment for e-Learning • Establish the Education Resources Sharing System • Reduce gap between technology & practical use • Globalization of e-Learning
3. KOe. L Vision of e-Lifelong Learning Society Improve Quality of Public Education Through e-Learning Develop Key Human Resources through e-Cluster § Integrate centralized e-Learning projects § Build e-cluster § Customize programs for teachers § Improve university competitiveness Collaborative Network • Collaborative system Between ministries And organizations Develop Vocational Education § Diversify specialized e-Learning institutes § Provide customized e-Learning service Regional Integration Through e-Community § Improve information accessibility for the disadvantaged § Establish regional e-Community Revise Laws & Regulations Increase Public Awareness • Enactment for e-Learning • Establish the Education Resources Sharing System • Reduce gap between technology & practical use • Globalization of e-Learning
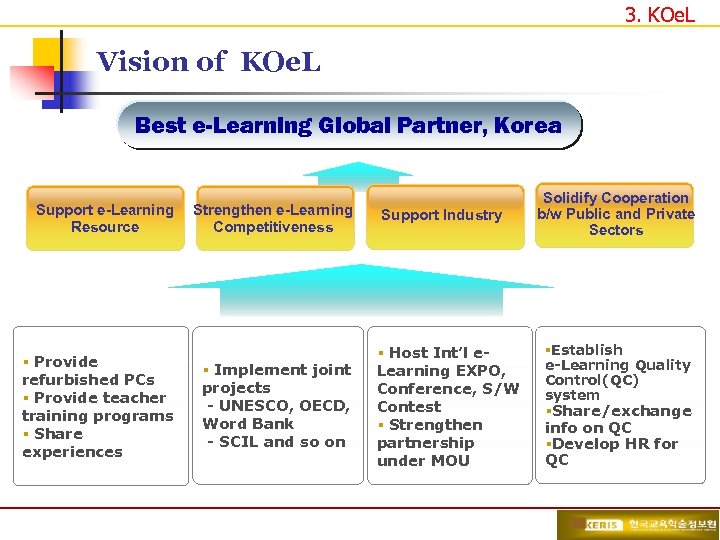 3. KOe. L Vision of KOe. L Best e-Learning Global Partner, Korea Support e-Learning Resource § Provide refurbished PCs § Provide teacher training programs § Share experiences Strengthen e-Learning Competitiveness § Implement joint projects - UNESCO, OECD, Word Bank - SCIL and so on Support Industry § Host Int’l e. Learning EXPO, Conference, S/W Contest § Strengthen partnership under MOU Solidify Cooperation b/w Public and Private Sectors §Establish e-Learning Quality Control(QC) system §Share/exchange info on QC §Develop HR for QC
3. KOe. L Vision of KOe. L Best e-Learning Global Partner, Korea Support e-Learning Resource § Provide refurbished PCs § Provide teacher training programs § Share experiences Strengthen e-Learning Competitiveness § Implement joint projects - UNESCO, OECD, Word Bank - SCIL and so on Support Industry § Host Int’l e. Learning EXPO, Conference, S/W Contest § Strengthen partnership under MOU Solidify Cooperation b/w Public and Private Sectors §Establish e-Learning Quality Control(QC) system §Share/exchange info on QC §Develop HR for QC
 3. KOe. L Global Partnership for ICT use in Education § Support for teacher development and infrastructure to contribute to global education and reducing the digital divide 2002 -05 2006 2007 Teacher Development Support 540 455 409 Infrastructure Support 4, 460 4, 227 4, 300 Countries Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Philippines, Malaysia, Viet Nam n Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka n Yemen, Iraq n Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia n Dominican Rep, Guatemala, Colombia n Kenya, Congo n Sharing n Dominican Rep Experience on 2 3 n Uzbekistan, Azerbaijan the Use of ICT n Cambodia, Sri Lanka, Indonesia in Education ** APEC e-Learning Training Program : China, Indonesia, Viet Nam, Thailand, Philippines, Chile, Mexico, Peru (127)
3. KOe. L Global Partnership for ICT use in Education § Support for teacher development and infrastructure to contribute to global education and reducing the digital divide 2002 -05 2006 2007 Teacher Development Support 540 455 409 Infrastructure Support 4, 460 4, 227 4, 300 Countries Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Philippines, Malaysia, Viet Nam n Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka n Yemen, Iraq n Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia n Dominican Rep, Guatemala, Colombia n Kenya, Congo n Sharing n Dominican Rep Experience on 2 3 n Uzbekistan, Azerbaijan the Use of ICT n Cambodia, Sri Lanka, Indonesia in Education ** APEC e-Learning Training Program : China, Indonesia, Viet Nam, Thailand, Philippines, Chile, Mexico, Peru (127)
 3. KOe. L Global Partnership for ICT use in Education
3. KOe. L Global Partnership for ICT use in Education
 3. KOe. L Malaysia n 24. 4 million people in 329, 750 KM 2 n GDP: USD 5, 040 n n 93% of the land is digitalized as of 1998 and planned to link every home w/ broadband by 2015 Vision 2020 by Ministry of Education n Reengineer educational system and meet individual learning needs n Adopt ICT as a tool for reducing information divide among schools n n Computers w/ internet equipped in almost every schools n n Adopt ICT as a tool for increasing effectiveness and productivity of school & class management Pilot projects w/ model schools for Smart School Project Sustainable policy development with funding, ICT leadership training need to be followed
3. KOe. L Malaysia n 24. 4 million people in 329, 750 KM 2 n GDP: USD 5, 040 n n 93% of the land is digitalized as of 1998 and planned to link every home w/ broadband by 2015 Vision 2020 by Ministry of Education n Reengineer educational system and meet individual learning needs n Adopt ICT as a tool for reducing information divide among schools n n Computers w/ internet equipped in almost every schools n n Adopt ICT as a tool for increasing effectiveness and productivity of school & class management Pilot projects w/ model schools for Smart School Project Sustainable policy development with funding, ICT leadership training need to be followed
 3. KOe. L Socialist Republic of Viet Nam n n 84. 4 million people in 329, 560 KM 2 GDP: USD 612 The first priority of OCA fund goes to ICT project Every high school and 80% of primary and middle schools was provided w/ internet as of 2003 n n 1 pc, 20 students For sustainable development n n Provide Vietnamese internet content Develop ICT human resources
3. KOe. L Socialist Republic of Viet Nam n n 84. 4 million people in 329, 560 KM 2 GDP: USD 612 The first priority of OCA fund goes to ICT project Every high school and 80% of primary and middle schools was provided w/ internet as of 2003 n n 1 pc, 20 students For sustainable development n n Provide Vietnamese internet content Develop ICT human resources
 3. KOe. L The People’s Republic of Bangladesh n n n 144. 3 million people in 147, 570 KM 2 GDP: USD 420 ICT Master Plan for 2003~2015 n Promote ICT use in education in secondary and higher education Computers w/ internet in governmental offices and National Univ. of Lao Primitive stages in informatization at primary and secondary stage n No formal computer curriculum in teacher colleges n BANBEIS, BCC, universities provide ICT training for teachers
3. KOe. L The People’s Republic of Bangladesh n n n 144. 3 million people in 147, 570 KM 2 GDP: USD 420 ICT Master Plan for 2003~2015 n Promote ICT use in education in secondary and higher education Computers w/ internet in governmental offices and National Univ. of Lao Primitive stages in informatization at primary and secondary stage n No formal computer curriculum in teacher colleges n BANBEIS, BCC, universities provide ICT training for teachers
 3. KOe. L Lao People’s Democratic Republic n 6. 2 million people in 238, 300 KM 2 n GDP: USD 542 n ICT Master Plan for 2003~2015 n Promote ICT use in education in secondary and higher education n Computers w/ internet in governmental offices and National Univ. of Lao n Primitive stages in informatization at primary and secondary stage
3. KOe. L Lao People’s Democratic Republic n 6. 2 million people in 238, 300 KM 2 n GDP: USD 542 n ICT Master Plan for 2003~2015 n Promote ICT use in education in secondary and higher education n Computers w/ internet in governmental offices and National Univ. of Lao n Primitive stages in informatization at primary and secondary stage
 3. KOe. L e-Learning Global Seminars & HRD § Co-host bi-lateral seminars § Korea-Mongolia (August, 2006, Ulaanbaatar) § Korea-Israel (April, Jerusalem, Tel Aviv) § Korea-France (November, Paris) § Participated in by experts from university and industry § Provide teacher training programs on ICT use in education § Co-host multi-lateral conferences § ASEM/ASEF e-Learning Colloquy § 10 th UNESCO-APEID International Conference § Host e-Learning international EXPO Korea § 10 countries (18 overseas/80 domestic), 17, 000 visitors
3. KOe. L e-Learning Global Seminars & HRD § Co-host bi-lateral seminars § Korea-Mongolia (August, 2006, Ulaanbaatar) § Korea-Israel (April, Jerusalem, Tel Aviv) § Korea-France (November, Paris) § Participated in by experts from university and industry § Provide teacher training programs on ICT use in education § Co-host multi-lateral conferences § ASEM/ASEF e-Learning Colloquy § 10 th UNESCO-APEID International Conference § Host e-Learning international EXPO Korea § 10 countries (18 overseas/80 domestic), 17, 000 visitors
 3. KOe. L Future oriented R&D § Joint research with UNESCO to support less developed countries § Joint research with IO/overseas institutes for future learning § Lead OECD “New Millenium Learners Project” § u-Learning Project with SCIL § Establish e-Learning Quality Assurance system and international network § Set up a u-Class at KERIS
3. KOe. L Future oriented R&D § Joint research with UNESCO to support less developed countries § Joint research with IO/overseas institutes for future learning § Lead OECD “New Millenium Learners Project” § u-Learning Project with SCIL § Establish e-Learning Quality Assurance system and international network § Set up a u-Class at KERIS
 AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 KOe. L For All THANK YOU! Myung-sook PANG, Ph. D. , KERIS jean@keris. or. kr
AGORA-Seminar, Seoul, June 4 -5, 2007 KOe. L For All THANK YOU! Myung-sook PANG, Ph. D. , KERIS jean@keris. or. kr


