60e9e92336cba8ecdf5b9cd4a799b22b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Agile Software Development Values through Practices C Sc 335 Rick Mercer
Agile Software Development Values through Practices C Sc 335 Rick Mercer
 Values: Communication – Client centric (Clients/PMs/SLs write stories) – Analysis & Design sessions (continuous) – Pair programming (will do this) – Iteration planning (first one this week) • What to do in the next iteration/sprint (there’ll be 3) – Retrospectives / Stand up meeting: Answer • What did I do? What do I plan to do? and what’s 2 in my way?
Values: Communication – Client centric (Clients/PMs/SLs write stories) – Analysis & Design sessions (continuous) – Pair programming (will do this) – Iteration planning (first one this week) • What to do in the next iteration/sprint (there’ll be 3) – Retrospectives / Stand up meeting: Answer • What did I do? What do I plan to do? and what’s 2 in my way?
 Values: Simplicity – Choose the simplest thing that will work – Choose the simplest design, technology, algorithm, technique 3
Values: Simplicity – Choose the simplest thing that will work – Choose the simplest design, technology, algorithm, technique 3
 Values: Feedback very important – Small Iterations – Pair programming – Constant code review (pair programming) – Continuous integration (add often to the build—sync your code with the system) • Check out, run all test including your new tests and code, if all pass, check in the updated system • Avoid or reduce branches (the source of conflicts) – Automated unit tests (JUnit, for example) 4
Values: Feedback very important – Small Iterations – Pair programming – Constant code review (pair programming) – Continuous integration (add often to the build—sync your code with the system) • Check out, run all test including your new tests and code, if all pass, check in the updated system • Avoid or reduce branches (the source of conflicts) – Automated unit tests (JUnit, for example) 4
 Values: Feedback Compiler feedback: seconds Pair programming feedback: half minutes – Complete all tasks completed in a pair programming mode. Unit test feedback: few minutes Acceptance testing: half hours – Customers write these, we are not doing this in 335 Customer feedback: daily (or several times/week) Iteration feedback: when tasks are started, completed, or blocked 5
Values: Feedback Compiler feedback: seconds Pair programming feedback: half minutes – Complete all tasks completed in a pair programming mode. Unit test feedback: few minutes Acceptance testing: half hours – Customers write these, we are not doing this in 335 Customer feedback: daily (or several times/week) Iteration feedback: when tasks are started, completed, or blocked 5
 Practices: On-site customer Many software projects fail because they do not deliver software that meets needs A real client should be part of the team – Defines / decides the needs – Answers questions and resolves issues – Prioritizes features – Helps prevents devs from making decisions like: "They probably wanted us to. . ” Consider your PM playing this role 6
Practices: On-site customer Many software projects fail because they do not deliver software that meets needs A real client should be part of the team – Defines / decides the needs – Answers questions and resolves issues – Prioritizes features – Helps prevents devs from making decisions like: "They probably wanted us to. . ” Consider your PM playing this role 6
 Practices: Simple design The “right” design – Runs all tests – No code duplication, No code duplication – Short methods 7
Practices: Simple design The “right” design – Runs all tests – No code duplication, No code duplication – Short methods 7
 Practices: Testing Software should be tested, but it is often spotty or overlooked Automatic testing (JUnit, for example) helps us know that a feature works and it will work after refactoring, additional code, and other changes Provides confidence in the program 8
Practices: Testing Software should be tested, but it is often spotty or overlooked Automatic testing (JUnit, for example) helps us know that a feature works and it will work after refactoring, additional code, and other changes Provides confidence in the program 8
 Testing Write tests at the same time as production code – Unit tests developer – Feature/acceptance tests customer (not in 335) Don't need a test for every method (but why not) Testing can be used to drive development and design of code – But it helps to have an overall architecture first (see your UML class diagram, which is subject to change 9
Testing Write tests at the same time as production code – Unit tests developer – Feature/acceptance tests customer (not in 335) Don't need a test for every method (but why not) Testing can be used to drive development and design of code – But it helps to have an overall architecture first (see your UML class diagram, which is subject to change 9
 Regression Testing – re-testing of a previously tested program following modification to ensure that faults have not been introduced or uncovered as a result of changes. – Regression tests are designed for repeatability, and are often used when testing a second or later version of the system under test – Regression testing can be carried out on all 10 applications, including e-Commerce and web-
Regression Testing – re-testing of a previously tested program following modification to ensure that faults have not been introduced or uncovered as a result of changes. – Regression tests are designed for repeatability, and are often used when testing a second or later version of the system under test – Regression testing can be carried out on all 10 applications, including e-Commerce and web-
 Testing Strong emphasis on regression testing – Unit tests need to execute all the time Unit tests pass 100% Other testing frameworks include – SUnit (Smalltalk), Http. Unit (Web. Apps), Ace. Unit (C), CPPUnit (C++), Py. Unit (Python) – For a complete list, see http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_unit_testing_frameworks 11
Testing Strong emphasis on regression testing – Unit tests need to execute all the time Unit tests pass 100% Other testing frameworks include – SUnit (Smalltalk), Http. Unit (Web. Apps), Ace. Unit (C), CPPUnit (C++), Py. Unit (Python) – For a complete list, see http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_unit_testing_frameworks 11
 Can't unit test always Won’t have unit tests for – GUIs: There are testing frameworks to simulate and test user interaction, but not this course • Just added to Web. Cat – Network, use visual inspection while running – Views, animation, drawing: visually inspect • this is system verification too – Randomness: Some strategies might have 12 some randomness, which can be hard to
Can't unit test always Won’t have unit tests for – GUIs: There are testing frameworks to simulate and test user interaction, but not this course • Just added to Web. Cat – Network, use visual inspection while running – Views, animation, drawing: visually inspect • this is system verification too – Randomness: Some strategies might have 12 some randomness, which can be hard to
 Practices: Refactoring Restructure code without changing the functionality Goal: Keep design simple – Change bad design when you find it – Remove “dead” code Examples at Martin Fowler's Web site: http: //www. refactoring. com/ see online catalog 13
Practices: Refactoring Restructure code without changing the functionality Goal: Keep design simple – Change bad design when you find it – Remove “dead” code Examples at Martin Fowler's Web site: http: //www. refactoring. com/ see online catalog 13
 Practices: Pair programming Write production code with 2 people on one machine – Person 1: Implements the method (Driver) – Person 2: Thinks strategically about potential improvements, test cases, issues (Observer or Navigator) Pairs change all the time. Has advantages such as – No single expert on any part of the system – Continuous code reviews, fewer defects – Cheaper in the long run, and more fun Issues with Pair Programming: 14
Practices: Pair programming Write production code with 2 people on one machine – Person 1: Implements the method (Driver) – Person 2: Thinks strategically about potential improvements, test cases, issues (Observer or Navigator) Pairs change all the time. Has advantages such as – No single expert on any part of the system – Continuous code reviews, fewer defects – Cheaper in the long run, and more fun Issues with Pair Programming: 14
 Practices: Collective ownership All code can be changed by anybody on the team Everybody is required to improve any portion of bad code s/he sees Everyone has responsibility for the system Individual code ownership tends to create "experts", the "experts" tend to create difficult team situations – Every year in 335. . . 15
Practices: Collective ownership All code can be changed by anybody on the team Everybody is required to improve any portion of bad code s/he sees Everyone has responsibility for the system Individual code ownership tends to create "experts", the "experts" tend to create difficult team situations – Every year in 335. . . 15
 Practices: Continuous integration Integration happens after a few hours of development Checkout repo with your changes, – which may require handling conflicts of two people have modified the same class or method Make sure all tests pass (green bar) In case of errors: – Do not put changes into the repo, fix them first Check in the system to the common repository 16
Practices: Continuous integration Integration happens after a few hours of development Checkout repo with your changes, – which may require handling conflicts of two people have modified the same class or method Make sure all tests pass (green bar) In case of errors: – Do not put changes into the repo, fix them first Check in the system to the common repository 16
 Continuous Integration Find problems early Can see if a change breaks the system more quickly -- while you remember the details Add to the build in small increments 17
Continuous Integration Find problems early Can see if a change breaks the system more quickly -- while you remember the details Add to the build in small increments 17
 Practices: Coding standards Coding Standard – Naming conventions and style – Least amount of work possible: Code should exist once and only once – Everyone always use Java 6 or Java 7 Team has to adopt a coding standard – Makes it easier to understand other people’s code – Avoids code changes due to syntactic preferences 18
Practices: Coding standards Coding Standard – Naming conventions and style – Least amount of work possible: Code should exist once and only once – Everyone always use Java 6 or Java 7 Team has to adopt a coding standard – Makes it easier to understand other people’s code – Avoids code changes due to syntactic preferences 18
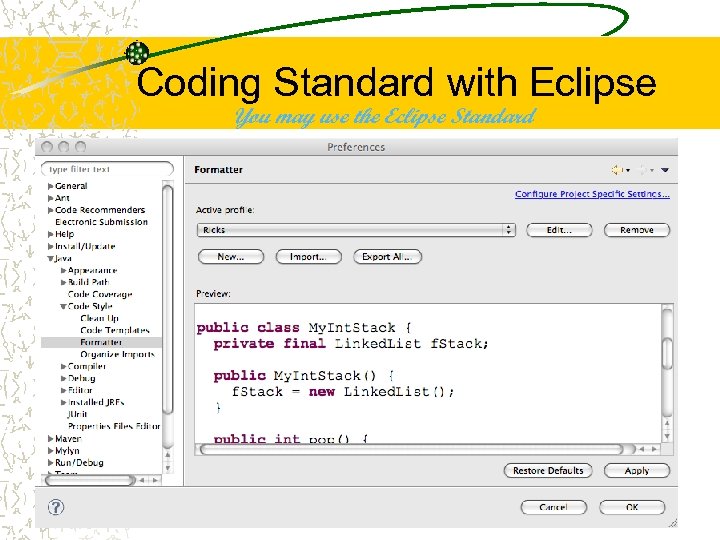 Coding Standard with Eclipse You may use the Eclipse Standard 19
Coding Standard with Eclipse You may use the Eclipse Standard 19


