 Agile Methods
Agile Methods
 Agile Process/Method • lightweight processes/methods that can be used to manage and control software and product development using iterative, incremental practices. • The main concept is to improve software processes. • The focus on Engineering Practices • Examples: – XP – Scrum – Crystal Methodologies
Agile Process/Method • lightweight processes/methods that can be used to manage and control software and product development using iterative, incremental practices. • The main concept is to improve software processes. • The focus on Engineering Practices • Examples: – XP – Scrum – Crystal Methodologies
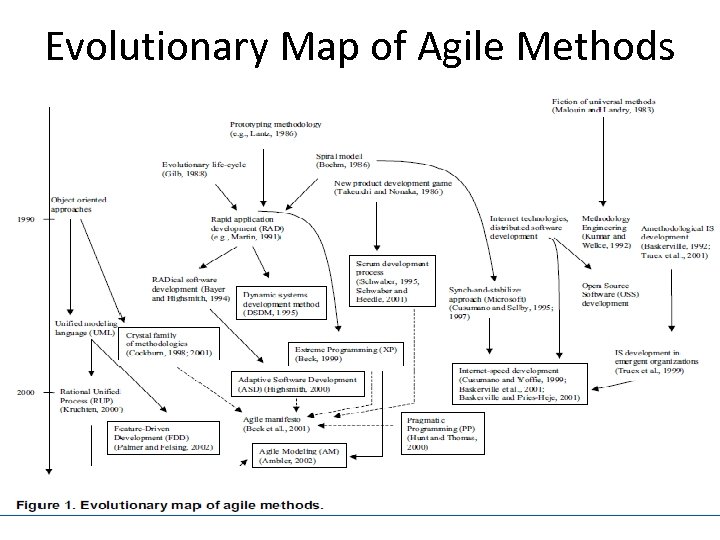 Evolutionary Map of Agile Methods
Evolutionary Map of Agile Methods
 Agile Principles The main principles of Agile Process Development are and as summarized from (Beck et al. , 2001): • The main priority is to satisfy the customer needs through incremental delivery approach. • Requirements change is managed and control. • Delivering build by build (i. e. portion if the
Agile Principles The main principles of Agile Process Development are and as summarized from (Beck et al. , 2001): • The main priority is to satisfy the customer needs through incremental delivery approach. • Requirements change is managed and control. • Delivering build by build (i. e. portion if the
 Agile Principles • The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation. • Working software is the primarily measure of process. • Sustainable pace is one core values of agile processes. Sponsors, developers and users are responsible to maintain a constant pace. • Continuous focus in technical excellence and prober design enhances agility. • Simplicity--the art of maximizing the amount of work not done--is essential. • The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from selforganizing teams. • At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Agile Principles • The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation. • Working software is the primarily measure of process. • Sustainable pace is one core values of agile processes. Sponsors, developers and users are responsible to maintain a constant pace. • Continuous focus in technical excellence and prober design enhances agility. • Simplicity--the art of maximizing the amount of work not done--is essential. • The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from selforganizing teams. • At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
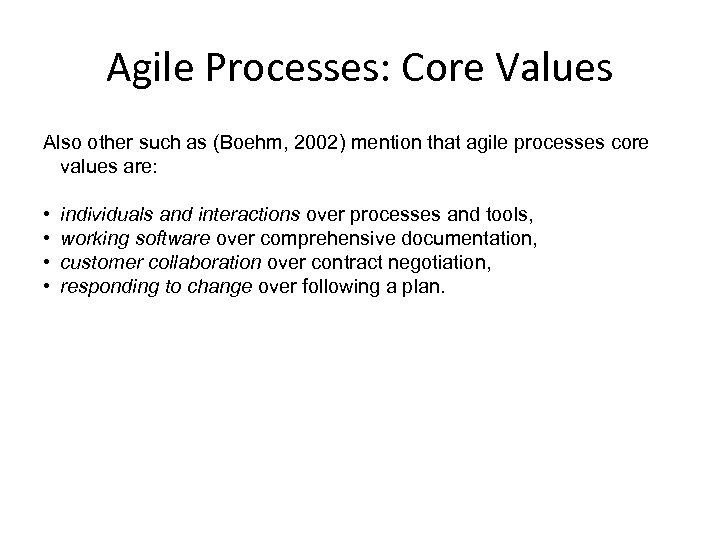 Agile Processes: Core Values Also other such as (Boehm, 2002) mention that agile processes core values are: • • individuals and interactions over processes and tools, working software over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, responding to change over following a plan.
Agile Processes: Core Values Also other such as (Boehm, 2002) mention that agile processes core values are: • • individuals and interactions over processes and tools, working software over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, responding to change over following a plan.
 Agile Processes: a Review • Premium people(Boehm, 2002) • Critical systems--leery(Boehm, 2002) • Agile methods or processes claiming high quality products as results of their use and with excessive cost. • Agile methods or processes claiming simplicity and speed.
Agile Processes: a Review • Premium people(Boehm, 2002) • Critical systems--leery(Boehm, 2002) • Agile methods or processes claiming high quality products as results of their use and with excessive cost. • Agile methods or processes claiming simplicity and speed.
![References 1. BECK, K. , et al. (2001). Manifesto for Agile Software Development [Online]. References 1. BECK, K. , et al. (2001). Manifesto for Agile Software Development [Online].](https://present5.com/presentation/fb6485f4c3781e754f10baa5847ab9b6/image-8.jpg) References 1. BECK, K. , et al. (2001). Manifesto for Agile Software Development [Online]. Available: http: //www. agilemanifesto. org/principles. html [Accessed April 26 2011]. 2. BOEHM, B. (2002). Get Ready for Agile Methods, with Care. IEEE Computer, 64 - 69. 3. NAWROCKI, J. R. , WALTER, B. & WOJCIECHOWSKI, A. (2002(. Comparison of CMM Level 2 and e. Xtreme Programming. The 7 th European Conference on Software Quality. Helsinki, Finland: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 4. SEDDON, J. (2000). The Case Against ISO 9000, Dublin, Oak Tree Press. 5. VRIENS, C. (2003). Certifying for CMM Level 2 and ISO 9001 with XP@Scrum. Agile Development Conference (ADC). Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE Computer Society. 6. ABRAHAMSSON, P. , et al. (2003). New Directions on Agile Methods: A Comparative Analysis. 25 th International Conference in Software Engineering (ICSE'03) Portland, Oregon - USA.
References 1. BECK, K. , et al. (2001). Manifesto for Agile Software Development [Online]. Available: http: //www. agilemanifesto. org/principles. html [Accessed April 26 2011]. 2. BOEHM, B. (2002). Get Ready for Agile Methods, with Care. IEEE Computer, 64 - 69. 3. NAWROCKI, J. R. , WALTER, B. & WOJCIECHOWSKI, A. (2002(. Comparison of CMM Level 2 and e. Xtreme Programming. The 7 th European Conference on Software Quality. Helsinki, Finland: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 4. SEDDON, J. (2000). The Case Against ISO 9000, Dublin, Oak Tree Press. 5. VRIENS, C. (2003). Certifying for CMM Level 2 and ISO 9001 with XP@Scrum. Agile Development Conference (ADC). Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE Computer Society. 6. ABRAHAMSSON, P. , et al. (2003). New Directions on Agile Methods: A Comparative Analysis. 25 th International Conference in Software Engineering (ICSE'03) Portland, Oregon - USA.