 Aggregate Demand & Supply Part I: Demand
Aggregate Demand & Supply Part I: Demand
 Bringing Prices Forward In neither Keynesian Cross nor IS - LM model are prices explicit and obvious Yet, inflation was viewed as central problem by end of 1960 s and more so after Oil Shock '73 -74 So, theory was revised to highlight price & inflation This was done through "aggregate supply & demand model"
Bringing Prices Forward In neither Keynesian Cross nor IS - LM model are prices explicit and obvious Yet, inflation was viewed as central problem by end of 1960 s and more so after Oil Shock '73 -74 So, theory was revised to highlight price & inflation This was done through "aggregate supply & demand model"
 Aggregate Demand Can we derive a relationship between aggregate demand output like Y = f(P) from what we have developed so far? Yes, because prices are included in analysis of money demand, i. e. , Md = f(i, Y, P) We postulate that d. Md/d. P > 0, that is to say as prices rise, so does the demand for money because more money is needed to buy the same amount of higher priced stuff
Aggregate Demand Can we derive a relationship between aggregate demand output like Y = f(P) from what we have developed so far? Yes, because prices are included in analysis of money demand, i. e. , Md = f(i, Y, P) We postulate that d. Md/d. P > 0, that is to say as prices rise, so does the demand for money because more money is needed to buy the same amount of higher priced stuff
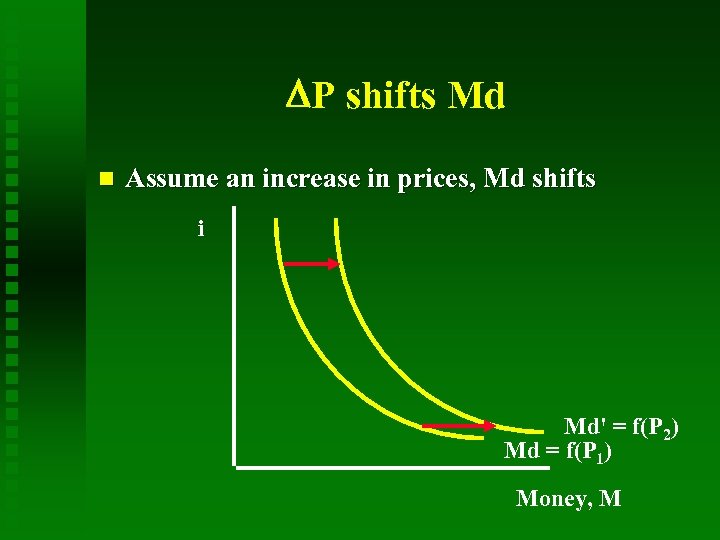 P shifts Md Assume an increase in prices, Md shifts i Md' = f(P 2) Md = f(P 1) Money, M
P shifts Md Assume an increase in prices, Md shifts i Md' = f(P 2) Md = f(P 1) Money, M
 Effects of Price Change Shift in Md raises interest Rise in interest will reduce investment Rise in interest will reduce consumption Rise in prices will reduce real wealth and thus consumption
Effects of Price Change Shift in Md raises interest Rise in interest will reduce investment Rise in interest will reduce consumption Rise in prices will reduce real wealth and thus consumption
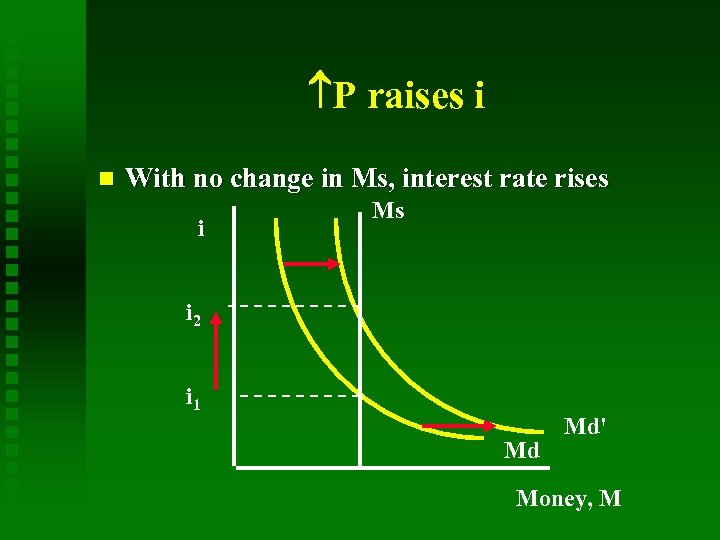 P raises i With no change in Ms, interest rate rises i Ms i 2 i 1 Md Md' Money, M
P raises i With no change in Ms, interest rate rises i Ms i 2 i 1 Md Md' Money, M
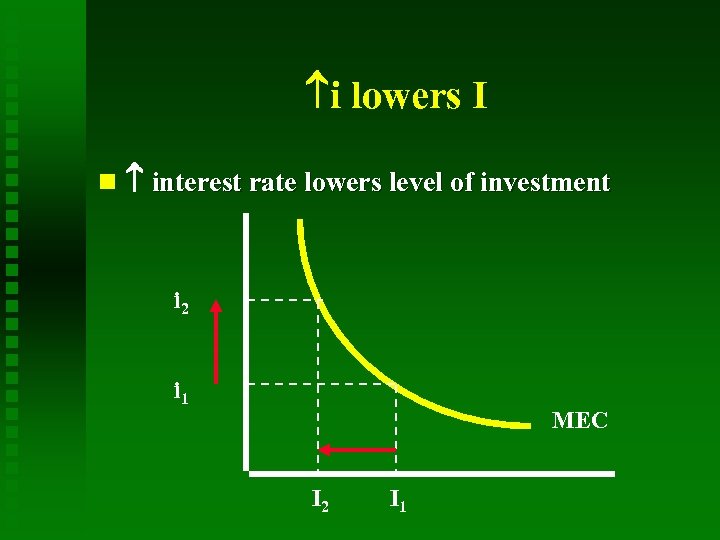 i lowers I interest rate lowers level of investment i 2 i 1 MEC I 2 I 1
i lowers I interest rate lowers level of investment i 2 i 1 MEC I 2 I 1
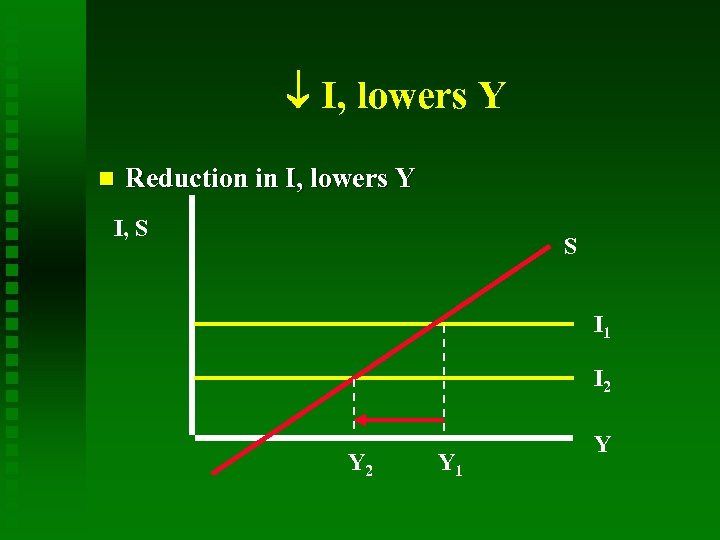 I, lowers Y Reduction in I, lowers Y I, S S I 1 I 2 Y 1 Y
I, lowers Y Reduction in I, lowers Y I, S S I 1 I 2 Y 1 Y
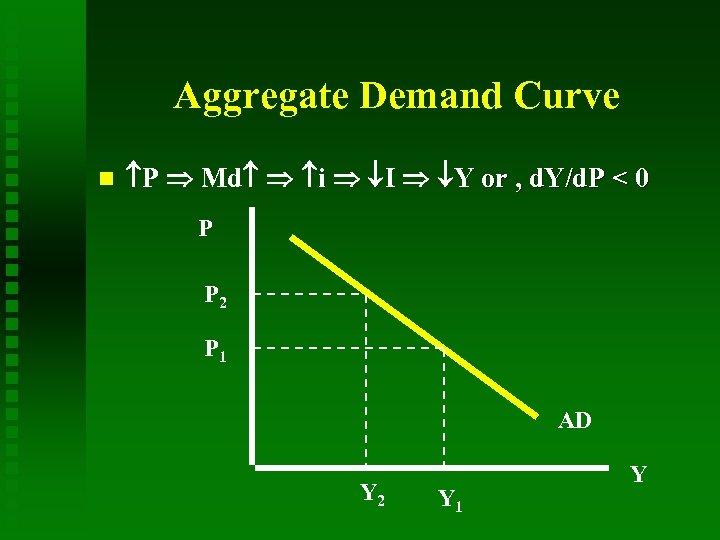 Aggregate Demand Curve P Md i I Y or , d. Y/d. P < 0 P P 2 P 1 AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
Aggregate Demand Curve P Md i I Y or , d. Y/d. P < 0 P P 2 P 1 AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
 Consumption & Interest By the time the AS&AD curves were developed, consumer credit was well advanced, so we also know that changes in interest rates affect consumption expenditures (on durables) Therefore just as I = f(i), So, too, does C = f(i) as well as f(Y) So price changes that raise i will lower C as well as I
Consumption & Interest By the time the AS&AD curves were developed, consumer credit was well advanced, so we also know that changes in interest rates affect consumption expenditures (on durables) Therefore just as I = f(i), So, too, does C = f(i) as well as f(Y) So price changes that raise i will lower C as well as I
 Real Balance Effect In modern consumption theory, it is generally assumed that consumption is a function not only of Y and of i, but also of real wealth In otherwords the greater your real wealth, the more you are likely to spend Changes in prices change real wealth, price increases reduce it, price reductions raise it, and therefore have an impact on consumption and thus on Y.
Real Balance Effect In modern consumption theory, it is generally assumed that consumption is a function not only of Y and of i, but also of real wealth In otherwords the greater your real wealth, the more you are likely to spend Changes in prices change real wealth, price increases reduce it, price reductions raise it, and therefore have an impact on consumption and thus on Y.
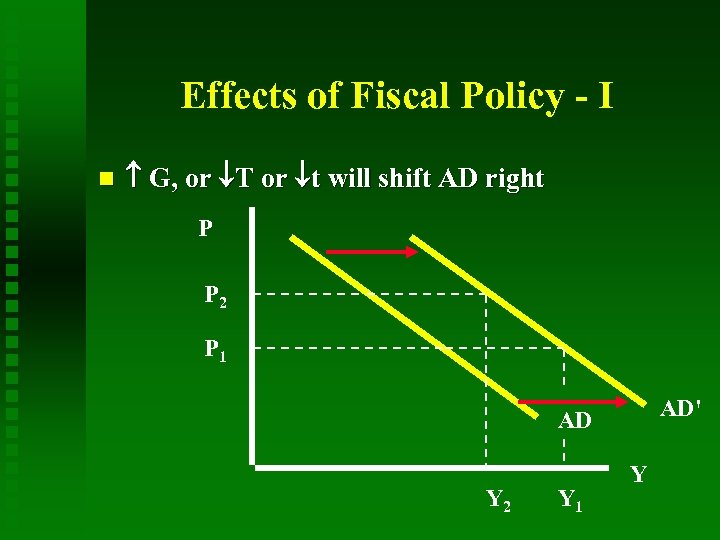 Effects of Fiscal Policy - I G, or T or t will shift AD right P P 2 P 1 AD' AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
Effects of Fiscal Policy - I G, or T or t will shift AD right P P 2 P 1 AD' AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
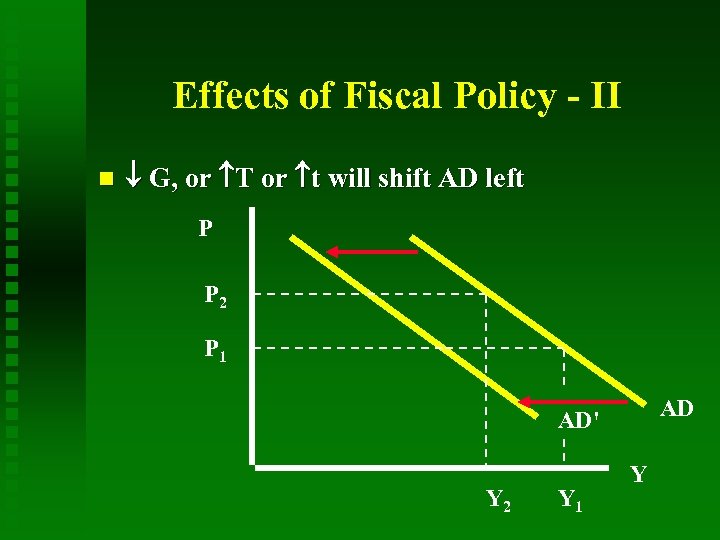 Effects of Fiscal Policy - II G, or T or t will shift AD left P P 2 P 1 AD AD' Y 2 Y 1 Y
Effects of Fiscal Policy - II G, or T or t will shift AD left P P 2 P 1 AD AD' Y 2 Y 1 Y
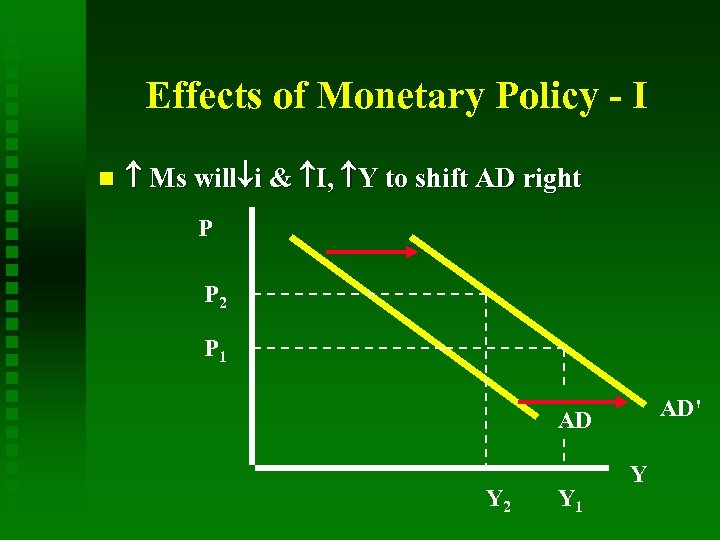 Effects of Monetary Policy - I Ms will i & I, Y to shift AD right P P 2 P 1 AD' AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
Effects of Monetary Policy - I Ms will i & I, Y to shift AD right P P 2 P 1 AD' AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
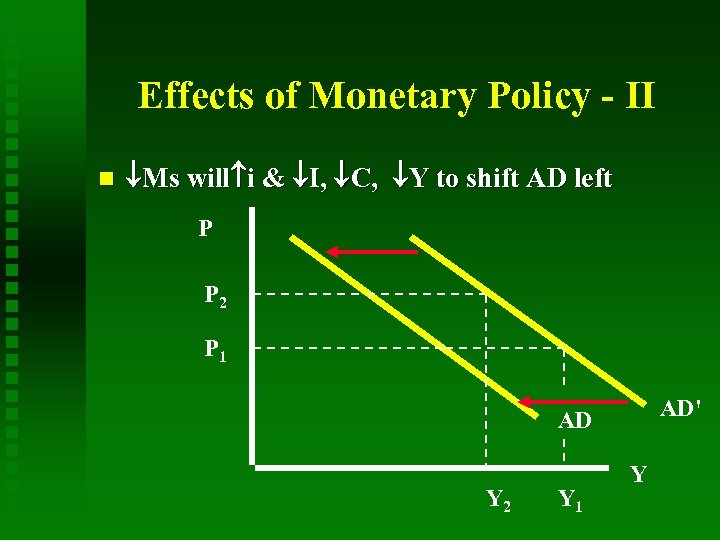 Effects of Monetary Policy - II Ms will i & I, C, Y to shift AD left P P 2 P 1 AD' AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
Effects of Monetary Policy - II Ms will i & I, C, Y to shift AD left P P 2 P 1 AD' AD Y 2 Y 1 Y
 --END--
--END--