e0c4644ef4a107fd9163a1603e7022ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Agenda • How Yale came to consider ITIL • Yale’s ITIL Project Portfolio: – Phase 1 – Learning about the Framework – Phase 2 (present)- Incident, Problem and Change Mgt. – Phase 3 (future)- Service Catalog, SLM, Configuration Mgt. 2
Agenda • How Yale came to consider ITIL • Yale’s ITIL Project Portfolio: – Phase 1 – Learning about the Framework – Phase 2 (present)- Incident, Problem and Change Mgt. – Phase 3 (future)- Service Catalog, SLM, Configuration Mgt. 2
 Why ITIL? • Yale’s traditional Siloe’d IT organization – The bar keeps getting raised, increasing demands – Do more with less – Technology more complex, interrelated 3
Why ITIL? • Yale’s traditional Siloe’d IT organization – The bar keeps getting raised, increasing demands – Do more with less – Technology more complex, interrelated 3
 Why ITIL? • Integration – Yale’s Unique Challenge – Merged Med and Central IT Organizations (Nov. 2005) – Suddenly, a much larger organization – Suddenly, two different cultures forced to cooperate 4
Why ITIL? • Integration – Yale’s Unique Challenge – Merged Med and Central IT Organizations (Nov. 2005) – Suddenly, a much larger organization – Suddenly, two different cultures forced to cooperate 4
 5
5
 Phase 1 – Acquiring ITIL Knowledge • Organizational Change Management – Any BPM redesign project is fundamentally about organizational change management – Kotter’s 8 Steps – ADKAR (Prosci) 6
Phase 1 – Acquiring ITIL Knowledge • Organizational Change Management – Any BPM redesign project is fundamentally about organizational change management – Kotter’s 8 Steps – ADKAR (Prosci) 6
 Phase 1 – Acquiring ITIL Knowledge • Kotter’s 8 Steps (John Kotter, Leading Change) – Create a Sense of Urgency – Form a Guiding Coalition – Create a Vision for the Change – Communicate the Vision – Remove Obstacles – Create Short Term Wins – Build on the Change – Anchor the Changes in the Corp Culture 7
Phase 1 – Acquiring ITIL Knowledge • Kotter’s 8 Steps (John Kotter, Leading Change) – Create a Sense of Urgency – Form a Guiding Coalition – Create a Vision for the Change – Communicate the Vision – Remove Obstacles – Create Short Term Wins – Build on the Change – Anchor the Changes in the Corp Culture 7
 Phase 1 – Form Guiding Coalition • Executive Sponsorship • Change Agents in organization • Training (Summer, Fall 2006) – ITIL Foundations – ITIL Practitioner – BPM Concepts 8
Phase 1 – Form Guiding Coalition • Executive Sponsorship • Change Agents in organization • Training (Summer, Fall 2006) – ITIL Foundations – ITIL Practitioner – BPM Concepts 8
 Phase 1 – Form Process Project Plans • Process Projects – Generic Deliverables – Documented and formalized process and procedures – Documented and formalized process policies – Automation requirements defined and customized within technology availability and constraints – Documented and defined awareness campaign and training activities for process implementation. – Documented and formalized management reports and key performance indicators – Documented and formalized ongoing roles and responsibilities for the management and continued ownership and improvement of the process 9
Phase 1 – Form Process Project Plans • Process Projects – Generic Deliverables – Documented and formalized process and procedures – Documented and formalized process policies – Automation requirements defined and customized within technology availability and constraints – Documented and defined awareness campaign and training activities for process implementation. – Documented and formalized management reports and key performance indicators – Documented and formalized ongoing roles and responsibilities for the management and continued ownership and improvement of the process 9
 Phase 2 – Incident, Problem, Change Mgt. • Redesign of Incident and Problem processes in Client Support (begun Oct. 2006) – No new tool– processes first – Approx 80 people, 1 of 4 Departments • Reworked Existing Ticketing System to enable Problem Management • Experimented with naming Process Managers 10
Phase 2 – Incident, Problem, Change Mgt. • Redesign of Incident and Problem processes in Client Support (begun Oct. 2006) – No new tool– processes first – Approx 80 people, 1 of 4 Departments • Reworked Existing Ticketing System to enable Problem Management • Experimented with naming Process Managers 10
 Phase 2 – Creation of Service Desk • Combine 2 units into one Service Desk Unit (begun Winter, 2007) – Client Accounts and Access – Help Desk – Still would not be Single Point of Contact • This remains an incomplete transition 11
Phase 2 – Creation of Service Desk • Combine 2 units into one Service Desk Unit (begun Winter, 2007) – Client Accounts and Access – Help Desk – Still would not be Single Point of Contact • This remains an incomplete transition 11
 Phase 2 – SOP Definition • Purchased BPM modeling software • Trained Business and Process Analysts – Began with 3 part-time – Later promote a HD staffer to permanent position • Formed committees to define SOPs, Standardize Supporting Processes – E. g. – Moves, compromised machines, account setups – Feedback loop 12
Phase 2 – SOP Definition • Purchased BPM modeling software • Trained Business and Process Analysts – Began with 3 part-time – Later promote a HD staffer to permanent position • Formed committees to define SOPs, Standardize Supporting Processes – E. g. – Moves, compromised machines, account setups – Feedback loop 12
 Phase 2 – Expand Scope and Engage Enabling Technology • Expand to Include Change Management (begun, Summer 2007) – Managed Workstation (dependency) • Expand Scope to Include Infrastructure Group – Approx. doubles organizational scope, 2 of 4 Deps. • Increased Risk – Expands complexity – Cultural issues magnify hurdle of Org. Change Mgt. 13
Phase 2 – Expand Scope and Engage Enabling Technology • Expand to Include Change Management (begun, Summer 2007) – Managed Workstation (dependency) • Expand Scope to Include Infrastructure Group – Approx. doubles organizational scope, 2 of 4 Deps. • Increased Risk – Expands complexity – Cultural issues magnify hurdle of Org. Change Mgt. 13
 14
14
 Phase 2 – Enabling Technology • Increased Scope- heightens need for unifying tool – Vendors have hit the ITIL compliant space – Speak to Gartner • Further increases complexity – Time to evaluate software – Time to negotiate contract – Time to negotiate SOW (January 2008) 15
Phase 2 – Enabling Technology • Increased Scope- heightens need for unifying tool – Vendors have hit the ITIL compliant space – Speak to Gartner • Further increases complexity – Time to evaluate software – Time to negotiate contract – Time to negotiate SOW (January 2008) 15
 Phase 2 – Enabling Technology • Training – Need to train in house people to assist in process accommodation to technology – Take over software maintenance and enhancements • Consultants – Work on joint project to deliver configured software 16
Phase 2 – Enabling Technology • Training – Need to train in house people to assist in process accommodation to technology – Take over software maintenance and enhancements • Consultants – Work on joint project to deliver configured software 16
 Phase 2 – Enabling Technology • Originally slated to go live with enabling technology in April, 2008 • Delays due to contract negotiation, consultant availability • Currently training staff in use of the tool for Incident and Change Management • System in production June 2 • June 30 official tool of record 17
Phase 2 – Enabling Technology • Originally slated to go live with enabling technology in April, 2008 • Delays due to contract negotiation, consultant availability • Currently training staff in use of the tool for Incident and Change Management • System in production June 2 • June 30 official tool of record 17
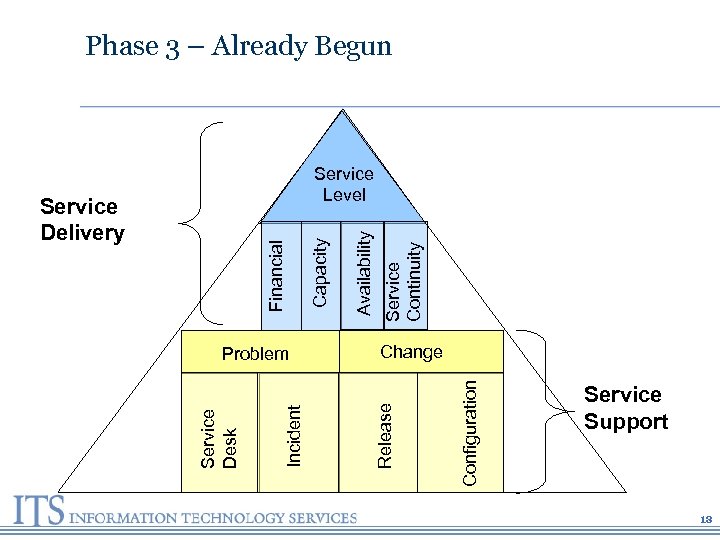 Configuration Release Problem Service Continuity Availability Capacity Financial Service Delivery Incident Service Desk Phase 3 – Already Begun Service Level Change Service Support 18
Configuration Release Problem Service Continuity Availability Capacity Financial Service Delivery Incident Service Desk Phase 3 – Already Begun Service Level Change Service Support 18
 Phase 3 – Planned July 2008, June 2009 • Incident, Problem, Change – Implement CSI – Increase Organizational Scope • Knowledge Management – Integrated with Incident and Problem Management 19
Phase 3 – Planned July 2008, June 2009 • Incident, Problem, Change – Implement CSI – Increase Organizational Scope • Knowledge Management – Integrated with Incident and Problem Management 19
 Phase 3 – Planned July 2008, June 2009 • Service Level Management – Already begun – OLA, SLA definition • Service Catalog 1 – Service Definition 20
Phase 3 – Planned July 2008, June 2009 • Service Level Management – Already begun – OLA, SLA definition • Service Catalog 1 – Service Definition 20
 Phase 3 – Planned July 2008, June 2009 • Configuration Management – CMDB Definition • Change Management matured to include Release 21
Phase 3 – Planned July 2008, June 2009 • Configuration Management – CMDB Definition • Change Management matured to include Release 21
 Is ITIL for you? • ITIL specifies the “what” not the “how” – Ideal for higher ed, for which commercial models often don’t fit • Gartner findings – Most organizations implement ITIL to improve quality, not reduce cost – The biggest challenge to ITIL implementations is the culture change 22
Is ITIL for you? • ITIL specifies the “what” not the “how” – Ideal for higher ed, for which commercial models often don’t fit • Gartner findings – Most organizations implement ITIL to improve quality, not reduce cost – The biggest challenge to ITIL implementations is the culture change 22
 First Steps: Acquire Knowledge & Training • High level sponsor • Introductory workshop • Appoint an ITIL project manager – ITIL expertise – Process mapping and redesign expertise • Train a subgroup 23
First Steps: Acquire Knowledge & Training • High level sponsor • Introductory workshop • Appoint an ITIL project manager – ITIL expertise – Process mapping and redesign expertise • Train a subgroup 23
 First Steps: Implementation • Start with Service Desk and Incident Management OR Change Management • Put process before tools • Review current implementations, including processes and tools (Remedy, RT, Pinnacle) and target improvements 24
First Steps: Implementation • Start with Service Desk and Incident Management OR Change Management • Put process before tools • Review current implementations, including processes and tools (Remedy, RT, Pinnacle) and target improvements 24
 Parting words • ITIL is about change • Serious change takes 3 -5 years • You can adapt ITIL to your organization as much as you adapt your organization to ITIL 25
Parting words • ITIL is about change • Serious change takes 3 -5 years • You can adapt ITIL to your organization as much as you adapt your organization to ITIL 25
 Questions? Bill Cunningham bill. cunningham@yale. edu John Guidone john. guidone@yale. edu 26
Questions? Bill Cunningham bill. cunningham@yale. edu John Guidone john. guidone@yale. edu 26
 J Conclusion 27
J Conclusion 27
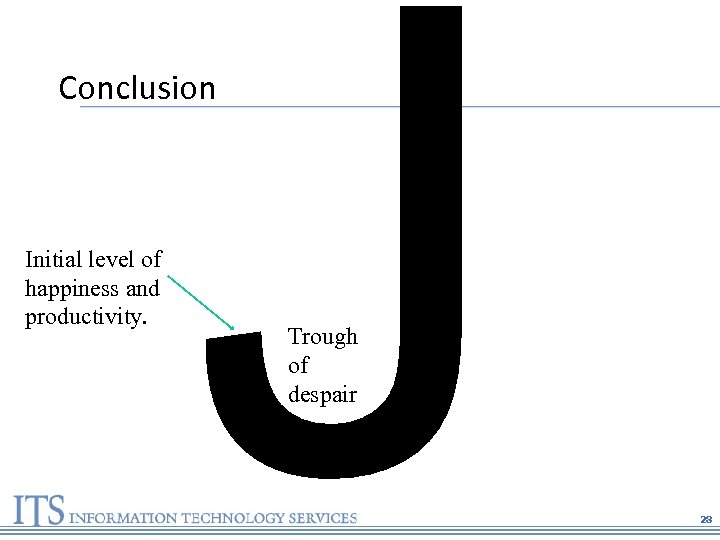 J Conclusion Initial level of happiness and productivity. Trough of despair 28
J Conclusion Initial level of happiness and productivity. Trough of despair 28


