9b42549af53662ef4e08775b7037dce7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Agenda 11/7 1. 2. 3. 4. Current Events Ch. 6 Lecture- Market Equilibrium (RS) Ch. 5 & 6 Vocab WS HW: Test and notebook next Tue. 11/14
Agenda 11/7 1. 2. 3. 4. Current Events Ch. 6 Lecture- Market Equilibrium (RS) Ch. 5 & 6 Vocab WS HW: Test and notebook next Tue. 11/14
 Ch. 6 -Market Equilibrium
Ch. 6 -Market Equilibrium
 SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER p Equilibrium (E) refers to a situation in which the price has reached the level where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. (Q ) = (Q ) S D
SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER p Equilibrium (E) refers to a situation in which the price has reached the level where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. (Q ) = (Q ) S D
 SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER p Equilibrium Price (EP) n The price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded. n On a graph, it is the price at which the supply and demand curves intersect. p Equilibrium Quantity (EQ) n The quantity supplied and the quantity demanded at the equilibrium price. n On a graph it is the quantity at which the supply and demand curves intersect.
SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER p Equilibrium Price (EP) n The price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded. n On a graph, it is the price at which the supply and demand curves intersect. p Equilibrium Quantity (EQ) n The quantity supplied and the quantity demanded at the equilibrium price. n On a graph it is the quantity at which the supply and demand curves intersect.
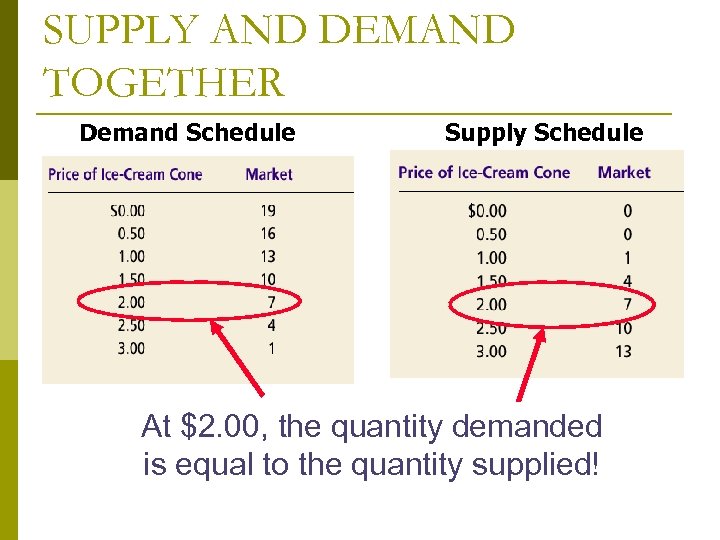 SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER Demand Schedule Supply Schedule At $2. 00, the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied!
SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER Demand Schedule Supply Schedule At $2. 00, the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied!
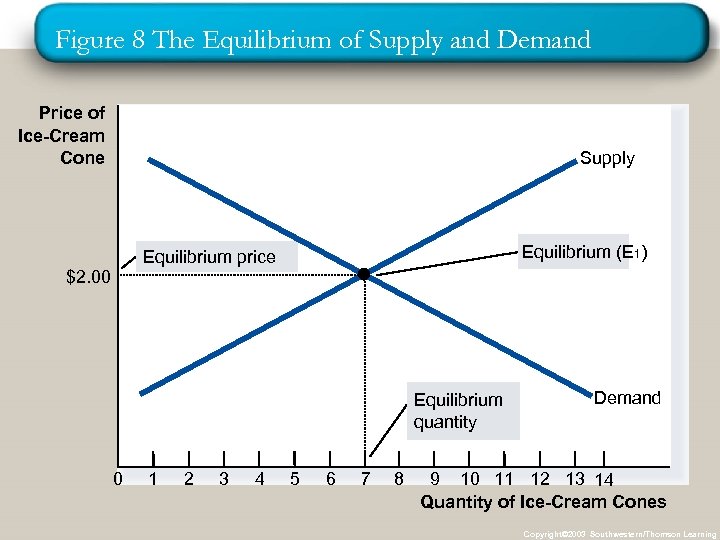 Figure 8 The Equilibrium of Supply and Demand Price of Ice-Cream Cone Supply Equilibrium (E 1) Equilibrium price $2. 00 Equilibrium quantity 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Demand 9 10 11 12 13 14 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
Figure 8 The Equilibrium of Supply and Demand Price of Ice-Cream Cone Supply Equilibrium (E 1) Equilibrium price $2. 00 Equilibrium quantity 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Demand 9 10 11 12 13 14 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
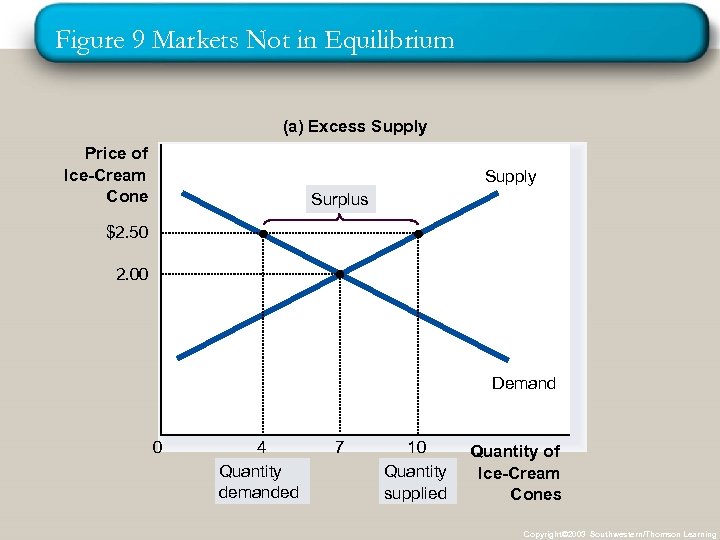 Figure 9 Markets Not in Equilibrium (a) Excess Supply Price of Ice-Cream Cone Supply Surplus $2. 50 2. 00 Demand 0 4 Quantity demanded 7 10 Quantity supplied Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
Figure 9 Markets Not in Equilibrium (a) Excess Supply Price of Ice-Cream Cone Supply Surplus $2. 50 2. 00 Demand 0 4 Quantity demanded 7 10 Quantity supplied Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
 p Surplus Equilibrium n (Read don’t write – the graph just told you this ; )When price > equilibrium price, then quantity supplied > quantity demanded. p. There is excess supply or a surplus. p(WRITE ; ) Suppliers will lower the price to increase sales, thereby moving toward equilibrium.
p Surplus Equilibrium n (Read don’t write – the graph just told you this ; )When price > equilibrium price, then quantity supplied > quantity demanded. p. There is excess supply or a surplus. p(WRITE ; ) Suppliers will lower the price to increase sales, thereby moving toward equilibrium.
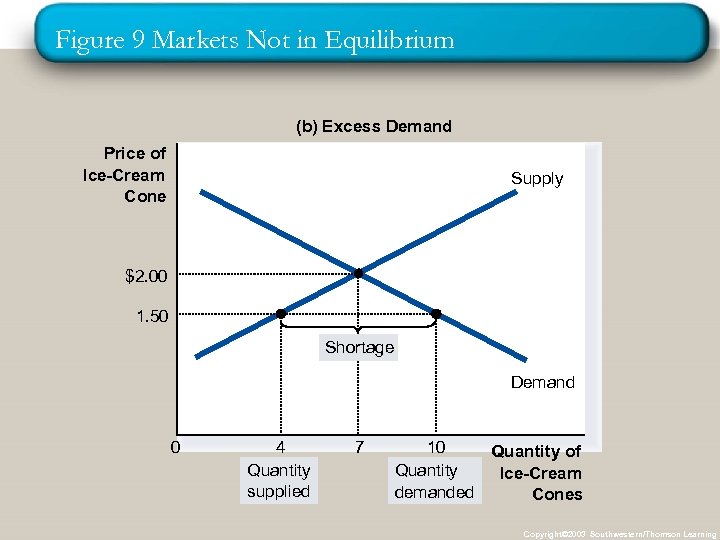 Figure 9 Markets Not in Equilibrium (b) Excess Demand Price of Ice-Cream Cone Supply $2. 00 1. 50 Shortage Demand 0 4 Quantity supplied 7 10 Quantity of Quantity Ice-Cream demanded Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
Figure 9 Markets Not in Equilibrium (b) Excess Demand Price of Ice-Cream Cone Supply $2. 00 1. 50 Shortage Demand 0 4 Quantity supplied 7 10 Quantity of Quantity Ice-Cream demanded Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
 p Shortage Equilibrium n (Read don’t write – the graph just told you this ; ) When price < equilibrium price, then quantity demanded > the quantity supplied. p. There is excess demand or a shortage. p (WRITE ; ) Suppliers will raise the price due to too many buyers chasing too few goods, thereby moving toward equilibrium.
p Shortage Equilibrium n (Read don’t write – the graph just told you this ; ) When price < equilibrium price, then quantity demanded > the quantity supplied. p. There is excess demand or a shortage. p (WRITE ; ) Suppliers will raise the price due to too many buyers chasing too few goods, thereby moving toward equilibrium.
 p Law of supply and demand Equilibrium n The claim that the price of any good adjusts to bring the Qs and the Qd for that good into balance. Market Equilibrium Indiana Jones
p Law of supply and demand Equilibrium n The claim that the price of any good adjusts to bring the Qs and the Qd for that good into balance. Market Equilibrium Indiana Jones
 Assignment 1. 2. Ch. 6 Vocab. WS Book assignment -p. 146 - #1 - 5 -p. 126 #1 -p. 130 #1, 3, and 4 -p. 137 #2
Assignment 1. 2. Ch. 6 Vocab. WS Book assignment -p. 146 - #1 - 5 -p. 126 #1 -p. 130 #1, 3, and 4 -p. 137 #2
 Agenda 11/8 Finish Ch. 6 Lecture 2) Ch. 6 book questions & Practice Exam questions 3) Handout Supplementary Notes 4) Test & Notebook next Tue. 11/14 1)
Agenda 11/8 Finish Ch. 6 Lecture 2) Ch. 6 book questions & Practice Exam questions 3) Handout Supplementary Notes 4) Test & Notebook next Tue. 11/14 1)
 Three Steps to Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium Decide whether the event shifts the supply or demand curve (or both). p Decide whether the curve(s) shift(s) to the left or to the right. p Use the supply-and-demand diagram to see how the shift affects equilibrium price and quantity. p
Three Steps to Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium Decide whether the event shifts the supply or demand curve (or both). p Decide whether the curve(s) shift(s) to the left or to the right. p Use the supply-and-demand diagram to see how the shift affects equilibrium price and quantity. p
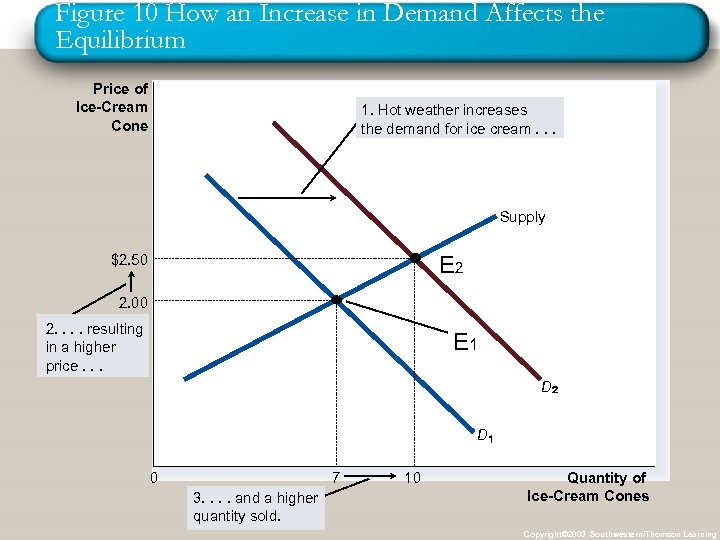 Figure 10 How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium Price of Ice-Cream Cone 1. Hot weather increases the demand for ice cream. . . Supply E 2 $2. 50 2. 00 2. . resulting in a higher price. . . E 1 D D 0 7 3. . and a higher quantity sold. 10 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
Figure 10 How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium Price of Ice-Cream Cone 1. Hot weather increases the demand for ice cream. . . Supply E 2 $2. 50 2. 00 2. . resulting in a higher price. . . E 1 D D 0 7 3. . and a higher quantity sold. 10 Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
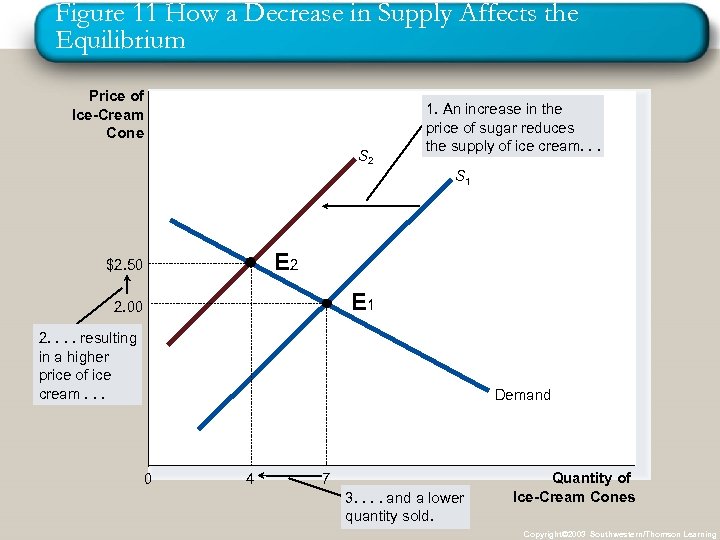 Figure 11 How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium Price of Ice-Cream Cone S 2 1. An increase in the price of sugar reduces the supply of ice cream. . . S 1 E 2 $2. 50 E 1 2. 00 2. . resulting in a higher price of ice cream. . . Demand 0 4 7 3. . and a lower quantity sold. Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
Figure 11 How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium Price of Ice-Cream Cone S 2 1. An increase in the price of sugar reduces the supply of ice cream. . . S 1 E 2 $2. 50 E 1 2. 00 2. . resulting in a higher price of ice cream. . . Demand 0 4 7 3. . and a lower quantity sold. Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Copyright© 2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
 Shifts that change Equilibrium Holy Shift!
Shifts that change Equilibrium Holy Shift!
 Watch & Learn Price Floors & Ceilings
Watch & Learn Price Floors & Ceilings
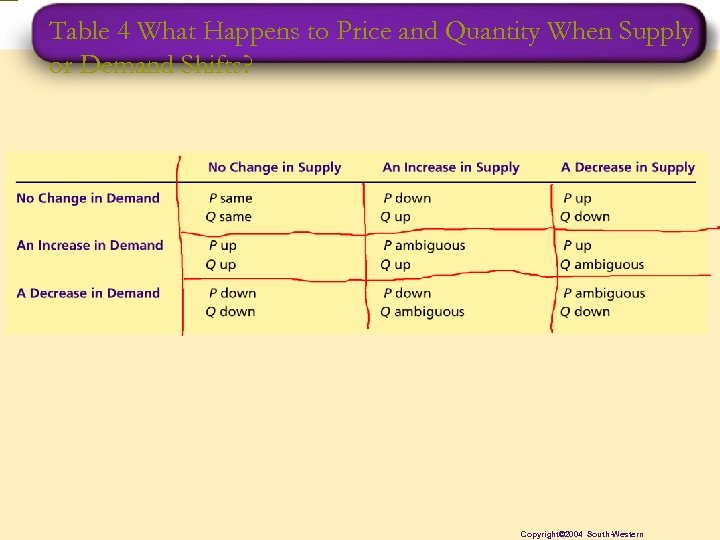 Table 4 What Happens to Price and Quantity When Supply or Demand Shifts? Copyright© 2004 South-Western
Table 4 What Happens to Price and Quantity When Supply or Demand Shifts? Copyright© 2004 South-Western
 Homework Assignment P. 165 #11 -15, 22, and 23 p Practice Exam Questions p
Homework Assignment P. 165 #11 -15, 22, and 23 p Practice Exam Questions p
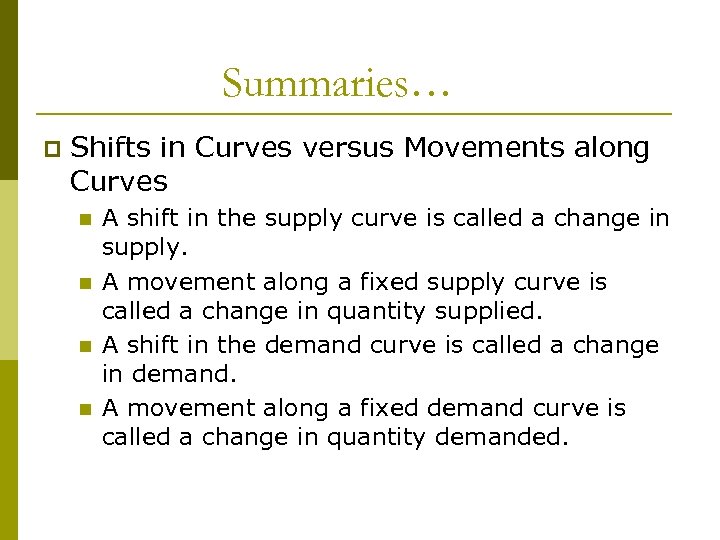 Three Steps to Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium Summaries… p Shifts in Curves versus Movements along Curves n n A shift in the supply curve is called a change in supply. A movement along a fixed supply curve is called a change in quantity supplied. A shift in the demand curve is called a change in demand. A movement along a fixed demand curve is called a change in quantity demanded.
Three Steps to Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium Summaries… p Shifts in Curves versus Movements along Curves n n A shift in the supply curve is called a change in supply. A movement along a fixed supply curve is called a change in quantity supplied. A shift in the demand curve is called a change in demand. A movement along a fixed demand curve is called a change in quantity demanded.
 Summary Economists use the model of supply and demand to analyze competitive markets. p In a competitive market, there are many buyers and sellers, each of whom has little or no influence on the market price. p
Summary Economists use the model of supply and demand to analyze competitive markets. p In a competitive market, there are many buyers and sellers, each of whom has little or no influence on the market price. p
 Summary p The demand curve shows how the quantity of a good depends upon the price. n n n According to the law of demand, as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded rises. Therefore, the demand curve slopes downward. In addition to price, other determinants of how much consumers want to buy include income, the prices of complements and substitutes, tastes, expectations, and the number of buyers. If one of these factors changes, the demand curve shifts.
Summary p The demand curve shows how the quantity of a good depends upon the price. n n n According to the law of demand, as the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded rises. Therefore, the demand curve slopes downward. In addition to price, other determinants of how much consumers want to buy include income, the prices of complements and substitutes, tastes, expectations, and the number of buyers. If one of these factors changes, the demand curve shifts.
 Summary p The supply curve shows how the quantity of a good supplied depends upon the price. n n n According to the law of supply, as the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied rises. Therefore, the supply curve slopes upward. In addition to price, other determinants of how much producers want to sell include input prices, technology, expectations, and the number of sellers. If one of these factors changes, the supply curve shifts.
Summary p The supply curve shows how the quantity of a good supplied depends upon the price. n n n According to the law of supply, as the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied rises. Therefore, the supply curve slopes upward. In addition to price, other determinants of how much producers want to sell include input prices, technology, expectations, and the number of sellers. If one of these factors changes, the supply curve shifts.
 Summary Market equilibrium is determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. p At the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. p The behavior of buyers and sellers naturally drives markets toward their equilibrium. p
Summary Market equilibrium is determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. p At the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. p The behavior of buyers and sellers naturally drives markets toward their equilibrium. p
 Summary To analyze how any event influences a market, we use the supply-and-demand diagram to examine how the even affects the equilibrium price and quantity. p In market economies, prices are the signals that guide economic decisions and thereby allocate resources. p
Summary To analyze how any event influences a market, we use the supply-and-demand diagram to examine how the even affects the equilibrium price and quantity. p In market economies, prices are the signals that guide economic decisions and thereby allocate resources. p
 Summary Video p 30 minute review video by Mr. Clifford ; ) p https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=gd. Xo Dk. Cfc. M 8
Summary Video p 30 minute review video by Mr. Clifford ; ) p https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=gd. Xo Dk. Cfc. M 8


