fd84a479f319d68603d3df44b942336a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 65

Aged and Disabled Waiver (ADW) PERSON-CENTERED PLANNING Cecilia Brown, Quality Assurance Training Webinar December, 2015

Training Goals § To understand the concepts of person-centered planning. § To know the assessment-planning process. § To understand how to do the new person-centered assessment, the new service plan and Personal Attendant Log (PAL). § To know how to monitor the services as documented on the service plan and PAL. § To understand case protocol for problem solving. 1

Planning is Important § § § § § “I know you want to do that, but we can’t do it. ” “You have to follow policy. ” “We need a day of the week on the plan. ” “Let’s come up with a plan to reduce your falls. ” “Policy limits travel to 300 miles now. ” “What day do you usually go grocery shopping? ” “In your words, what is your goal? ” “Why? ” “We can’t do that. ” “Do you need help getting in the shower? ” “What’s your daughter’s number? ” Do you ever feel like this? There is a lot to do and a lot to remember, but planning is the most important part of your job. 2

What is Person-Centered Planning? § Person-centered planning is a process-oriented approach which focuses on the person and his/her needs by putting him/her in charge of defining the direction for his/her life, not on the systems that may or may not be available. § The primary focus of person-centered planning: § Is about the person § Is not about the medical problems 3

Case Manager’s Role § Facilitate the planning process. § Promote person-centered planning. § Encourage the discussion of the recipient’s goals, strengths, needs and preferences. § Ensure recipient’s risks, health and welfare addressed. § Address services, informal supports and resources. § Assist recipient with the service plan disagreement section. § Review the assessment with the recipient. § Provide copies of the person-centered assessment and the service plan to the recipient or legal representative. 4
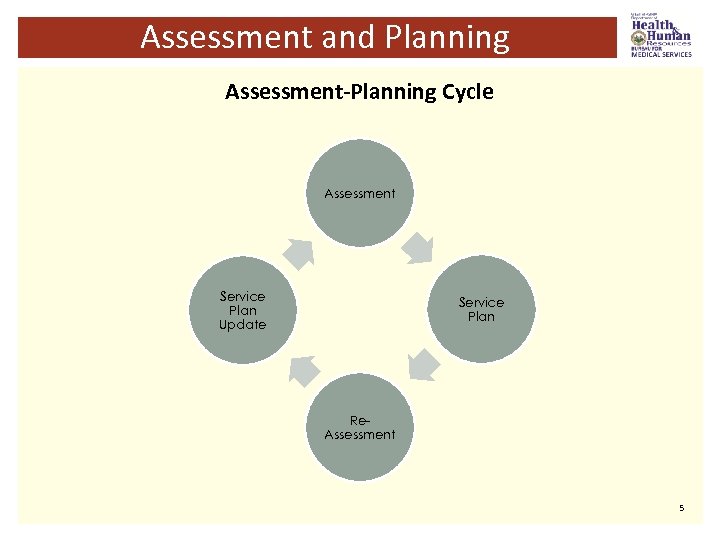
Assessment and Planning Assessment-Planning Cycle Assessment Service Plan Update Service Plan Re. Assessment 5

CMS Requirements § Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) requirements include: Choice § Preference § Individual needs § Cultural considerations § § Ensures: Health and welfare § Risks § § Identifies: Strengths § Recipient goals § Services and resources § 6

Assessment and Service Plan When? § Interim service plan § Initial person-centered assessment and service plan § Six-month person-centered assessment and service plan § Annual person-centered assessment and service plan § Change in Aged and Disabled Waiver (ADW) recipient’s need § Change in level of service 7

Assessment and Planning Process Ensure that a legal representative is present, if needed. Develop rapport and engage with the recipient. Educate on the service plan and assessment process. Review the assessment findings. Solicit input from recipient regarding goals, choice, preferences and needs. § Assist in the development of the service plan. § Ensure needed services, informal supports and resources are identified. § Ensure assessed risks are addressed and plan for emergencies. § § § 8
Person-Centered Assessment Start with the assessment. Understand the person first, then begin planning. Begin here. Person- Centered Assessment. 9

Section One-Case Management There are two sections: Case Management and Registered Nurse. Risks: § Discuss each risk with the person and mark yes or no. § Even if you mark “yes, ” you may also mark “no plan needed. ” Then, state the reason no plan is needed in the comment section. § For example, a person smokes but is not interested in quitting. Mark “no plan needed. ” Educate and document that the person chooses not to stop smoking at this time. It is not required to add this type of risk to the service plan as the plan is intended for risks that are being addressed. § It is expected that any health and safety risk must be addressed on the service plan, even if the person does not want to address it. § For example, smoking while using oxygen. 10

Section One-Case Management (Cont. ) Medical: § Enter the information for the person’s primary care physician or medical specialists such as a physical therapist, cardiologist, etc. § Coordination of healthcare is a new requirement from CMS and will be included in the provider monitoring. This area is used to assess for assistance with access to medical care. If you mark “yes” for “do you think you need referrals, ” you must list this on the resources/needs section of the service plan. § For example, a person needs a new primary care physician. 11

Section One-Case Management (Cont. ) Social: This section is an opportunity to determine the person’s level of interaction with others and their community (community activities). § It is valuable to understand the person. It is not only about their “medical issues or their functional abilities” (person-centered). § For example, if the person never leaves the home, community integration is important. § Type of Work and Education: § For example, person was a nurse. There is a good understanding of the assessment process. Another example, person was a business manager and the person was accustomed to making their own decisions about employees. Identified Service and Resource Needs: Mark those that apply (“x”). Enter the name of the provider and phone number when indicated. Signatures and Dates: § Case Manager, RN and ADW recipient must sign and date the person-centered assessment in the appropriate sections. 12

Section Two-RN Assessment Functional Assessment: The RN will assess the person’s Activities of Independent Living and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (ADLs and IADLs). Indicate the level of assistance that the person will need: § § § I = independent S = supervised P = partial T = total Describe what the worker will need to do to assist the person with this activity. § § For example, “Left side paralysis, hand items to person’s right hand in shower. ” “Hand tremors, unable to hold fork when eating”; “dressing , person needs help to button or zip clothes. ” In the comment section, describe the essential errands and community activities in detail. For example, “Kroger’s in Charleston for grocery once a week on Fridays”; “South Charleston rite aid pharmacy pick up once a month”; “hairdresser on Mondays every week, ” etc. Describe any other activities: § For example, outline equipment that needs cleaned (wheelchair, etc. ). Or anything not covered above. 13

Section Two - RN Assessment (Cont. ) Nursing Assessment: § The nursing assessment is a systemic review of the person. § Mark an “x” beside each condition that applies to the person. § Indicate the “specific status” in the right hand column. § For example, tremors. Document that it is hand tremors. This information is helpful for the worker who will know that the person may need additional assistance with eating. This is important information for the RN to develop the service plan or Personal Attendant Log (PAL). 14

Person-Centered Assessment Describe RN recommendations: This area may include medical information that is critical to the planning process and is one of the primary purposes of having the RN as a part of the planning team. § Changes in needs: Document any changes in the ADW recipient since the last assessment or the last Pre-Admission Screening (PAS). § For example, hospital admission, recent change in condition or functional ability, etc. § This area is useful for requests for changes in service level. § Signatures: The ADW person and the RN must sign and date the RN assessment section. Comments: the RN may use this section to document a justification for an activity that may take longer or need additional assistance. § § § For example, shortness of breath. Showering, walking to and from the car for essential errands may take longer, etc. 15

Discontinued Service Plan Addendum The service plan addendum has been discontinued. There are now two ways to update the service plan now. § The service plan (pages 1 and 2) § The Personal Attendant Log (PAL, pages 3 and 4) 16

Personal Attendant Log (PAL) The old Plan of Care was discontinued. The new PAL replaces the old Plan of Care. The PAL has been incorporated into the service plan. The PAL has become pages 3 and 4 of the service plan. The PAL is to be completed by the RN at the planning meeting. The PAL (pages 3 and 4) is a stand-alone document for the worker to use as daily documentation for personal attendant services. § Following the worker’s completion of the PAL, the RN must review the PAL, sign, date and comment for any changes on page 4. § § § 17

Personal Attendant Log (PAL) (Cont. ) The Personal Attendant Log (PAL): § Ensures the worker knows what to do, how to do it and when to do it. § Protects the health and welfare of the ADW recipient. § Reduces risk for the recipient, worker and the agency. § Ensures the recipient knows what to expect. § Outlines worker duties to enable the RN to supervise the personal attendant services and the worker. § Reduces potential for misuse or abuse of service. 18

The Service Plan The New Service Plan-December 1, 2015 Date I. Initial Six Month Annual Dual Services DEMOGRAPHICS: Last Name: Medicaid ID (and PPL ID): Case Management Agency or Personal Options Resource Consultant(Name/Phone): Primary Personal Attendant Agency Name/Number: Legal Representative Name/Phone: Personal Options Budget: I. Change in Need/Service Level First Name: Service Level/Hours: Anchor Date: Plan Begin Date: Plan End Date: Secondary Personal Attendant Agency Name/Phone: Informal Support Name(s)/Phone: Take Me Home WV: GOALS AND PREFERENCES: What are my goals? (In own words, what I expect from the program): Describe your personal strengths. How can my program support my goals? List specific things you do or do not want your worker to do for you. 19

Service Plan-Section I and II Demographics: § Complete the demographics, date of the plan an “x” for type of plan (annual, etc. ), provider name/Personal Options, Personal Options Budget and an “x” for Take Me Home, WV. § Enter either service level or service hours maximum. § Reminder: Recipients will not receive ALL service hours as it is not possible within a month to do so. Goals and Preferences: § In the person’s own words, list “their goals, ” how the program can support their goals, their strengths and specific tasks they do or do not want the worker to do. 20

Service Plan Section II-Examples § Goals: “I want to be able to stay in my apartment”; “I need help with taking a bath and getting my meals. ” Do not list “help with ADL’s. ” § How can my program support my goals? “Need a worker in the mornings and evenings to help get me up and back to bed”; “I want a worker that knows how to get my wheel chair in and out of the house”; “my worker needs to be here on time because there is no one here with me after my son leaves for work. ” § Personal strengths: “I never give up”; “I am strong willed”; “People tell me I’m always positive”; “I am a quick learner. ” § Things you do/don’t want worker to do: “I want my worker to fix breakfast by 9: 00 a. m. because I’m a diabetic”; “I don’t want my worker to do my laundry”; “I don’t want my worker to take me to the grocery store. My daughter does that. ” 21

Risk Plan-Section III § Locate the risks from the person-centered assessment. Any risk that is marked yes and not marked as “no plan needed, ” must be listed on the service plan and have a risk plan to address the issue. § Describe the risk: “fall risk”; “smokes with oxygen on”; “wanders in the evening. ” § Describe how the risk will be addressed: “Contact PCP regarding need for a new walker”; “educated recipient about not smoking while oxygen is on or in the house”; “person will not be left alone in the evening (family will be there when worker leaves the home). ” 22
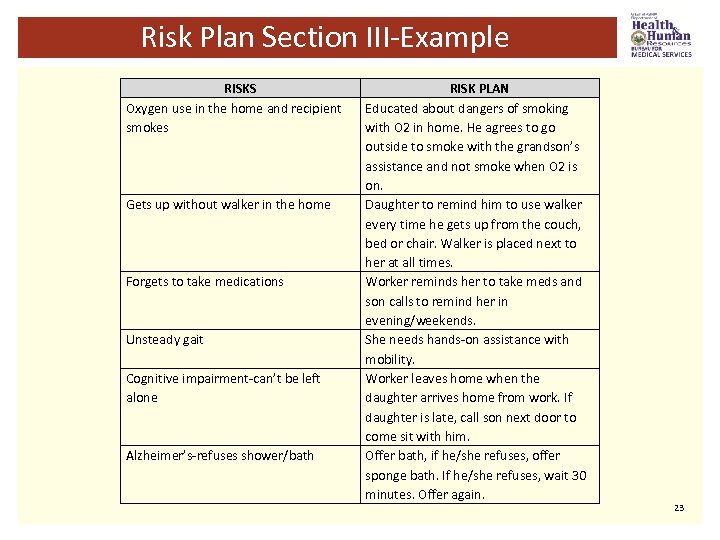
Risk Plan Section III-Example RISKS Oxygen use in the home and recipient smokes Gets up without walker in the home Forgets to take medications Unsteady gait Cognitive impairment-can’t be left alone Alzheimer’s-refuses shower/bath RISK PLAN Educated about dangers of smoking with O 2 in home. He agrees to go outside to smoke with the grandson’s assistance and not smoke when O 2 is on. Daughter to remind him to use walker every time he gets up from the couch, bed or chair. Walker is placed next to her at all times. Worker reminds her to take meds and son calls to remind her in evening/weekends. She needs hands-on assistance with mobility. Worker leaves home when the daughter arrives home from work. If daughter is late, call son next door to come sit with him. Offer bath, if he/she refuses, offer sponge bath. If he/she refuses, wait 30 minutes. Offer again. 23
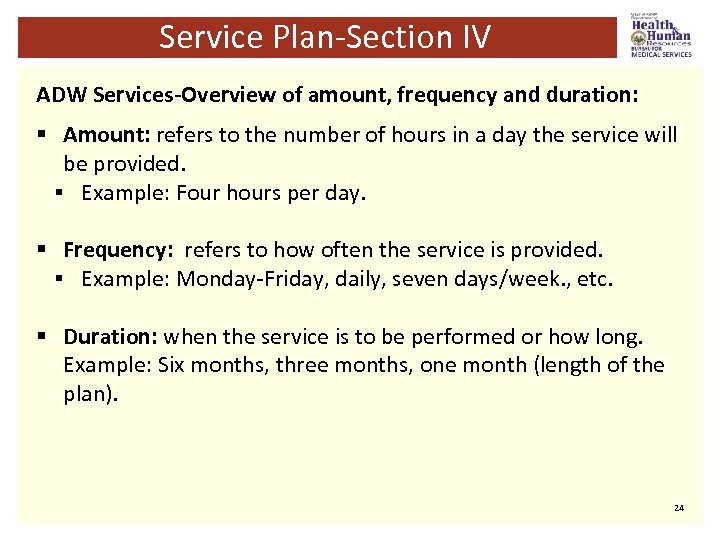
Service Plan-Section IV ADW Services-Overview of amount, frequency and duration: § Amount: refers to the number of hours in a day the service will be provided. § Example: Four hours per day. § Frequency: refers to how often the service is provided. § Example: Monday-Friday, daily, seven days/week. , etc. § Duration: when the service is to be performed or how long. Example: Six months, three months, one month (length of the plan). 24
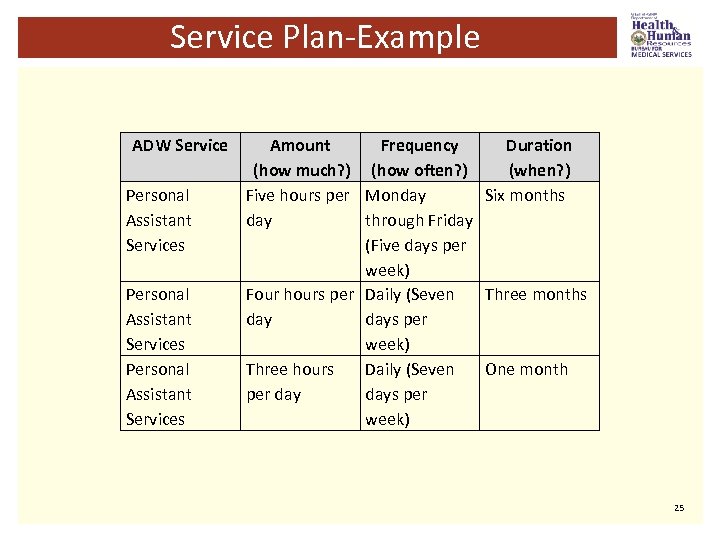
Service Plan-Example ADW Service Personal Assistant Services Amount Frequency Duration (how much? ) (how often? ) (when? ) Five hours per Monday Six months day through Friday (Five days per week) Four hours per Daily (Seven Three months days per week) Three hours Daily (Seven One month per days per week) 25
Other Services Needed Provider Describe Service Amount, Frequency and Duration Case Management Best case manager Minimum monthly ever or more frequent as needed for six- month plan period Skilled Nursing- Love my waiver § 1 x/month §Monthly Review of nurse for six-month POC plan period §Skilled Nursing § 1 x/Six Assessment month and annually Transportation. Love my waiver §Essential Errands nurse § 1 x/weekly for 6 §Community months Activity § 1 x/weekly for six months Home Health Great home health RN weekly visits for agency three-month plan period Home Health Great home health PT three times per agency week for four weeks 26

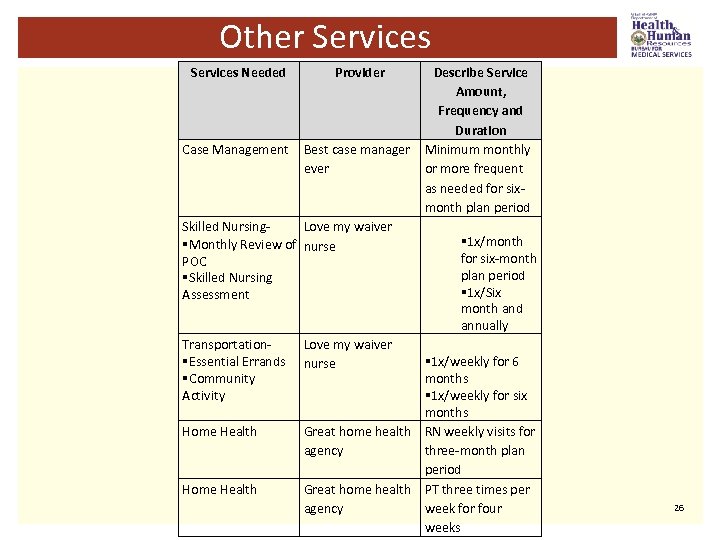
Unexpected Needs § Note: document unplanned and unexpected needs. This is to ensure the needs of the recipient are met. Clearly document on the RN contact form, case management form or the Personal Attendant Log (PAL). “What? I didn’t know about that. ” 27

Resource Plan-Section V § Identify from the person-centered assessment, the resources that the person needs in the left column. § Example: food stamps, food pantry, housing, etc. § On the right column, describe where you are referring the person. § Example: Charleston Housing for senior high rise application, Department of Health and Human Resources (DHHR) for food stamp application, meals for all food pantry, etc. 28
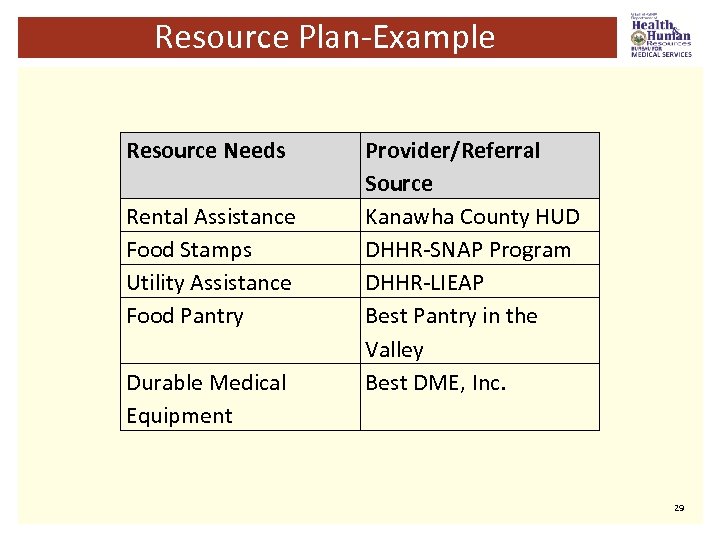
Resource Plan-Example Resource Needs Rental Assistance Food Stamps Utility Assistance Food Pantry Durable Medical Equipment Provider/Referral Source Kanawha County HUD DHHR-SNAP Program DHHR-LIEAP Best Pantry in the Valley Best DME, Inc. 29

Home and Community-Based Setting (HCBS)-Section VI § This is a new CMS requirement for ADW recipients regarding their residence (HCBS setting). It cannot be an “institution or institutionallike” (such as a personal care home, etc. ). § There is a specific criterion that is necessary for the home setting and for the person to receive the service in that setting. This is a brief description of what an HCBS setting looks like, so the Case Manager is knowledgeable about the setting requirements and the person can begin to understand it. § Transition plan for HCBS setting? This question is mandatory because the HCBS setting is a CMS requirement. § If someone answers no, discuss a plan for transition to an HCBS setting. Example: person is in a personal care home or a nursing home. Document the date of the discussion in a case note, plans for transition and date of transition. 30

Home and Community-Based Setting (HCBS)-Section VI (Cont. ) The new service plan includes a question about where the recipient lives. Waiver services must not be provided in an “institution or an institution-like” setting. Choice is included. Where I live: I choose to live in a home that is in the community (not an institution) where I have a choice of who lives with me, what I do in my home, who I talk with on the phone, visitors coming into my home, my meals, how I manage my resources and who I interact with outside my home. Yes or No 31

Initial Service Planning Meeting The initial service planning meeting now includes the RN. The RN will complete the Personal Attendant Log (PAL). The RN will bring his/her expertise to the planning team. The nurse is back. 32

Personal Attendant Log-Section VII Personal Attendant Log (PAL) (pages 3 and 4 of the service plan): § The PAL replaces the old “Plan of Care” and is now a part of the service plan. This easily allows for more updates. § The nurse is now a required attendee at the initial service planning meeting as well as the annual and six month planning meeting. § The service plan update form has been deleted; however, there is a new process for service plan updates. 33

RN-Development of the PAL § The RN assists the recipient in completion of the PAL with the Case Manager’s input. § Not only is the PAL a plan for the direct care services, but it is a stand-alone document for the worker to record the daily services/activities. § Planned Hours/Days: The RN or Resource Consultant documents the planned hours/day and days/week. § Describe Activities: Indicate how the activity is to be performed (independent, supervised, partial or total). Give directions to the worker and describe it. § RN In/Out: At the top, RN documents time in/out as it is a requirement for billing skilled nursing services. 34

RN-Development of the PAL (Cont. ) § Service Level/Hours: Either service level or number of hours is acceptable here. Please explain to the recipient of services that this is the maximum amount and it is not expected that the service plan or PAL will maximize these hours. It is based upon the person’s needs, not the number of hours that can be maximized in a month’s time. § Essential Errands: This is a plan, and errands must be discussed at the planning meeting and addressed in detail. This area must include the purpose of the errand, the destination, frequency and the day of the week. § Community Activities: This is a plan, and community activities must be discussed at the time of the planning meeting and addressed in detail. This area must include the purpose of the errand, the destination, frequency and the day of the week. § Other: This section is to describe other areas that are not listed on the PAL. § Example: “Remind recipient to use hearing aid daily. ” § Special Instructions for transportation example: “Assist person in/out of the car. ” 35

RN-Review of the PAL § § § Following the worker’s completion of the daily documentation on the PAL, the RN will review and approve the PAL. The RN will monitor the service, verify services, dates and signatures were provided, ensure accuracy of the service and ensure form is correctly completed. The RN must sign the back of the PAL and date it to verify that the RN review was conducted. Comment area is for documenting any issues with the service/recipient or minor changes in the PAL. § Example: Worker came in one hour later on Tuesday because he was just discharged from the hospital. Minor changes are acceptable (if it is a continuous change, the RN must do a PAL update). The worker must also document in the comments section at the bottom when there is a change in day/time or activity for the day. Please note that this section will also be used for a PAL update. Wellness scale: RN will monitor the wellness scale. The scale can be an indicator for the nurse to determine how the person is doing. Changes up or down in the scale may indicate a change in the person’s needs, medical condition or environment. 36

RN-PAL Update § The RN may update the PAL when there is a need to change the hours, days of the week or the activities on the PAL. § Changes to the PAL must be documented on a new form. The RN will update on the front and back of the form. § The RN must speak with the recipient either by phone or in person. Document on page four how the changes were verified with the ADW person, initial it and date it. § A copy of the PAL update must be forwarded to the Case Manager. § The Case Manager or Resource Consultant must initial and date the new PAL update under “PAL update” on page three and attach it to the service plan. § The new PAL update becomes a part of the service plan. The Case Manager will document a new date on page one under “change in need/service level” indicating that there has been a change to the service plan. The new PAL update is attached to the service plan. 37

Worker Daily Documentation-PAL § § § The PAL, page three and four, will be the worker’s daily documentation and will be a stand-alone document. Once the PAL is completed, a copy of the page may be provided to the worker to use as his/her documentation for the service provided. By having a copy of page three and four as the actual worksheet, it will reduce any errors created when the information is transferred over to a new document. The worker must circle the day service was provided; enter time in/out, total hours and check the box if they provided service to one person during the service time (one staff to one ADW person at a time). Initial each box on the correct day for each activity that was performed on that day. On page four, the worker will document start and stop time for travel, total number of miles driven and how much time was spent driving. Enter the destination (where they went) and the purpose for the travel; whether it was an essential errand or community activity; and if the person was with them during the travel and activity. The ADW person is to initial each entry to verify it was completed. The documentation must include where the worker went, including the name of the store and town (some towns have more than one grocery store) and the purpose of the travel (traveled to Nitro Walmart for grocery shopping). 38

Worker Daily Documentation-PAL (Cont. ) § Wellness scale: The worker is to ask the recipient the following question each day and write the date and wellness scale number at the bottom of page four. This change was requested by Medicaid Fraud. The worker must complete the wellness scale. § Wellness scale § “Using a scale from one to 10 (one is poor and 10 is great) how are you today? ” § At the end of the PAL time frame, the worker must sign, date and print their name on page four of the PAL. § Comments section: § The worker will use this section to document occasional variations in the activities. § Example: arrived at 7: 00 a. m. for meals as informal support was in the hospital today. § In the comments section, the worker may document any additional information on the wellness status. 39

ADW Recipient’s Documentation-PAL § The ADW recipient must initial each day that services were provided. By initialing, the person is verifying that the worker came during the times documented, provided the activities documented and provided the transportation documented. § The recipient (or legal representative) must sign on page four verifying services documented on the PAL were provided. § Please ensure that the recipient knows and understands the fraud statement above the signature. 40

Emergency Back-Up Plan (Case Manager) § Informal support: Describe the activities that the informal support will be performing for the person and the specific times/days, and who provides it. § This area is specific to health and safety and ensures that the person has someone to provide those necessary supports when no formal support is available. § Example of activities: Daughter does bathing on the weekends; niece provides evening meals; all supports provided by grandson when the worker is not in the home, etc. 41

Signatures and Disagreement Service Plan Signatures and Plan Disagreement: § Required signatures/dates: Recipient/legal representative; Case Manager (CM) and RN for Traditional; Resource Consultant for Personal Options; Case Manager or RN if recipient on the Personal Options Program chooses Case Management or Skilled Nursing Services; and anyone else the person requests to attend the planning meeting. § New CMS requirement, plan disagreement: a person may disagree with the plan. § They cannot disagree with a policy (see transportation services example on the service plan). § The Case Manager or the Resource Consultant documents the reason for the disagreement and assists the person in facilitating discussion in the meeting to find solutions. Once a solution is found, the CM documents the solution on the Service Plan. 42

Service Plan Disagreement § If the person does not agree, the person may file a grievance. The CM must educate the person about the grievance process when this occurs. § Example of a disagreement: “I want services on the weekend and the nurse says they can’t do it. ” § Example that is not a disagreement: “I want to go 400 miles a month on my transportation” is not a disagreement. Policy stipulates a limit of 300 miles per month, and the service plan does not override ADW policy. § Examples of potential solutions: Personal Attendant (PA) agency will use a secondary PA agency to provide weekend hours; person wants to transfer to a new agency. CM will assist. 43

Personal Options § Service Plan: Personal Options recipients must use the same service plan as recipients in traditional services. § Assessment - Without Case Management: Personal Options recipients who do not have Case Management will have the Personal Options Assessment. It is specifically designed for the self-directed recipient in the Personal Options Program. § Assessment-With Case Management: Personal Options recipients who have Case Management will have the personcentered assessment completed. 44

Personal Options Assessment Complete the demographics and directions to the home. Goals and resources: § This section is the beginning of person-centered planning. The Case Manager will begin to discuss the person’s preferences, their goals for the program and the types of supports that are available or needed. § It is best to ask open-ended questions and provide examples. Describe this area in the person’s own words. § Example of goals: “I want to stay in my own home as long as I can”; “I need someone to help me with meals and taking a bath”; “I never want to go back to the nursing home. ” Do not enter “help with ADLs” as this is not typical language that a person would say. § Finance: The reason for asking this question is to determine the level of financial risk for this person. If a person requires assistance, this can be a risk for the person. The Case Manager may want to suggest preventive measures. 45

Personal Options Assessment (Cont. ) Healthcare: § § § Coordination of healthcare: This is a new requirement from CMS and will be included in the provider monitoring. If you mark “yes” for “do you think you need referrals, ” you must list this on the resources/needs section of the service plan. § Example: Person needs a new primary care physician. Legal representative: Indicate with an “x” beside the appropriate response and enter the name and contact information for the legal representative. Enter the date that a copy of the document is provided to the Resource Consultant. If the Resource Consultant requested a copy and did not receive it, indicate this response. Check the equipment in place currently and document the equipment that is needed. § Example: Needs new wheel chair, etc. Enter the name and contact information of the person’s primary care physician, physical therapist or other medical professionals. What medical conditions affect my areas of need or assistance? § Place an “x” beside areas that apply to the person. 46

Personal Options § What are the services and resources that you need? This is a short list of potential areas of need for the person. Risks: Discuss each risk area with the person. For each risk identified, document a plan to address the risk. § Example: risk identified is fall risk. Risk plan: she will remove scatter rugs to prevent falling. Identified service and resource needs: Mark an “x” for those that apply(name/number). Personal attendant services: § For each area, document the level of assistance needed (Independent, Supervised, Partial, Total). § Describe what the employee will need to do to assist the person with this activity. Examples: “Hand items to person’s right hand in shower. ” “Assist with fork and knife when eating”; “Assist with buttons and zippers shirts and pants. ” § In the essential errands and community activities section, describe the activity, the destination and when the employee will take the person. Example: “Kroger's in Charleston for grocery 1 x/week on Fridays”; “South Charleston Rite Aid pharmacy pick up 1 x/month on Mondays’; “hair dresser on Monday's 1 x/week, ” etc. 47

Personal Attendant Updates (PAL): Changes in days, hours or activities. § Step One: RN makes changes to the PAL days, hours or activities. RN documents on page four date of change and initials. Verifies recipient approval was by phone or in person. RN sends PAL update to CM. § Step Two: CM initials/dates for receipt of the new PAL with changes in days, hours or activities. CM attaches new PAL to current service plan. PAL becomes a part of the service plan. 48

Service Plan Updates: Risk plan, services or resource plan updates. § Step 1: CM enters the date of the service plan change under “change in need/service level. ” There is room for several dates in changes. § Step 2: CM enters new risk, new service or new resource needed by the recipient. CM initials and dates each one added. There are three ways to make changes: risks, service and resources. § Step 3: Once the CM has made the changes on the service plan update, the new service plan update is to be sent to the RN at the Personal Attendant Agency to be attached to the current service plan (including the PAL) in the recipient’s agency chart. 49

Case Protocol Problem Solving: No staff in the home Suggestions for the following areas: § Remote location § No shows/call offs § Mental conditions/substance use § Program noncompliance § Unsafe environment 50

Unsafe Environment Procedural Guidelines First step: Action by the agency 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Refer to Adult Protective Services. Ensure the person’s health and safety. Submit an incident in the Incident Management System (IMS). Document everything, and ask staff to document or provide statements. Refer to law enforcement for illegal issues. Develop and implement a behavior contract. Ensure the legal representative and primary care physician are aware of the issues. Second step: Formal Request for Technical Assistance • Ensure that steps one through six are completed prior to contacting Bureau of Senior Services (Bo. SS) for technical assistance. 1. Request technical assistance by sending an email to seniorservicesmedicaid@wv. gov. 51

Program Noncompliance Procedural Guidelines First step: Action by the agency 1. Determine a consistent history of noncompliance with policy, plans or failure to maintain a safe environment for staff going into the home. 2. Evidence must exist on an ongoing basis so document everything (RN notes, CM notes, or other staff documentation). 3. Provide to the ADW recipient their rights and responsibilities on the program. Educate on program policy and plans. Provide Medicaid Fraud and Recipient Fraud handouts, if applicable. Verify with signatures and dates. Ensure both CM and RN are aware of and addressing issues. 4. Develop and implement a behavior contract. 5. Ensure the legal representative and primary care physician are aware of the issues. 6. Refer to Adult Protective Services and law enforcement and submit an incident in Incident Management System (IMS), if applicable. Ensure everyone’s health and safety. 7. Continue to provide/offer staff (if safe). Document refusal to allow staff in home. Second step: Formal Request for Technical Assistance 1. Ensure that steps one through seven are completed prior to contacting Bo. SS for technical assistance. 2. Request technical assistance by sending an email to seniorservicesmedicaid@wv. gov. 52

What is an Unsafe Environment? “An unsafe environment is the threat of harm or harm that has already occurred. ” § Threat of harm to the worker. § Illegal activity or drug activity in the home. § Physical harm to the worker. § Property damage threatening harm to the worker. § Unsafe use or possession of guns in the home. § Illegal substances or stolen goods in the home. § Any other imminent risk to the worker. 53

Program Noncompliance “Program noncompliance is consistently not following program policies or plans. ” § Not verifying services by signing/dating/initialing documentation. Refusal to turn in paperwork or allow worker to implement the Service Plan (or PAL). Refusal to follow service plan Refusal to allow staff in the home for visits or services. Demanding workers to leave, yelling, cussing, slamming doors, phone hang-ups, etc. Refusal to open door or respond to calls from staff. § Refusal to allow assessments or plans to be conducted per policy. § Not maintaining a safe environment for the worker. Other areas of policy or plan noncompliance. § § § 54
Inability to Maintain Safely in Home Inability to maintain of ADW services to maintain person safely in the home: A person’s medical condition has degenerated to the point that it is no longer feasible to maintain the person safely in his/her home using ADW services. Even the addition of personal care services, if applicable, are not sufficient to meet the needs of the person. Examples of inability of ADW services to maintain person safely in home: Staff are unable to complete tasks on the service plan due to the person’s health and/or physical condition. Person’s condition is such that the person cannot safely be in the home untended for any period of time and there is no one available to provide the care after agency staff leave. Repeated admissions to the hospital due to insufficient/unavailable care. 55

Inability to Maintain Safely in Home First step: action by the agency Ensure everyone’s health and safety. Refer to Adult Protective Services. Submit an incident in the WV Incident Management System (IMS). Document everything and ask workers, medical staff, etc. to document or provide statements. • Develop and implement a behavior contract that either includes an agreement from the person to go to a nursing facility or to live with a loved one who can adequately care for their needs permanently or until the issues can be resolved. • Ensure the legal representative and primary care physician are aware of the issues in the home. Second step: Formal request for technical assistance • • • Ensure that steps 1 -6 are completed prior to contacting boss for technical assistance unless it is so severe that it is felt that a behavior contract would not suffice or the person will not agree to sufficient behavior contract. Request technical assistance by sending an email to seniorservicesmedicaid@wv. Gov 56

Request to Close: Inability to Maintain Third step: request to close case due to inability of ADW services to maintain person safely in his/her home • • • Submit a letter describing the overall situation that led to person no longer being safe in home with ADW services on agency letterhead with signature. Complete request to close case and fax to boss. Attach evidence of the inability of the person to be maintained safely in the home Include incident reports from the WV Incident Management System. Evidence of referral to Adult Protective Services. Include statements from workers. Send copies of RN, Case Manager, Resource Consultant or staff notes or other documentation regarding the inability of the person to safely stay in his/her home with ADW services. Attach any other evidence that supports the inability of the person to safely stay in his/her home with ADW services. Do not close the case unless you have heard from boss. If you have not heard from Bo. SS within three (3) business days of contacting them last about the case, call the staff person at boss. Bo. SS will never ask a provider to place a worker in harm’s way. Boss will not make a decision about an agency’s employee. Boss will educate the agency about risk. 57

Request to Close-Unsafe Third step: Request to close case for unsafe environment. 1. Submit a letter describing the overall unsafe environment on agency letterhead with signature. Complete request to close case and fax to Bo. SS. 2. Attach evidence of the unsafe environment (remember, case could go to hearing): a. Incident reports. b. Evidence of referral to APS. c. Police reports. d. Statements from workers. e. Copies of RN and/or CM notes, Resource Consultant notes and daily documentation regarding the unsafe environment. f. Any other evidence that supports the existence of the unsafe environment. 3. Do not close the case unless you have heard from Bo. SS. 4. Bo. SS will never ask a provider to place a worker in harm’s way. 5. Bo. SS will not make a decision about an agency’s employee. Bo. SS will educate the agency about risk. 58

Request to Close-Noncompliance Third step: Request to close case for ADW recipient for noncompliance. 1. Submit a summary letter on agency letterhead with signature, describing the consistent history of noncompliance by the ADW person. Complete in full the Request to Discontinue Services (marked noncompliance) and fax with evidence to Bo. SS. 2. Attach evidence of the noncompliance (remember, the case could go to a hearing): a. Incident reports, if applicable. b. Evidence of referral to APS and police reports, if applicable. c. Statements or other documentation from agency staff. d. Copies of RN and/or CM notes, Resource Consultant notes or daily documentation verifying the noncompliance. e. Any other evidence that supports the existence of consistent noncompliance with the program. 3. Do not close the case unless you have heard from Bo. SS. 4. Bo. SS will not make a decision about an agency’s employees. Bo. SS will educate the agency about risk. 59

Post Test Reminder: On the next two slides, you will take the Person- Centered Planning post test. Person-Centered Planning Certificate: Please make sure that you have an agency representative or employer to verify the post test and sign your Training Certificate on the last slide. Keep a copy of your Person-Centered Planning Training Certificate in your personnel file. 60

Person-Centered Planning Post Test 1. My role as a Case Manager is to facilitate planning, encourage discussion of goals, strengths, preferences, address services, risks and resources. True or False? 2. In the risk section of the person-centered assessment, any risk that affects health and welfare must be addressed with risk plan on the service plan. True or False? 3. The new HCBS setting section is a new area required by CMS which outlines where the person can receive waiver services. True or False? 4. The recipient’s personal strengths ands goal are no longer required on the service plan. True or False? 5. Service name, amount, frequency and duration applies to all ADW services. True or False? 61

Person-Centered Planning Post Test (Cont. ) 6. A transition plan is required for anyone not living in an HCBS setting. True or False? 7. On a PAL update, the RN can change the hours, day of the week or activity, verify with a recipient by phone or in person and send the update to the Case Manager. True or False? 8. The new Wellness Scale is completed by the RN every six months. True or False? 9. The worker must document in/out times for the service and whether the service was a 1: 1 ratio (one worker to one recipient). True or False? 10. The Personal Options recipient service plan describes what the employee will do to assist the person. True or False? 62

Person-Centered Planning Certificate AGED AND DISABLED WAIVER TRAINING CERTIFICATE Name of the Training: Person-Centered Planning Date of Training Webinar: Name of the Employee (Worker): Congratulations. You have successfully completed the Aged and Disabled Waiver Person- Centered Planning training webinar and passed the post test. Training/Post Test Verification Signature(Agency/Employer): Date: Worker/Employee Signature: Date: 63

Contact Information ADW TRAINING CONTACT INFORMATION: BUREAU FOR MEDICAL SERVICES 350 CAPITOL STREET, ROOM 251 CHARLESTON, WV 25301 PHONE: 304 -558 -1700 EMAIL: SUSAN. A. GIVEN@WV. GOV WV BUREAU OF SENIOR SERVICES PHONE: 304 -558 -3317 FAX: 304 -558 -6647 EMAIL: ARLENE. M. HUDSON@WV. GOV 64
fd84a479f319d68603d3df44b942336a.ppt