3a1d83ea81557f4dd496eb2c03ea1c8a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Age of Imperialism Africa Middle East India China Click a location above to read information about Imperialism in that region. Fill out your Age of Imperialism note sheet as you follow through.
Age of Imperialism Africa Middle East India China Click a location above to read information about Imperialism in that region. Fill out your Age of Imperialism note sheet as you follow through.
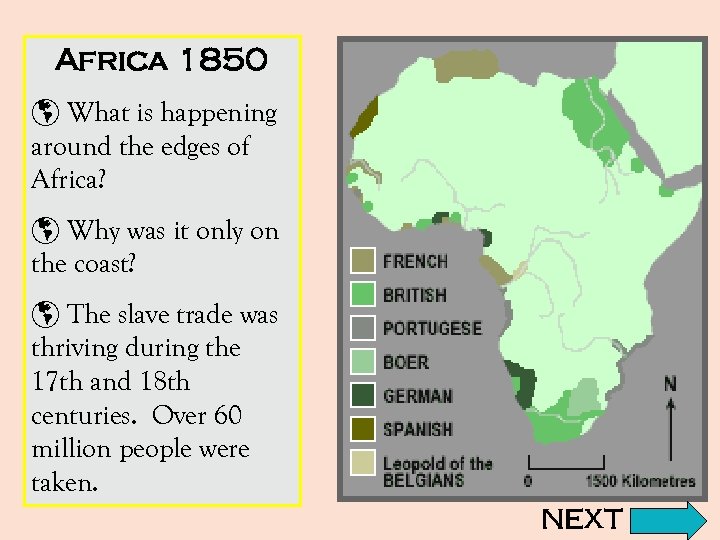 Africa 1850 þ What is happening around the edges of Africa? þ Why was it only on the coast? þ The slave trade was thriving during the 17 th and 18 th centuries. Over 60 million people were taken. NEXT
Africa 1850 þ What is happening around the edges of Africa? þ Why was it only on the coast? þ The slave trade was thriving during the 17 th and 18 th centuries. Over 60 million people were taken. NEXT
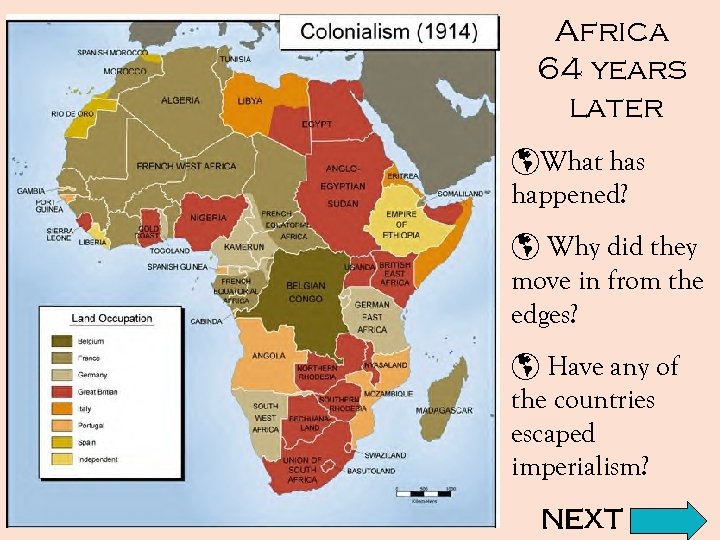 Africa 64 years later þWhat has happened? þ Why did they move in from the edges? þ Have any of the countries escaped imperialism? NEXT
Africa 64 years later þWhat has happened? þ Why did they move in from the edges? þ Have any of the countries escaped imperialism? NEXT
 Scramble for Africa In 1652 the Dutch established a port in southern Africa called Cape Town. Over the next 150 years the Dutch (also know as Afrikaners) acquired more land that became known as the Cape colony. The British knowing the economic value of the port seized power in the early 1800’s. After several conflicts and wars between the two, the British were victorious and established the Union of South Africa. As one black African writer of the time said, “The Union is to be a Union of the two races, namely the British and the Afrikaners the African is to be excluded. ” NEXT
Scramble for Africa In 1652 the Dutch established a port in southern Africa called Cape Town. Over the next 150 years the Dutch (also know as Afrikaners) acquired more land that became known as the Cape colony. The British knowing the economic value of the port seized power in the early 1800’s. After several conflicts and wars between the two, the British were victorious and established the Union of South Africa. As one black African writer of the time said, “The Union is to be a Union of the two races, namely the British and the Afrikaners the African is to be excluded. ” NEXT
 NEXT
NEXT
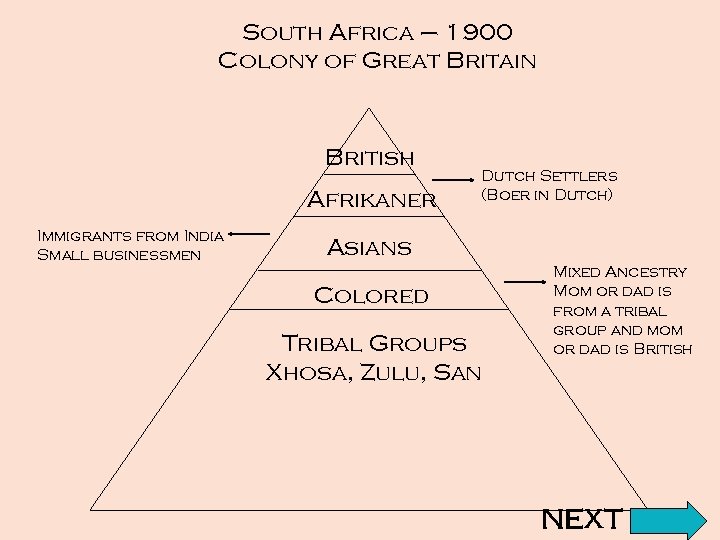 South Africa – 1900 Colony of Great Britain British Afrikaner Immigrants from India Small businessmen Dutch Settlers (Boer in Dutch) Asians Colored Tribal Groups Xhosa, Zulu, San Mixed Ancestry Mom or dad is from a tribal group and mom or dad is British NEXT
South Africa – 1900 Colony of Great Britain British Afrikaner Immigrants from India Small businessmen Dutch Settlers (Boer in Dutch) Asians Colored Tribal Groups Xhosa, Zulu, San Mixed Ancestry Mom or dad is from a tribal group and mom or dad is British NEXT
 Imperialism in Africa • Britain, France, Germany, Portugal, Belgium, Spain & Italy established colonies throughout Africa • Transatlantic Slave Trade – Forced Africans to leave their societies and shipped them to other countries • Boer War – Discovery of gold in the Transvaal, a settlement of Dutch Boers, led to conflict between Britain and the Boers – Britain prevailed and by 1919 established the Union of South Africa • Berlin Conference (1884 – 1885) – 14 Competing nations met to draw boundaries dividing Africa among themselves (Africans were not invited). There was no regard for African Ethnic or Linguistic groups or boundary lines Home
Imperialism in Africa • Britain, France, Germany, Portugal, Belgium, Spain & Italy established colonies throughout Africa • Transatlantic Slave Trade – Forced Africans to leave their societies and shipped them to other countries • Boer War – Discovery of gold in the Transvaal, a settlement of Dutch Boers, led to conflict between Britain and the Boers – Britain prevailed and by 1919 established the Union of South Africa • Berlin Conference (1884 – 1885) – 14 Competing nations met to draw boundaries dividing Africa among themselves (Africans were not invited). There was no regard for African Ethnic or Linguistic groups or boundary lines Home
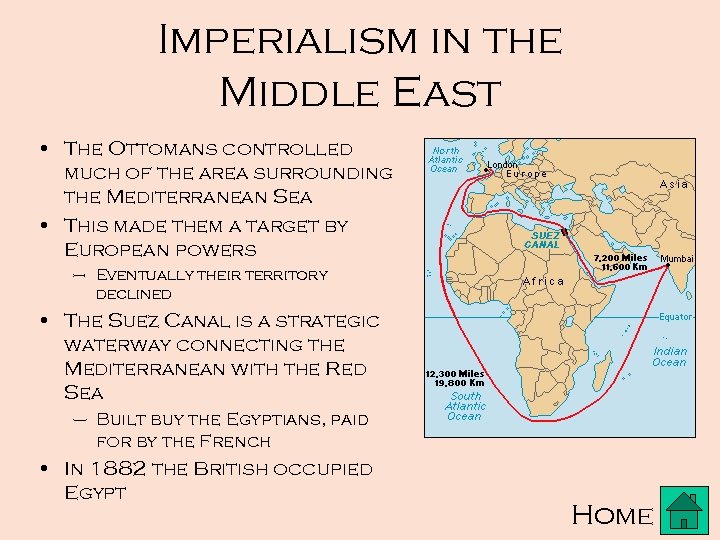 Imperialism in the Middle East • The Ottomans controlled much of the area surrounding the Mediterranean Sea • This made them a target by European powers – Eventually their territory declined • The Suez Canal is a strategic waterway connecting the Mediterranean with the Red Sea – Built buy the Egyptians, paid for by the French • In 1882 the British occupied Egypt Home
Imperialism in the Middle East • The Ottomans controlled much of the area surrounding the Mediterranean Sea • This made them a target by European powers – Eventually their territory declined • The Suez Canal is a strategic waterway connecting the Mediterranean with the Red Sea – Built buy the Egyptians, paid for by the French • In 1882 the British occupied Egypt Home
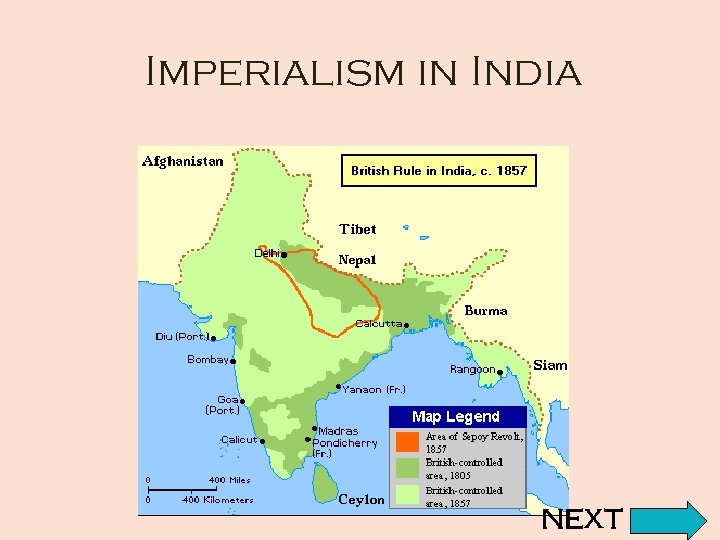 Imperialism in India NEXT
Imperialism in India NEXT
 India’s Blended Culture • India had waves of invasion over the past 3, 000 years – Language differences – Caste System - 4 castes (class). There were also untouchables those who were considered impure & thus outside the social structure. – Religious differences NEXT
India’s Blended Culture • India had waves of invasion over the past 3, 000 years – Language differences – Caste System - 4 castes (class). There were also untouchables those who were considered impure & thus outside the social structure. – Religious differences NEXT
 NEXT Religions in India Hinduism (14% of world population) (6% of world population) Islam Buddhism Shi’as (Iran) Sunnis (4 out of every 5) (21% of the world population) Christianity Protestant Catholic Eastern Orthodox Sikhism (. 36% of world population) Judaism Orthodox Conservative Reform (. 2% of world population) Lutheran Baptist Presbyterian (33. 5% of world population) Not specifically a religion of India, but a major world religion for comparison purposes
NEXT Religions in India Hinduism (14% of world population) (6% of world population) Islam Buddhism Shi’as (Iran) Sunnis (4 out of every 5) (21% of the world population) Christianity Protestant Catholic Eastern Orthodox Sikhism (. 36% of world population) Judaism Orthodox Conservative Reform (. 2% of world population) Lutheran Baptist Presbyterian (33. 5% of world population) Not specifically a religion of India, but a major world religion for comparison purposes
 British Reach India • The British established the East India Company, by 1700 the trading company was thriving. • The British started to get involved in government and other business affaires. • To protect their interested, they created native Indian troops called the Sepoys. NEXT
British Reach India • The British established the East India Company, by 1700 the trading company was thriving. • The British started to get involved in government and other business affaires. • To protect their interested, they created native Indian troops called the Sepoys. NEXT
 British Reach India • 4 factors helped the British: – – British were technologically advanced Divisions within India The British were well organized British brought stability NEXT
British Reach India • 4 factors helped the British: – – British were technologically advanced Divisions within India The British were well organized British brought stability NEXT
 “Jewel in the Crown” • By the 19 th century, Britain considered India the most valuable of all of the colonies. • The British sent a Viceroy (governor) to run India in 1858. • British built railroads, improved health standards, installed telephones and water systems. NEXT
“Jewel in the Crown” • By the 19 th century, Britain considered India the most valuable of all of the colonies. • The British sent a Viceroy (governor) to run India in 1858. • British built railroads, improved health standards, installed telephones and water systems. NEXT
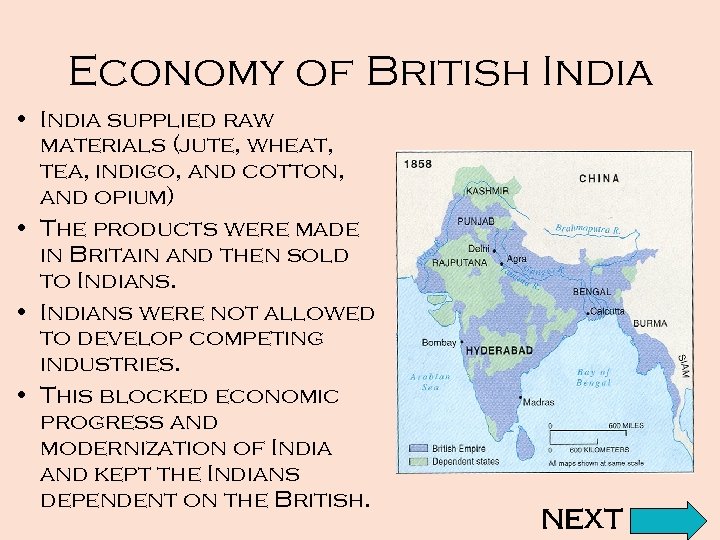 Economy of British India • India supplied raw materials (jute, wheat, tea, indigo, and cotton, and opium) • The products were made in Britain and then sold to Indians. • Indians were not allowed to develop competing industries. • This blocked economic progress and modernization of India and kept the Indians dependent on the British. NEXT
Economy of British India • India supplied raw materials (jute, wheat, tea, indigo, and cotton, and opium) • The products were made in Britain and then sold to Indians. • Indians were not allowed to develop competing industries. • This blocked economic progress and modernization of India and kept the Indians dependent on the British. NEXT
 Indian Nationalist Movement • Indians knew they were second class citizens in their own land. • Sepoy Mutiny (rebellion) – 1857, Indian soldiers rebelled when asked to use meat covered cartridges - Sepoys hung. – After the mutiny Britain took complete control of India. Home • Indians had difficulty uniting because of distrust between the Hindus and Muslims.
Indian Nationalist Movement • Indians knew they were second class citizens in their own land. • Sepoy Mutiny (rebellion) – 1857, Indian soldiers rebelled when asked to use meat covered cartridges - Sepoys hung. – After the mutiny Britain took complete control of India. Home • Indians had difficulty uniting because of distrust between the Hindus and Muslims.
 NEXT
NEXT
 Imperialism in China • For much of China’s existence they were able to stay isolated from the rest of the world because they were self sufficient • In small regions China exports tea and receives silver from GB in exchange = trade imbalance. • Opium, made from the poppy plant, is a habit forming pain killer. • England used this to trade for tea instead of silver – balancing trade. • By 1835, 12 M Chinese were addicted NEXT
Imperialism in China • For much of China’s existence they were able to stay isolated from the rest of the world because they were self sufficient • In small regions China exports tea and receives silver from GB in exchange = trade imbalance. • Opium, made from the poppy plant, is a habit forming pain killer. • England used this to trade for tea instead of silver – balancing trade. • By 1835, 12 M Chinese were addicted NEXT
 Opium War Breaks Out • China’s letter to Queen Victoria requesting them to stop importing opium was ignored. • Opium War – a conflict between Britain and China, lasting from 1839 to 1842, over Britain’s opium trade in China. • English naval and weapons technology defeats the Chinese. • Treaty of Nanjing signed in 1842 gives England Hong Kong for 99 years, returned to China in 1997 NEXT
Opium War Breaks Out • China’s letter to Queen Victoria requesting them to stop importing opium was ignored. • Opium War – a conflict between Britain and China, lasting from 1839 to 1842, over Britain’s opium trade in China. • English naval and weapons technology defeats the Chinese. • Treaty of Nanjing signed in 1842 gives England Hong Kong for 99 years, returned to China in 1997 NEXT
 The Taiping Rebellion • Hong Xiuquan, dreamed of a “Heavenly Kingdom of Great Peace” where there is no poverty • Taiping Rebellion – a mid 19 th century rebellion against the Qing Dynasty in China, led by Hong Xiuquan • By 1840’s, Hong led 1 million rebels, consisting of both men and women, captured Nanjing, (his new capital) and controlled Southeastern China • The Qing Dynasty retakes control by 1864 with British and French help • At least 20 million people starve afterwards NEXT
The Taiping Rebellion • Hong Xiuquan, dreamed of a “Heavenly Kingdom of Great Peace” where there is no poverty • Taiping Rebellion – a mid 19 th century rebellion against the Qing Dynasty in China, led by Hong Xiuquan • By 1840’s, Hong led 1 million rebels, consisting of both men and women, captured Nanjing, (his new capital) and controlled Southeastern China • The Qing Dynasty retakes control by 1864 with British and French help • At least 20 million people starve afterwards NEXT
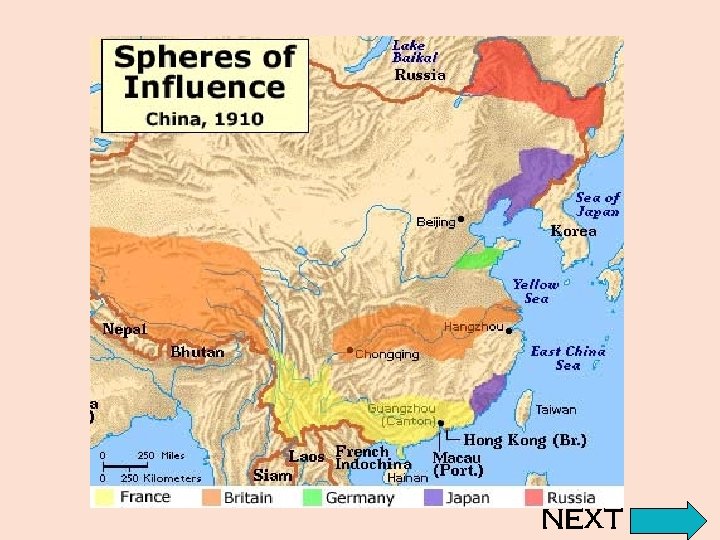
 Other Nations Step In • China’s perceived weakness caused other nations to attack China and later sign treaties giving those nations control over China • Sphere of Influence – a foreign region in which a nation has control over trade and other economic activities • Open Door Policy – a policy, proposed by the United States in 1899, under which all nations would have equal access to trade in China NEXT
Other Nations Step In • China’s perceived weakness caused other nations to attack China and later sign treaties giving those nations control over China • Sphere of Influence – a foreign region in which a nation has control over trade and other economic activities • Open Door Policy – a policy, proposed by the United States in 1899, under which all nations would have equal access to trade in China NEXT
 The Boxer Rebellion • Poor peasants and workers hated foreign influence and formed the “Society of Harmonious Fists” • Boxer Rebellion – a 1900 rebellion in China, aimed at ending foreign influence in the country • A multi-national force of British, German, French, Austrian, Italian, Russian and Japanese defeated the Boxers and saved the foreigners • However, Chinese nationalism continued to grow • In 1911 the New Republic of China led by Sun Yat-sen was formed as a result of a revolution that over threw the Qing Dynasty Home
The Boxer Rebellion • Poor peasants and workers hated foreign influence and formed the “Society of Harmonious Fists” • Boxer Rebellion – a 1900 rebellion in China, aimed at ending foreign influence in the country • A multi-national force of British, German, French, Austrian, Italian, Russian and Japanese defeated the Boxers and saved the foreigners • However, Chinese nationalism continued to grow • In 1911 the New Republic of China led by Sun Yat-sen was formed as a result of a revolution that over threw the Qing Dynasty Home


