ad0f90641177c380b6a1016564a01aa1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 74
 AGE OF EXPLORATION
AGE OF EXPLORATION
 EUROPE IN 1400’S n European population had increased n Demand for Eastern goods is high n Most valued items were spices n Major source of spices was the Moluccas, an island chain in present-day Indonesia n Europeans will call them the Spice Islands
EUROPE IN 1400’S n European population had increased n Demand for Eastern goods is high n Most valued items were spices n Major source of spices was the Moluccas, an island chain in present-day Indonesia n Europeans will call them the Spice Islands
 MOLUCCA’S SPICES n PEPPER n CLOVES n NUTMEG n CINNAMON
MOLUCCA’S SPICES n PEPPER n CLOVES n NUTMEG n CINNAMON
 MOTIVES FOR SEEKING SPICES n Explorers want to find new trade routes to spices-Spice trade dominated by Italian and Muslim traders (land routes) n Europeans wanted to cut out the “Middleman” in Spice trade n Europeans wanted to convert non. Christians to Christianity n Wanted to learn about new lands
MOTIVES FOR SEEKING SPICES n Explorers want to find new trade routes to spices-Spice trade dominated by Italian and Muslim traders (land routes) n Europeans wanted to cut out the “Middleman” in Spice trade n Europeans wanted to convert non. Christians to Christianity n Wanted to learn about new lands
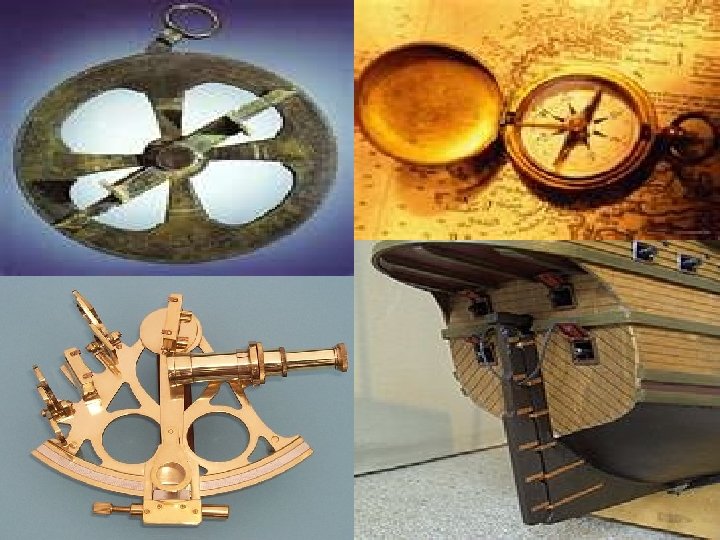
 TECHNOLOGY n n n CARTOGRAPHERS—created more accurate maps and sea charts ASTROLABE—find ship’s latitude at sea MAGNETIC COMPASS—used to determine direction SEXTANT—used to determine altitude of the sun or stars which could find latitude CARAVEL—Portuguese ship design that used square sails and lateen (triangular) sails STERNPOST RUDDER—steering the ship
TECHNOLOGY n n n CARTOGRAPHERS—created more accurate maps and sea charts ASTROLABE—find ship’s latitude at sea MAGNETIC COMPASS—used to determine direction SEXTANT—used to determine altitude of the sun or stars which could find latitude CARAVEL—Portuguese ship design that used square sails and lateen (triangular) sails STERNPOST RUDDER—steering the ship

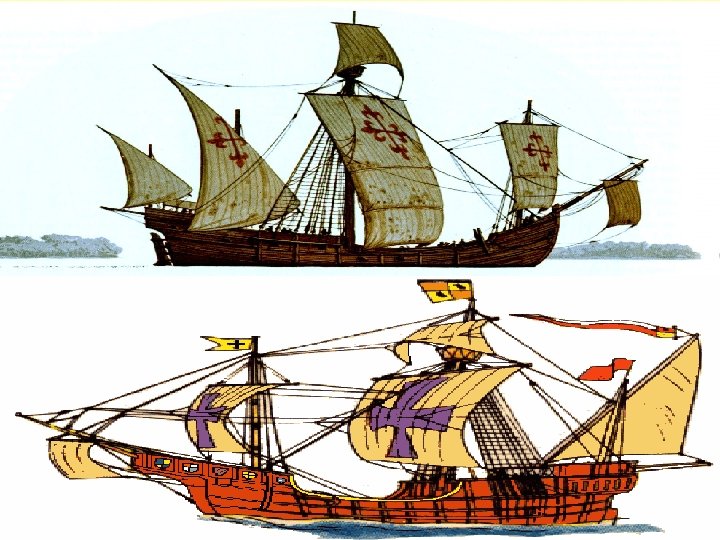
 PORTUGUESE: LEADER IN AGE OF EXPLORATION n Prince Henry (the Navigator) wanted to find source of African gold, share in the slave trade and start a crusade with the Muslims in Africa—rumor was that Prestor John had built Christian kingdom in Africa n Established school of navigation at Sagres n Portuguese will discover Madeira, Azores, Cape Verde and Canary Islands n First to bring slaves from Africa to Europe in 1441
PORTUGUESE: LEADER IN AGE OF EXPLORATION n Prince Henry (the Navigator) wanted to find source of African gold, share in the slave trade and start a crusade with the Muslims in Africa—rumor was that Prestor John had built Christian kingdom in Africa n Established school of navigation at Sagres n Portuguese will discover Madeira, Azores, Cape Verde and Canary Islands n First to bring slaves from Africa to Europe in 1441
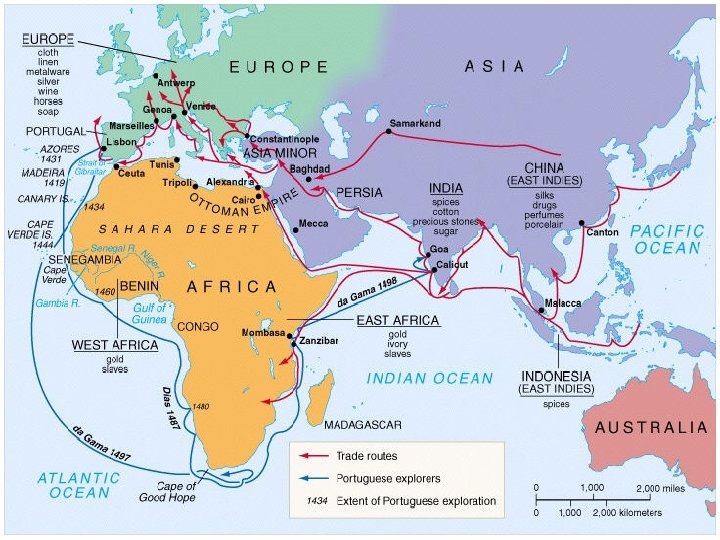
 Portuguese Exploration cont. n By 1471 Portuguese in control of West African trade in gold— (Gold Coast) n 1488 Bartholomeu Dias will be the first to round the tip of southern Africa (Cape of Storms) n Returned to Portugal to report finding route around Africa to King John II— renamed Cape of Storms the Cape of Good Hope
Portuguese Exploration cont. n By 1471 Portuguese in control of West African trade in gold— (Gold Coast) n 1488 Bartholomeu Dias will be the first to round the tip of southern Africa (Cape of Storms) n Returned to Portugal to report finding route around Africa to King John II— renamed Cape of Storms the Cape of Good Hope
 n In 1497 Vasco da Gama will be the first to sail around Africa then all the way to India n Voyage was very profitable—starts the Portuguese Empire in Asia
n In 1497 Vasco da Gama will be the first to sail around Africa then all the way to India n Voyage was very profitable—starts the Portuguese Empire in Asia
 SPANISH EXPLORATION n In 1492 Christopher Columbus (Italian) will be given 3 ships by Isabella and Ferdinand of Spain n Believed he could sail West to reach the East n Problems included underestimation of the circumference of the earth and no knowledge of North and South America
SPANISH EXPLORATION n In 1492 Christopher Columbus (Italian) will be given 3 ships by Isabella and Ferdinand of Spain n Believed he could sail West to reach the East n Problems included underestimation of the circumference of the earth and no knowledge of North and South America
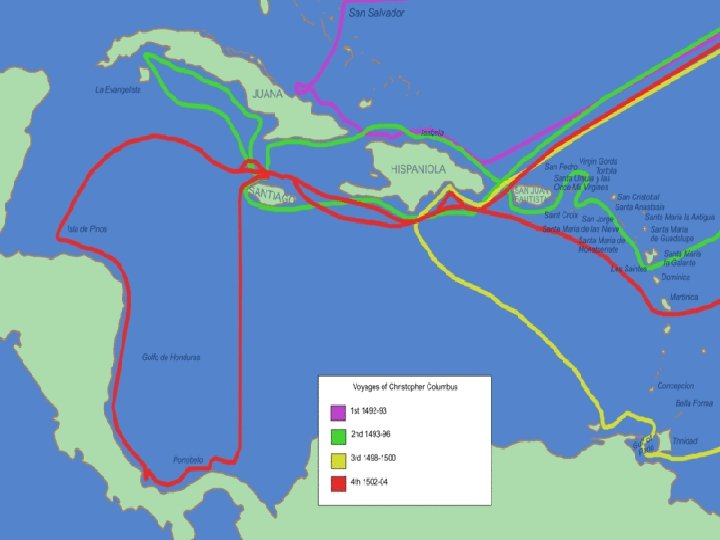
 COLUMBUS’ VOYAGE n Set sail on August 3, 1492 and will reach San Salvador (Bahamas) on October 12, 1492 n Believed he had reached the East Indies but had “discovered” the West Indies (New World) n Columbus called the natives Indians (why? )--first Europeans to be introduced to tobacco n Never found the vast amounts of gold or spices
COLUMBUS’ VOYAGE n Set sail on August 3, 1492 and will reach San Salvador (Bahamas) on October 12, 1492 n Believed he had reached the East Indies but had “discovered” the West Indies (New World) n Columbus called the natives Indians (why? )--first Europeans to be introduced to tobacco n Never found the vast amounts of gold or spices
 PORTUGAL AND SPAIN DISPUTE Spain and Portugal disputed each others claims n Pope Alexander VI settled dispute by drawing up Line of Demarcation n Treaty of Tordesillas moved line further West which gave Portugal Brazil n
PORTUGAL AND SPAIN DISPUTE Spain and Portugal disputed each others claims n Pope Alexander VI settled dispute by drawing up Line of Demarcation n Treaty of Tordesillas moved line further West which gave Portugal Brazil n
 OTHER EXPLORERS n n Pedro Cabral (Portugal) landed in Brazil and claimed area for Portugal Amerigo Vespucci (Italian) will say that Columbus had discovered a New World—German mapmakers will name new lands Americas Vasco de Balboa will cross the Isthmus of Panama—discover South Seas (Pacific Ocean) Juan Ponce de Leon will seek the mythical “Fountain of Youth”—explored Florida
OTHER EXPLORERS n n Pedro Cabral (Portugal) landed in Brazil and claimed area for Portugal Amerigo Vespucci (Italian) will say that Columbus had discovered a New World—German mapmakers will name new lands Americas Vasco de Balboa will cross the Isthmus of Panama—discover South Seas (Pacific Ocean) Juan Ponce de Leon will seek the mythical “Fountain of Youth”—explored Florida
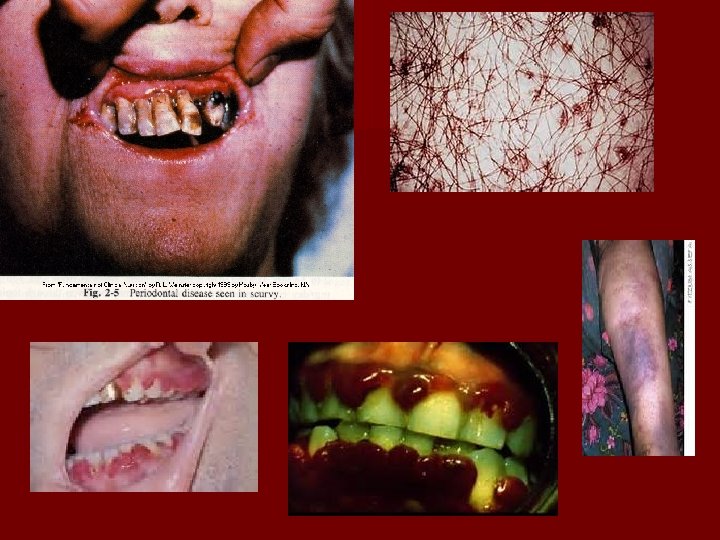
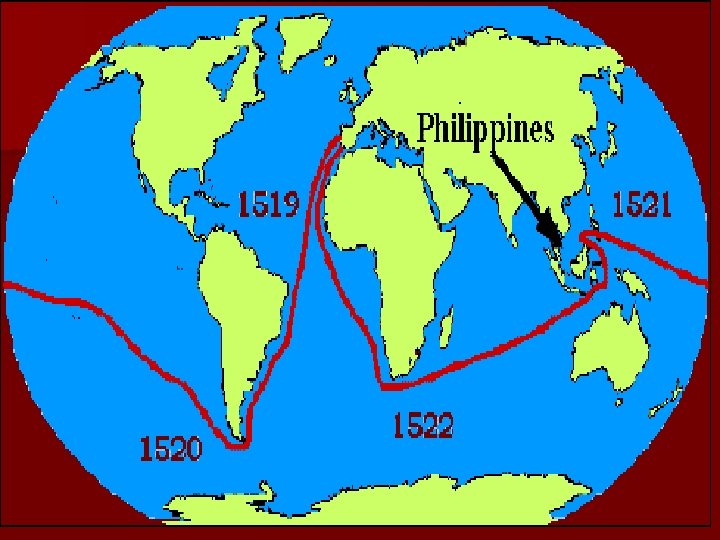
 VOYAGE OF MAGELLAN n Ferdinand Magellan will be the leader of the voyage that will be the first to circumnavigate the earth n Renamed the South Sea the Pacific Ocean n Many sailors suffered from scurvy, a disease caused by a lack of vitamin C n Encountered islands that he called the Philippines where he gets killed
VOYAGE OF MAGELLAN n Ferdinand Magellan will be the leader of the voyage that will be the first to circumnavigate the earth n Renamed the South Sea the Pacific Ocean n Many sailors suffered from scurvy, a disease caused by a lack of vitamin C n Encountered islands that he called the Philippines where he gets killed
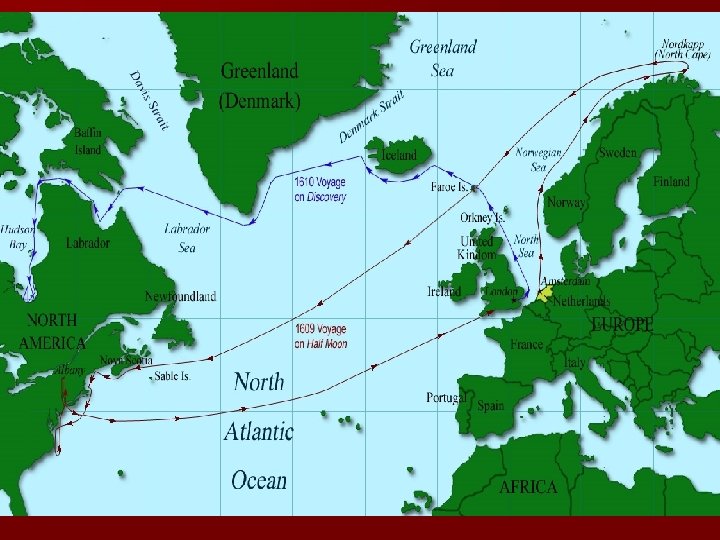
 SEARCH FOR NORTHWEST PASSAGE Other European nations (England, France, Dutch) will ignore Treaty of Tordesillas n Explorers searching for Northwest Passage an all water route through North America n John Cabot (Italian) sailing for the English explored the N. American coast from Delaware to Newfoundland (basis for England’s claim to N. America) n Henry Hudson (English) sailing for the Dutch explored river and bay that bears his name n
SEARCH FOR NORTHWEST PASSAGE Other European nations (England, France, Dutch) will ignore Treaty of Tordesillas n Explorers searching for Northwest Passage an all water route through North America n John Cabot (Italian) sailing for the English explored the N. American coast from Delaware to Newfoundland (basis for England’s claim to N. America) n Henry Hudson (English) sailing for the Dutch explored river and bay that bears his name n
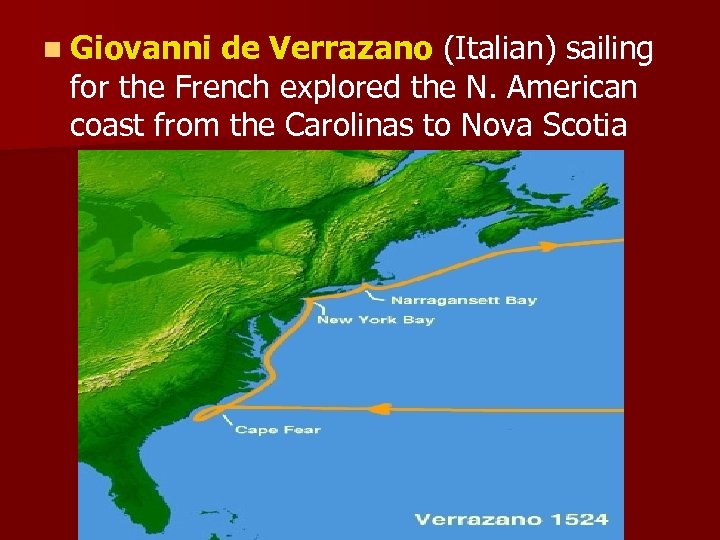 n Giovanni de Verrazano (Italian) sailing for the French explored the N. American coast from the Carolinas to Nova Scotia
n Giovanni de Verrazano (Italian) sailing for the French explored the N. American coast from the Carolinas to Nova Scotia
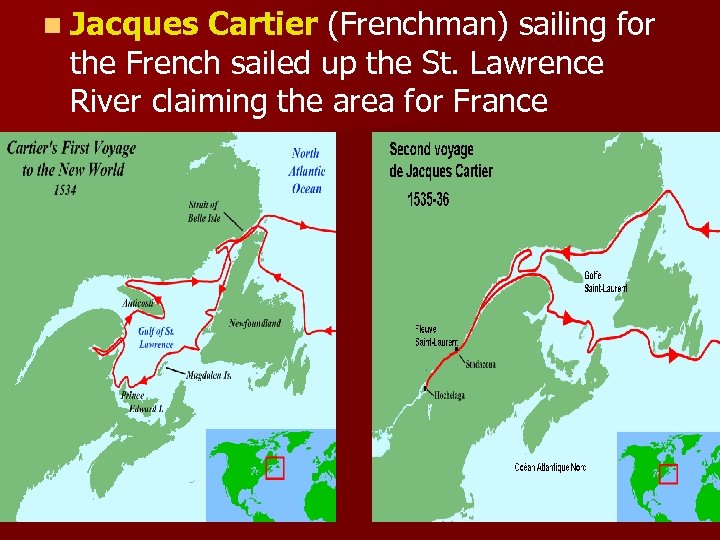 n Jacques Cartier (Frenchman) sailing for the French sailed up the St. Lawrence River claiming the area for France
n Jacques Cartier (Frenchman) sailing for the French sailed up the St. Lawrence River claiming the area for France
 PORTUGUESE EMPIRE n n n Six months after Da Gama’s return the Portuguese sent their fleet to India Portuguese interested in obtaining spices Arab (Muslim) traders tried to resist but Portuguese had mounted cannons on ships In 1509 Afonso de Albuquerque, Portugal’s most able naval commander, began to establish Portugal’s empire in Asia (small trading posts) Will use brutal and ruthless methods to gain control of area—wanted to control the strait of Malacca, gateway to the Spice Islands—control spice trade for over 100 years
PORTUGUESE EMPIRE n n n Six months after Da Gama’s return the Portuguese sent their fleet to India Portuguese interested in obtaining spices Arab (Muslim) traders tried to resist but Portuguese had mounted cannons on ships In 1509 Afonso de Albuquerque, Portugal’s most able naval commander, began to establish Portugal’s empire in Asia (small trading posts) Will use brutal and ruthless methods to gain control of area—wanted to control the strait of Malacca, gateway to the Spice Islands—control spice trade for over 100 years
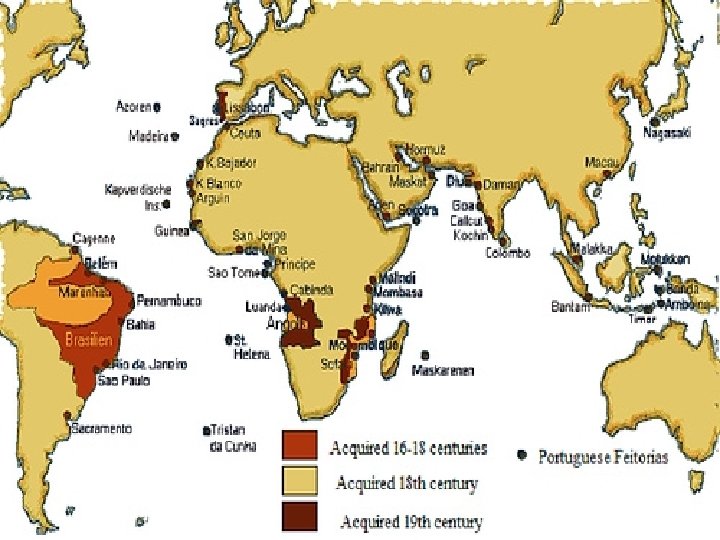
 Portuguese will face stiff competition for the spice trade—France, England the Dutch were all seeking footholds in Asia n Dutch will be the most successful—established Dutch East India Company n First multinational corporation—first to sell stocks—could wage wars, sign treaties, coin money, and imprison and execute n Dutch will attack Portuguese ships at every opportunity—eventually replaced the Portuguese in controlling spice trade n French and English will concentrate efforts in India—will become rivals in Asia n
Portuguese will face stiff competition for the spice trade—France, England the Dutch were all seeking footholds in Asia n Dutch will be the most successful—established Dutch East India Company n First multinational corporation—first to sell stocks—could wage wars, sign treaties, coin money, and imprison and execute n Dutch will attack Portuguese ships at every opportunity—eventually replaced the Portuguese in controlling spice trade n French and English will concentrate efforts in India—will become rivals in Asia n
 SPAINS CONQUEST OF THE AMERICAS n Spanish quickly settled the islands of the Caribbean (Hispaniola, Cuba and Puerto Rico)—Cuba became the jumping off point for exploration of the New World n Relationship with native population changed—began to exploit the natives n Spanish crown granted conquistadors, conquerors the right to establish outposts in the New World n Motto became “God, glory and gold”
SPAINS CONQUEST OF THE AMERICAS n Spanish quickly settled the islands of the Caribbean (Hispaniola, Cuba and Puerto Rico)—Cuba became the jumping off point for exploration of the New World n Relationship with native population changed—began to exploit the natives n Spanish crown granted conquistadors, conquerors the right to establish outposts in the New World n Motto became “God, glory and gold”
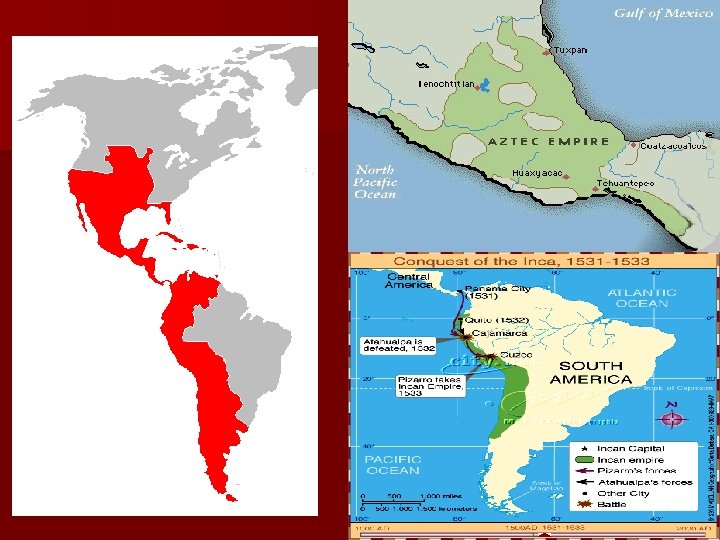
 CONQUEST OF THE AZTECS Expeditions sent out by governor, Diego Valasquez, from Cuba to explore Yucatan and Gulf of Mexico n Hernan Cortez was commissioned to explore, trade, and search for Christian captives—one of the first conquistadors or conquerors n Set sail from Cuba on Feb. 18, 1519—several artillery pieces, 16 horsemen, 500 or so infantry n Upon landing Cortez founded city of Villa Rica de la Vera Cruz—goal became conquest of Mexico n
CONQUEST OF THE AZTECS Expeditions sent out by governor, Diego Valasquez, from Cuba to explore Yucatan and Gulf of Mexico n Hernan Cortez was commissioned to explore, trade, and search for Christian captives—one of the first conquistadors or conquerors n Set sail from Cuba on Feb. 18, 1519—several artillery pieces, 16 horsemen, 500 or so infantry n Upon landing Cortez founded city of Villa Rica de la Vera Cruz—goal became conquest of Mexico n
 n n n Given young native woman named Malinche who will serve as his translator, advisor and later his mistress Learned that many conquered natives hated the Aztecs because they practiced human sacrifice—main god was Huitzilopochtli, who symbolized the sun blazing at high noon The sun, the source of all life, had to be kept moving in its orbit if darkness was not to overtake the world To keep it moving the Aztecs believed it must be fed precious fluids----human blood Aztec leader was Moctezuma (II)—thought Cortes was Quetzalcoatl, Aztec god
n n n Given young native woman named Malinche who will serve as his translator, advisor and later his mistress Learned that many conquered natives hated the Aztecs because they practiced human sacrifice—main god was Huitzilopochtli, who symbolized the sun blazing at high noon The sun, the source of all life, had to be kept moving in its orbit if darkness was not to overtake the world To keep it moving the Aztecs believed it must be fed precious fluids----human blood Aztec leader was Moctezuma (II)—thought Cortes was Quetzalcoatl, Aztec god

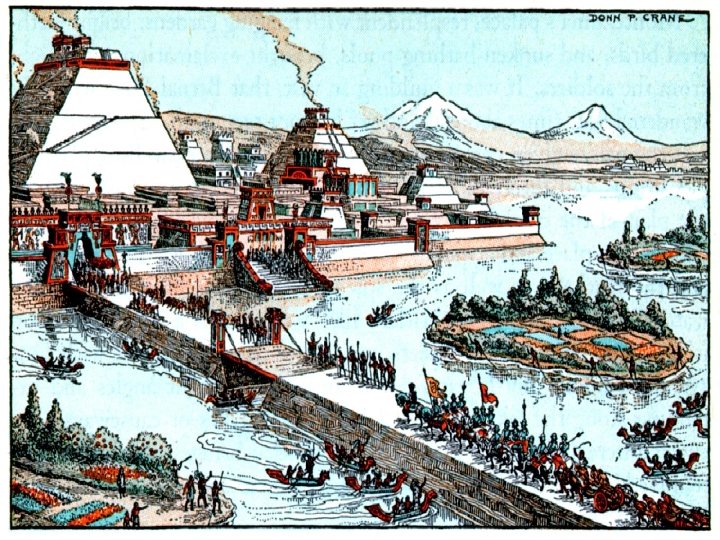
 n Cortes and his men allowed to enter the capital of Tenochtitlan n Relationship quickly broke down and Moctezuma was taken prisoner by Spanish n Aztecs rose up against Spanish— Moctezuma killed and Spanish forced to flee the city n Later returned with allies and destroyed the city—Mexico City built and became capital of New Spain
n Cortes and his men allowed to enter the capital of Tenochtitlan n Relationship quickly broke down and Moctezuma was taken prisoner by Spanish n Aztecs rose up against Spanish— Moctezuma killed and Spanish forced to flee the city n Later returned with allies and destroyed the city—Mexico City built and became capital of New Spain

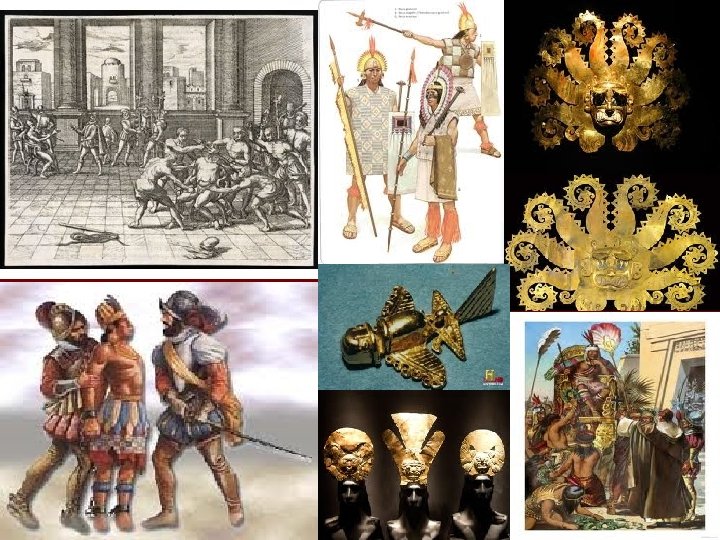
 n n n Francisco Pizarro will be inspired by Cortes Will search for the Inca Civilization in Peru (Andes Mountains) Arrived in 1532 and the Inca were just recovering from a civil war Inca leader was Atahualpa who will be taken prisoner and held for ransom (13, 420 pounds of gold and 26, 000 pounds of silver) Later murdered after paying ransom Inca capital of Cuzco was taken— Pizarro later killed by own men
n n n Francisco Pizarro will be inspired by Cortes Will search for the Inca Civilization in Peru (Andes Mountains) Arrived in 1532 and the Inca were just recovering from a civil war Inca leader was Atahualpa who will be taken prisoner and held for ransom (13, 420 pounds of gold and 26, 000 pounds of silver) Later murdered after paying ransom Inca capital of Cuzco was taken— Pizarro later killed by own men

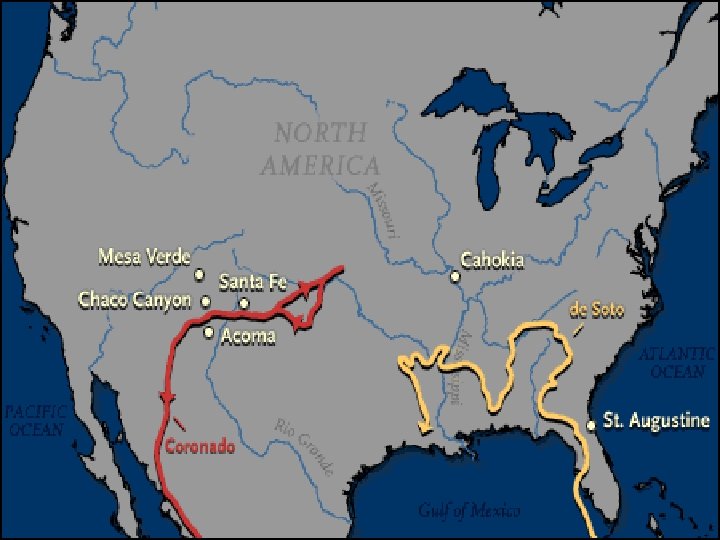
 OTHER SPANISH CONQUISTADORS n Francisco Coronado will lead expedition in search of El Dorado—first Europeans to see the Grand Canyon and the Great Plains n Hernando de Soto explored the Southeastern United States in search of gold—first Europeans to see the Mississippi River
OTHER SPANISH CONQUISTADORS n Francisco Coronado will lead expedition in search of El Dorado—first Europeans to see the Grand Canyon and the Great Plains n Hernando de Soto explored the Southeastern United States in search of gold—first Europeans to see the Mississippi River

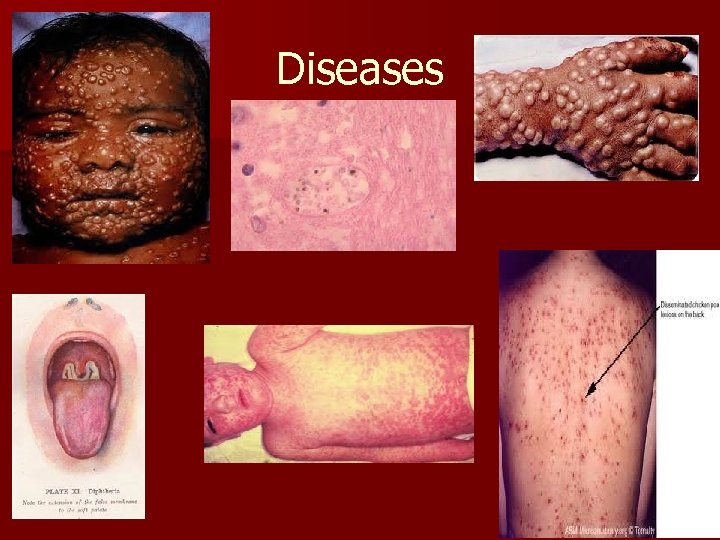
 REASONS FOR SPANISH SUCCESS AGAINST NATIVE POPULATION n n Superior military technology—horse, cannons, muskets, and armor/metal helmets Division and discontent among Natives—Spanish used hatred of conquered natives against Aztecs and Incas Diseases severely weakened natives—small pox, chicken pox, measles etc. Aztec and Inca convinced that the world was ending—gods had abandoned them—some will still resist
REASONS FOR SPANISH SUCCESS AGAINST NATIVE POPULATION n n Superior military technology—horse, cannons, muskets, and armor/metal helmets Division and discontent among Natives—Spanish used hatred of conquered natives against Aztecs and Incas Diseases severely weakened natives—small pox, chicken pox, measles etc. Aztec and Inca convinced that the world was ending—gods had abandoned them—some will still resist
 Diseases
Diseases
 SPANISH EMPIRE OF THE AMERICAS n Spanish empire stretched from California to South America—divided in to 5 provinces—New Spain (Mexico) and Peru were the most important n Monarchy set up the Council of the Indies to pass laws for the colonies (located in Spain) n Viceroys ruled colonies in the monarchs name
SPANISH EMPIRE OF THE AMERICAS n Spanish empire stretched from California to South America—divided in to 5 provinces—New Spain (Mexico) and Peru were the most important n Monarchy set up the Council of the Indies to pass laws for the colonies (located in Spain) n Viceroys ruled colonies in the monarchs name
 n RCC played major role in the Spanish colonies—converting natives to Christianity was very important to Spain n Missionaries (Jesuits, Franciscans, Dominicans) baptized natives whether they wanted it or not n RCC tried to change the culture of Native Americans (Spanish language and western clothing etc. ) n Served the government and regulated activities of Spanish settlers
n RCC played major role in the Spanish colonies—converting natives to Christianity was very important to Spain n Missionaries (Jesuits, Franciscans, Dominicans) baptized natives whether they wanted it or not n RCC tried to change the culture of Native Americans (Spanish language and western clothing etc. ) n Served the government and regulated activities of Spanish settlers
 n Strict regulation of economies of colonies n Colonies could only export items to Spain and could buy only Spanish goods (could not trade with other European countries or colonies in the Americas) n Spanish introduced sugar cane to West Indies (sugar, molasses, and rum) n Grown on plantations (large estates run by an owner or overseer) which required many workers n Cruel labor practices caused the death of many natives
n Strict regulation of economies of colonies n Colonies could only export items to Spain and could buy only Spanish goods (could not trade with other European countries or colonies in the Americas) n Spanish introduced sugar cane to West Indies (sugar, molasses, and rum) n Grown on plantations (large estates run by an owner or overseer) which required many workers n Cruel labor practices caused the death of many natives
 n Spanish government granted settlers encomiendas (the right to demand labor or tribute from Native Americans) n Used system to enslave Native Americans which caused population decline (mines and plantations) n Bartolome de las Casas, Dominican priest condemned the treatment of natives —pleaded for laws to protect them n New Laws of the Indies passed in 1542 which allowed natives to grow crops and own cattle
n Spanish government granted settlers encomiendas (the right to demand labor or tribute from Native Americans) n Used system to enslave Native Americans which caused population decline (mines and plantations) n Bartolome de las Casas, Dominican priest condemned the treatment of natives —pleaded for laws to protect them n New Laws of the Indies passed in 1542 which allowed natives to grow crops and own cattle
 n Native Americans forced to become peons, workers forced to labor for landlord in order to pay off their debts n Las Casas encouraged the importation of Africans to fill labor shortage— 1) immune to tropical diseases 2) had skills in farming, mining and metal working 3) accustomed to working in heat n Las Casas later regretted suggestion and worked hard to help Africans
n Native Americans forced to become peons, workers forced to labor for landlord in order to pay off their debts n Las Casas encouraged the importation of Africans to fill labor shortage— 1) immune to tropical diseases 2) had skills in farming, mining and metal working 3) accustomed to working in heat n Las Casas later regretted suggestion and worked hard to help Africans
 NEW SOCIAL ORDER IN THE SPANISH COLONIES n n n Peninsulares—Spanish born in Spain will dominate New Spain Creoles—Spanish born in the New World— parents were peninsulares Mestizos—were of Native American and Spanish ancestry Mulattoes—were of African and Spanish ancestry Zamboes were of African and Native ancestry Not many Spanish women came to New World
NEW SOCIAL ORDER IN THE SPANISH COLONIES n n n Peninsulares—Spanish born in Spain will dominate New Spain Creoles—Spanish born in the New World— parents were peninsulares Mestizos—were of Native American and Spanish ancestry Mulattoes—were of African and Spanish ancestry Zamboes were of African and Native ancestry Not many Spanish women came to New World
 PORTUGUESE IN THE NEW WORLD n Settlers exploited the land n Brazil wood exported n Settlers turned to plantation agriculture (sugar cane and cattle raising) n Millions of Africans sent to Brazil— more sent to Brazil than any other colony in New World n New culture developed which blended Portuguese, African and Native American
PORTUGUESE IN THE NEW WORLD n Settlers exploited the land n Brazil wood exported n Settlers turned to plantation agriculture (sugar cane and cattle raising) n Millions of Africans sent to Brazil— more sent to Brazil than any other colony in New World n New culture developed which blended Portuguese, African and Native American
 NORTH AMERICAN COLONIZATION
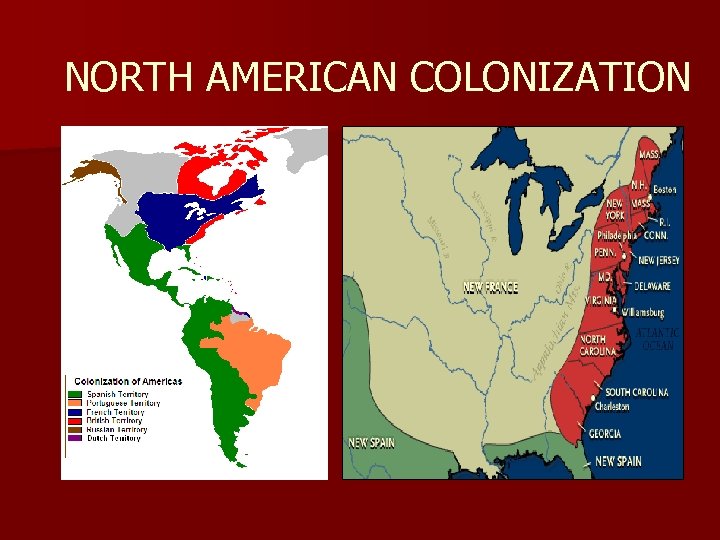
NORTH AMERICAN COLONIZATION
 n England, France and Dutch Netherlands will take very little interest in North America in the 1500 s (lack of gold/silver) n Unable to find Northwest Passage n Dutch under the Dutch West India Company will establish colony called New Netherlands n Peter Minuit is named governor—great land purchase—Manhattan Island n Dutch granted large estates to patroons, wealthy landowners—eventually lost colony to English (New York)
n England, France and Dutch Netherlands will take very little interest in North America in the 1500 s (lack of gold/silver) n Unable to find Northwest Passage n Dutch under the Dutch West India Company will establish colony called New Netherlands n Peter Minuit is named governor—great land purchase—Manhattan Island n Dutch granted large estates to patroons, wealthy landowners—eventually lost colony to English (New York)
 n n n French concentrated on economic benefit of new lands Furs were in demand in Europe (beaver) Also exploited fishing areas First permanent settlement established by Samuel de Champlain at Quebec in 1608 Government did not encourage settlement—only Catholics allowed to come to New France DID NOT WANT THE LAND
n n n French concentrated on economic benefit of new lands Furs were in demand in Europe (beaver) Also exploited fishing areas First permanent settlement established by Samuel de Champlain at Quebec in 1608 Government did not encourage settlement—only Catholics allowed to come to New France DID NOT WANT THE LAND
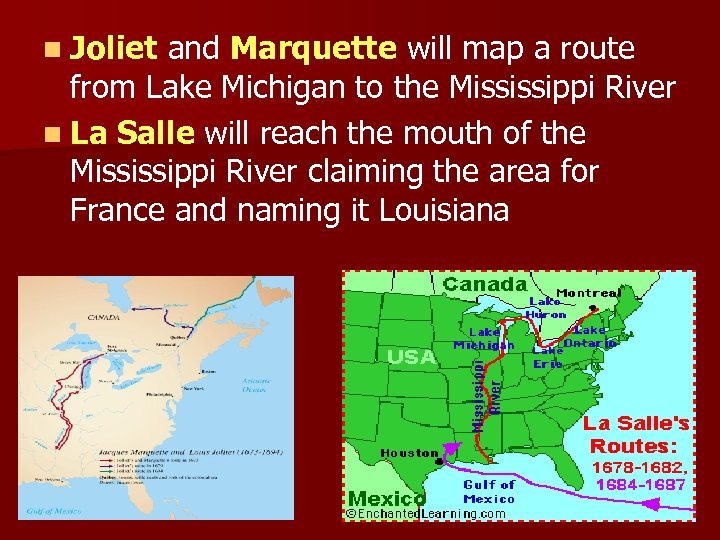 n Joliet and Marquette will map a route from Lake Michigan to the Mississippi River n La Salle will reach the mouth of the Mississippi River claiming the area for France and naming it Louisiana
n Joliet and Marquette will map a route from Lake Michigan to the Mississippi River n La Salle will reach the mouth of the Mississippi River claiming the area for France and naming it Louisiana
 ENGLISH SETTLEMENT IN THE NEW WORLD n Established the first permanent colony at Jamestown in 1607—English government encouraged settlement and population grew quickly n Colonists came to escape religious persecution and a chance for a better life n English settlers wanted the land— constant strife between natives and colonists
ENGLISH SETTLEMENT IN THE NEW WORLD n Established the first permanent colony at Jamestown in 1607—English government encouraged settlement and population grew quickly n Colonists came to escape religious persecution and a chance for a better life n English settlers wanted the land— constant strife between natives and colonists
 n Bitter rivalry developed between the English and the French—war will erupt and both sides used Native American tribes to help them fight n The Seven Years’ War or French and Indian War was the most famous
n Bitter rivalry developed between the English and the French—war will erupt and both sides used Native American tribes to help them fight n The Seven Years’ War or French and Indian War was the most famous
 IMPACT OF COLONIZATION n Native Americans taught settlers about planting and growing crops— taught them how to hunt and trap n Trappers adopted Native American clothing and married native women n Europeans cheated Native Americans out of their land, introduced them to alcoholic drinks and swindled them in trades
IMPACT OF COLONIZATION n Native Americans taught settlers about planting and growing crops— taught them how to hunt and trap n Trappers adopted Native American clothing and married native women n Europeans cheated Native Americans out of their land, introduced them to alcoholic drinks and swindled them in trades
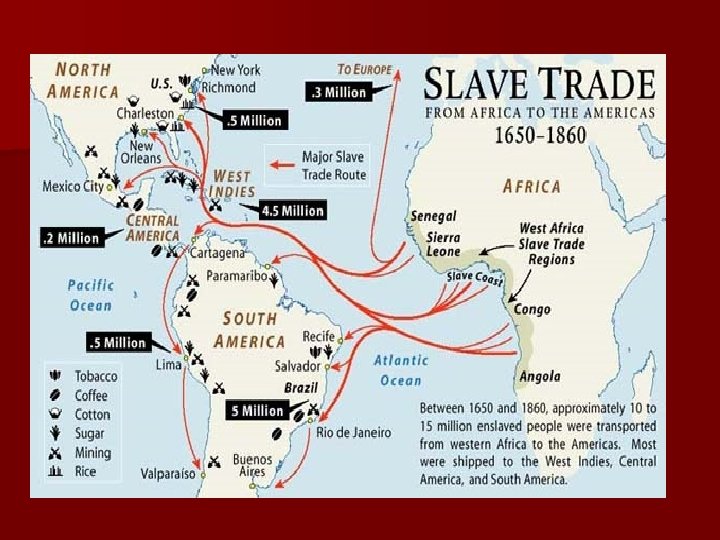
 ATLANTIC SLAVE TRADE (Triangular Trade) Plantations (sugar, tobacco, and later cotton) needed large supplies of workers to make them profitable—Native American pop. declined rapidly so Africans were brought in n Slavery in the Americas based largely on race and became hereditary—Africans were viewed as naturally inferior by Europeans n Became known as Atlantic Slave Trade— estimated that between 9. 5 to 11 million Africans imported n
ATLANTIC SLAVE TRADE (Triangular Trade) Plantations (sugar, tobacco, and later cotton) needed large supplies of workers to make them profitable—Native American pop. declined rapidly so Africans were brought in n Slavery in the Americas based largely on race and became hereditary—Africans were viewed as naturally inferior by Europeans n Became known as Atlantic Slave Trade— estimated that between 9. 5 to 11 million Africans imported n
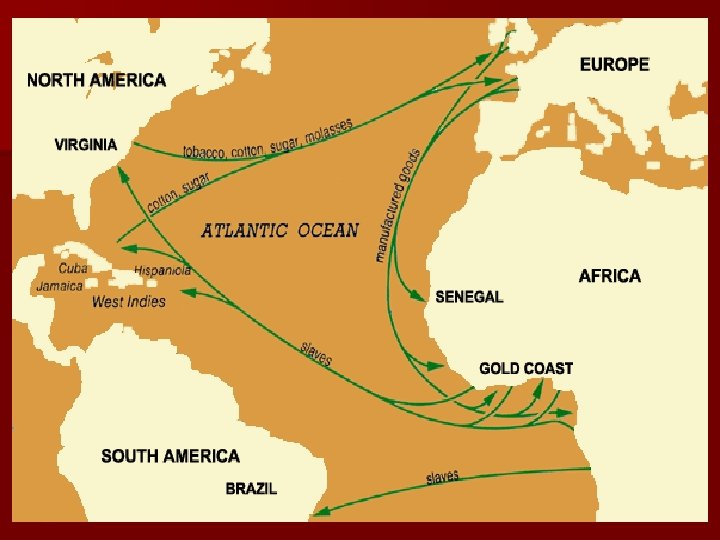
 African rulers and merchants were willing to participate in slave trade (little difference in selling to Westerners instead of Muslims) n African slavers captured other Africans and brought them to the coast where they were purchased by Europeans (Europeans forbidden to go inland to capture slaves themselves) n Slaves exchanged for guns, gold and other goods n
African rulers and merchants were willing to participate in slave trade (little difference in selling to Westerners instead of Muslims) n African slavers captured other Africans and brought them to the coast where they were purchased by Europeans (Europeans forbidden to go inland to capture slaves themselves) n Slaves exchanged for guns, gold and other goods n
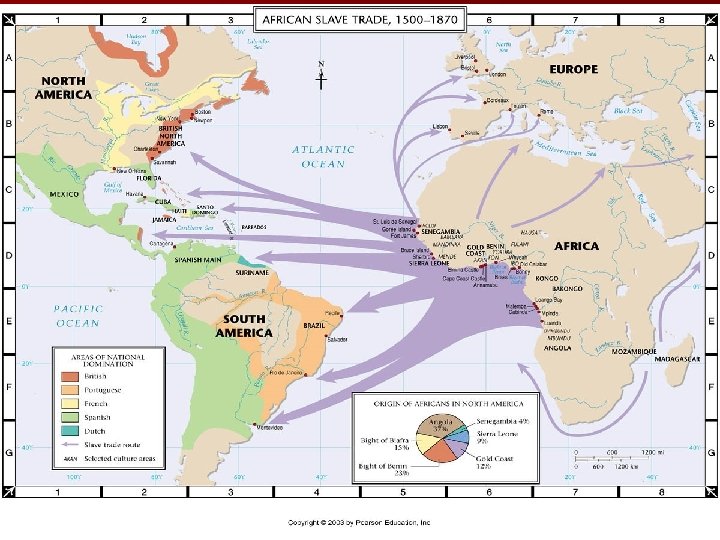
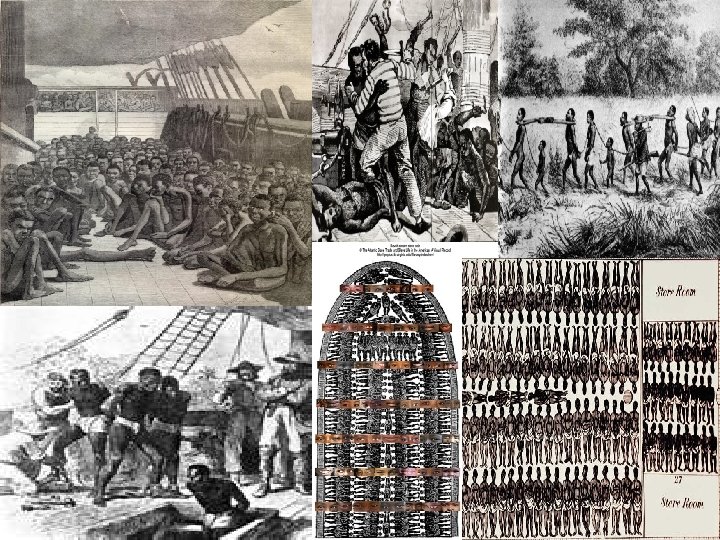
 n The MIDDLE PASSAGE voyage of African slaves to the Americas known as the Middle Passage n It made up part of what is called the Transatlantic Slave Triangle n Characterized by sickening cruelty and brutality—whippings and beatings were common—seasickness and other diseases devastated the slaves on their journey (floating coffins) n Estimated that 20% of slaves died on way
n The MIDDLE PASSAGE voyage of African slaves to the Americas known as the Middle Passage n It made up part of what is called the Transatlantic Slave Triangle n Characterized by sickening cruelty and brutality—whippings and beatings were common—seasickness and other diseases devastated the slaves on their journey (floating coffins) n Estimated that 20% of slaves died on way

 African Diaspora n Resulted from the forced migration of millions of slaves (West Africa) mostly to North America and South America n Diaspora of their culture, food traditions, and languages n Colonization resulted in a mixing of the biota of Eurasia, Africa, and the Americas n Plant and animal species indigenous to a given place or region transferred
African Diaspora n Resulted from the forced migration of millions of slaves (West Africa) mostly to North America and South America n Diaspora of their culture, food traditions, and languages n Colonization resulted in a mixing of the biota of Eurasia, Africa, and the Americas n Plant and animal species indigenous to a given place or region transferred
 Virgin Soil Epidemic n When a disease is first introduced to a place or region in which it had not been previously known, the people indigenous to that place have little or no acquired immunity to that disease n Virgin soil-epidemics of diseases such as small pox and measles among Native Americans killed at least 90% of the native population between 1500 -1700
Virgin Soil Epidemic n When a disease is first introduced to a place or region in which it had not been previously known, the people indigenous to that place have little or no acquired immunity to that disease n Virgin soil-epidemics of diseases such as small pox and measles among Native Americans killed at least 90% of the native population between 1500 -1700
 Impact of Slavery Destroyed culture of many African societies—lost generations of the strongest and ablest African men and women—many claim this is the reason for under-development of Africa today n Caused depopulation of areas of Western Africa n Fueled conflict on the continent that still has lasting effects today n The stigma of slavery has been difficult to erase in the modern world n
Impact of Slavery Destroyed culture of many African societies—lost generations of the strongest and ablest African men and women—many claim this is the reason for under-development of Africa today n Caused depopulation of areas of Western Africa n Fueled conflict on the continent that still has lasting effects today n The stigma of slavery has been difficult to erase in the modern world n
 END OF SLAVERY n Between 1807 -1820, most European nations abolished the slave trade n Slavery itself will not be abolished until a few decades later (no new slaves were legally imported from Africa) n Those already enslaved in Europe and New World continued to be enslaved n In some cases freed slaves returned to Africa (Liberia)
END OF SLAVERY n Between 1807 -1820, most European nations abolished the slave trade n Slavery itself will not be abolished until a few decades later (no new slaves were legally imported from Africa) n Those already enslaved in Europe and New World continued to be enslaved n In some cases freed slaves returned to Africa (Liberia)
 MODERN SLAVERY n n n There are more people in slavery now than in any other time in history. (27 million) The value of slaves has decreased. Slavery still exist in the United States. (1 million) Human trafficking has recently been described as “the fastest growing criminal enterprise in the world” (7 billion dollars a year) The least known method of slavery is the most widely used. (Bonded slavery—debt) Average cost of a slave is $90. 00
MODERN SLAVERY n n n There are more people in slavery now than in any other time in history. (27 million) The value of slaves has decreased. Slavery still exist in the United States. (1 million) Human trafficking has recently been described as “the fastest growing criminal enterprise in the world” (7 billion dollars a year) The least known method of slavery is the most widely used. (Bonded slavery—debt) Average cost of a slave is $90. 00
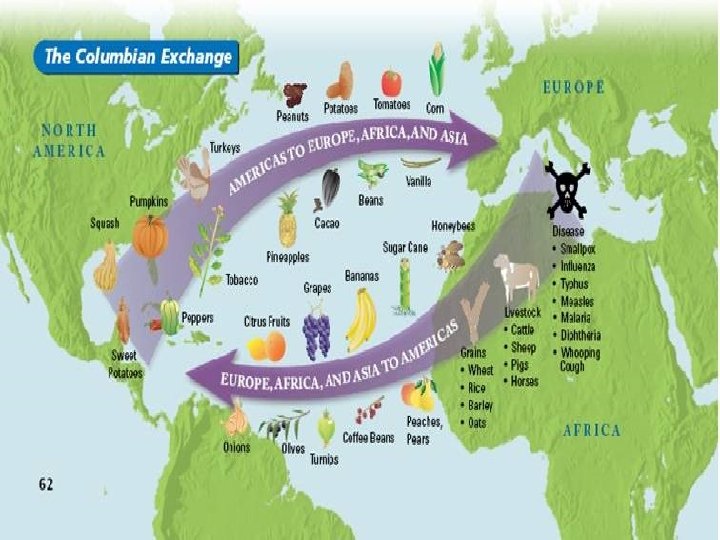
 COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE n n n Columbus started a vast global exchange Plants, animals, people, technology and disease were exchanged New foods brought from Americas to Europe included tomato, sweet potato, pumpkins, squash, beans, pineapples and peppers—tobacco and cacao (chocolate) Corn and potato were the most important Asia and Africa also shared in the Columbian Exchange as new foods were introduced
COLUMBIAN EXCHANGE n n n Columbus started a vast global exchange Plants, animals, people, technology and disease were exchanged New foods brought from Americas to Europe included tomato, sweet potato, pumpkins, squash, beans, pineapples and peppers—tobacco and cacao (chocolate) Corn and potato were the most important Asia and Africa also shared in the Columbian Exchange as new foods were introduced
 n Europe to Americas wheat, melons, grapes, rice, barley, peaches, pears and olives n From Asia and Africa the Europeans brought banana, sugar cane, coconut palms and coffee bean n Europeans brought the horse, cows, pigs, goats, chickens, sheep and honey bee to Americas n Diseases brought to Americas included small pox, influenza, measles, malaria n Americas sent syphilis
n Europe to Americas wheat, melons, grapes, rice, barley, peaches, pears and olives n From Asia and Africa the Europeans brought banana, sugar cane, coconut palms and coffee bean n Europeans brought the horse, cows, pigs, goats, chickens, sheep and honey bee to Americas n Diseases brought to Americas included small pox, influenza, measles, malaria n Americas sent syphilis
 COMMERCIAL REVOLUTION Economic changes caused inflation, a rapid rise in prices linked to a sharp increase in the amount of money available n Causes—population grew and the demand for goods and services rose—goods became scarce so prices rose (law of supply/demand) n Also caused by increased flow of silver and gold into Europe from the Americas—more money in circulation n
COMMERCIAL REVOLUTION Economic changes caused inflation, a rapid rise in prices linked to a sharp increase in the amount of money available n Causes—population grew and the demand for goods and services rose—goods became scarce so prices rose (law of supply/demand) n Also caused by increased flow of silver and gold into Europe from the Americas—more money in circulation n
 n Expanded trade and the push for overseas empires spurred the growth of capitalism, the investment of money to make a profit n New business men called entrepreneurs, people willing to take business risks in the hope of making a profit expanded into overseas ventures n Risky business because of piracy and shipwrecks n Capitalists developed new ways to create wealth
n Expanded trade and the push for overseas empires spurred the growth of capitalism, the investment of money to make a profit n New business men called entrepreneurs, people willing to take business risks in the hope of making a profit expanded into overseas ventures n Risky business because of piracy and shipwrecks n Capitalists developed new ways to create wealth
 n n n From Arabs they adapted methods of bookkeeping to show profits and loses Developed insurance to reduce the risk of financial disaster Joint-stock companies allowed people to pool large amounts of capital, money to invest into overseas ventures Partnerships formed so people would not lose all their money in investment Capitalists diversified their investments Developed the putting out system or domestic system (goods produced in the countryside)
n n n From Arabs they adapted methods of bookkeeping to show profits and loses Developed insurance to reduce the risk of financial disaster Joint-stock companies allowed people to pool large amounts of capital, money to invest into overseas ventures Partnerships formed so people would not lose all their money in investment Capitalists diversified their investments Developed the putting out system or domestic system (goods produced in the countryside)
 MERCANTILISM New economic system—stresses exporting more than a country imports (don’t buy from enemies) n Wealth is measured in terms of commodities, especially gold and silver, rather than in terms of productivity and income-producing investments n Make country self-sufficient—colonies very important to mother country 1) provide raw materials 2) provided closed markets for mother country’s manufactured goods 3) regulate economy 4) nations imposed tariffs, taxes on imports n
MERCANTILISM New economic system—stresses exporting more than a country imports (don’t buy from enemies) n Wealth is measured in terms of commodities, especially gold and silver, rather than in terms of productivity and income-producing investments n Make country self-sufficient—colonies very important to mother country 1) provide raw materials 2) provided closed markets for mother country’s manufactured goods 3) regulate economy 4) nations imposed tariffs, taxes on imports n


