3a6ee059175be74b9d4931368f5eb7d2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Age Banding in Retirement Planning © 2002 Dr. Somnath Basu

Presentation by Dr. Somnath Basu Professor of Finance School of Business California Lutheran University 805 -493 -3980 basu@clunet. edu

v

The Retirement Objective v The need to maintain our standard of living during retirement v Time horizon typically backed out of the mortality tables and clientspecific information v Risk-return subjectively dependant on clients
Traditional View: Weaknesses v. Replacement ratio: (e. g. 40 -90%) ØNo formal model to compute this ratio § Conservative – Aggressive v Assumes expenses during retirement increase at the inflation rate ØLeisure/Healthcare inflation app 7%

Traditional View: Weakness v. Investment horizon & allocation Ø Single basket v. Risk management Ø Choice of securities v. Incorporating Long Term Care, etc Ø Inflexible

Alternate View v Retirement is dynamic Ø No different from any other stage of life v Typical observations Ø Leisure spending to healthcare spending Ø Life-cycle dynamics

Alternative View v. Generality of Model ØRetirement at any other age ØDifferent activities, etc Ø Life cycle changes can occur with any frequency -- 2 yrs, 5 yrs, etc

The Age-Banding Model: Case Studies v. Case 1 : The Smiths Ø Individual and spouse q Both around 60 years ØExpect to retire in 5 years ØExpect to live in retirement for about 30 years v. Case 2: Ms. Jones Ø 35 year old individual Ø Single, mid-career

The Age-Banding Model: Case Studies

Planning for Retirement Needs
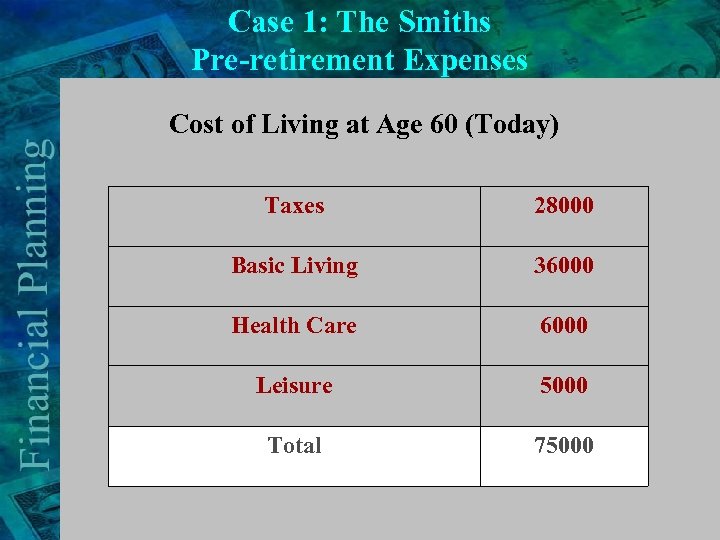
Case 1: The Smiths Pre-retirement Expenses Cost of Living at Age 60 (Today) Taxes 28000 Basic Living 36000 Health Care 6000 Leisure 5000 Total 75000
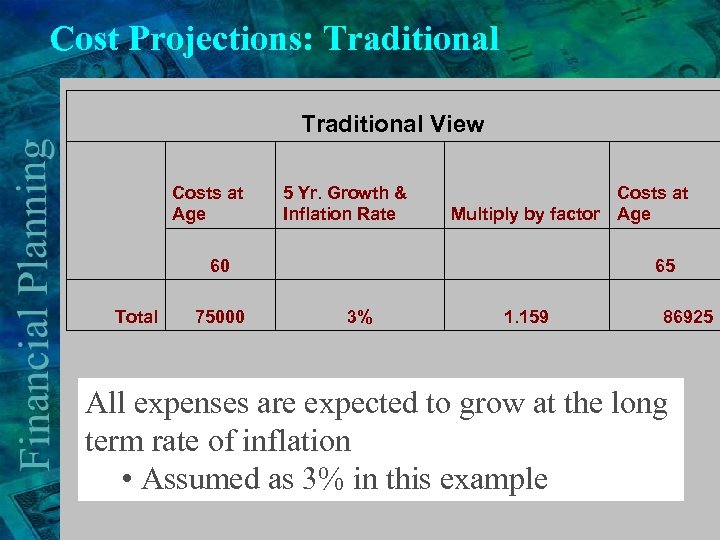
Cost Projections: Traditional View Costs at Age Total 60 75000 5 Yr. Growth & Inflation Rate Costs at Multiply by factor Age 3% 65 1. 159 86925 All expenses are expected to grow at the long term rate of inflation • Assumed as 3% in this example
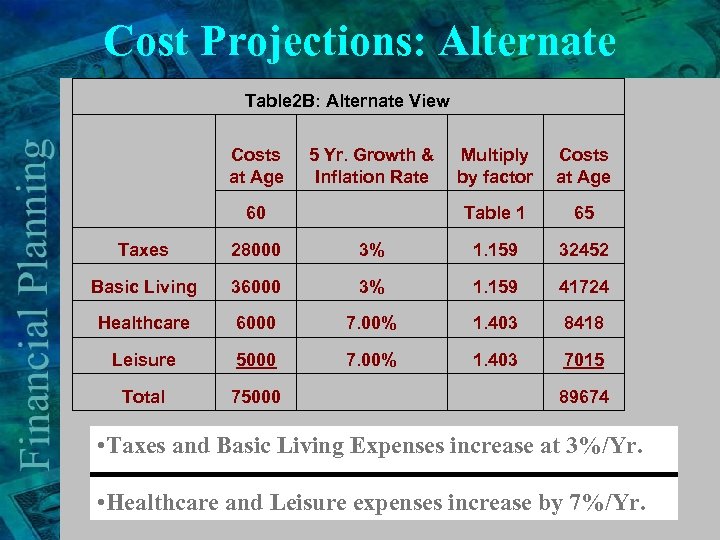
Cost Projections: Alternate Table 2 B: Alternate View Costs at Age 5 Yr. Growth & Multiply Inflation Rate by factor Costs at Age 60 Table 1 65 Taxes 28000 3% 1. 159 32452 Basic Living 36000 3% 1. 159 41724 Healthcare 6000 7. 00% 1. 403 8418 Leisure 5000 7. 00% 1. 403 7015 Total 75000 89674 • Taxes and Basic Living Expenses increase at 3%/Yr. • Healthcare and Leisure expenses increase by 7%/Yr.
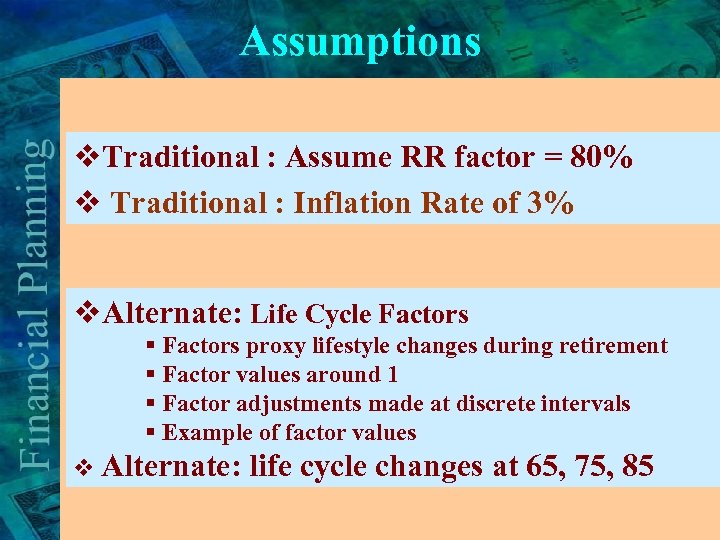
Assumptions v. Traditional : Assume RR factor = 80% v Traditional : Inflation Rate of 3% v. Alternate: Life Cycle Factors § Factors proxy lifestyle changes during retirement § Factor values around 1 § Factor adjustments made at discrete intervals § Example of factor values v Alternate: life cycle changes at 65, 75, 85
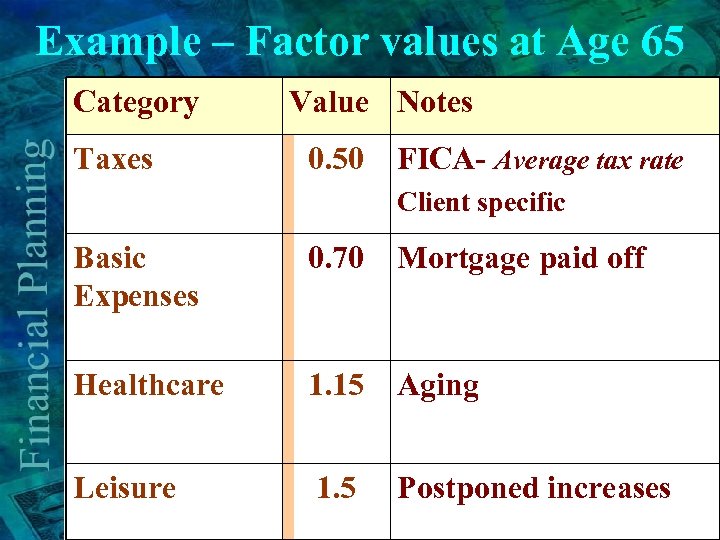
Example – Factor values at Age 65 Category Taxes Value Notes 0. 50 FICA- Average tax rate Client specific Basic Expenses 0. 70 Mortgage paid off Healthcare 1. 15 Aging Leisure 1. 5 Postponed increases
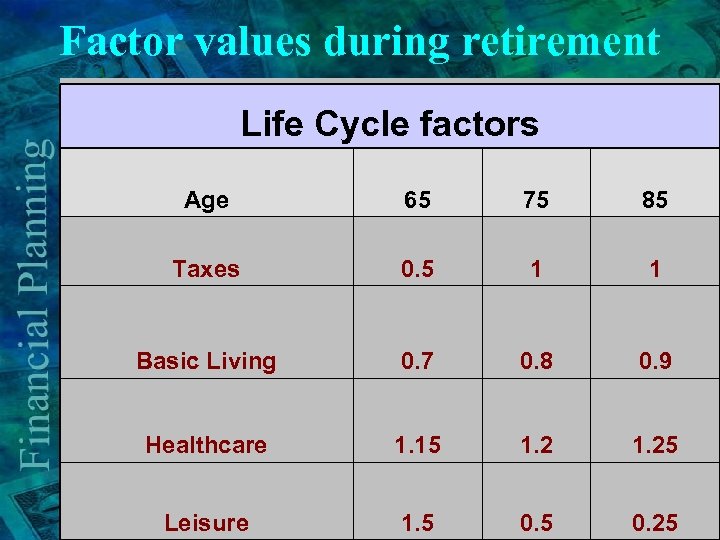
Factor values during retirement Life Cycle factors Age 65 75 85 Taxes 0. 5 1 1 Basic Living 0. 7 0. 8 0. 9 Healthcare 1. 15 1. 25 Leisure 1. 5 0. 25
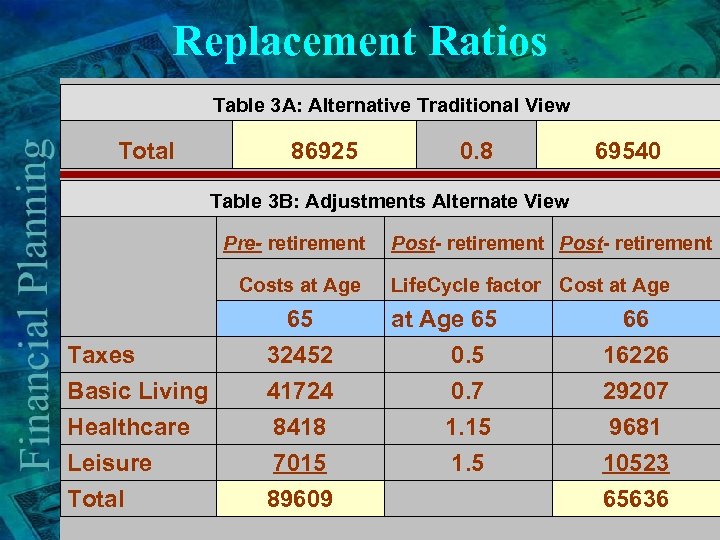
Replacement Ratios Total Table 3 A: Alternative Traditional View 86925 0. 8 69540 Table 3 B: Adjustments Alternate View Pre- retirement Costs at Age 65 Taxes Basic Living Healthcare Leisure Total 32452 41724 8418 7015 89609 Post- retirement Life. Cycle factor Cost at Age 65 0. 7 1. 15 1. 5 66 16226 29207 9681 10523 65636
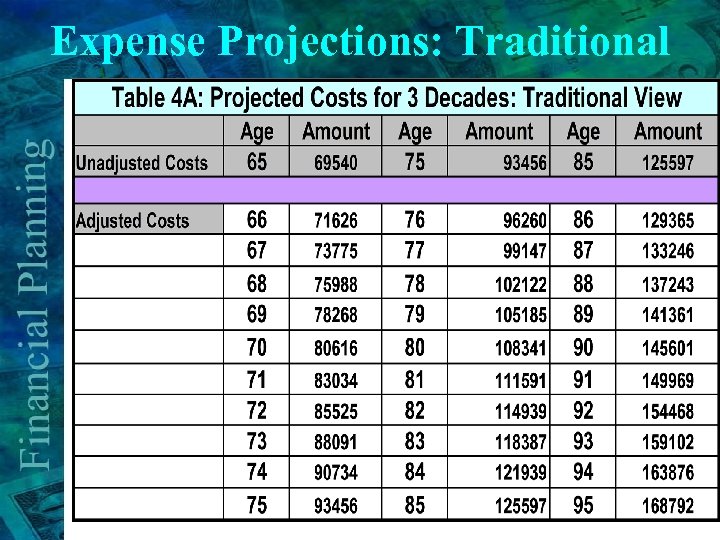
Expense Projections: Traditional
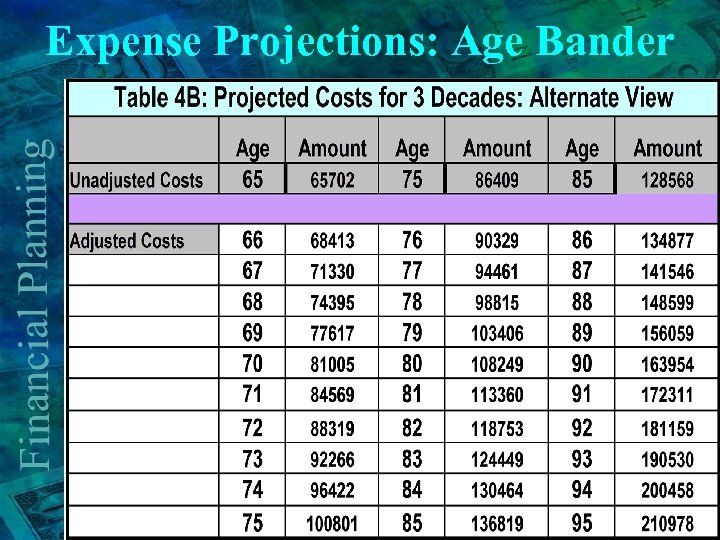
Expense Projections: Age Bander
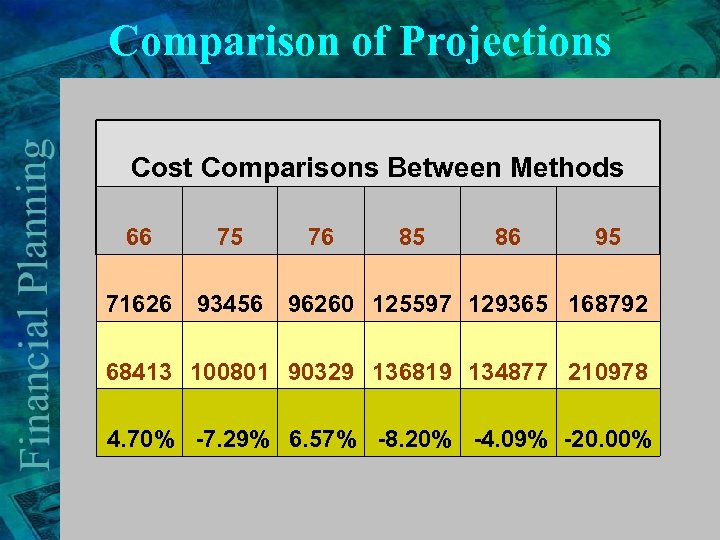
Comparison of Projections Cost Comparisons Between Methods 66 75 71626 93456 76 85 86 95 96260 125597 129365 168792 68413 100801 90329 136819 134877 210978 4. 70% -7. 29% 6. 57% -8. 20% -4. 09% -20. 00%
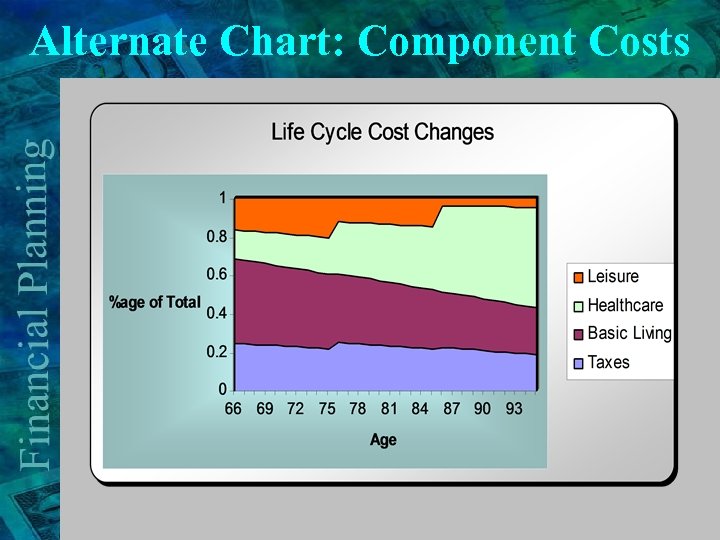
Alternate Chart: Component Costs
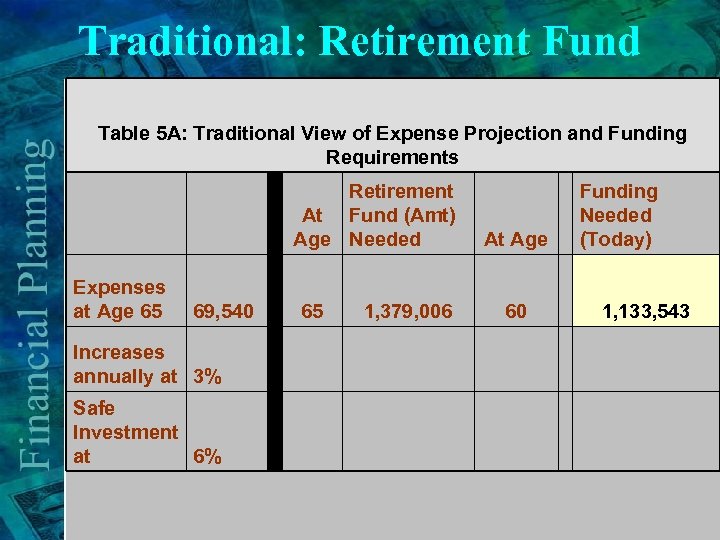
Traditional: Retirement Fund Table 5 A: Traditional View of Expense Projection and Funding Requirements Expenses at Age 65 69, 540 Retirement At Fund (Amt) Age Needed Funding Needed At Age (Today) 65 1, 379, 006 60 1, 133, 543 Increases annually at 3% Safe Investment at 6%

Alternate: Funding Requirements v Expenses recorded separately for 3 decades v (66 -75, 76 -85, 86 -95) § 3 dedicated portfolios. § Differential returns : § 6%, 8% and 10% for 5, 15, 25 year portfolio v Retirees are more risk averse than others Ø A circuit breaker for risk § 5 year cushion
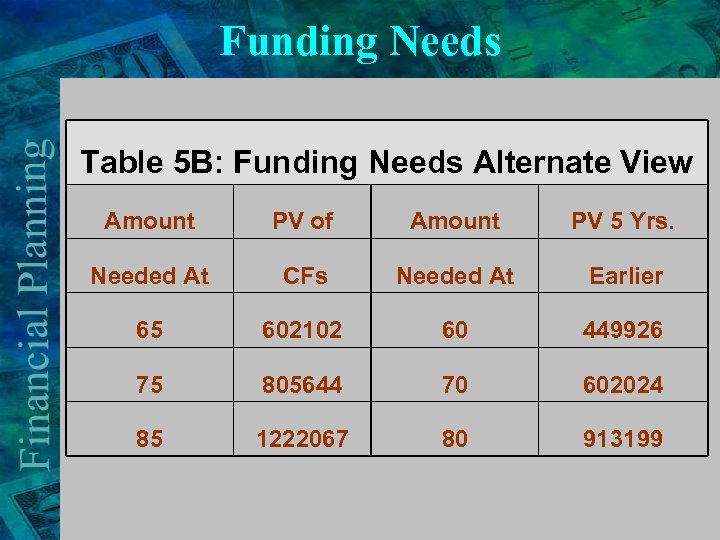
Funding Needs Table 5 B: Funding Needs Alternate View Amount PV of Amount PV 5 Yrs. Needed At CFs Needed At Earlier 65 602102 60 449926 75 805644 70 602024 85 1222067 80 913199
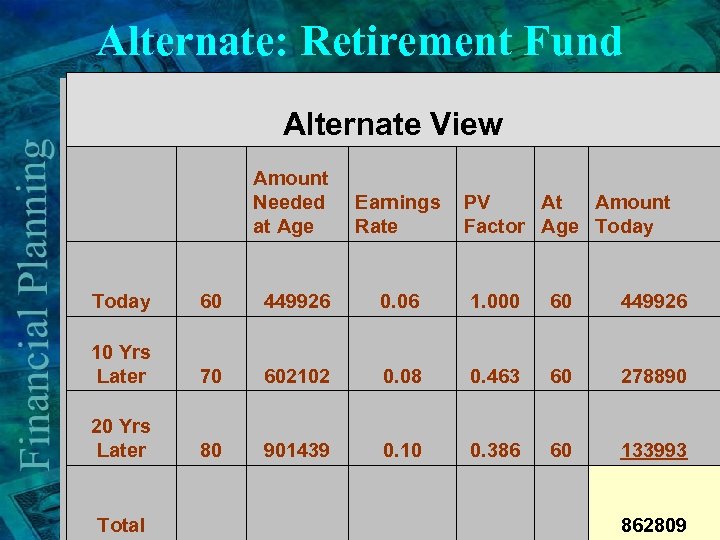
Alternate: Retirement Fund Alternate View Amount Needed at Age Earnings PV At Amount Rate Factor Age Today 60 449926 0. 06 1. 000 60 449926 10 Yrs Later 70 602102 0. 08 0. 463 60 278890 20 Yrs Later 80 901439 0. 10 0. 386 60 133993 Total 862809
Asset Allocation 25% Equity 75% Bonds
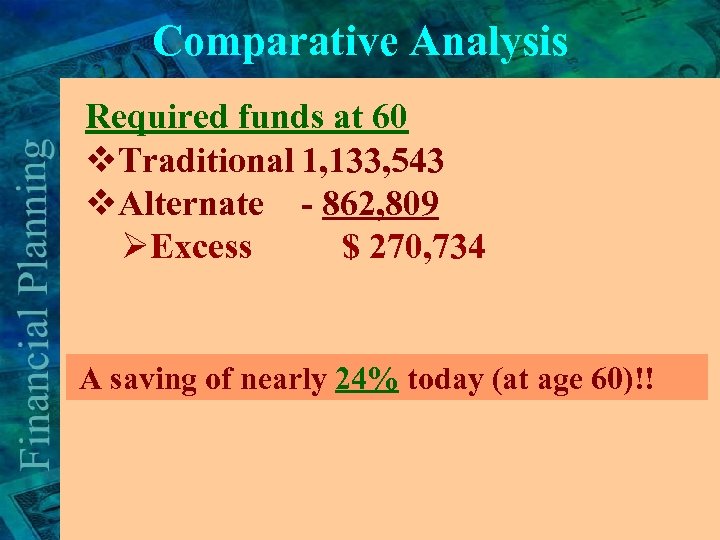
Comparative Analysis Required funds at 60 v. Traditional 1, 133, 543 v. Alternate - 862, 809 ØExcess $ 270, 734 A saving of nearly 24% today (at age 60)!!

Case Study 2: Ms. Jones

Case Study 2 v. Assume (simplifying) that the same retirement expenses are projected Ø 3 portfolios - 30 year – 12% - 40 year – 13. 5% - 50 year – 15% Individual has 50 years for managing portfolio
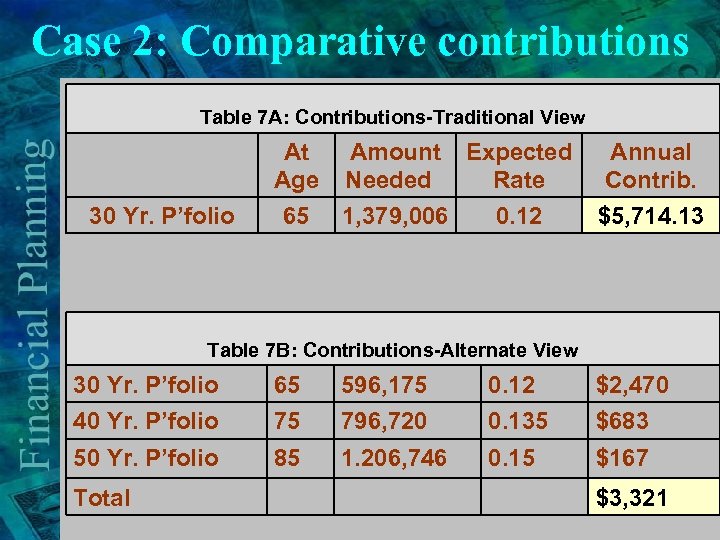
Case 2: Comparative contributions Table 7 A: Contributions-Traditional View 30 Yr. P’folio At Amount Expected Annual Age Needed Rate Contrib. 65 1, 379, 006 0. 12 $5, 714. 13 Table 7 B: Contributions-Alternate View 30 Yr. P’folio 40 Yr. P’folio 65 75 596, 175 796, 720 0. 12 0. 135 $2, 470 $683 50 Yr. P’folio 85 1. 206, 746 0. 15 $167 Total $3, 321

Case 2: Comparative Analysis
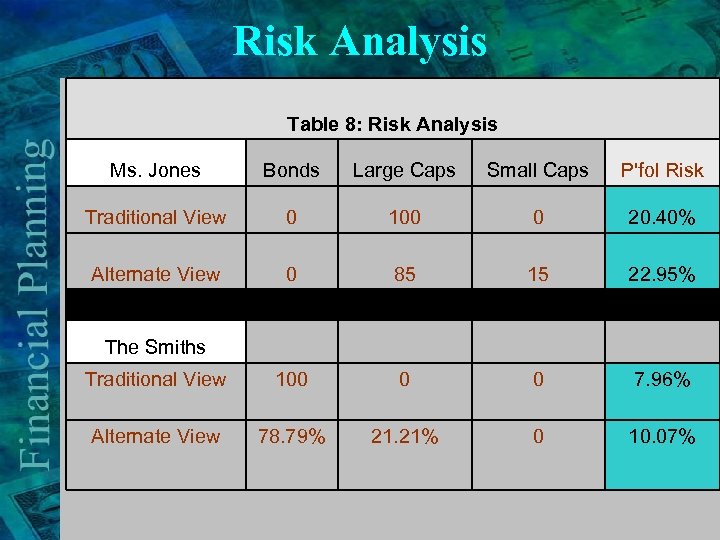
Risk Analysis Table 8: Risk Analysis Ms. Jones Bonds Large Caps Small Caps P'fol Risk Traditional View 0 100 0 20. 40% Alternate View 0 85 15 22. 95% The Smiths Traditional View 100 0 0 7. 96% Alternate View 78. 79% 21. 21% 0 10. 07%

Risk Analysis: Ms. Jones

Risk Analysis: The Smiths v Risk Increase = 2. 1% v Reduction in funding needs = 24% Ø $270, 000 v Time to manage risk = 25 years

Risk Analysis: 60 year old couple v. Additional risk considerations Ø 5 year safety cushion Ø First 10 years risk free – same as traditional Ø More precise expense estimation mitigates risk Ø Buy two $50, 000 (from savings) of fixed income securities with maturities of 15 and 25 yr. §Most of the risk increase goes away

Generality of model v Income netting: Ø Social security Ø GACs (risk adjusted), etc. v Point estimates: Ø Estimate of effects of inflation, returns, etc can be made using range estimates rather than single point estimates Ø Introduce additional statistical analysis
Generality of model v Life cycle decades & expenses ØAny time span (1 year, 5 year, etc can be used) § Continuous time modeling v Breakup expenses (e. g. healthcare) into component costs for further fine – tuning v Time Long Term Care policy benefits to various phases of retirement

The End Thank You
3a6ee059175be74b9d4931368f5eb7d2.ppt