2719aa8f8f56fc45a49a7c86c8fd76a4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Telecom Signaling Networks and Service Forum January 18, 2006 Amsterdam
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Telecom Signaling Networks and Service Forum January 18, 2006 Amsterdam
 AG Projects I am Adrian Georgescu Qo. S in Next Generation Networks
AG Projects I am Adrian Georgescu Qo. S in Next Generation Networks
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks I work for AG Projects, which is developing solutions for convergence of the Telecom and Internet
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks I work for AG Projects, which is developing solutions for convergence of the Telecom and Internet
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks The opinions expressed in this presentation belong to myself, my company and most of my friends
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks The opinions expressed in this presentation belong to myself, my company and most of my friends
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet is a dumb network, the services (applications) are performed at the edge
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet is a dumb network, the services (applications) are performed at the edge
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Dumb means: Internet role is simply to locate and route packets to the destination IP address
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Dumb means: Internet role is simply to locate and route packets to the destination IP address
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet model is a “best-effort” with no guarantee
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet model is a “best-effort” with no guarantee
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Don’t be fooled by the wording “no guarantee”
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Don’t be fooled by the wording “no guarantee”
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks All of you are using it today for your day to day work
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks All of you are using it today for your day to day work
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Best Effort is for the Best Reasons!
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Best Effort is for the Best Reasons!
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Because allowing innovation is what made Internet a success!
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Because allowing innovation is what made Internet a success!
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Ethernet is the most successful network transport protocol on Earth despite the fact that it does not have any Qo. S management built-in!
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Ethernet is the most successful network transport protocol on Earth despite the fact that it does not have any Qo. S management built-in!
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Because it could be upgraded to 10, 1000, 10000 Mbit/s without having to change a bit of the routing protocol or the applications on top of it!
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Because it could be upgraded to 10, 1000, 10000 Mbit/s without having to change a bit of the routing protocol or the applications on top of it!
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks PSTN is a “guaranteed” transport medium with switched circuits (paths)
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks PSTN is a “guaranteed” transport medium with switched circuits (paths)
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks The question today is: How do I guarantee a voice call will work with the expectation that it will not fail or it provides the quality we use to experience from PSTN?
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks The question today is: How do I guarantee a voice call will work with the expectation that it will not fail or it provides the quality we use to experience from PSTN?
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks - We build IMS, we apply telco logic on top of Internet - We build and deploy bandwidth management systems, Pocket Cable, MPLS and others - Buy our own technology, it has Qo. S just stick with our proprietary stuff! The answers you get today from you vendors:
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks - We build IMS, we apply telco logic on top of Internet - We build and deploy bandwidth management systems, Pocket Cable, MPLS and others - Buy our own technology, it has Qo. S just stick with our proprietary stuff! The answers you get today from you vendors:
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Unfortunately, these answers do not address the problem They address only your pocket!
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Unfortunately, these answers do not address the problem They address only your pocket!
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks 50 millions users of Skype proved that users are prepared to trade all PSTN “guarantees” with a new Internet application
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks 50 millions users of Skype proved that users are prepared to trade all PSTN “guarantees” with a new Internet application
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Lets try to find some real solutions which are also cost effective!
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Lets try to find some real solutions which are also cost effective!
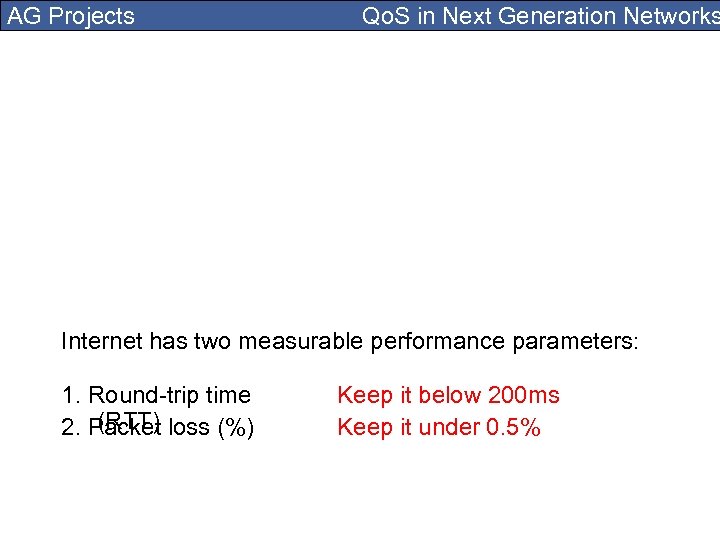 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet has two measurable performance parameters: 1. Round-trip time (RTT) 2. Packet loss (%) Keep it below 200 ms Keep it under 0. 5%
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet has two measurable performance parameters: 1. Round-trip time (RTT) 2. Packet loss (%) Keep it below 200 ms Keep it under 0. 5%
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks And two ways to deliver data: 1. UDP protocol (no guarantee of delivery but good for RT) 2. TCP protocol (guarantee of the delivery, very good for signaling bad for RT)
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks And two ways to deliver data: 1. UDP protocol (no guarantee of delivery but good for RT) 2. TCP protocol (guarantee of the delivery, very good for signaling bad for RT)
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks And all these are confined into a bandwidth “force-field”
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks And all these are confined into a bandwidth “force-field”
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Given enough bandwidth, no quality problem exists
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Given enough bandwidth, no quality problem exists
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Is cheaper to increase the bandwidth than to build systems that managed the lack of it
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Is cheaper to increase the bandwidth than to build systems that managed the lack of it
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Do you imagine today a Qo. S management system for old dial-up Internet instead of going to broadband?
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Do you imagine today a Qo. S management system for old dial-up Internet instead of going to broadband?
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Building Qo. S management systems is difficult, noninteroperable and expensive By the time such systems are deployed the bandwidth has doubled or more already, and you are stuck with a solution build for the past
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Building Qo. S management systems is difficult, noninteroperable and expensive By the time such systems are deployed the bandwidth has doubled or more already, and you are stuck with a solution build for the past
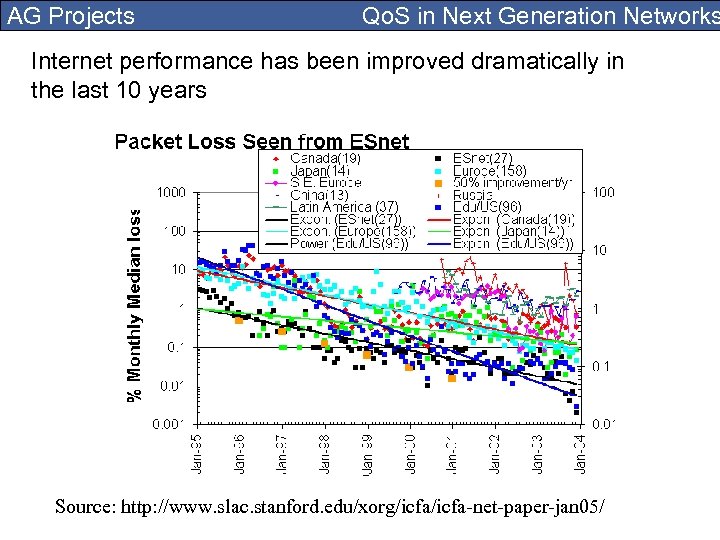 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet performance has been improved dramatically in the last 10 years Source: http: //www. slac. stanford. edu/xorg/icfa-net-paper-jan 05/
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Internet performance has been improved dramatically in the last 10 years Source: http: //www. slac. stanford. edu/xorg/icfa-net-paper-jan 05/
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Complex systems cannot provide a solution for lack of bandwidth, any system added in the chain will put strains on Qo. S as well
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Complex systems cannot provide a solution for lack of bandwidth, any system added in the chain will put strains on Qo. S as well
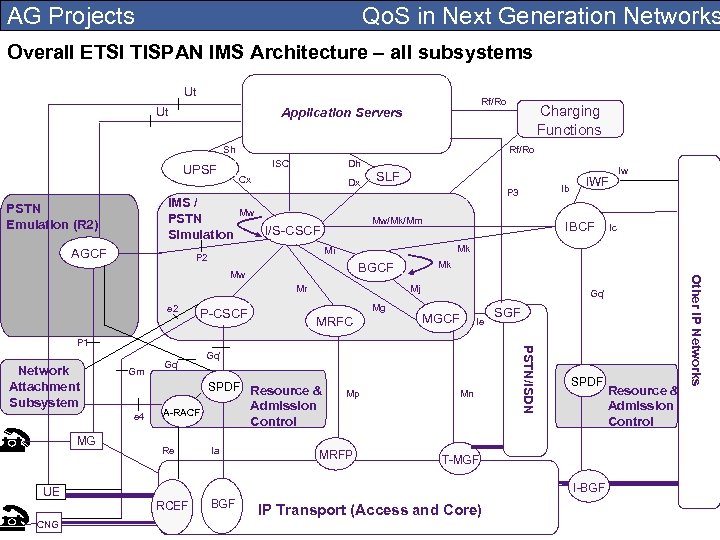 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Overall ETSI TISPAN IMS Architecture – all subsystems Rf/Ro Ut Ut Rf/Ro Application Servers Sh AGCF Dh Cx IMS / PSTN Simulation PSTN Emulation (R 2) Rf/Ro ISC UPSF Dx Mw SLF Mg MRFC Gq' MGCF Ie Re Ia MRFP Mn SPDF T-MGF I-BGF UE RCEF CNG Admission Control A-RACF Mp PSTN/ISDN SPDF Resource & e 4 MG Gq' SGF BGF IP Transport (Access and Core) Resource & Admission Control Other IP Networks Mj P 1 Gm Ic Mk BGCF Mr Network Attachment Subsystem Iw Mk Mw Gq' IWF IBCF Mi P-CSCF Ib P 3 Mw/Mk/Mm I/S-CSCF P 2 e 2 Charging Functions
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Overall ETSI TISPAN IMS Architecture – all subsystems Rf/Ro Ut Ut Rf/Ro Application Servers Sh AGCF Dh Cx IMS / PSTN Simulation PSTN Emulation (R 2) Rf/Ro ISC UPSF Dx Mw SLF Mg MRFC Gq' MGCF Ie Re Ia MRFP Mn SPDF T-MGF I-BGF UE RCEF CNG Admission Control A-RACF Mp PSTN/ISDN SPDF Resource & e 4 MG Gq' SGF BGF IP Transport (Access and Core) Resource & Admission Control Other IP Networks Mj P 1 Gm Ic Mk BGCF Mr Network Attachment Subsystem Iw Mk Mw Gq' IWF IBCF Mi P-CSCF Ib P 3 Mw/Mk/Mm I/S-CSCF P 2 e 2 Charging Functions
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks To improve the quality of service experienced by your end-users you can follow common-sense best practices:
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks To improve the quality of service experienced by your end-users you can follow common-sense best practices:
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks 1. In the core, monitor the network to avoid congestion, network loads of 30%-40% are considered adequate for quality of service and for congestion avoidance 2. At the edge (last mile), provision two paths from the IAD to the first IP switch. This way RT applications will not collide with non-RT applications. Invest in last mile bandwidth upgrades instead of Qo. S management systems for it 3. In case of packet-loss use smart applications that automatically fail-over to other hosting center 4. Don’t tunnel signaling and media to home network (like IMS does), use geographical distribution of resources 5. Use Internet codecs like i. LBC or Speex instead of G. 7 xx
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks 1. In the core, monitor the network to avoid congestion, network loads of 30%-40% are considered adequate for quality of service and for congestion avoidance 2. At the edge (last mile), provision two paths from the IAD to the first IP switch. This way RT applications will not collide with non-RT applications. Invest in last mile bandwidth upgrades instead of Qo. S management systems for it 3. In case of packet-loss use smart applications that automatically fail-over to other hosting center 4. Don’t tunnel signaling and media to home network (like IMS does), use geographical distribution of resources 5. Use Internet codecs like i. LBC or Speex instead of G. 7 xx
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Remember that: Qo. S systems do not create bandwidth!
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks Remember that: Qo. S systems do not create bandwidth!
 AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks This presentation is available at: http: //ag-projects. com
AG Projects Qo. S in Next Generation Networks This presentation is available at: http: //ag-projects. com
 AG Projects Thank you, Adrian Georgescu ag@ag-projects. com Qo. S in Next Generation Networks
AG Projects Thank you, Adrian Georgescu ag@ag-projects. com Qo. S in Next Generation Networks


