d9ddf4053f0c2b28b142fcf0edea9e37.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 AFRL / FAA Programs Status Report Lt. Matt Manger Rome Research Site 6 May 2003 1
AFRL / FAA Programs Status Report Lt. Matt Manger Rome Research Site 6 May 2003 1
 Overview • Cyber. Wolf • Air Force Enterprise Defense (AFED) • Distributed Agents for Information Warfare (DAIWatch) 2
Overview • Cyber. Wolf • Air Force Enterprise Defense (AFED) • Distributed Agents for Information Warfare (DAIWatch) 2
 3
3
 Cyber. Wolf Outline • Program Description – Objective – Problem Statement – Architecture – Implementation – Device Experts (DE) • Task Goals • Progress 4
Cyber. Wolf Outline • Program Description – Objective – Problem Statement – Architecture – Implementation – Device Experts (DE) • Task Goals • Progress 4
 Cyberwolf Objective • Objective – Develop a versatile, scaleable, and extensible enterprise security management and CND tool – Utilizes expert system rule-based correlation of IDS and network management events • Goal – Reduce the workload of network security personnel responsible for maintaining security of the enterprise while at the same time providing more accurate network situational assessment information 5
Cyberwolf Objective • Objective – Develop a versatile, scaleable, and extensible enterprise security management and CND tool – Utilizes expert system rule-based correlation of IDS and network management events • Goal – Reduce the workload of network security personnel responsible for maintaining security of the enterprise while at the same time providing more accurate network situational assessment information 5
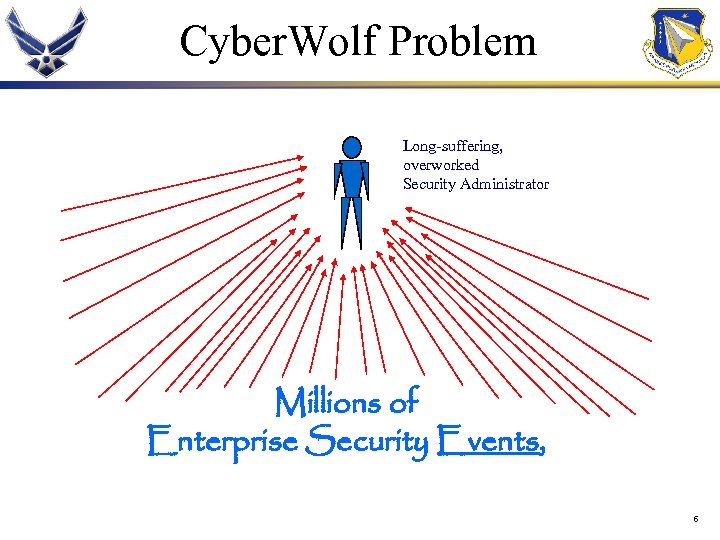 Cyber. Wolf Problem Long-suffering, overworked Security Administrator Millions of Enterprise Security Events, 6
Cyber. Wolf Problem Long-suffering, overworked Security Administrator Millions of Enterprise Security Events, 6
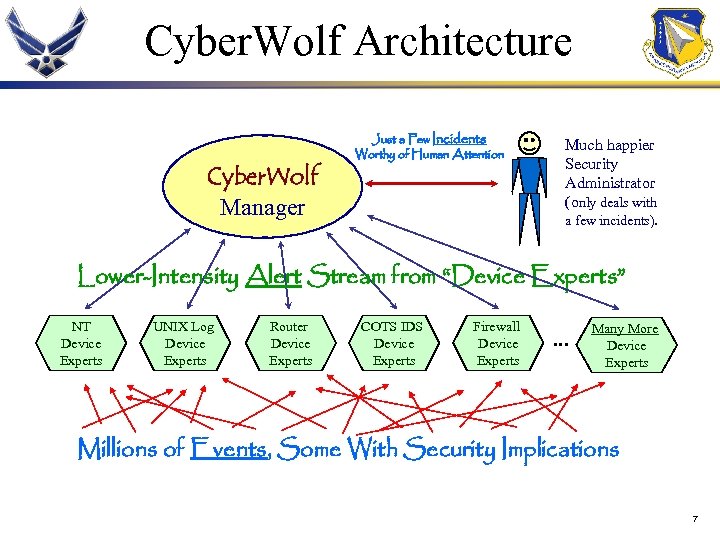 Cyber. Wolf Architecture Cyber. Wolf Manager Just a Few Incidents Worthy of Human Attention Much happier Security Administrator (only deals with a few incidents). Lower-Intensity Alert Stream from “Device Experts” NT Device Experts UNIX Log Device Experts Router Device Experts COTS IDS Device Experts Firewall Device Experts … Many More Device Experts Millions of Events, Some With Security Implications 7
Cyber. Wolf Architecture Cyber. Wolf Manager Just a Few Incidents Worthy of Human Attention Much happier Security Administrator (only deals with a few incidents). Lower-Intensity Alert Stream from “Device Experts” NT Device Experts UNIX Log Device Experts Router Device Experts COTS IDS Device Experts Firewall Device Experts … Many More Device Experts Millions of Events, Some With Security Implications 7
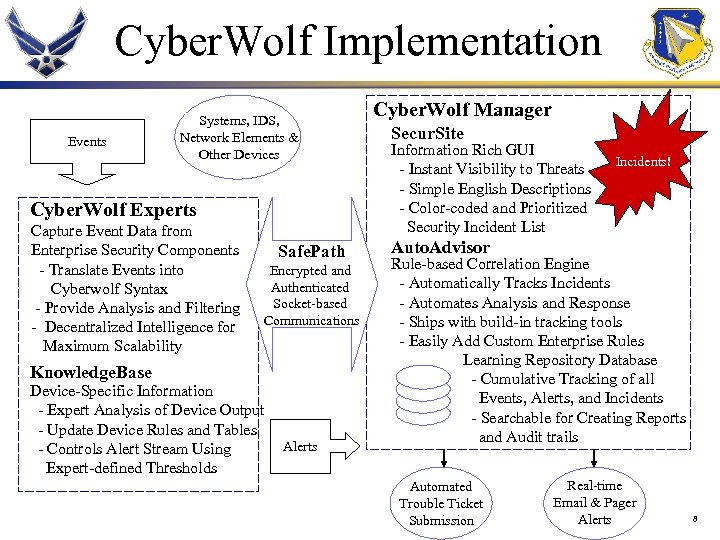 Cyber. Wolf Implementation Events Systems, IDS, Network Elements & Other Devices Cyber. Wolf Experts Capture Event Data from Enterprise Security Components - Translate Events into Cyberwolf Syntax - Provide Analysis and Filtering - Decentralized Intelligence for Maximum Scalability Safe. Path Encrypted and Authenticated Socket-based Communications Knowledge. Base Device-Specific Information - Expert Analysis of Device Output - Update Device Rules and Tables - Controls Alert Stream Using Expert-defined Thresholds Alerts Cyber. Wolf Manager Secur. Site Information Rich GUI - Instant Visibility to Threats - Simple English Descriptions - Color-coded and Prioritized Security Incident List Incidents! Auto. Advisor Rule-based Correlation Engine - Automatically Tracks Incidents - Automates Analysis and Response - Ships with build-in tracking tools - Easily Add Custom Enterprise Rules Learning Repository Database - Cumulative Tracking of all Events, Alerts, and Incidents - Searchable for Creating Reports and Audit trails Automated Trouble Ticket Submission Real-time Email & Pager Alerts 8
Cyber. Wolf Implementation Events Systems, IDS, Network Elements & Other Devices Cyber. Wolf Experts Capture Event Data from Enterprise Security Components - Translate Events into Cyberwolf Syntax - Provide Analysis and Filtering - Decentralized Intelligence for Maximum Scalability Safe. Path Encrypted and Authenticated Socket-based Communications Knowledge. Base Device-Specific Information - Expert Analysis of Device Output - Update Device Rules and Tables - Controls Alert Stream Using Expert-defined Thresholds Alerts Cyber. Wolf Manager Secur. Site Information Rich GUI - Instant Visibility to Threats - Simple English Descriptions - Color-coded and Prioritized Security Incident List Incidents! Auto. Advisor Rule-based Correlation Engine - Automatically Tracks Incidents - Automates Analysis and Response - Ships with build-in tracking tools - Easily Add Custom Enterprise Rules Learning Repository Database - Cumulative Tracking of all Events, Alerts, and Incidents - Searchable for Creating Reports and Audit trails Automated Trouble Ticket Submission Real-time Email & Pager Alerts 8
 Cyber. Wolf Device Experts Each DE utilizes less than 3% of CPU during operation • Gauntlet v 4. 5/5. 5 Firewall DE • Side. Winder Firewall DE • Raptor Firewall DE • Pix Firewall DE • Zone Alarm DE • Black Ice DE • Real. Secure v 6. 0 IDS DE • Net. Radar IDS DE • Snort IDS DE • • • HP Openview NNM DE SNMP DE Nmap DE Cisco Router DE Ascend Router DE Windows 95/98/NT/2000 DE Solaris DE Linux DE ASIM/CIDDs 9
Cyber. Wolf Device Experts Each DE utilizes less than 3% of CPU during operation • Gauntlet v 4. 5/5. 5 Firewall DE • Side. Winder Firewall DE • Raptor Firewall DE • Pix Firewall DE • Zone Alarm DE • Black Ice DE • Real. Secure v 6. 0 IDS DE • Net. Radar IDS DE • Snort IDS DE • • • HP Openview NNM DE SNMP DE Nmap DE Cisco Router DE Ascend Router DE Windows 95/98/NT/2000 DE Solaris DE Linux DE ASIM/CIDDs 9
 Cyber. Wolf / FAA Goals • Phase 1 – Demo of Cyber. Wolf’s automated attack analytics capabilities for the CSIRC • Phase 2 – Input from ISS sensors not currently connected to the CSIRC (ISS Real. Secure). Removal of discrepancies of sensor input including false positives, data reduction, cross correlation and integration. 10
Cyber. Wolf / FAA Goals • Phase 1 – Demo of Cyber. Wolf’s automated attack analytics capabilities for the CSIRC • Phase 2 – Input from ISS sensors not currently connected to the CSIRC (ISS Real. Secure). Removal of discrepancies of sensor input including false positives, data reduction, cross correlation and integration. 10
 Cyber. Wolf / FAA Progress • Money on contract in late February • Beginning evaluation later this month • Contract to be completed by September 11
Cyber. Wolf / FAA Progress • Money on contract in late February • Beginning evaluation later this month • Contract to be completed by September 11
 Air Force Enterprise Defense (AFED) 12
Air Force Enterprise Defense (AFED) 12
 AFED Outline • Program Description – Quad Chart – Components – Architecture – Capabilities • Task Goals • Progress 13
AFED Outline • Program Description – Quad Chart – Components – Architecture – Capabilities • Task Goals • Progress 13
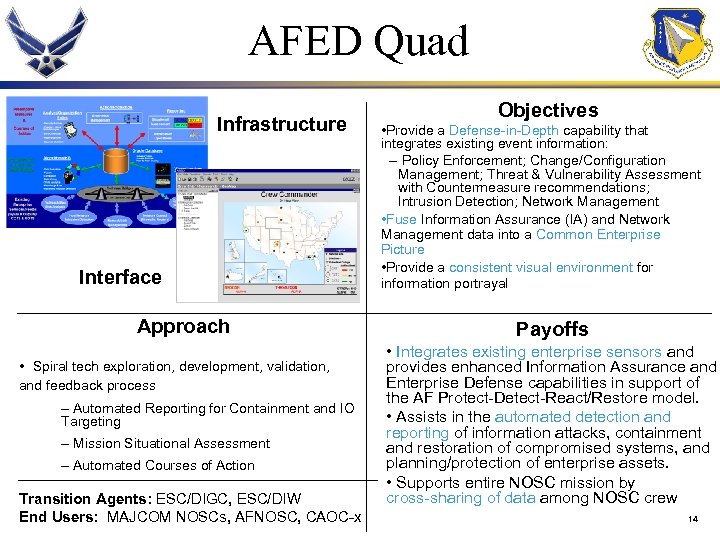 AFED Quad Infrastructure Interface Approach • Spiral tech exploration, development, validation, and feedback process – Automated Reporting for Containment and IO Targeting – Mission Situational Assessment – Automated Courses of Action Transition Agents: ESC/DIGC, ESC/DIW End Users: MAJCOM NOSCs, AFNOSC, CAOC-x Objectives • Provide a Defense-in-Depth capability that integrates existing event information: – Policy Enforcement; Change/Configuration Management; Threat & Vulnerability Assessment with Countermeasure recommendations; Intrusion Detection; Network Management • Fuse Information Assurance (IA) and Network Management data into a Common Enterprise Picture • Provide a consistent visual environment for information portrayal Payoffs • Integrates existing enterprise sensors and provides enhanced Information Assurance and Enterprise Defense capabilities in support of the AF Protect-Detect-React/Restore model. • Assists in the automated detection and reporting of information attacks, containment and restoration of compromised systems, and planning/protection of enterprise assets. • Supports entire NOSC mission by cross-sharing of data among NOSC crew 14
AFED Quad Infrastructure Interface Approach • Spiral tech exploration, development, validation, and feedback process – Automated Reporting for Containment and IO Targeting – Mission Situational Assessment – Automated Courses of Action Transition Agents: ESC/DIGC, ESC/DIW End Users: MAJCOM NOSCs, AFNOSC, CAOC-x Objectives • Provide a Defense-in-Depth capability that integrates existing event information: – Policy Enforcement; Change/Configuration Management; Threat & Vulnerability Assessment with Countermeasure recommendations; Intrusion Detection; Network Management • Fuse Information Assurance (IA) and Network Management data into a Common Enterprise Picture • Provide a consistent visual environment for information portrayal Payoffs • Integrates existing enterprise sensors and provides enhanced Information Assurance and Enterprise Defense capabilities in support of the AF Protect-Detect-React/Restore model. • Assists in the automated detection and reporting of information attacks, containment and restoration of compromised systems, and planning/protection of enterprise assets. • Supports entire NOSC mission by cross-sharing of data among NOSC crew 14
 AFED Goals • Merge network management and security tools and data to provides a better enterprise picture • Provide analysts with improved host, security, and course of action information – Simplify access to data via drill down menus from the same GUI • Reduce the workload of analysts – Provide data correlation capabilities • Combines network and host based sensors • Demonstrates R&D technology to operational units 15
AFED Goals • Merge network management and security tools and data to provides a better enterprise picture • Provide analysts with improved host, security, and course of action information – Simplify access to data via drill down menus from the same GUI • Reduce the workload of analysts – Provide data correlation capabilities • Combines network and host based sensors • Demonstrates R&D technology to operational units 15
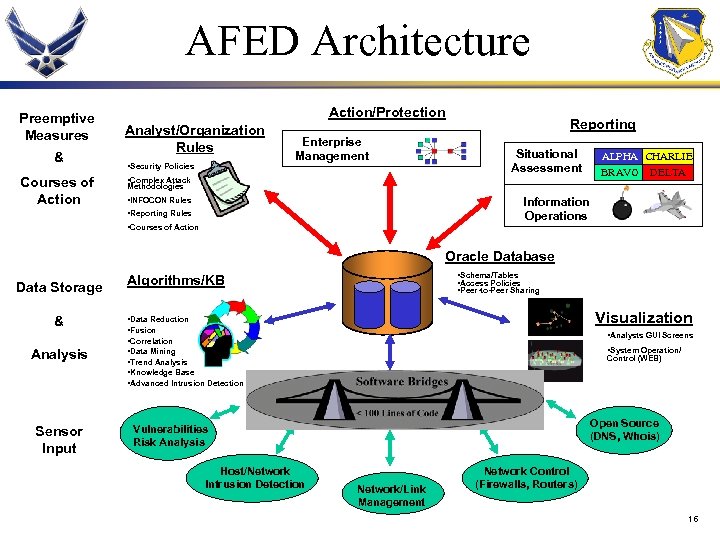 AFED Architecture Preemptive Measures & Courses of Action/Protection Analyst/Organization Rules • Security Policies Enterprise Management Reporting Situational Assessment • Complex Attack ALPHA CHARLIE BRAVO DELTA Methodologies Information Operations • INFOCON Rules • Reporting Rules • Courses of Action Oracle Database Data Storage & Analysis Sensor Input • Schema/Tables • Access Policies • Peer-to-Peer Sharing Algorithms/KB Visualization • Data Reduction • Fusion • Correlation • Data Mining • Trend Analysis • Knowledge Base • Advanced Intrusion Detection • Analysts GUI Screens • System Operation/ Control (WEB) Open Source (DNS, Whois) Vulnerabilities Risk Analysis Host/Network Intrusion Detection Network/Link Management Network Control (Firewalls, Routers) 16
AFED Architecture Preemptive Measures & Courses of Action/Protection Analyst/Organization Rules • Security Policies Enterprise Management Reporting Situational Assessment • Complex Attack ALPHA CHARLIE BRAVO DELTA Methodologies Information Operations • INFOCON Rules • Reporting Rules • Courses of Action Oracle Database Data Storage & Analysis Sensor Input • Schema/Tables • Access Policies • Peer-to-Peer Sharing Algorithms/KB Visualization • Data Reduction • Fusion • Correlation • Data Mining • Trend Analysis • Knowledge Base • Advanced Intrusion Detection • Analysts GUI Screens • System Operation/ Control (WEB) Open Source (DNS, Whois) Vulnerabilities Risk Analysis Host/Network Intrusion Detection Network/Link Management Network Control (Firewalls, Routers) 16
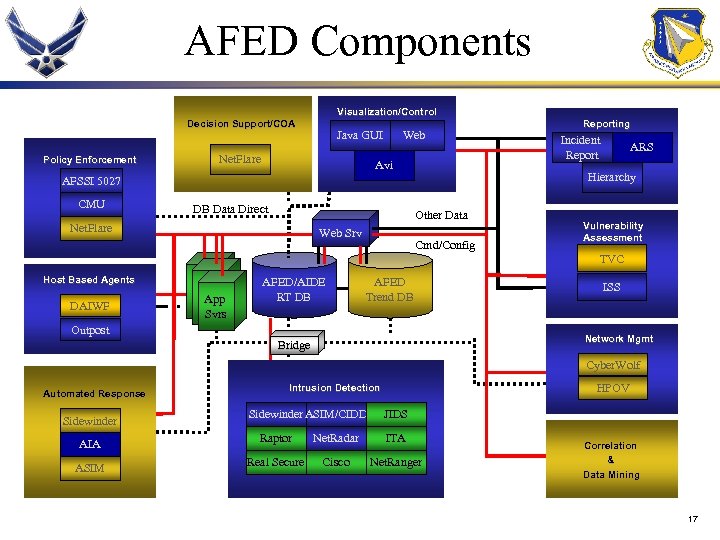 AFED Components Visualization/Control Decision Support/COA Policy Enforcement Java GUI Net. Flare Web Avi DB Data Direct Other Data Net. Flare Web Srv Incident Report ARS Hierarchy AFSSI 5027 CMU Reporting Cmd/Config Vulnerability Assessment TVC Host Based Agents DAIWF App Svrs AFED/AIDE RT DB AFED Trend DB Outpost ISS Network Mgmt Bridge Cyber. Wolf Automated Response Sidewinder HPOV Intrusion Detection Sidewinder ASIM/CIDD JIDS AIA Raptor Net. Radar ITA ASIM Real Secure Cisco Net. Ranger Correlation & Data Mining 17
AFED Components Visualization/Control Decision Support/COA Policy Enforcement Java GUI Net. Flare Web Avi DB Data Direct Other Data Net. Flare Web Srv Incident Report ARS Hierarchy AFSSI 5027 CMU Reporting Cmd/Config Vulnerability Assessment TVC Host Based Agents DAIWF App Svrs AFED/AIDE RT DB AFED Trend DB Outpost ISS Network Mgmt Bridge Cyber. Wolf Automated Response Sidewinder HPOV Intrusion Detection Sidewinder ASIM/CIDD JIDS AIA Raptor Net. Radar ITA ASIM Real Secure Cisco Net. Ranger Correlation & Data Mining 17
 AFED Capabilities • Intrusion Detection – Merges event and session data from COTS/GOTS sensors (e. g. , ASIM/CIDDS, Netradar, Real Secure, …) – Translates outputs into standard categories • Visualization – Provide a consistent visual environment – Data views customized for crew positions • Policy Enforcement – Allows users to define and alert on site policies – Allows sites to map network and monitors changes in host OS and services • DAA/CTO – Automates DAA and CTO processes – Verify and update CTO information via monitoring 18
AFED Capabilities • Intrusion Detection – Merges event and session data from COTS/GOTS sensors (e. g. , ASIM/CIDDS, Netradar, Real Secure, …) – Translates outputs into standard categories • Visualization – Provide a consistent visual environment – Data views customized for crew positions • Policy Enforcement – Allows users to define and alert on site policies – Allows sites to map network and monitors changes in host OS and services • DAA/CTO – Automates DAA and CTO processes – Verify and update CTO information via monitoring 18
 AFED Capabilities • Vulnerability Assessment – Commercial Network scanner integrated – Host based checks performed • Network Management – Provides correlation between network events and intrusion events – Provides access to host software and hardware inventories to assist identifying vulnerabilities, and security compliance • Modeling & Simulation – Allows decision makers to perform tradeoff analysis of course-of-actions • Reporting – Automate the reporting process 19
AFED Capabilities • Vulnerability Assessment – Commercial Network scanner integrated – Host based checks performed • Network Management – Provides correlation between network events and intrusion events – Provides access to host software and hardware inventories to assist identifying vulnerabilities, and security compliance • Modeling & Simulation – Allows decision makers to perform tradeoff analysis of course-of-actions • Reporting – Automate the reporting process 19
 AFED / FAA Goals • Optimization of IDS rule sets – Using AFED, operator reduced daily events by 60% at AFRL site • Cross site/sensor correlation – Hierarchical reporting capability • Comparison of different sensors 20
AFED / FAA Goals • Optimization of IDS rule sets – Using AFED, operator reduced daily events by 60% at AFRL site • Cross site/sensor correlation – Hierarchical reporting capability • Comparison of different sensors 20
 AFED / FAA Progress • Funds contracted in late February • Received 1 months worth of sensor data – Awaiting additional sensor’s data • Data loaded into AFED database and appropriate data views created • Administrator beginning to examine/optimize rule set 21
AFED / FAA Progress • Funds contracted in late February • Received 1 months worth of sensor data – Awaiting additional sensor’s data • Data loaded into AFED database and appropriate data views created • Administrator beginning to examine/optimize rule set 21
 Distributed Agents for Information Warfare (DAIWatch) 22
Distributed Agents for Information Warfare (DAIWatch) 22
 DAIWatch Outline • Program Description – Discriminators – Architecture – Technology – Benefits • Task Goals • Progress 23
DAIWatch Outline • Program Description – Discriminators – Architecture – Technology – Benefits • Task Goals • Progress 23
 DAIWatch Discriminators DAIWatch. TM provides information security protection against the most sophisticated attackers including the Cyber Terrorist vs. the current emphasis of commercial products on hackers • Firewalls and related layered products cannot protect the network from internal activities: DAIWatch approach is host based. • Current technologies are signature based: DAIWatch uses activity recognition • Existing Systems are stovepiped: DAIWatch integrates across existing information system monitors • Current Software is static: DAIWatch uses smart dynamic agents. 24
DAIWatch Discriminators DAIWatch. TM provides information security protection against the most sophisticated attackers including the Cyber Terrorist vs. the current emphasis of commercial products on hackers • Firewalls and related layered products cannot protect the network from internal activities: DAIWatch approach is host based. • Current technologies are signature based: DAIWatch uses activity recognition • Existing Systems are stovepiped: DAIWatch integrates across existing information system monitors • Current Software is static: DAIWatch uses smart dynamic agents. 24
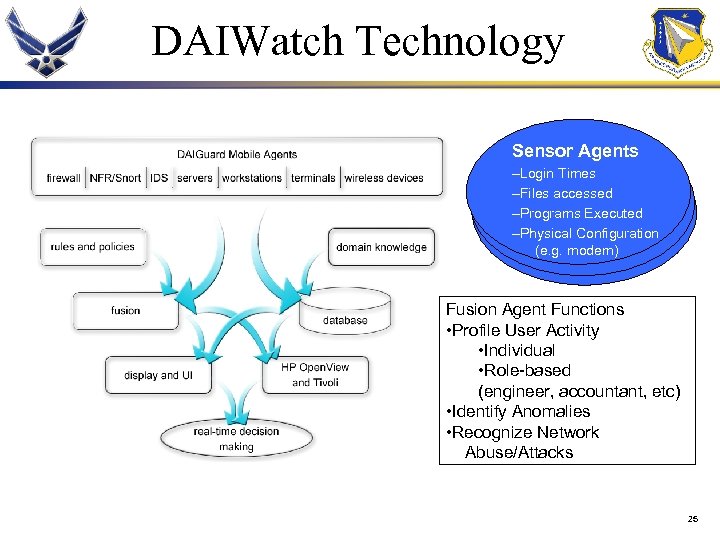 DAIWatch Technology Sensor Agents –Login Times –Files accessed –Programs 1 Executed –Physical Configuration (e. g. modem) Fusion Agent Functions • Profile User Activity • Individual • Role-based (engineer, accountant, etc) • Identify Anomalies • Recognize Network Abuse/Attacks 25
DAIWatch Technology Sensor Agents –Login Times –Files accessed –Programs 1 Executed –Physical Configuration (e. g. modem) Fusion Agent Functions • Profile User Activity • Individual • Role-based (engineer, accountant, etc) • Identify Anomalies • Recognize Network Abuse/Attacks 25
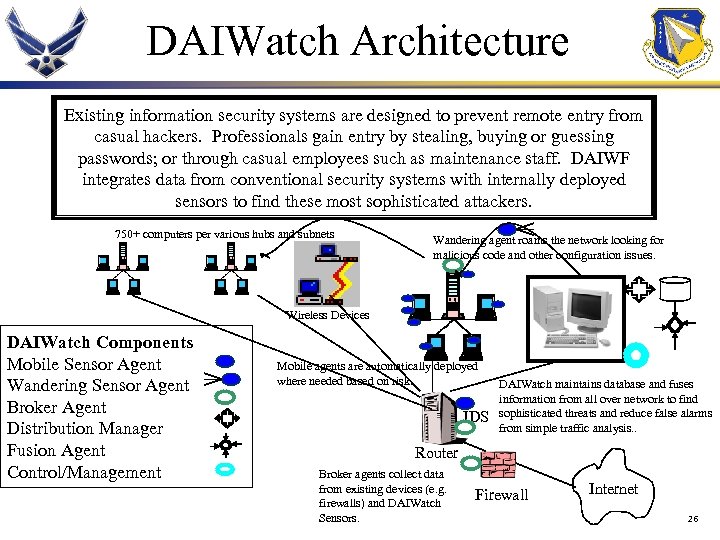 DAIWatch Architecture Existing information security systems are designed to prevent remote entry from casual hackers. Professionals gain entry by stealing, buying or guessing passwords; or through casual employees such as maintenance staff. DAIWF integrates data from conventional security systems with internally deployed sensors to find these most sophisticated attackers. 750+ computers per various hubs and subnets Wandering agent roams the network looking for malicious code and other configuration issues. Wireless Devices DAIWatch Components Mobile Sensor Agent Wandering Sensor Agent Broker Agent Distribution Manager Fusion Agent Control/Management Mobile agents are automatically deployed where needed based on risk. IDS DAIWatch maintains database and fuses information from all over network to find sophisticated threats and reduce false alarms from simple traffic analysis. . Router Broker agents collect data from existing devices (e. g. firewalls) and DAIWatch Sensors. Firewall Internet 26
DAIWatch Architecture Existing information security systems are designed to prevent remote entry from casual hackers. Professionals gain entry by stealing, buying or guessing passwords; or through casual employees such as maintenance staff. DAIWF integrates data from conventional security systems with internally deployed sensors to find these most sophisticated attackers. 750+ computers per various hubs and subnets Wandering agent roams the network looking for malicious code and other configuration issues. Wireless Devices DAIWatch Components Mobile Sensor Agent Wandering Sensor Agent Broker Agent Distribution Manager Fusion Agent Control/Management Mobile agents are automatically deployed where needed based on risk. IDS DAIWatch maintains database and fuses information from all over network to find sophisticated threats and reduce false alarms from simple traffic analysis. . Router Broker agents collect data from existing devices (e. g. firewalls) and DAIWatch Sensors. Firewall Internet 26
 DAIWatch Benefits Next Generation Network Security Manager Focused on Sophisticated Attacks • Protects the Network - Recognizes Network Attacks, Especially Sophisticated Ones (Eg. Man-in-the-middle) Including Insider/Masquerader Threats • Reduces Liability Exposure - Improves Compliance With New Government Mandates (E. G. GLB, Unauthorized Access) • Saves Money (H/W) - Identifies Network Abuse (Webservers, Login Anomalies, Software Install, Policy Violations, Etc. ) • Saves Money (Staff) - Reduces System Administration Time Via Reasoning, Presentation and Drilldown of Data From Other Security Products • Improves Effectiveness of Security System - Identifies Intentional and Inadvertent Security Holes (Eg. Mis-configured Firewall) 27
DAIWatch Benefits Next Generation Network Security Manager Focused on Sophisticated Attacks • Protects the Network - Recognizes Network Attacks, Especially Sophisticated Ones (Eg. Man-in-the-middle) Including Insider/Masquerader Threats • Reduces Liability Exposure - Improves Compliance With New Government Mandates (E. G. GLB, Unauthorized Access) • Saves Money (H/W) - Identifies Network Abuse (Webservers, Login Anomalies, Software Install, Policy Violations, Etc. ) • Saves Money (Staff) - Reduces System Administration Time Via Reasoning, Presentation and Drilldown of Data From Other Security Products • Improves Effectiveness of Security System - Identifies Intentional and Inadvertent Security Holes (Eg. Mis-configured Firewall) 27
 DAIWatch / FAA Goals • Provide real time insider and outsider threat analysis for all network areas including health status of the network. • Phase 1 – Deploy to limited number of machines and receive accreditation to progress • Phase 2 – Initial deployment of approximately 40 -50 hosts would provide an opportunity for demonstrating the assessment and value of this tool in a controlled network environment. 28
DAIWatch / FAA Goals • Provide real time insider and outsider threat analysis for all network areas including health status of the network. • Phase 1 – Deploy to limited number of machines and receive accreditation to progress • Phase 2 – Initial deployment of approximately 40 -50 hosts would provide an opportunity for demonstrating the assessment and value of this tool in a controlled network environment. 28
 DAIWatch / FAA Progress • • Funds contracted on 12 March 2003 FAA received DAIWatch Server ORINCON/FAA set up the server and configured DAIWatch 1 Windows 2000 client installed and running Undergoing 1 week evaluation Waiting for approval software evaluation board Status / User Meeting on 15 May - ORINCON/FAA 29
DAIWatch / FAA Progress • • Funds contracted on 12 March 2003 FAA received DAIWatch Server ORINCON/FAA set up the server and configured DAIWatch 1 Windows 2000 client installed and running Undergoing 1 week evaluation Waiting for approval software evaluation board Status / User Meeting on 15 May - ORINCON/FAA 29
 Summary • Cyber. Wolf • Air Force Enterprise Defense (AFED) • Distributed Agents for Information Warfare (DAIWatch) 30
Summary • Cyber. Wolf • Air Force Enterprise Defense (AFED) • Distributed Agents for Information Warfare (DAIWatch) 30
 Questions? ? Lt. Matt Manger Rome Research Site Matthew. Manger@rl. af. mil (315) 330 -1874 6 May 2003 31
Questions? ? Lt. Matt Manger Rome Research Site Matthew. Manger@rl. af. mil (315) 330 -1874 6 May 2003 31


