8aa0637c163aef3f5ebdbc6ae2b9dc55.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO HEALTHCARE Y S Rajan Hon. Distinguished Professor, ISRO/DOS, Bangalore Chairperson, Board of Governors, NIT, Manipur ysrajan 1944@gmail. com www. ysrajan. com Distinguished Guest Lecture delivered at , International Institute of Health Management Research New Delhi on 25 th July 2014, 1

KEY CONSIDERATIONS • ACCESS: NOT 24 X 7 FOR MOST INDIANS • AFFORDABLE: NOT FREE • REGULARITY, YES!! • FOR ALL: YES!! YESS!!! 2

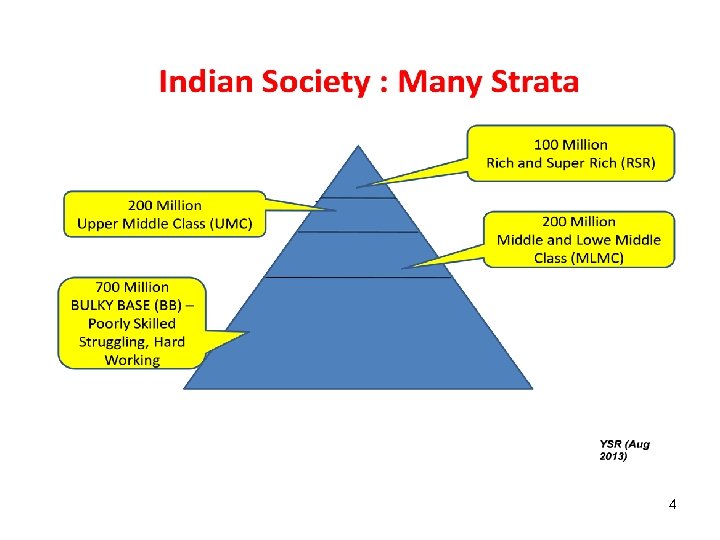
INDIANS NOT ALL SAME • INDIANS ARE NOW 125 CRORES GROWING STILL, MAY REACH 160 • EXISTENTIAL REALITIES OF THEIR LIVES VARY IN GREAT CONTRASTS • PUBLIC DISCOURSE IS OFTEN HIJACKED BY A VOCAL MINORITY, INFLUENTIAL, CONNECTED…… 3
4

HEALTHCARE EXPECTATIONS VARY…. . • ALL THROUGH THE PYRAMID • NOT DEPENDENT ON SINGLE PARAMETER LIKE INCOME, EDUCAITON LEVEL, ETC. , • ALMOST ALL INDIANS LOOK AT MODERN ALLOPATHY WITH MANY GLASSES! 5

EXPECATATIONS VARY…. (contd) • RICH AND SUPERRICH (RSR) (INCLUDES VVIPS’s AND VIP’s) CAN GET WHATEVER THEY WANT: VARIATIONS DEPENDING UPON THEIR LOCAL BACKGROUNDS…. . SAY FROM RURAL INDIA TO CORPORATE WORLD, TO PEOPLE IN POWER………… • UPPER MIDDLE CLASS (UMC) DESIRES EVERYTHING WHICH RSR HAS, BUT MONEY COSTRAINT. THE PRIVATE SECTOR HOSPITAL BOOM IS MAINLY DUE TO THEM AND SOME RSR. 6

EXPECATATIONS VARY…. (contd) • Middle and Lower Middle class (MLMC) are cash constrained would like to have access to good Govt. hospitals, Afraid of health care costs of big private hospitals. • A nascent Health Insurance sector is growing around UMC’s and MMC’s. • Indians at the Bulky Base (BB) are afraid of falling sick. They get some alternate medicines or medicines given by pharma stores. Only when in deeper trouble they seek to visit a formal doctor or private doctor, PHC’s etc, Their health care expectations are minimal. 7

HEALTHCARE ACCESS STATISTICS • HUGE DEMAND – SUPPLY GAP - 0. 7 hospital beds per 1000 (World 3. 96) - 0. 59 doctors per 1000 (World 2. 25) – Two thirds of these doctors in urban areas - 75% services for dental, orthopedics, vascular diseases in PRIVATE SECTOR - 40% services of communicable diseases in PRIVATE SECTOR - 68% of est. 15077 hospitals are in private sector - Private sector has 75% specialists and 85% of technology (contd…. ) 8

HEALTHCARE ACCESS STATISTICS (contd……) • Growth of Private Sector Services - Hospital Beds 28% in 1973; 61% in 1996 about 78% in 2009 - Bed occupancy is 44% in private sector and 66% in public sector. - Indian health care industry CAGR 16% - Medical tourism CAGR 30% - Less than 10% population covered by Health Insurance (Courtesy: Achla Khanna, TIFAC from various sources) 9

AFFORDABLE ACCESS FOR BULKY BASE (BB) • BB are mostly in rural areas and in the urban slums. • Those in urban slums can land up in a Govt hospitals with long queues. • Those in rural have only 0. 2 doctors per 1000 persons. They have to rush to nearby towns, poorly equipped. PHC’s in villages, have few diagnostic capacity • Also qualified doctors would not like to be in rural area for their career/personal reasons. 10

AFFORDABLE ACCESS FOR BULKY BASE (BB) (Contd……. ) • Modern clinical delivery without minimum lab test, xray and ultrasound is almost impossible. No good clinical judgment by doctor possible. Even for “telemedicine” some basic data is required to be seen by the physician. • As a follow up to Technology Vision for India 2020 by TIFAC, Mobile Diagnostic Lab was conceived by a group of doctors, Lead person, Dr. (Col. ) Retd. Chandrasekhar Pant, an eminent radiologist. • First major demo at Uttarakhand by TIFAC and State Govt. 11

MOBILE DIAGNOSTIC CENTRE • Doctors and paramedics stay at Almora, good school/other facilities. 10 days at a stratch go round village routes – about 5 days off (two slots) (Kumoon region) • 24 ft long bus chassis. 12. 5 KVA noise free/vibration less diesel generator, as electricity is big problem in most of India (400 million uncovered; many more erratic supplies in rural / urban areas). Equipment cannot function, without a diesel generator; therefore efficiency of delivery high with DG. 12

MOBILE DIAGNOSTIC CENTRE (Contd…) • X-ray, Ultrasound, lab and ECG, gynaecological table and small pharma. Collection of hospital waste under the bus to be disposed safety, a computer, small pharma supply for a few day stock foldable tent to top for epidemic type cases, a flat screen t. V for entertainment. • One Lady doctor, one male physician, • Radiologist, Paramedics for the equipment, a multi utility technician- they followed the van in Quals (Contd…. . ) 13

MOBILE DIAGNOSTIC CENTRE (Contd…) • Operational responsibility by a local engineering college BISR – fully empowered. TIFAC & Uttarakhand Govt. shared operational expenses. TIFAC all the developmental cost of Mobile Centre. • Many other innovative administrative / incentive / management methods. • Total camps in 5 ½ years (20. 10. 2002 to 31. 03. 08) were 1018, almost one camp every alternate day. • Treating about 1, 000 patients. 54% were BPL. 60% women. Only one scheduled camp was missed during the 5 ½ years. 14

SUCCESSFUL REPLICATION • Success of TIFAC –Govt. of Uttarakhand model led to further replication. Go Uk and USAID expanded it further. • See USAID Report “Reaching Underserved Communities through Mobile Health Vans in Uttarakhand, India” March 2012. • Some quotes: Evaluation found BISR operated van had a strong management structure, demonstrated independence and ensured attendance, provided a wide range of services (contd………) 15

SUCCESSFUL REPLICATION (contd…) • Good quality services, and supplies and attended to a large number of patients. • The fixed-date approach adopted by TIFAC van was easy for the community to remember and together with excellent record of holding camps as planned, resulted in greater attendance in the camps. • The scale up (in partnership with USAID) started in 2009 and currently a total (contd…) 16

SUCCESSFUL REPLICATION (contd…) • of 30 MHV’s having 140 qualified staff are operating in four model schemes in Uttarakhand with at least 2 vans in each of the 14 districts. • FAST FORWARD…SCALING UP. . • GOI’s NRHM adopted this model and this has resulted in the launch of 1951 MMu in 442 districts spread all over India. PPP mods. 7097 Emergency Response vehicles and 7458 Ambulance… 17

AREAS FOR RESEARCH • Has this NRHM expansion also kept up with the quality and regularity of services as in Uttarakhand? • What about addition of “telemedicine services” through satellites, of consulting specialists? Technology-Business Model. User satisfaction? • Can it further explore other markets: Urban slum/lower middle class localities? Rural rich and middle class? Also innovative healthcum-tourism trips to Indians and foreigners? 18

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO MLMC. . • Govts usually respond to possibilities of delivery to BB as they are huge vote-bank. Then since UMC’s are the VOCAL POWER ELITES, it is fashionable to have AIIMS for each State etc. , through they are very costly. • Left in the lurch are the MLMC’s High end private sector hospitals too costly. Low end private sector too meager compared to the capabilities of Govt capitals which are not available, easily…. 19

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO MLMC (contd…) • Can there be higher end Mobile Centre for diagnosis in small / medium towns and large cities, may be two or three in TANDEM, bringing a very good diagnostic Hospitals in fixed-places-fixed-dates? • Then networked PRIVATE CLINICS to treat further. • May be all above covered by a special Insurance Policy. 20

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO MLMC (contd…) • Don’t ignore MLMC’s. They are about 200 million now. But as India grows large amount form BB will be shifted to MLMC’s. It may become about 500 million in a decade from now. • Huge market…. Think of business opportunities including for many from the neighbour hood, SAARC, ASEAN, AFRICA and Middle East. 21

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO UMC’s (contd…) • Their desires and demands are very huge but “pockets” have limitations. But it is a high value market. If India grows fast, UMC’s will be 300 million in about a decade-almost equivalent to the size of total of USA (318 million) • Many responsive technology-business innovations are required (including marketing) some examples… 22

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO UMC’s (contd…) • First they desire 24 x 7 attention: just as it is for ambulance or emergency. In this case a quick Check Van should go to the caller in about 15 min. Make essential checks. (It is not a big mobile van). It will naturally have high quality doctors-who can also communicate well. • Depending on the clinical needs and also based on the caller’s desires (UMC’s have 23

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO MLMC (contd…) • strong views and opinions, and “googled wisdom”. Arrange for immediate attention in the networked hospitals (Please remember the earlier statistics that private hospitals have only 44% occupancy of beds) • Innovative Health Insurance. . • More I leave to the innovative brains of IIMHR. 24

AFFORDABLE ACCESS TO RSR • The title should have been “Competitive delivery”. • How many of Indian RSR’s be attracted to Indian Hospitals? • How many foreign RSR’s & UMC’s be attracted to India? • This is ANOTHER BUSINESS MODEL. I like it because it can create huge income jobs for thousands of Indians. 25

OTHERS……… I have not addressed TRIBAL population in forests etc. , (about 50 million), or special need persons/physically challenged may be 100 million or the senior citizen 100 million and growing………………. . very specific and complex……………… 26

I DON’T WANT TO BORE YOU MORE! ASK QUESTIONS!! TRY TO DESTROY SOME OF MY ARGUMENTS!!!! 27

THANK YOU 28
8aa0637c163aef3f5ebdbc6ae2b9dc55.ppt