357fb7fd3a92596c140e9330ed08e5cc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78

AES 2011 Practice Management Course December 6, 2011 Gregory L. Barkley, M. D. Comprehensive Epilepsy Program Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, MI Associate Professor of Neurology Wayne State University

Outline 2012 Medicare Conversion Factor and SGR 2012 CPT Code Changes PQRI update e. Prescribing How to analyze your practice if the 27. 4% in the Conversion Factor is not overridden by Congress

Challenges in 2012 CMS cut Conversion Factor 7. 86% to $33. 9764 in 2011 due to reweighting of the work, practice expense and liability expense components of the relative value scale to maintain budget neutrality. CMS Final Rule cuts Conversion Factor in 2012 another 27. 4% to $24. 6712! PQRS changes for 2012 and beyond Electronic Prescribing penalties begin The legal battle over the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the proper title for the new health care reform law, is now being reviewed by the Supreme Court with a decision due by June 2012. Academic medical centers face increasing cuts in Federal and State support for patient care and training programs The failure of the “Super Committee” means across the board cuts in Federal Expenditures. Must upgrade electronic transfers from HIPAA X 12 4010 to 5010 by 1/1/2012
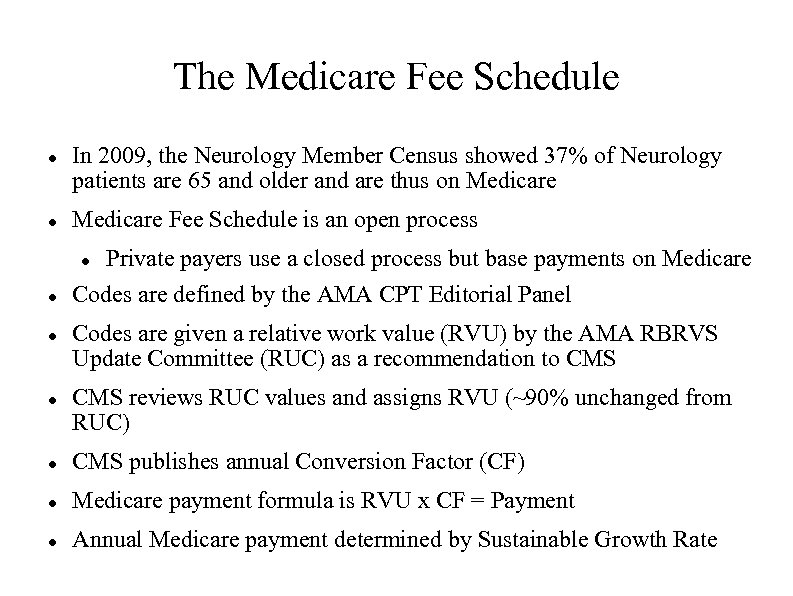
The Medicare Fee Schedule In 2009, the Neurology Member Census showed 37% of Neurology patients are 65 and older and are thus on Medicare Fee Schedule is an open process Private payers use a closed process but base payments on Medicare Codes are defined by the AMA CPT Editorial Panel Codes are given a relative work value (RVU) by the AMA RBRVS Update Committee (RUC) as a recommendation to CMS reviews RUC values and assigns RVU (~90% unchanged from RUC) CMS publishes annual Conversion Factor (CF) Medicare payment formula is RVU x CF = Payment Annual Medicare payment determined by Sustainable Growth Rate

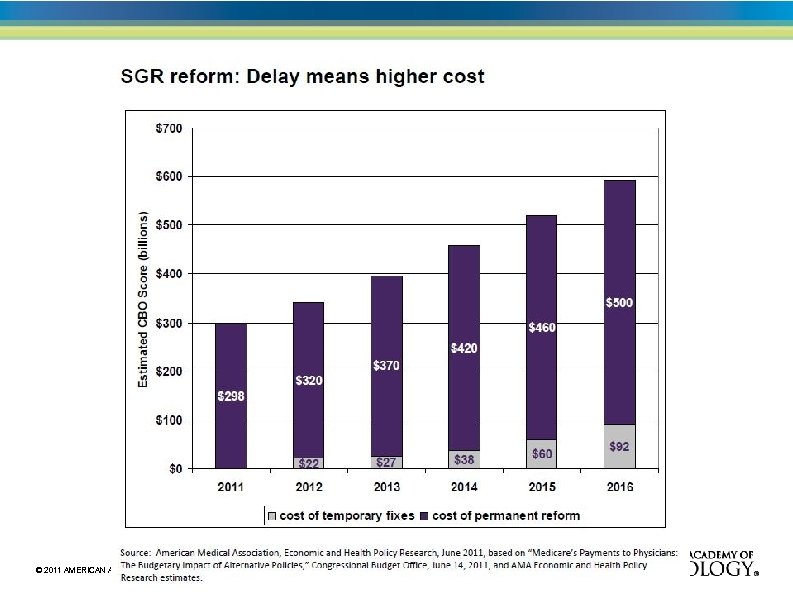
Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) Law passed in 1997, requires Medicare payments to follow a formula linked to the cost of medical care, MEI Medicare Economic Index (MEI) is a conservative government estimate of the rate of inflation of medical care Annual overrides have prevented decreased payments to physicians since 2002, but the law has not been changed so the deficit keeps building In 2011, temporary override prevented a 21% drop In 2012, payments will drop by 27. 4% unless another override is passed President Obama supports repeal of the SGR Total cost of repeal of the SGR will be $372 billion over 10 years Will Congress act to override the cuts?
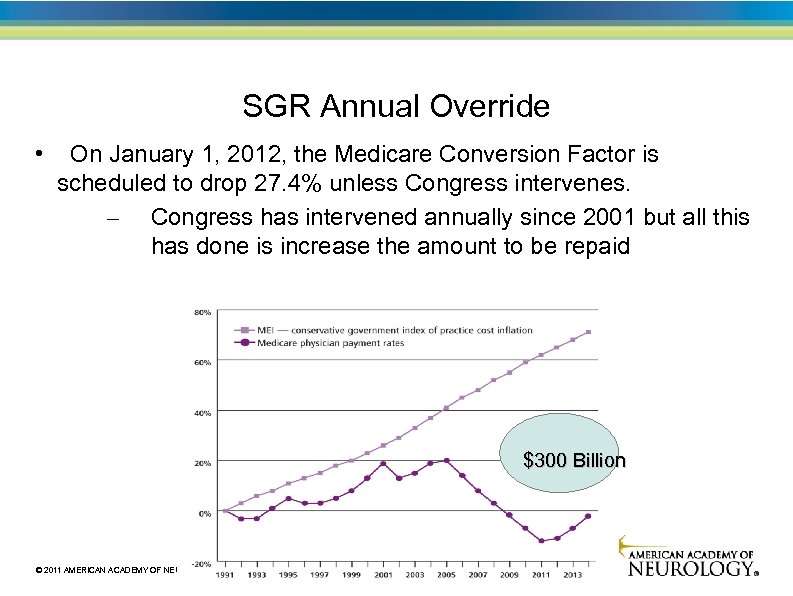
SGR Annual Override • On January 1, 2012, the Medicare Conversion Factor is scheduled to drop 27. 4% unless Congress intervenes. – Congress has intervened annually since 2001 but all this has done is increase the amount to be repaid $300 Billion © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY
© 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

What You Should Do Now • Call this AMA phone number: 800 -833 -6354 – Give your zip code and speak to staff for your 2 senators and representative • Call to ask for a permanent fix of the SGR formula before 1/1/12. Item 3. 1 proposed by 2010 Bowles-Simpson Report http: //www. fiscalcommission. gov/sites/fiscalcommission. gov/files/documents/The Momentof. Truth 12_1_2010. pdf • Or Go to this AMA website and fill in your information – Your senators and representative will receive the email http: //capwiz. com/ama/issues/alert/? alertid=53132696 © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

All Physicians are not Paid the Same, I New in 2011: some physicians are paid more by specialty Primary Care Incentive Payments (PCIP) now in place, 2011 -2015 Primary care physicians will be paid a 10% bonus for non-hospital E&M visits. The payments will be paid quarterly to primary care physicians. Does not apply to neurologists despite the attempts of the AAN to include neurologists.

All Physicians are not Paid the Same, II How much you are paid also depends on where you work Geographic Prof Cost Index (GPCI, or “gypsy”) adjusts fees based on regional cost differences Non-Facility(Office) Pricing Amount = [(Work RVU * Work GPCI) + (Transitioned Non-Facility Practice Expense (PE) RVU * PE GPCI) + (Malpractice (MP) RVU * MP GPCI)] * Conversion Factor (CF) The w. RVU section is weighted at 50%, The PE section is weighted at 45% and the malpractice section is weighted at 5% For neurology, a CMS estimate is that total expenses are physician work- 51%, practice expense- 45%, and PLI- 4% AMA estimates that the ACA will result in an increase in Medicare payments to physicians in 42 states by raising the work GPCI.

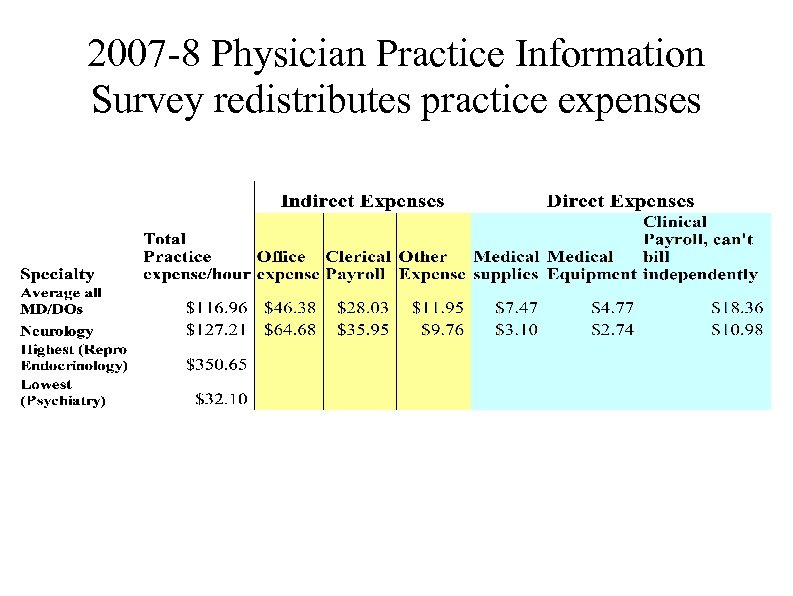
2007 -8 Physician Practice Information Survey redistributes practice expenses Average physician spends 2200 hours per year on patient care over 50 weeks Total direct and indirect office expenses are $127. 21 for average neurologist $116. 96/hr for average doctor Overall, there is a 3% increase in practice expense for neurologists Four year roll out of new practice expense payments 2010 -2013 Equipment is assumed to be used 50% of the time in a 48 hour work week except for CT/MRI which is assumed to be used 90% of time Increases in practice expense limited by budget neutrality resulting in decrease in the conversion factor and decreased payments for professional services

All Physicians are not Paid the Same, III Your type of practice and the site of service determines how you will be paid In private offices, payments are global In medical centers, payments to physicians are for professional fees only Technical payments by HOPPS as APCs to medical center Same applies to patients seen in emergency rooms who are not admitted For inpatients, payments to physicians are for professional fees only Technical payments are bundled IPPS as DRGs paid to hospital
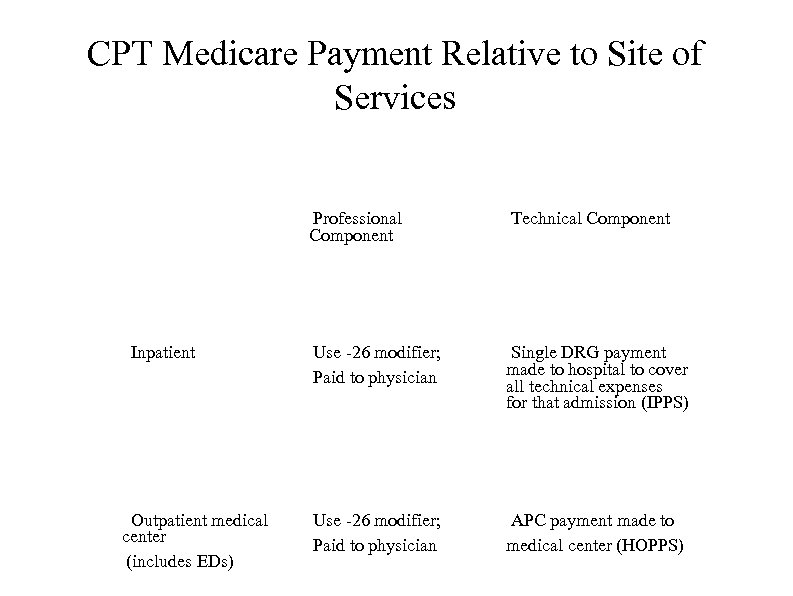
CPT Medicare Payment Relative to Site of Services Professional Component Inpatient Outpatient medical center (includes EDs) Technical Component Use -26 modifier; Paid to physician Single DRG payment made to hospital to cover all technical expenses for that admission (IPPS) Use -26 modifier; Paid to physician APC payment made to medical center (HOPPS)
2007 -8 Physician Practice Information Survey redistributes practice expenses
Annual Estimated Practice Expense for Neurologist
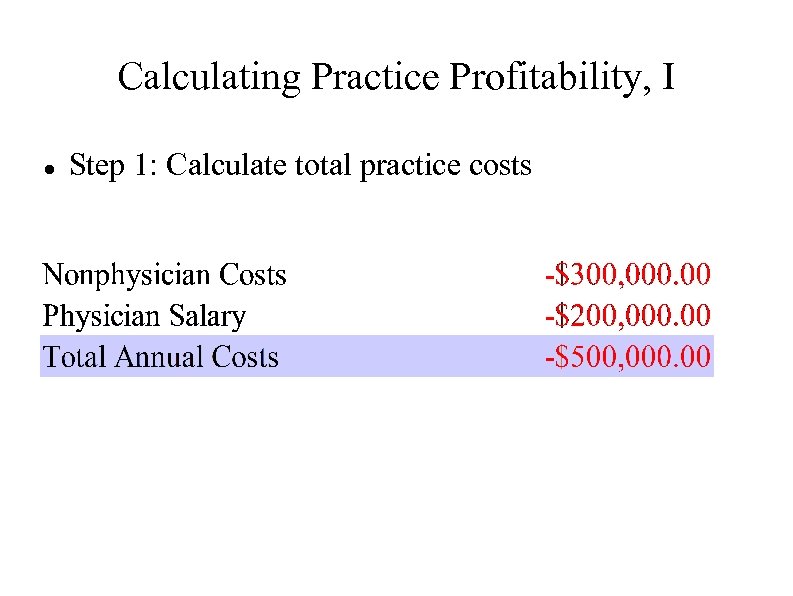
Calculating Practice Profitability, I Step 1: Calculate total practice costs
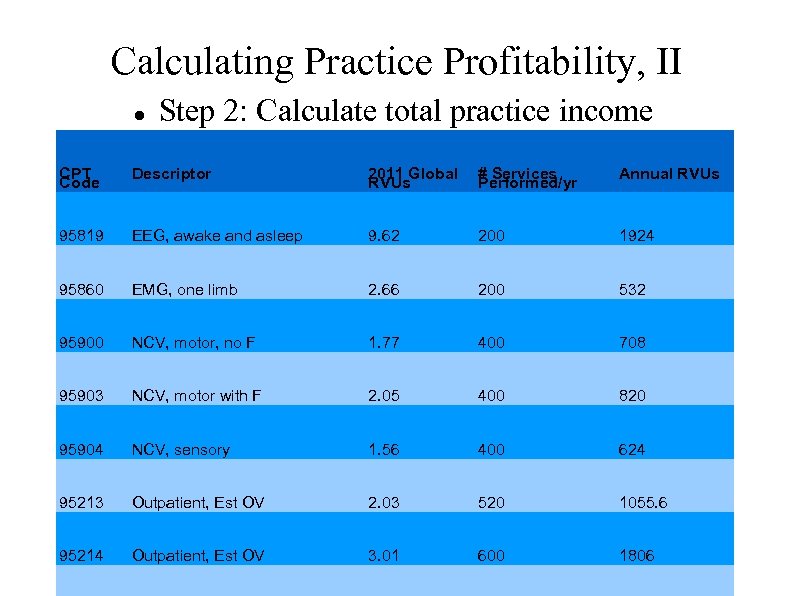
Calculating Practice Profitability, II Step 2: Calculate total practice income CPT Code Descriptor 2011 Global RVUs # Services Performed/yr Annual RVUs 95819 EEG, awake and asleep 9. 62 200 1924 95860 EMG, one limb 2. 66 200 532 95900 NCV, motor, no F 1. 77 400 708 95903 NCV, motor with F 2. 05 400 820 95904 NCV, sensory 1. 56 400 624 95213 Outpatient, Est OV 2. 03 520 1055. 6 95214 Outpatient, Est OV 3. 01 600 1806

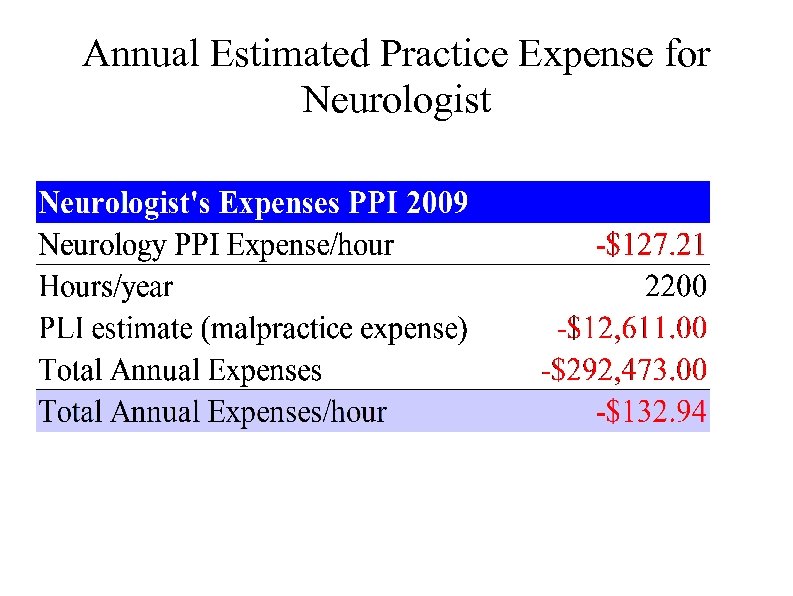
Calculating Practice Profitability, III Step 3: Calculate total practice costs For 2011, CMS payment is $33. 9764 • Will this be decreased 27. 4% in 2012? This gives this practice about a 10% margin of error or about a $60, 000 cushion in 2011 but. . .

Use Breakeven Analysis on Your Practice Service Income Analysis Determine your top 10 -20 services by CPT Code Include both E & M and procedure codes List your expense to provide the service List the payment by each payer Compare all EOBs (Explanation of Benefits) to contracted payment Vigorously pursue every discrepancy Compare payment to expenses to determine profit/loss per service

Can You Afford to Offer All of Your Present Services? Look at your service income analysis Which services are profitable and which are not? Do you offer some procedures that are consistently unprofitable? If it is an E & M service, does it produce a procedure that is profitable? Do you have some payers who consistently underpay your expense per RVU? Do a root cause analysis Is it because your costs are out of line? Are you not getting paid the contracted amount? Can you re-open negotiations about payment? Will you drop the payer if necessary?

Can You Afford To Go To The Hospital? In the ER and Hospital, you only collect professional fees Your practice expenses are low for seeing patients in hospital However, your office expenses continue when you are gone How much do you make per hour in the office vs. the hospital? Do hospitalized patients come to the office for follow up care and procedures? Do you offer office services that can provide revenue while you are away? EEG, EP, blood tests can be done while you are not present PA or NP with his/her own UPIN can see patients while you are away but not if they are billing “incident to” using your UPIN You must be present for an NP/PA to bill “incident to”

How to Improve Your Net Revenue, I Control costs Rent, supplies, staff each need to be scrutinized

How to Improve Your Net Revenue, II Check to make sure that your staff is not stealing from you If it involves money, someone will try and take it from you Set up checks & balances for all processes involving money Always have two people handling money Nearly 83% of 688 practice managers were affiliated at some point with medical offices where employee theft occurred (MGMA Survey 11/5/2010) Nearly 45% of practice managers reported cash stolen before or after it was recorded on the books. Profile of embezzler: first one in, last to leave, never takes a vacation, stops by on weekends, very friendly and helpful

HIPAA X 12 5010 Electronic Transaction Capture • All HIPAA X 12 Electronic Transactions with payors (e. g. eligibility verification claims, remittance advice) have to be upgraded from the current 4010 version to the newer 5010 version • This will enable payors to request more information in the future electronic transactions (adding more lines of information) • The change has to be operational by January 1, 2012 and it is a prerequisite for ICD 10 CM/PCS changes required by 10/1/2013 • Check your software to make sure that it is compliant now. You only have 3 weeks left to fix it. © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

2012 Practice Expense (PE) Changes • Third year of 4 year transition on PE methodology – CMS is using results of 2009 AMA Physician Practice Information Survey • • – www. ama-assn. org/go/ppisurvey Neurology $73 PE/hr, $127. 21 Total PE/hr; Overall increase 3% • Neurosurgery $81 PE/hr, $132. 52 Total PE/hr; Overall increase 2% Assume that imaging equipment such as CT and MRI is used 90% of the time instead of current 50% (plus multiple procedure payment reduction to Professional fee) – Other equipment remains at 50% usage for now – Work defined as 150, 000 minutes/year (48 hour work week)

2012 Three day payment rule • Physician practices which are wholly owned and operated by hospitals will have technical payments for all diagnostic services provided within three days of admission bundled with DRG • A PD modifier will be added to procedures. • Will start 1/1/2012 but there will be a phase-in period until July 1, 2012 to allow practices to adapt to changes

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95812, EEG 41 -60 minutes – – Total RVUs: 2011=9. 31, 2012=9. 70 Practice Expense: 2011=8. 16, 2012=9. 19 Professional: 2011=1. 60, 2012=1. 59 Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 08, No change • 95813, EEG > 1 hour – – Total RVUs: 2011=10. 48, 2012=10. 76 Practice Expense: 2011=8. 64, 2012=9. 95 Professional: 2011=2. 54, 2012=2. 54 Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 73, No change
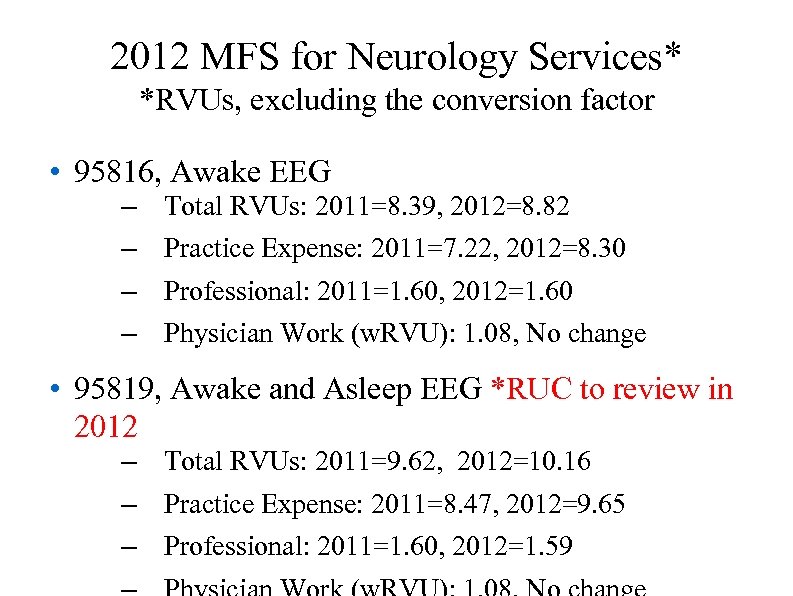
2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95816, Awake EEG – – Total RVUs: 2011=8. 39, 2012=8. 82 Practice Expense: 2011=7. 22, 2012=8. 30 Professional: 2011=1. 60, 2012=1. 60 Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 08, No change • 95819, Awake and Asleep EEG *RUC to review in 2012 – Total RVUs: 2011=9. 62, 2012=10. 16 – Practice Expense: 2011=8. 47, 2012=9. 65 – Professional: 2011=1. 60, 2012=1. 59

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95822, Sleep EEG – – Total RVUs: 2011=7. 84, 2012=9. 17 Practice Expense: 2011=7. 22, 2012=8. 66 Professional: 2011=1. 60, 2012=1. 59 Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 08, No change • 95824, EEG for Brain Death – – Total RVUs: 0. 00, No change Practice Expense: 0. 00, N/A Professional: 2011=1. 12, 2012=1. 11 Physician Work (w. RVU): 0. 74, No change

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95827, Overnight EEG – – Total RVUs: 2011=16. 52, 2012=18. 64 Practice Expense: 2011=15. 31, 2012=18. 12 Professional: 2011=1. 60, 2012=1. 60 Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 08, No change • 95829, Surgery Electrocorticogram – – Total RVUs: 2011=44. 12, 2012=42. 93 Practice Expense: 2011=37. 71, 2012=40. 06 Professional: 9. 11, 2012=9. 07 Physician Work (w. RVU): 6. 20, No change

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95950, Ambulatory Cassette EEG, unattended – Total RVUs: 2011=7. 99, 2012=7. 25 – Practice Expense: 2011=6. 38, 2012=6. 53 – Professional: 2011=2. 25, 2012=2. 23 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 51, No change • 95951, 24 Hour Video EEG – Total RVUs: 0. 00, *Carrier-defined technical expense – Practice Expense: *Carrier-defined technical expense – Professional: 2011=9. 14, 2012=9. 08 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 5. 99, No change – Hospital coders use 89. 19 for inpatient coding

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95953, 24 hour computerized digital EEG, unattended – Total RVUs: 2011=12. 19, 2012=9. 54 – Practice Expense: 2011=7. 56, 2012=8. 04 – Professional: 2011=4. 63, 2012=4. 58 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 3. 08 • 95956, 24 Hour attended EEG without video – Total RVUs: 2011=29. 82, 2012=31. 03 – Practice Expense: 2011=24. 6, 2012=29. 43 – Professional: 2011=5. 22, 2012=5. 21 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 3. 61 Cerebellum 2007 Weissman, Lichtman, Sanes

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95954, EEG with administration of drugs – Total RVUs: 2011=9. 15, 2012=9. 47 – Practice Expense: 2011=5. 8, 2012=8. 46 – Professional: 2011=3. 35, 2012=3. 46 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 2. 45 • 95955, EEG during surgery – Total RVUs: 2011=4. 96, 2012=4. 69 – Practice Expense: 2011=3. 48, 2012=4. 21 – Professional: 2011=1. 48, 2012=1. 49 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 01 Hippocampus 1995 Buzsaki and Sik

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95957, EEG Digital Analysis – Total RVUs: 2011=10. 01, 2012=9. 38 – Practice Expense: 2011=7. 05, 2012=8. 43 – Professional: 2011=2. 96, 2012=2. 93 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 98 • 95958, EEG monitoring, functional mapping (Wada Test) – Total RVUs: 2011=13. 39, 2012=10. 31 – Practice Expense: 2011=7. 08, 2012=9. 10 – Professional: 2011=5. 48, 2012=6. 27 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 4. 24

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95961, Electrode stimulation, brain, first hour – Total RVUs: 2011=7. 41, 2012=4. 99 – Practice Expense: 2011=2. 93, 2012=3. 52 – Professional: 2011=4. 48, 2012=4. 44 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 2. 97, no change • 95962, Electrode stimulation, brain, each additional hour – Total RVUs: 2011=6. 67, 2012=3. 73 – Practice Expense: 2011=1. 8, 2012=2. 19 – Professional: 2011=4. 79, 2012=4. 75 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 3. 21, no change

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • Technical Expenses not defined, only APCs assigned for MEG codes • 95965, MEG, spontaneous – Professional: 2012=12. 19 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 7. 99, no change • 95966, MEG, evoked, single – Professional: 2012=6. 08 – Physician Work 9 s. RVU): 3. 99, no change • 95967, MEG, evoked, each additional – Professional: 2012=5. 30 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 3. 49, no change

2012 MFS for Neurology Services* *RVUs, excluding the conversion factor • 95970, Analyze neurostimulator, no programming – Professional: 2012=1. 87 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 2011=0. 45, no change • 95974, Cranial neurostimulation, complex analysis and programming, first hour (3 or more parameters) – Professional: 2012=5. 59 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 3. 00, no change – Use -52 modifier if less than 30 minutes • 95975 Cranial neurostimulation, complex, each additional 30 minutes – Professional: 2012=3. 01 – Physician Work (w. RVU): 1. 70, no change

MEG Practice Expense Payment Rate The Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires that CMS establish the equipment utilization rate for CT, MR and PET at 75 percent. CMS had previously set the equipment utilization rate for this equipment at 90 percent, phasing in reduced payments over four years. This may result in changes to payment rates for CT and MR services. May affect MEG technical pricing since MEG grouped in imaging APCs
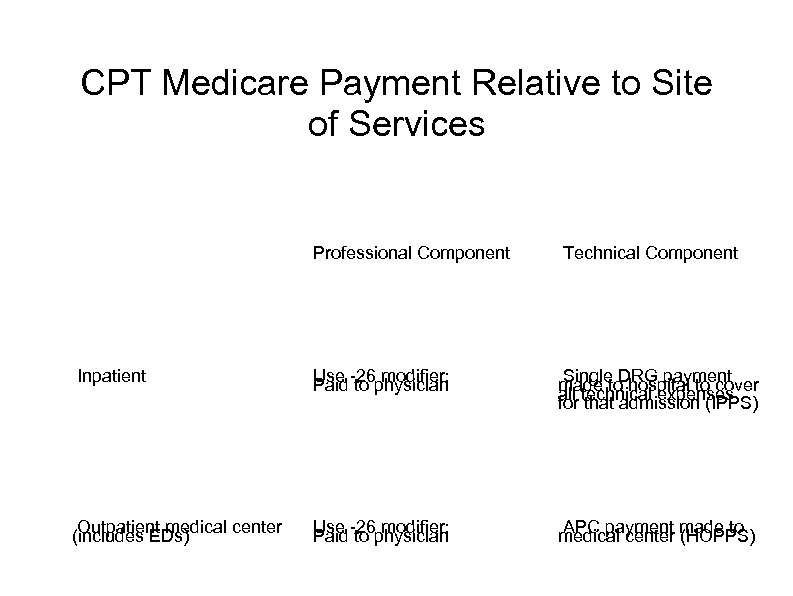
CPT Medicare Payment Relative to Site of Services Professional Component Technical Component Inpatient Use -26 modifier; Paid to physician Single DRG payment made to hospital to cover all technical expenses for that admission (IPPS) Outpatient medical center (includes EDs) Use -26 modifier; Paid to physician APC payment made to medical center (HOPPS)
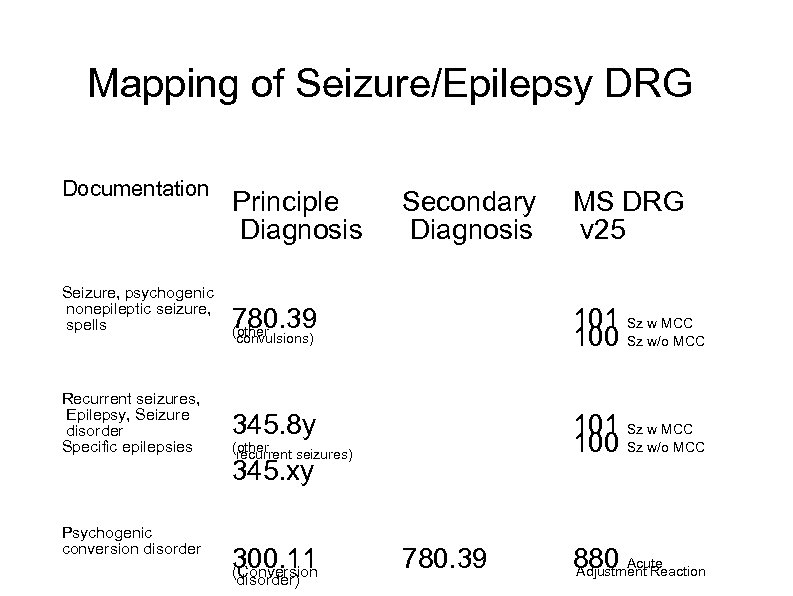
Mapping of Seizure/Epilepsy DRG Documentation Seizure, psychogenic nonepileptic seizure, spells Recurrent seizures, Epilepsy, Seizure disorder Specific epilepsies Psychogenic conversion disorder Principle Diagnosis Secondary Diagnosis MS DRG v 25 780. 39 (other 101 Sz w MCC 100 Sz w/o MCC 345. 8 y 101 Sz w MCC 100 Sz w/o MCC convulsions) (other recurrent seizures) 345. xy 300. 11 (Conversion disorder) 780. 39 880 Acute Adjustment Reaction

2012 Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System (HOPPS) Published 11/01/2011 http: //www. cms. gov/Hospital. Outpatient. PPS/HORD/list. asp Payment for the technical portion of CPT codes done on Medicare Outpatients Some outpatient procedures with HOPPS values have no payment assigned in MFS for doctors billing global – 95951 24 hour video EEG is “carrier priced” – 95965 MEG is “carrier priced” Payment for technical portion of Medicare inpatients is bundled into a single DRG payment Payment for technical fees in outpatients in private offices is in the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule • Billing “global” in private offices
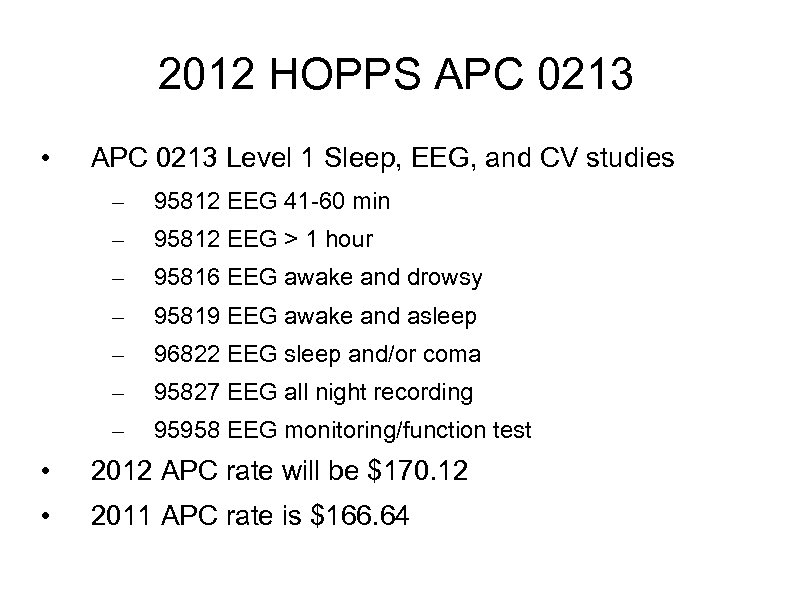
2012 HOPPS APC 0213 • APC 0213 Level 1 Sleep, EEG, and CV studies – 95812 EEG 41 -60 min – 95812 EEG > 1 hour – 95816 EEG awake and drowsy – 95819 EEG awake and asleep – 96822 EEG sleep and/or coma – 95827 EEG all night recording – 95958 EEG monitoring/function test • 2012 APC rate will be $170. 12 • 2011 APC rate is $166. 64

2011 HOPPS APC 0209 • APC 0209 Level II sleep, EEG, & CV – – – 95950 ambulatory cassette EEG 95951 24 hour video EEG 95953 ambulatory digital EEG 95956 24 hour EEG without video MSLP and polysomnograms • 2012 APC Rate will be $795. 16 • 2011 APC Rate is $780. 77

2011 HOPPS APC 218 • APC 218 Level II Nerve and Muscle Tests – 95970 Neurostimulation, analysis with no programming – 95954 EEG monitoring with drug administration • 2012 payment is $84. 19 • 2011 payment will be $80. 78
2011 HOPPS APC 216 • APC 216 Level III Nerve and Muscle Tests – 95961 Cortical Stimulation, 1 st hour – 95962 Cortical Stimulation, each additional hour • 2012 payment will be $185. 46 • 2011 payment is $186. 17 Chick retina 2008 Andy Fischer

2011 HOPPS APC 0692 • APC 0692 Level III Electronic Analysis of Devices – 95971 Analyze neurostim, simple – 95972 Analyze neurostim, complex – 95973 Analyze neurostim, complex – 95974 Cranial neurostim, complex – 95978 Analyze neurostim brain, 1 st hour – 95979 Analyze neurostim brain, each 1 hour – 95982 Low gain neurostim subseq w/ reprogram • 2012 payment will be $111. 63 • 2011 payment is $110. 95

2011 MEG HOPPs Technical payments for MEG studies in hospitalbased outpatient care facilities – Does not apply to free standing MEG sites • Carrier priced – Does not apply to MEG studies done on inpatients • Technical fees bundled to DRG Spiny neuron 2009 Deerinck and Ellisman

2011 HOPPS APC 0067 • APC 0065 Level III Stereotactic Radiosurgery, MRg. FUS, and MEG – 95965 MEG, spontaneous • 2012 payment will be $3, 373. 60 • 2011 payment is $3, 408. 69

2011 HOPPs APC 0065 Level I Stereotactic radiosurgery, Mrg. GUS, and MEG – 95966 MEG Evoked Response – 95967 Additional MEG Evoked Response 2012 payment will be $902. 53 2011 payment is $977. 12 Purkinje neurons 2003 Aric Agmon

PQRS 101 © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

CMS 2011 Physician Quality Reporting System Measure Specifications Manual for Claims and Registry Reporting of Individual Measures 571 pages of rules and listing of > 200 quality measures – https: //www. cms. gov/PQRS// • Tips for starting PQRS can be found here: http: //www. cms. gov/PQRS/03_How_To_Get_Started. asp#Top. Of. Page • AAN has selected out measures for neurologists (93 pages) http: //www. aan. com/go/practice/pay/pqrs • A table of the 2011 PQRS Measures, their rationale, and reporting method can be found here: http: //www. cms. gov/PQRS/Downloads/2011_Phys. Qual. Rptg_Measures. List_033111. pdf © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

Reporting of PQRS For any measure, there is a G-Code or CPT II code reported along with the encounter • Threshold for success is for 50% of encounters to be reported properly • Measures may be for inpatient or outpatient care • Most measures are for primary care • © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY
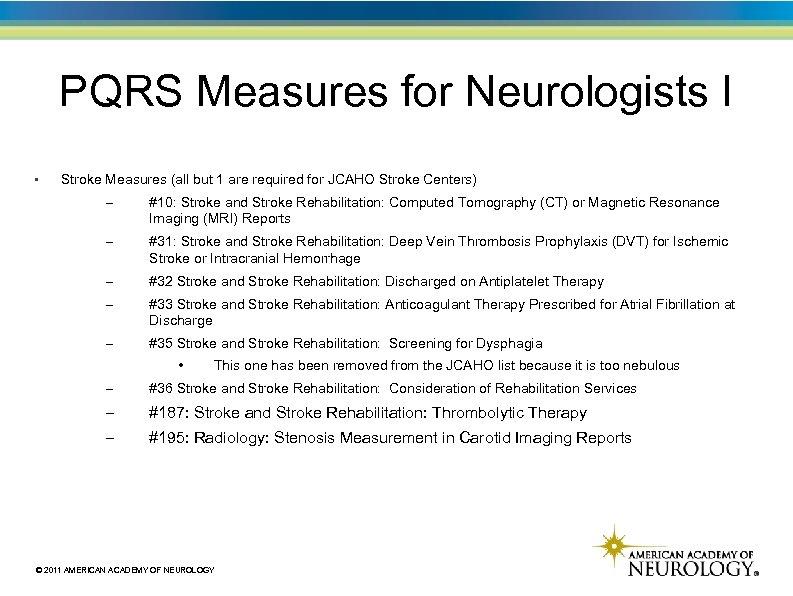
PQRS Measures for Neurologists I • Stroke Measures (all but 1 are required for JCAHO Stroke Centers) – #10: Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Reports – #31: Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Deep Vein Thrombosis Prophylaxis (DVT) for Ischemic Stroke or Intracranial Hemorrhage – #32 Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Discharged on Antiplatelet Therapy – #33 Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Anticoagulant Therapy Prescribed for Atrial Fibrillation at Discharge – #35 Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Screening for Dysphagia • This one has been removed from the JCAHO list because it is too nebulous – #36 Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Consideration of Rehabilitation Services – #187: Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Thrombolytic Therapy – #195: Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

PQRS Measures for Neurologists II • Depression Measures (Behavioral Neurology) – – #106: Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Diagnostic Evaluation – #107: Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Suicide Risk Assessment – • #9, Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Antidepressant Medication During Acute Phase for patients with MDD. #134: Screening for Clinical Depression and Follow-Up Plan General Medical and Preventative Care – #128: Preventative Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up – #130: Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record – #173: Preventative Care and Screening: Unhealthy Alcohol Use – Screening – #226: Preventative Care and Screening: Tobacco Use: Screening and Cessation Intervention – #124: Health Information Technology (HIT): Adoption/Use of Electronic Health Records (EHR) © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

PQRS Measures for Neurologists III • Elder Care – – #154 Falls: Risk Assessment – #155: Falls: Plan of Care – • #47: Advance Care Plan #181: Elder Maltreatment Screen and Follow-Up Plan Neuromuscular Neurology – #126: Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Peripheral Neuropathy - Neurologic Evaluation © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

Private Insurance Companies have Incentive Payment Plans Too • Major private insurance companies are establishing incentive payment plans • In Michigan, BCBSM has the Physician Group Incentive Plan, PGIP – PGIP has contracted with 40 organizations, 4200 practice units totalling >11, 000 physicians including >5600 specialists covering 1. 7 M residents of MI. – Funded by setting aside 4. 2% of Professional fee for most procedure codes – Twice yearly payouts • United. Healthcare is making 0% financing available for EHR purchases • Check with your major providers to see what incentives are available for you © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

e. Rx 101 © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

e. Rx Incentive Program, MIPPA of 2008 • • 5 year incentive program started in 2009 Penalty phase starts in 2012 – CMS Final Rule of 8/31/2011, 1% penalty on all Medicare Part B billing for 2012 for failure to e. Rx – Exemption applications until 11/1/2011 for MD/DO/NP/PA licensed after 6/30/2011 – No penalty if office visits make up <10% of Part B claims – No penalty if fewer than 100 Part B claims 1/1 to 6/30/11 https: //www. qualitynet. org/portal/server. pt/communications_support_system/234 © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

2013 e. Rx Incentive Program Do not despair, you can qualify for e. Rx for 2013 Send e. Rx on 25 office visits by 12/31/2011 – Must also include G-code, G 8553, on Part B claim • Will exempt you from the 1. 5% 2013 penalty on Part B billings – Will give you a bonus of 0. 5% of 2013 Part B billings • Free e. Rx software is available including – Practice Fusion* – National E-prescribing Safety Initiative (NEPSI)* – Nu. Nova* • • – *Software not reviewed or endorsed by AAN; other free e. Rx software may be available © 2011 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY

The Practice of Neurology, Looking Forward, I The current fee for service model will be gone in 5 years. In 2015, payment will be made on quality measures, not volume. OECD reports that global increase in the cost of health care has been driven the explosion in high tech diagnostic services, particularly CT and MRI. Examine your rates of using CT/MRI and other diagnostic tests and pharmaceutical choices you make as you care for your patients. Office procedures are particularly vulnerable. That means that the profit center for many of your practices may become a liability – You will be judged harshly for repeated EEGs, EMGs, any EP studies, etc. unless they meet some quality parameter Others will be watching to see if you are using these services frugally or not – You run the risk of being listed as a high utilizer and will be at risk for economic redlining

The Practice of Neurology, Looking Forward, II Be open to new ways of doing practice. The trends towards evidence-based practice pathways will accelerate. You will not be able to practice without an EHR which collects outcome data Incorporate general quality measures such as smoking cessation to your practice now as well as the epilepsy measures, stroke measures, and any future measures developed by the AAN Support the Neurology Brain PAC and join the NAEC which work to represent for your interests at a federal level
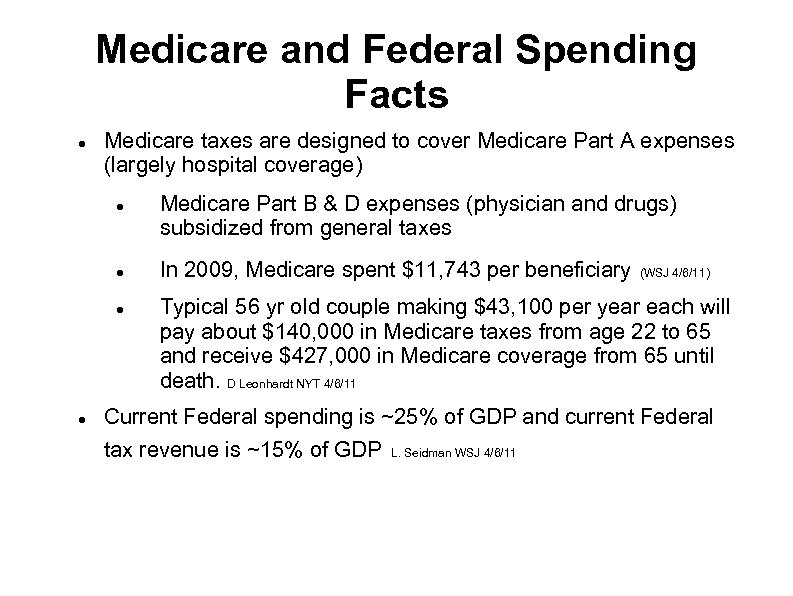
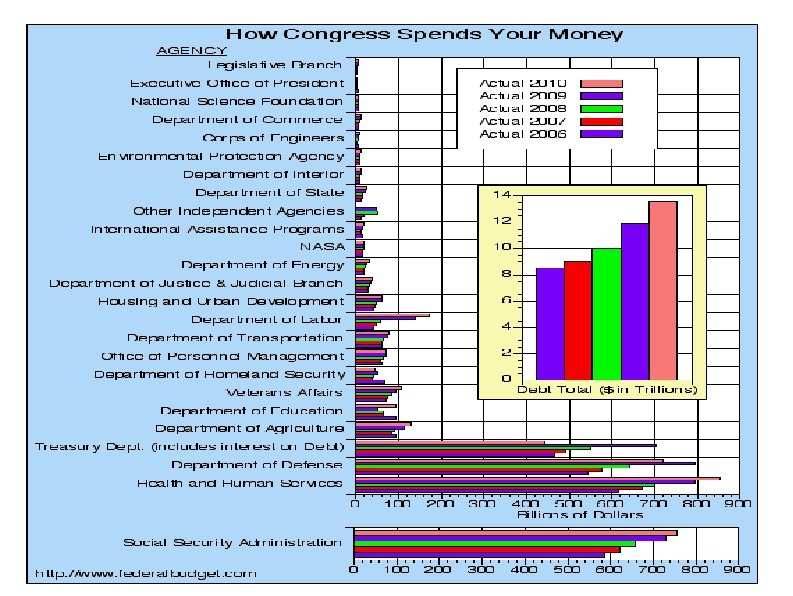
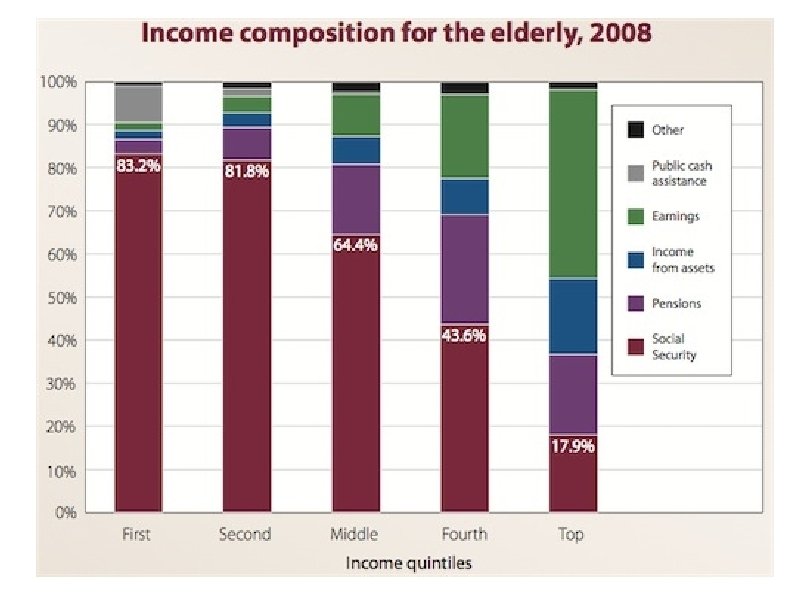
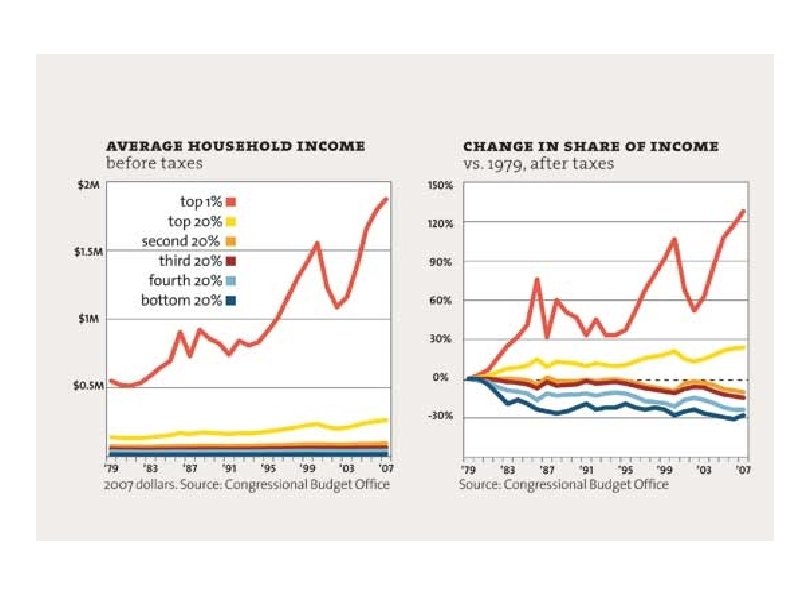
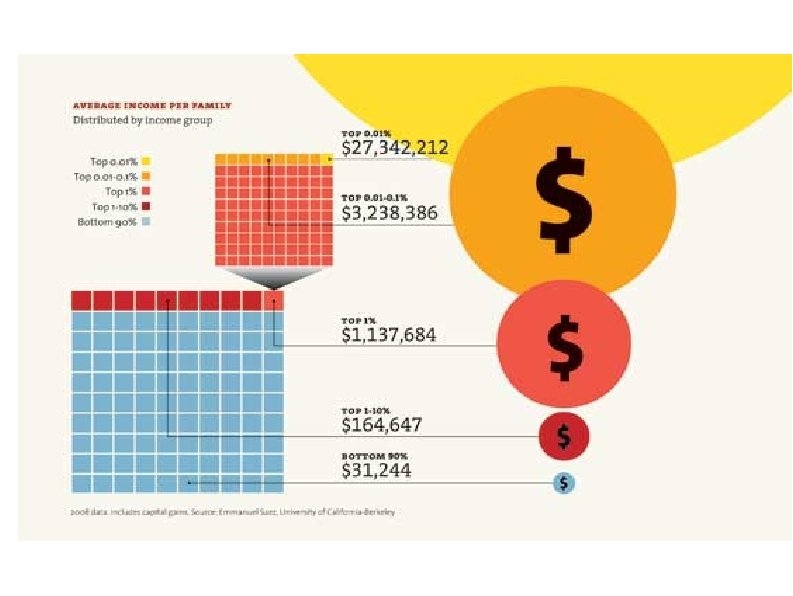
Medicare and Federal Spending Facts Medicare taxes are designed to cover Medicare Part A expenses (largely hospital coverage) Medicare Part B & D expenses (physician and drugs) subsidized from general taxes In 2009, Medicare spent $11, 743 per beneficiary (WSJ 4/6/11) Typical 56 yr old couple making $43, 100 per year each will pay about $140, 000 in Medicare taxes from age 22 to 65 and receive $427, 000 in Medicare coverage from 65 until death. D Leonhardt NYT 4/6/11 Current Federal spending is ~25% of GDP and current Federal tax revenue is ~15% of GDP L. Seidman WSJ 4/6/11
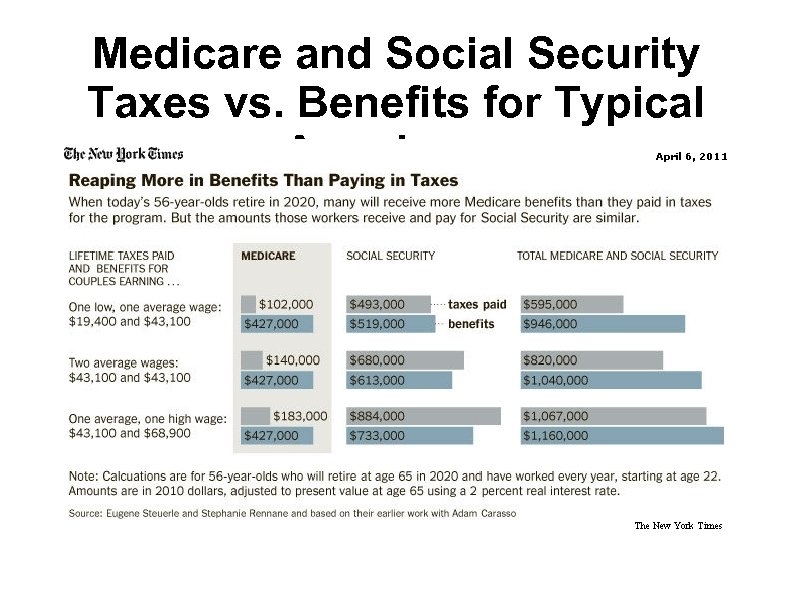
Medicare and Social Security Taxes vs. Benefits for Typical Americans



The Affordable Care Act, 2012 A hospital Value-Based Purchasing program Requires public reporting of quality measures Pays hospitals extra for achieving quality targets Begins Accountable Care Organizations Requires new standardized electronic exchange of health care information Requires ongoing and new Federal health programs to collect information on disparities Creates a new voluntary long-term care insurance program, CLASS

The Affordable Care Act, 2013 New funding is provided to Medicaid plans to expand preventative care services at little or no cost Authority to bundle payments to hospitals and providers under a pilot program will expand Medicaid payments to primary care providers will be increased to at least 100% of Medicare rates Additional funding to CHIP programs for children not eligible for Medicaid will be provided.

The Affordable Care Act, 2014, I The act prohibits discrimination due to pre-existing conditions or gender Eliminates higher rates in the individual insurance market based upon gender or health status Eliminates annual limits on health care coverage Insures coverage for individuals participating in clinical trials Provides tax credits to individuals between 100 and 400% of the poverty line and gives reduced co-payments and deductibles, Establishes Health Insurance Exchanges if an employer does not offer insurance Requires Members of Congress to get their insurance through Exchanges

The Affordable Care Act, 2014, II Increases the small business tax credit for up to 50% of employer's contribution Provides Medicaid to anyone who earns up to 133% of the poverty level Provides 100% reimbursement to the states for the extra costs Gives employees the funds that their employer would have spent to allow them to join a new Health Insurance Exchange Begins the individual mandate to purchase insurance

The Affordable Care Act, 2015 Physician payment will be tied to quality measures not volume IPAB, 15 member independent panel, appointed by President, confirmed by Senate begins to enforce upper limit on Medicare spending growth, set to be a fixed growth rate In 2018, IPAB, will enforce permanent maximum Medicare growth at per capita GDP growth plus 1% – It cannot change cost-sharing for covered Medicare services – It can cut Medicare payments for providers This will reward highly efficient providers and penalize less efficient ones

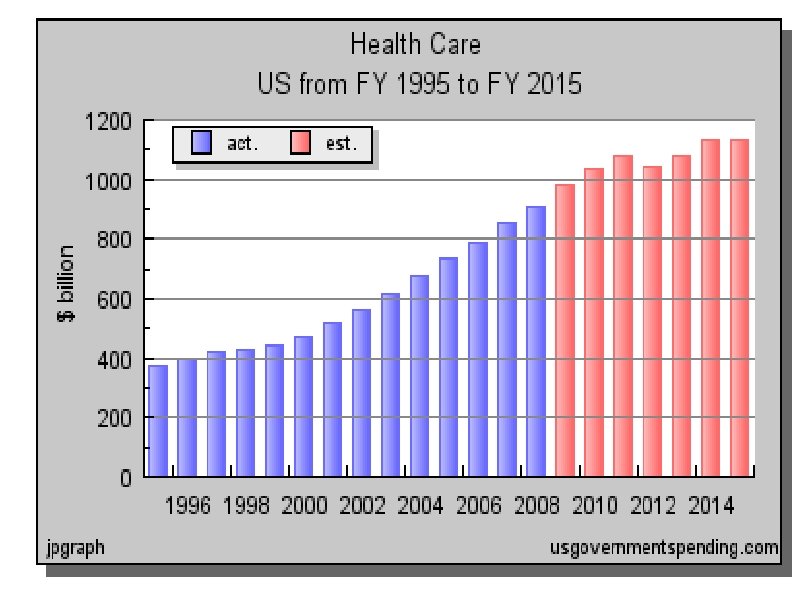
Financial Impact of the ACA Congressional Budget Office estimated that the ACA: Would reduce the deficit by $143 billion over the first decade Would reduce the deficit by $1. 2 trillion over the second decade. The graph on the next slide is taken from a web site sympathetic to the tea party movement and shows the “bending of the health care curve” cited by supporters of the ACA.

Support Your Patients – They need an incentive plan from you. The job you save may be your own. Unless you do funded research, you are in the service industry and your job depends upon having primary producers to pay for your services You should shop locally, particularly if you practice in a small town www. buymichiganproducts. com

Professionalism This has been a business talk, but do not forget why you became a physician in the first place You are expected to give back to the community by donating your talent, your time, and your money to support worthy causes These include: your hospital, nonprofit disease organizations such as the Epilepsy Foundation, the American Academy of Neurology, etc.
357fb7fd3a92596c140e9330ed08e5cc.ppt