 AE 440 Structures Discipline Lecture 6 Eric Loth For AE 440 A/C Lecture 1
AE 440 Structures Discipline Lecture 6 Eric Loth For AE 440 A/C Lecture 1
 Structures Responsibilities a. b. c. d. e. f. Determine V-n relationships and establish a V-n diagram Establish and maintain load paths Determine component materials (weights and dimensions to configuration) and consider environmental impact of acquisition, production and operations Determine landing gear configuration Carry out a detailed structural design of the wing box and wing attachment and structurally design landing gear (weights & dimensions to configuration) Employ FEM Analysis 2
Structures Responsibilities a. b. c. d. e. f. Determine V-n relationships and establish a V-n diagram Establish and maintain load paths Determine component materials (weights and dimensions to configuration) and consider environmental impact of acquisition, production and operations Determine landing gear configuration Carry out a detailed structural design of the wing box and wing attachment and structurally design landing gear (weights & dimensions to configuration) Employ FEM Analysis 2
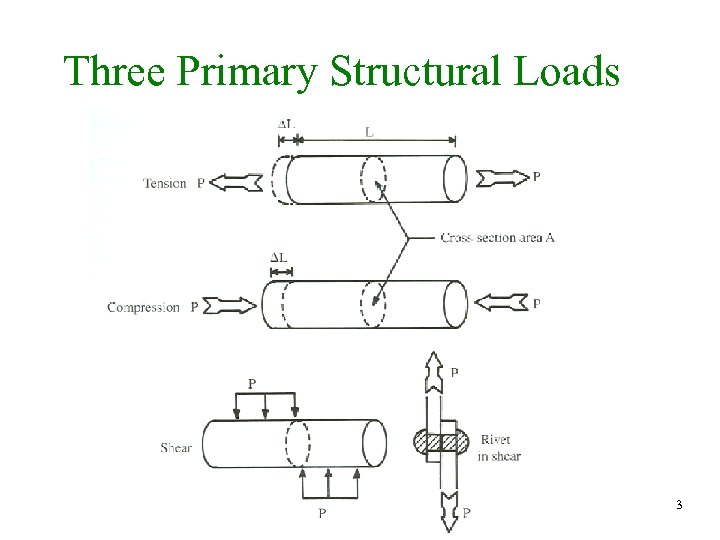 Three Primary Structural Loads 3
Three Primary Structural Loads 3
 Typical Aircraft Loads 4
Typical Aircraft Loads 4
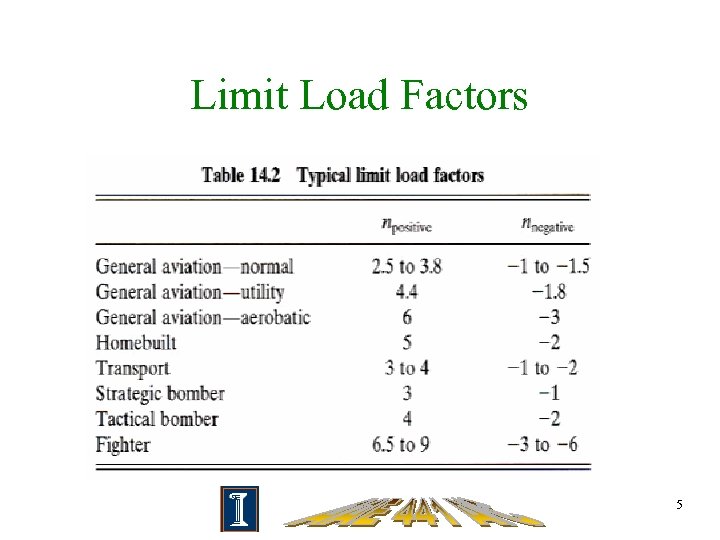 Limit Load Factors 5
Limit Load Factors 5
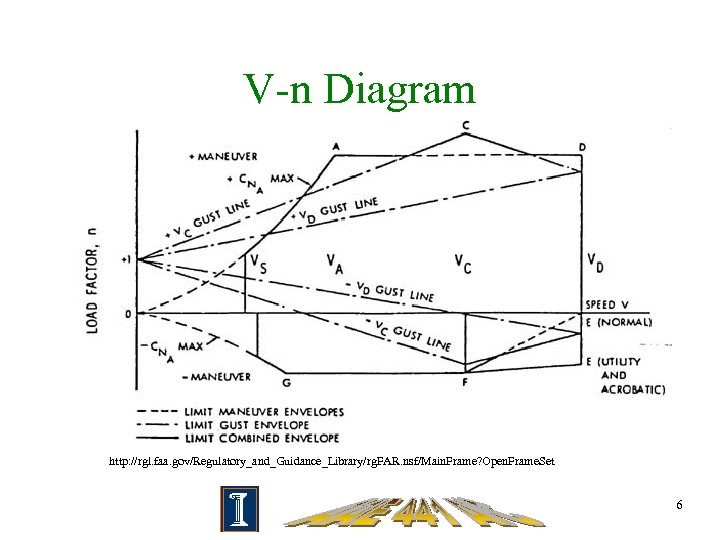 V-n Diagram http: //rgl. faa. gov/Regulatory_and_Guidance_Library/rg. FAR. nsf/Main. Frame? Open. Frame. Set 6
V-n Diagram http: //rgl. faa. gov/Regulatory_and_Guidance_Library/rg. FAR. nsf/Main. Frame? Open. Frame. Set 6
 Load Paths • How loads are transferred from one structural member to another • Wing skin—torsion and shear stress • Wing ribs—maintain shape and rigidity, transfer loads from skin to spars • Wing spars—bending moments • Fuselage—bulkheads, framers, stringers 7
Load Paths • How loads are transferred from one structural member to another • Wing skin—torsion and shear stress • Wing ribs—maintain shape and rigidity, transfer loads from skin to spars • Wing spars—bending moments • Fuselage—bulkheads, framers, stringers 7
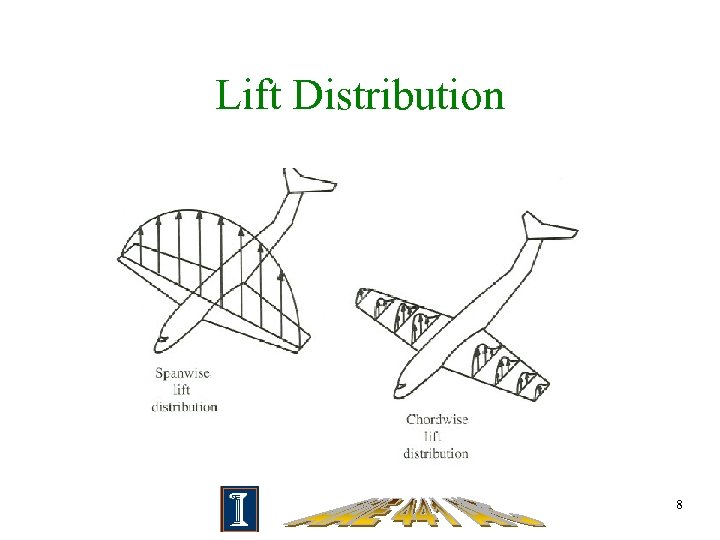 Lift Distribution 8
Lift Distribution 8
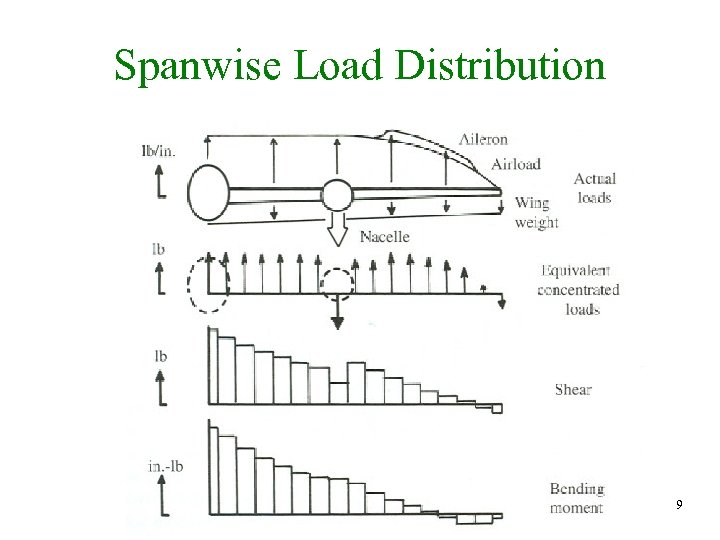 Spanwise Load Distribution 9
Spanwise Load Distribution 9
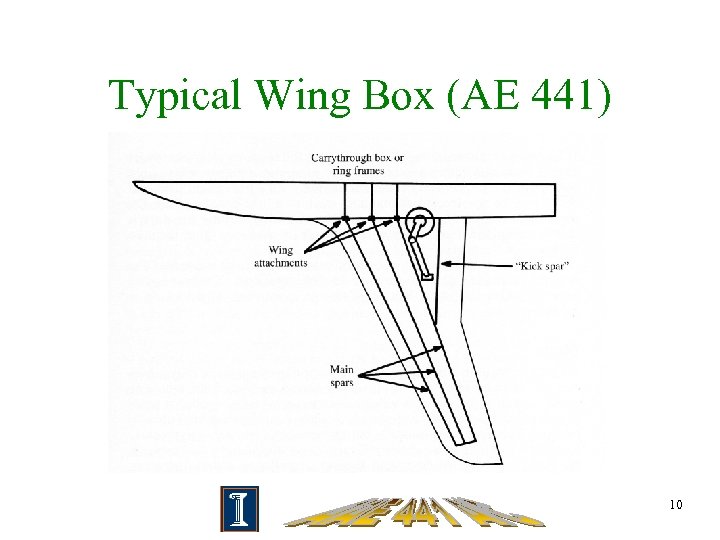 Typical Wing Box (AE 441) 10
Typical Wing Box (AE 441) 10
 Major Fuselage Loads • Empennage loads due to trim, maneuvering, turbulence and gusts • Pressure loads due to cabin pressurization • Landing gear loads due to landing impact, taxiing and ground maneuvering • Loads induced by the propulsion installation when the latter is attached to the fuselage 11
Major Fuselage Loads • Empennage loads due to trim, maneuvering, turbulence and gusts • Pressure loads due to cabin pressurization • Landing gear loads due to landing impact, taxiing and ground maneuvering • Loads induced by the propulsion installation when the latter is attached to the fuselage 11
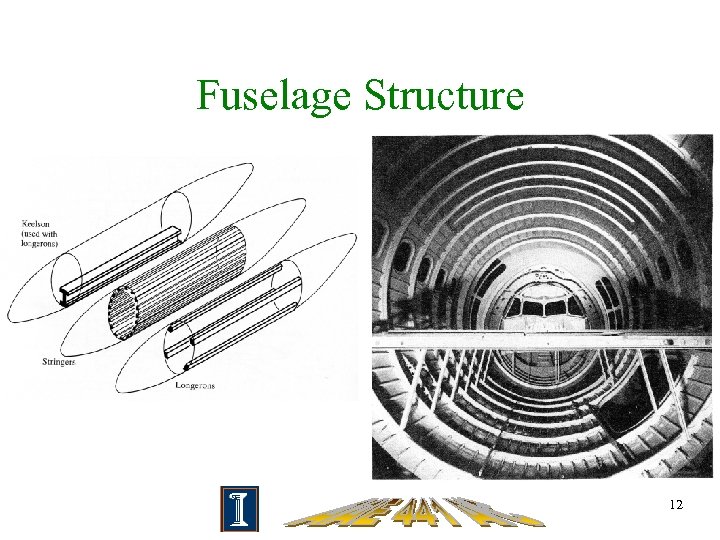 Fuselage Structure 12
Fuselage Structure 12
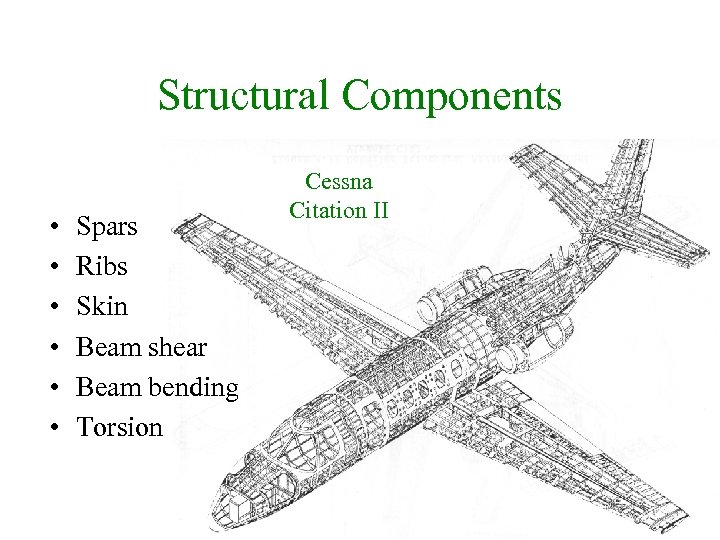 Structural Components • • • Spars Ribs Skin Beam shear Beam bending Torsion Cessna Citation II 13
Structural Components • • • Spars Ribs Skin Beam shear Beam bending Torsion Cessna Citation II 13
 Materials • Selection criteria – – Strength Stiffness Density Cost • Typical materials – – Aluminum Composites Steel Titanium • Mini-UAV materials – Plastic – Balsa – Fiber (cloth) 14
Materials • Selection criteria – – Strength Stiffness Density Cost • Typical materials – – Aluminum Composites Steel Titanium • Mini-UAV materials – Plastic – Balsa – Fiber (cloth) 14
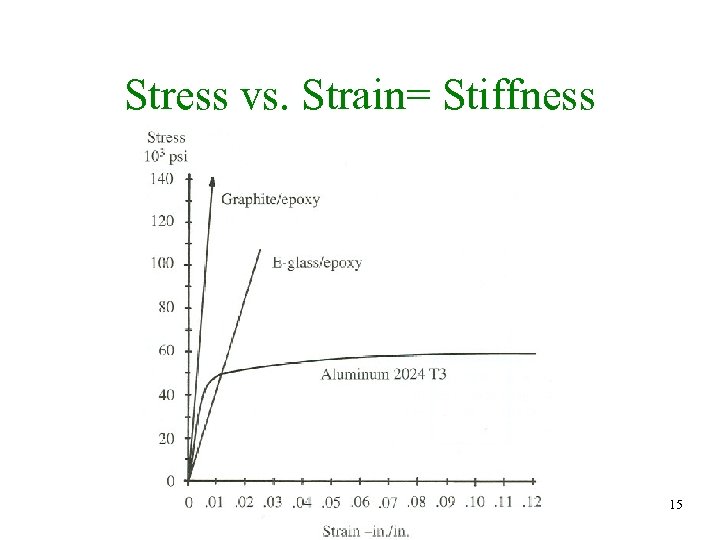 Stress vs. Strain= Stiffness 15
Stress vs. Strain= Stiffness 15
 Landing Gear Loads • Vertical loads primarily caused by non-zero touchdown rates and taxiing over rough surfaces • Longitudinal loads primarily caused by braking loads and rolling friction loads • Lateral loads primarily caused by ‘crabbed landings, ’ cross-wind taxiing and ground turning 16
Landing Gear Loads • Vertical loads primarily caused by non-zero touchdown rates and taxiing over rough surfaces • Longitudinal loads primarily caused by braking loads and rolling friction loads • Lateral loads primarily caused by ‘crabbed landings, ’ cross-wind taxiing and ground turning 16
 Common Landing Gear Configurations 17
Common Landing Gear Configurations 17
 Samples of Structural Results from Previous CDRs 18
Samples of Structural Results from Previous CDRs 18
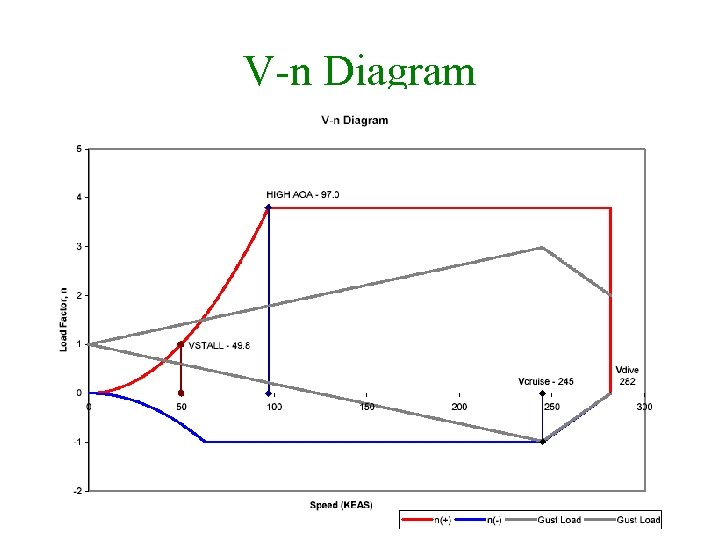 V-n Diagram 19
V-n Diagram 19
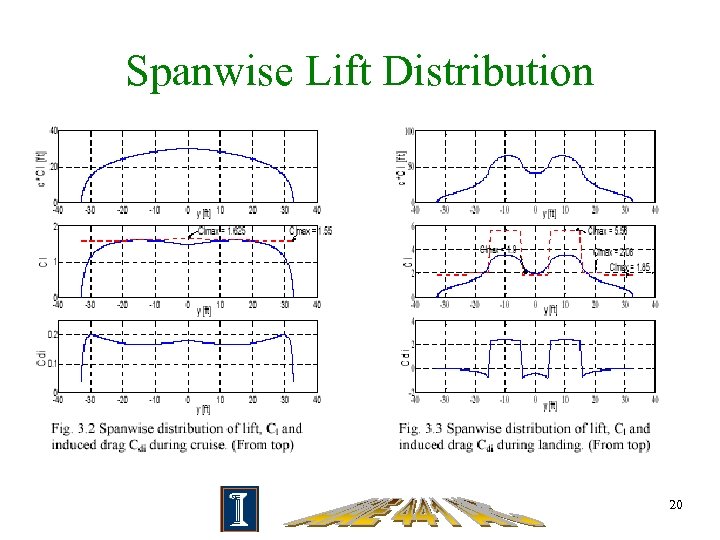 Spanwise Lift Distribution 20
Spanwise Lift Distribution 20
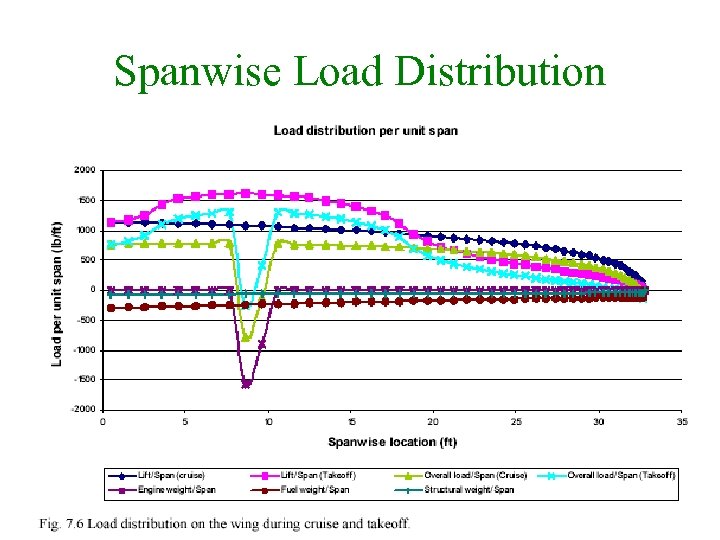 Spanwise Load Distribution 21
Spanwise Load Distribution 21
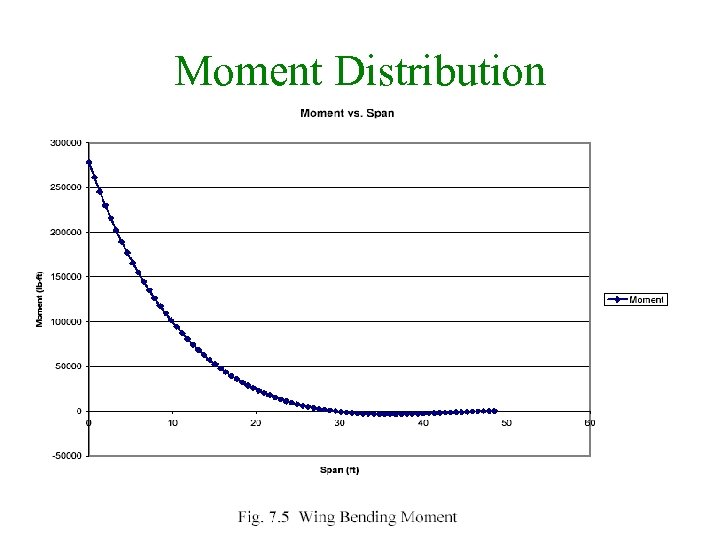 Moment Distribution 22
Moment Distribution 22
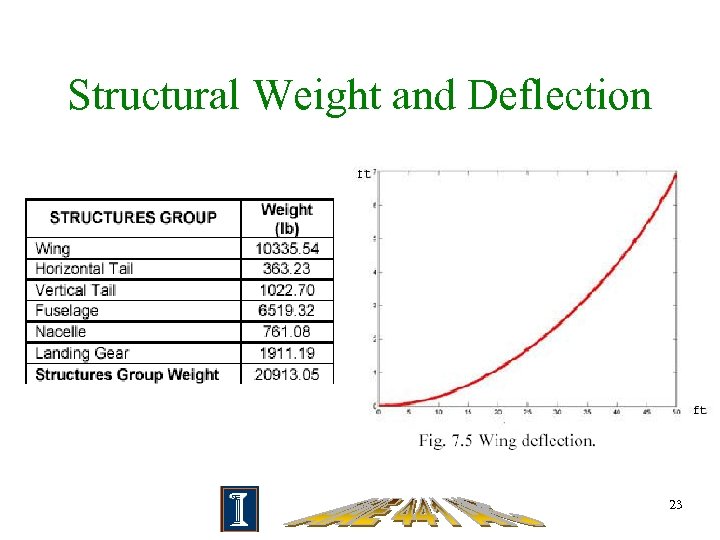 Structural Weight and Deflection 23
Structural Weight and Deflection 23
 Structural Configuration (441 level) I-beam gives good resistance to shear (web) and bending (caps) 24
Structural Configuration (441 level) I-beam gives good resistance to shear (web) and bending (caps) 24
 Structural Details (441 level) 25
Structural Details (441 level) 25