49dfda0e11b7842d835c22b7dcc9106a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45

ADVERTISING DECISIONS MBA 690

Lecture Outline 1. Importance of Advertising 2. Advertising and Social Issues 3. Systematic Steps for Managing Advertising Resources Mission Objectives Ad Budget Management of Ad Campaign Measuring ad Effectiveness
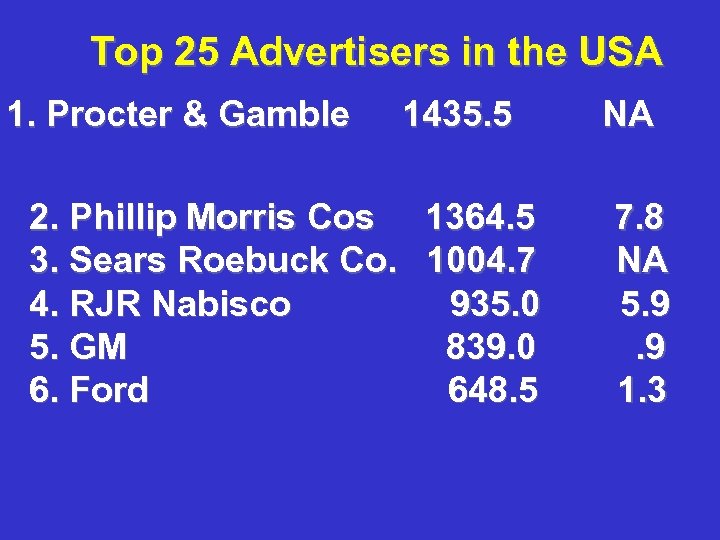
Top 25 Advertisers in the USA 1. Procter & Gamble 1435. 5 2. Phillip Morris Cos 1364. 5 3. Sears Roebuck Co. 1004. 7 4. RJR Nabisco 935. 0 5. GM 839. 0 6. Ford 648. 5 NA 7. 8 NA 5. 9. 9 1. 3
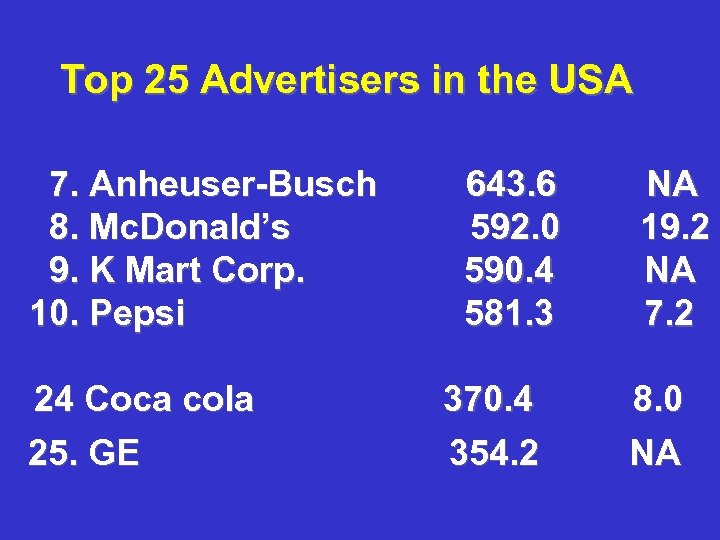
Top 25 Advertisers in the USA 7. Anheuser-Busch 8. Mc. Donald’s 9. K Mart Corp. 10. Pepsi 24 Coca cola 25. GE 643. 6 592. 0 590. 4 581. 3 370. 4 354. 2 NA 19. 2 NA 7. 2 8. 0 NA

In 1989, Top 25 Advertisers Spent: $15, 466, 400, 000. 00 Source: Bovee and Arens Contemporary Advertising

Systematic steps for managing advertising resources *Determine a mission for advertising *Determine an advertising budget *Design an advertising campaign *Develop a creative strategy and a media plan *Measuring advertising effectiveness

Advertising’s Mission 1. The role of advertising in the company’s promotion strategy

Advertising Objectives Advertising objectives should include four key points: 1. Definition of target audience 2. A statement of how target audience should change

3. A statement of how fast such a change should occur 4. A statement as to the degree of change desired Note: 1. Russell Colley’s DAGMAR 2. Classification of objectives inform, persuade, remind

Advertising Objectives Communication Hierarchy A Hierarchy of Effects Unawareness Awareness Interest Evaluation Trial Action (Innovationadoption model)

Advertising Objectives 1. Sales Objectives 2. Communication Objectives
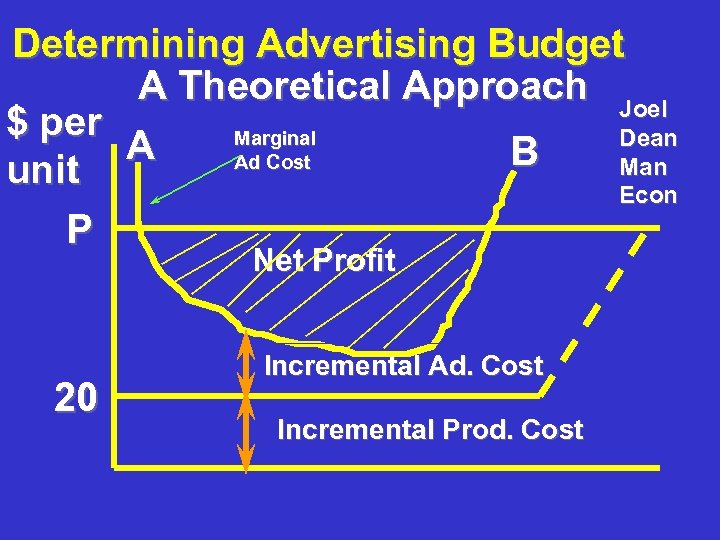
Determining Advertising Budget A Theoretical Approach Joel $ per Marginal Dean A B Ad Cost Man unit Econ P Net Profit 20 Incremental Ad. Cost Incremental Prod. Cost

Practical Methods of Setting Promotion Budget

Traditional Approaches Arbitrary Allocation % of Sales Return on Investment All You Can Afford Objective and Task Approach Competitive Parity Method

All You Can Afford Method Selling Price Retailer Margin %30 Wholesalers’ Selling P. Wholesalers’ Margin Manufacture’s Price Manufacture’s Product Cost Revenue minus Cost Specified 6% Profit Residual for Selling and Other Costs $1. 00 -. 30 $0. 70 -. 11 $0. 59 $0. 40 0. 19 0. 06 $. 13

Deciding on the Message * Message Generation * Message Evaluation * Message Execution * Social Responsibility Review

Message Evaluation Need for evaluative criteria: Desirability exclusiveness believability Example: rate the following two statements: 700 babies are born each day with birth defect your next baby could be born with a birth defect

Message Execution Not only what you say but how you say it is important Style Tone Words Format

Style 1. Information (computer ad) 2. Argument or Reason Why? (industrial how weight affects gas mileage) 3. Command (give the United Way) 4. Symbolic Association (Marlboro) 5. Imitation (Channel No. 5) 6. Emotional Appeals (March of Dime)

Tone Positive Humorous Fear appeal

The Fear Appeal Unpleasant or unfavorable consequence of not taking a suggested course of action Affect Facilitating Effect Intensity Inhibiting Effect Resultant Curve

Humor 1. Not effective in introducing a new product. 2. The brand must be clearly identified in the opening 10 seconds of a T. V. commercial. 3. Make sure that humor is compatible with the message itself.

Words Attention getting words such as: Be all you can be! Join the Army Format concerns with the questions of size, color, illustrations etc.

Social Responsibility Review Issues related to deception, bait and switch advertising, offending ethnic groups, racial minorities, etc.

Media Strategy Deciding on the Media 1. Choosing Among Media Type 2. Selecting Media Vehicle Geographic 3. Scheduling Seasonal Flighting

Deciding on the Media selection is the problem of finding the most cost-effective media to deliver the desired number of exposures to the target audience.

Reach: no. (or %) of different homes exposed to the advertising schedule during a given time period. Frequency: the number of times that the average home reached was exposed during that time period.

GRP Gross Rating Point R X F = E Note: you cannot optimize both R and F with a given advertising budget WE = R * F * I Impact: The qualitative value of an exposure through a given medium

Choosing Among Major Media Types Target-Audience Media Habits Product: food, dress, computers Message Technical Data; Info about sales for a weekend promotion Cost

Micro-scheduling Problem Calls for allocating advertising expenditures within a short period to obtain a maximum impact.
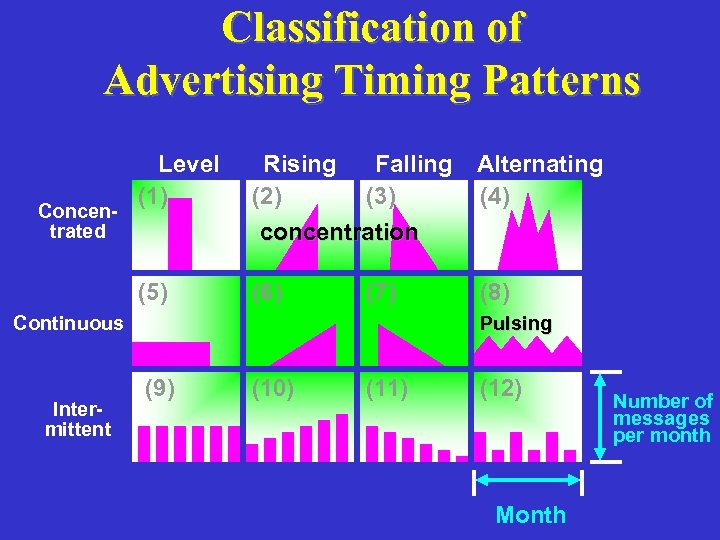
Classification of Advertising Timing Patterns Concentrated Level (1) Rising (2) Falling (3) concentration (5) (6) (7) (8) Pulsing Continuous Intermittent Alternating (4) (9) (10) (11) (12) Month Number of messages per month

Measuring Advertising Effectiveness Everybody’s Looking for the Holy Grail Sales School of Thought Communication School of Thought “Colley” “DAGMAR”

DAGMAR BY: Russel Colley Defining Advertising Goals for Measuring Advertising Results

Deceptive Advertisement What is Deception? If an advertisement leaves the consumer with an impression(s) and/or belief(s) different from what would normally be expected if the consumer had reasonable. . .

knowledge, and that impression(s)and/or belief(s) is factually untrue or potentially misleading, then deception is said to exist.

Types of Deception *Unconscionable lie -claim is completely false *Claim-Fact Discrepancy -a claim benefit that must be qualified for it to be properly understood and evaluated. *Claim-Belief Interaction -message is interpreted

through existing beliefs in such a way as to leave an erroneous impression about the product or service. Examples H C Credit card invitation letters

Are “Made In USA” Advertisements Deceptive?

Sales Promotions AMA defines sales promotion as: Those marketing activities, other than advertising and personal selling and publicity, that stimulate consumer purchasing and dealer effectiveness Ads: reason to buy Sales promotion: incentive to buy

Types of Sales promotion 1. Directed at ultimate consumers “consumer promotion: Sample, coupons, refund offers etc.

Types continued 2. Directed at channel members Trade promotion: advertising allowance, displays etc. 3. Directed at sales force Sales force promotion

Which sales promotion tool to use? It depends on: Objectives of sales promotion competitive environment, and cost effectiveness of each tool Objectives of Sales promotion

Management of Sales-Promotion Programs: *Planning Sales-Promotion Activities *the size of the incentive *conditions for participation *duration of promotion cont.

*distribution vehicle *timing of promotion Evaluation of sales promotion results Problem areas: forward buying diverting etc.

Implementing the Sales. Promotion Programs *Evaluating the Sales-Promotion Results
49dfda0e11b7842d835c22b7dcc9106a.ppt