a0e9475fcef997242642e5d9eff40039.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Advances in mobile communication: 5 G at a glance Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mehmet Toycan Communication Technologies Research Center, Electric & Electronic Engineering Department, Management Information Systems Department, Cyprus International University, Nicosia, North-Cyprus, Tel: +90 392 6711111, E-mail: mtoycan@ciu. edu. tr

Minsk, Republic of Belarus Outline ü Use of internet ü Review of mobile communication technologies ü Future network concepts ü 5 G Requirements and challanges ü 5 G technical discussion ü Conclusion
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Motivation Ø All applications -- voice, data, image, video, multimedia -- conveyed on an all digital, packetswitched, Burst mode, broadband, low latency network or “platform”. Ø A “network of networks” platform that uses common, open, non-proprietary standards and protocols (e. g. IP) Ø Demand for High Capacity networks with an extension to this platform using wireless technology to allow users to communicate anyplace, anytime, in any mode or combination of modes. Ø Energy efficient network architectures.
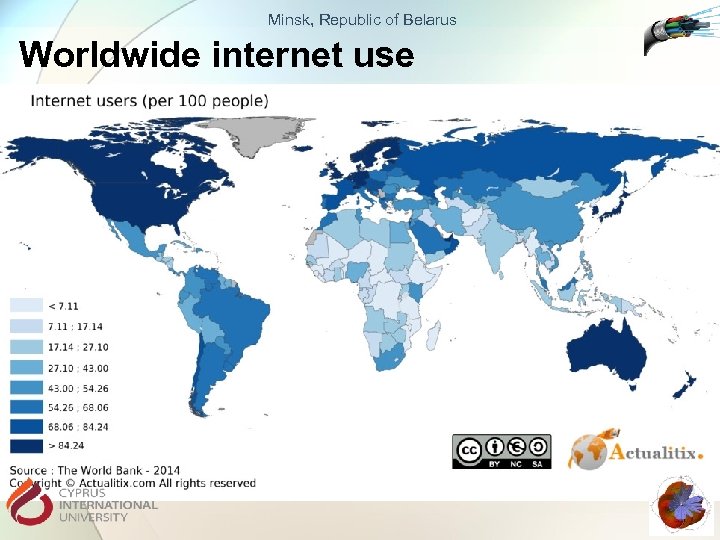
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Worldwide internet use
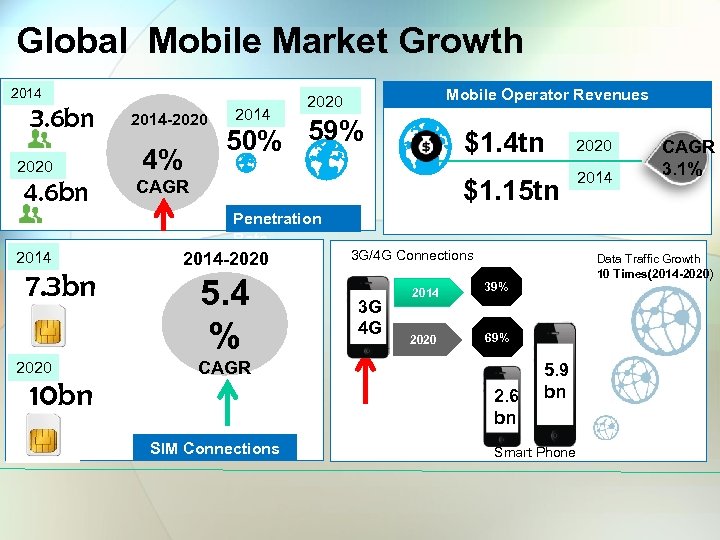
Global Mobile Market Growth 2014 3. 6 bn 2020 4. 6 bn Mobile Operator Revenues Overview 2020 2014 -2020 50% 59% 4% $1. 4 tn $1. 15 tn CAGR 2020 2014 CAGR 3. 1% Penetration Rate 2014 7. 3 bn 2020 10 bn 2014 -2020 5. 4 % 3 G/4 G Connections 3 G 4 G 2014 39% 2020 69% CAGR 2. 6 bn SIM Connections Data Traffic Growth 10 Times(2014 -2020) 5. 9 bn Smart Phone
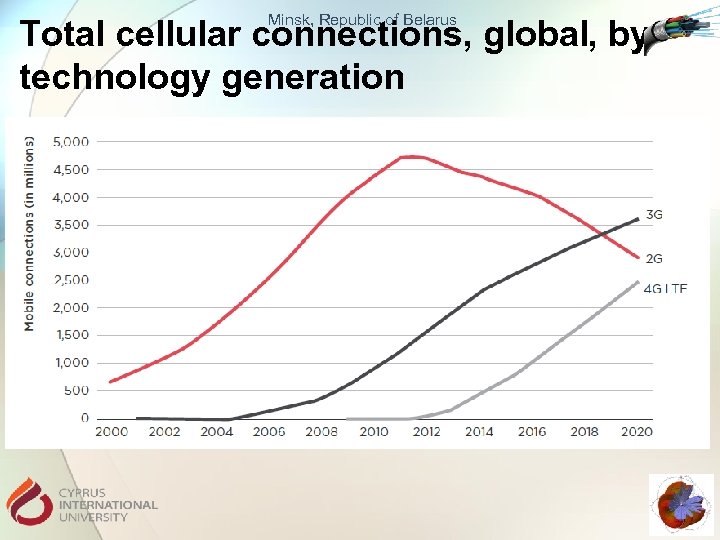
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Total cellular connections, global, by technology generation
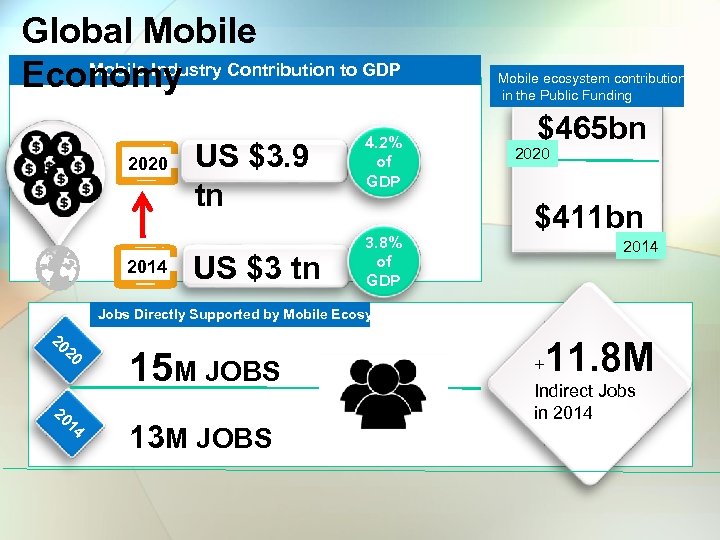
Global Mobile Industry Economy Contribution to GDP 2020 2014 US $3. 9 tn US $3 tn 4. 2% of GDP 3. 8% of GDP Mobile ecosystem contribution in the Public Funding $465 bn 2020 $411 bn 2014 Jobs Directly Supported by Mobile Ecosystem 20 20 20 14 15 M JOBS 13 M JOBS 11. 8 M + Indirect Jobs in 2014
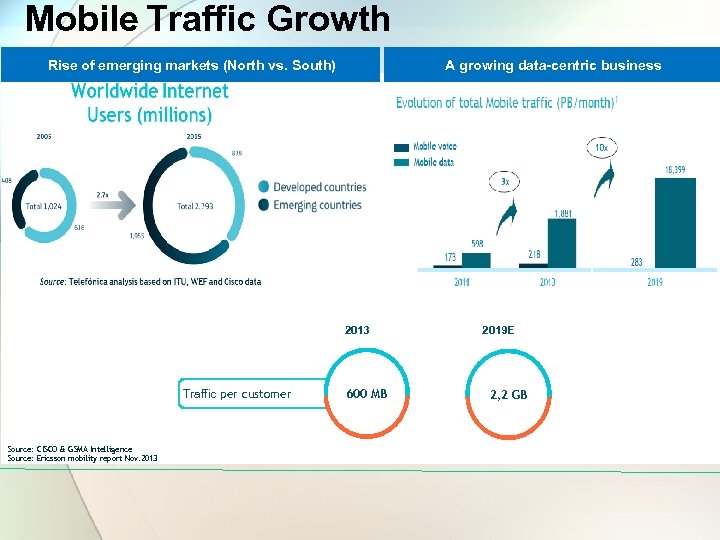
Mobile Traffic Growth Rise of emerging markets (North vs. South) A growing data-centric business 2013 Traffic per customer Source: CISCO & GSMA Intelligence Source: Ericsson mobility report Nov. 2013 600 MB 2019 E 2, 2 GB
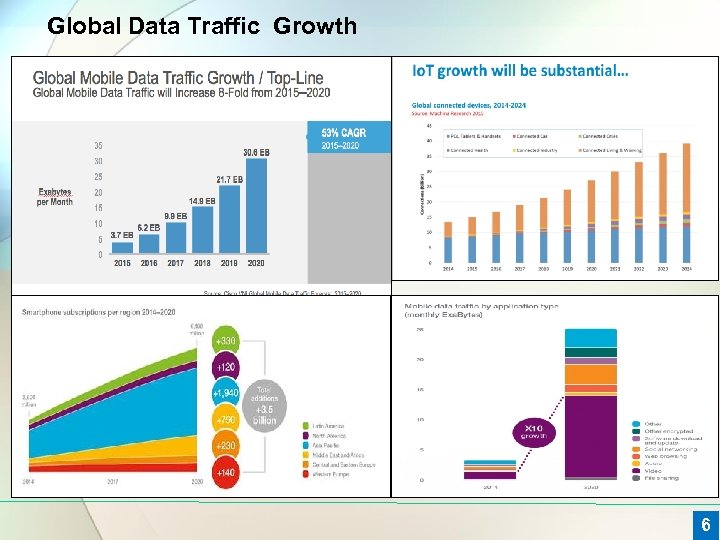
Global Data Traffic Growth 6
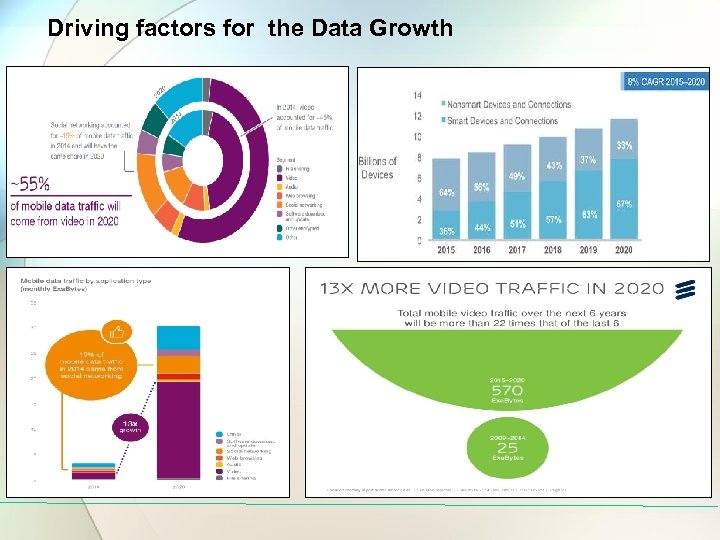
Driving factors for the Data Growth
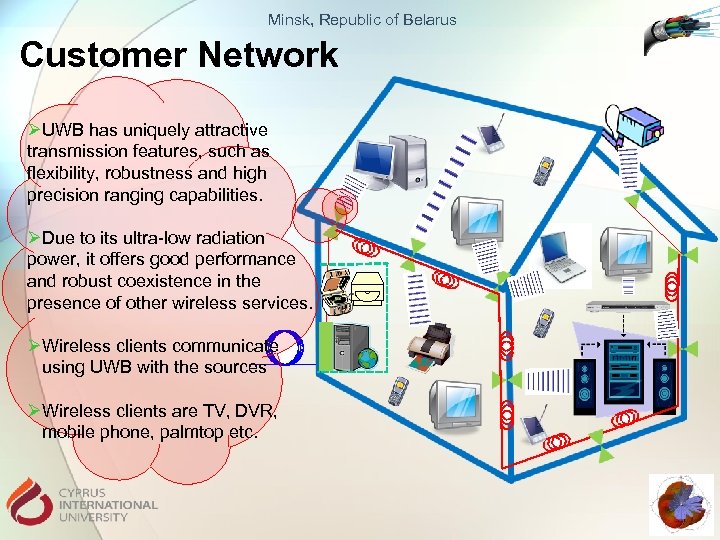
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Customer Network ØUWB has uniquely attractive transmission features, such as flexibility, robustness and high precision ranging capabilities. ØDue to its ultra-low radiation power, it offers good performance and robust coexistence in the presence of other wireless services. ØWireless clients communicate using UWB with the sources ØWireless clients are TV, DVR, mobile phone, palmtop etc.
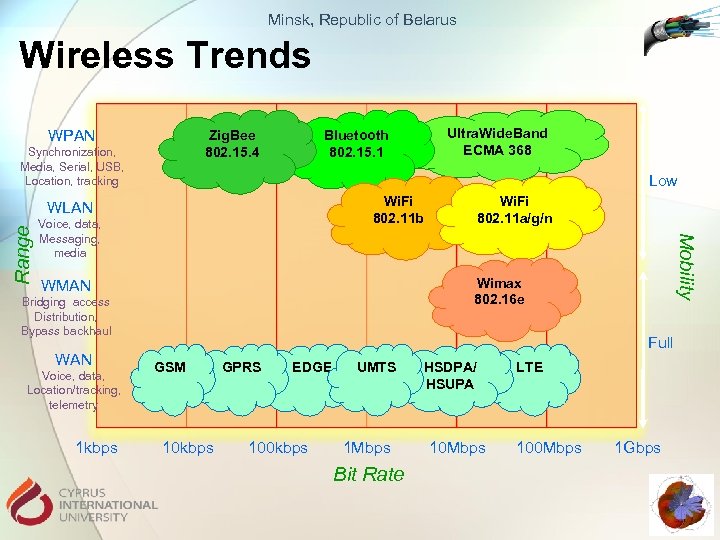
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Wireless Trends WPAN Zig. Bee 802. 15. 4 Synchronization, Media, Serial, USB, Location, tracking Low Wi. Fi 802. 11 b Voice, data, Messaging, media Wimax 802. 16 e WMAN Bridging access Distribution, Bypass backhaul Voice, data, Location/tracking, telemetry 1 kbps Wi. Fi 802. 11 a/g/n Mobility Range WLAN WAN Ultra. Wide. Band ECMA 368 Bluetooth 802. 15. 1 Full GSM 10 kbps GPRS EDGE 100 kbps UMTS 1 Mbps Bit Rate HSDPA/ HSUPA 10 Mbps LTE 100 Mbps 1 Gbps
Minsk, Republic of Belarus
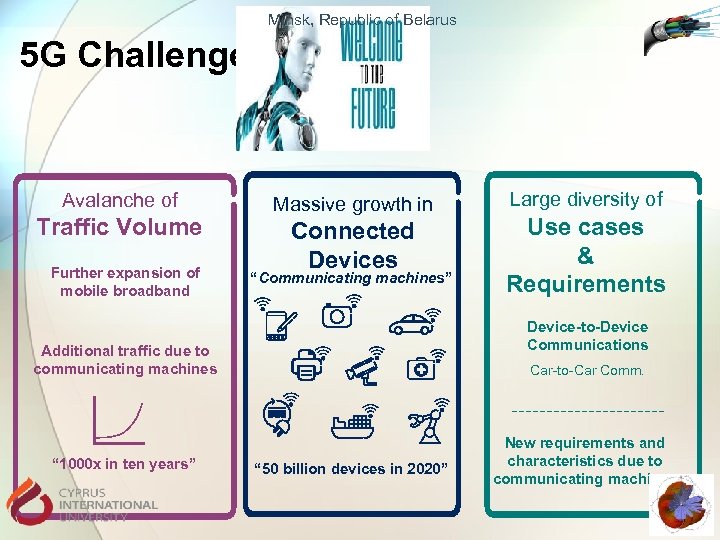
Minsk, Republic of Belarus 5 G Challenges Avalanche of Traffic Volume Further expansion of mobile broadband Massive growth in Connected Devices “Communicating machines” Use cases & Requirements Device-to-Device Communications Additional traffic due to communicating machines “ 1000 x in ten years” Large diversity of Car-to-Car Comm. “ 50 billion devices in 2020” New requirements and characteristics due to communicating machines
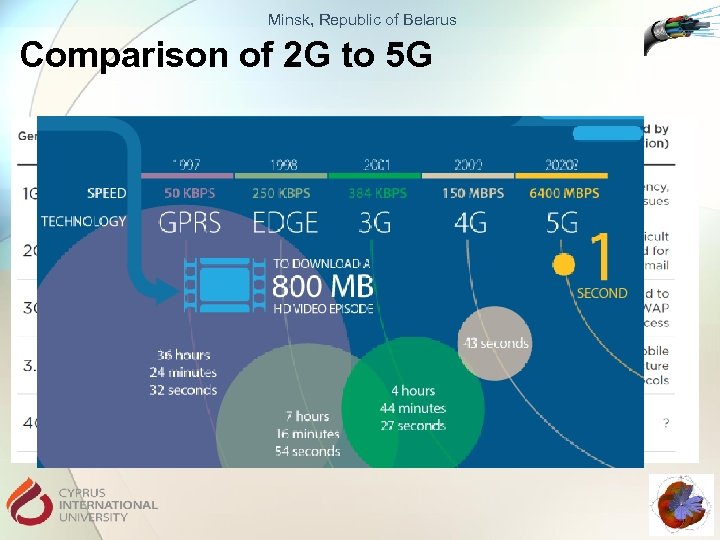
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Comparison of 2 G to 5 G

Minsk, Republic of Belarus 5 G Requirements • The three fundamental requirements for building 5 G wireless networks are: • Capabilities for supporting massive capacity and massive connectivity • • Support for an increasingly diverse set of services, application and users – • all with extremely diverging requirements for work and life • Flexible and efficient use of all available non-contiguous spectrum for • wildly different network deployment scenarios • These networks will need to match advances in fixed networking in terms of delivered quality of service, reliability and security. To do so, 5 G technologies will need to be capable of delivering fiber-like 10 Gb/s speeds to make possible ultra-high definition visual communications and immersive multimedia interactions. These technologies will
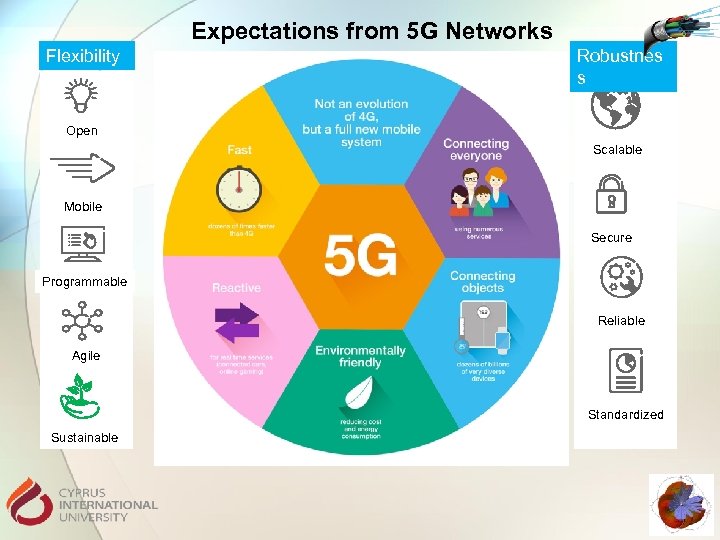
Expectations from 5 G Networks Flexibility Robustnes s Open Scalable Mobile Secure Programmable Reliable Agile Standardized Sustainable
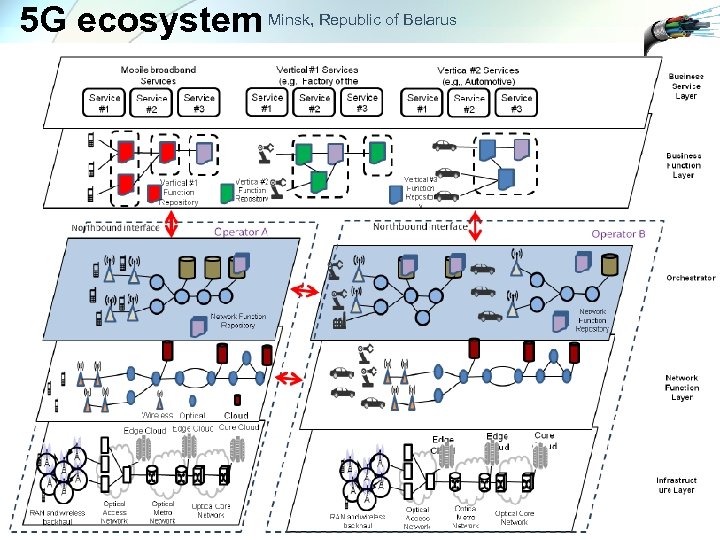
5 G ecosystem Minsk, Republic of Belarus
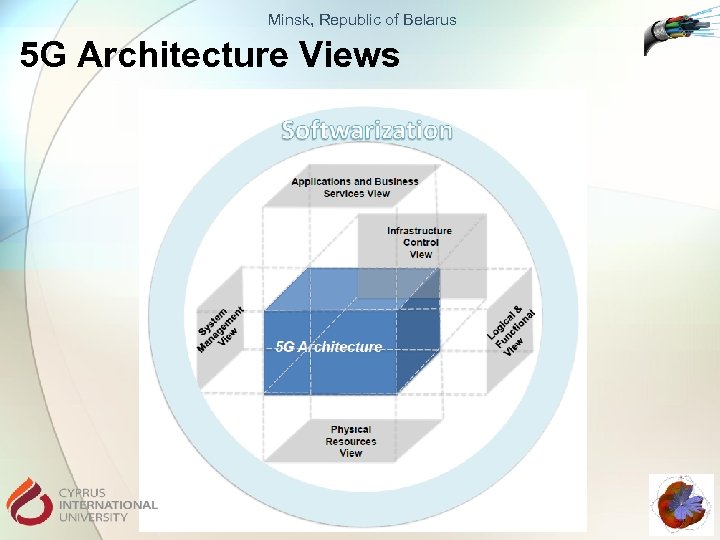
Minsk, Republic of Belarus 5 G Architecture Views
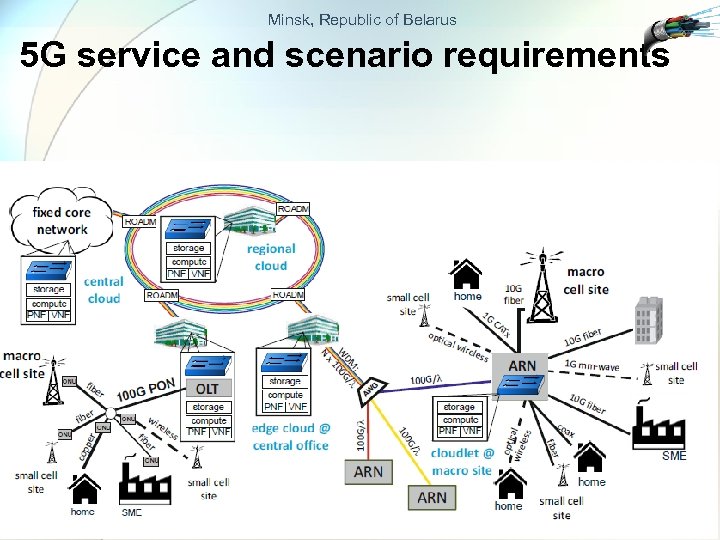
Minsk, Republic of Belarus 5 G service and scenario requirements
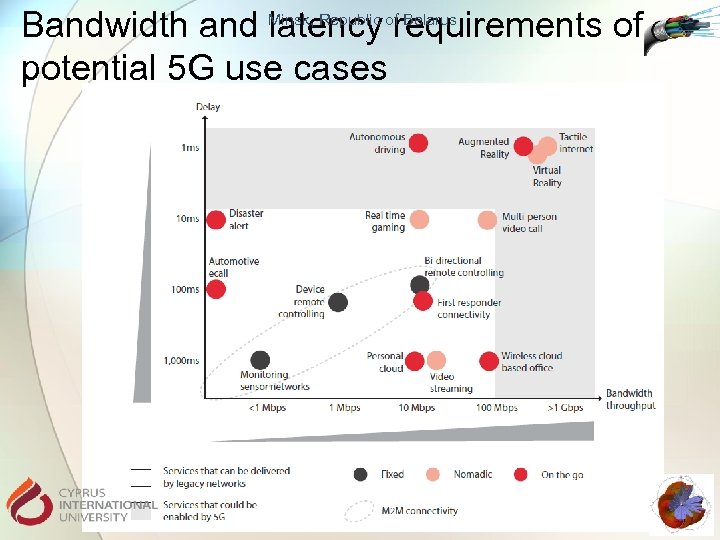
Bandwidth and Minsk, Republic ofrequirements of latency Belarus potential 5 G use cases
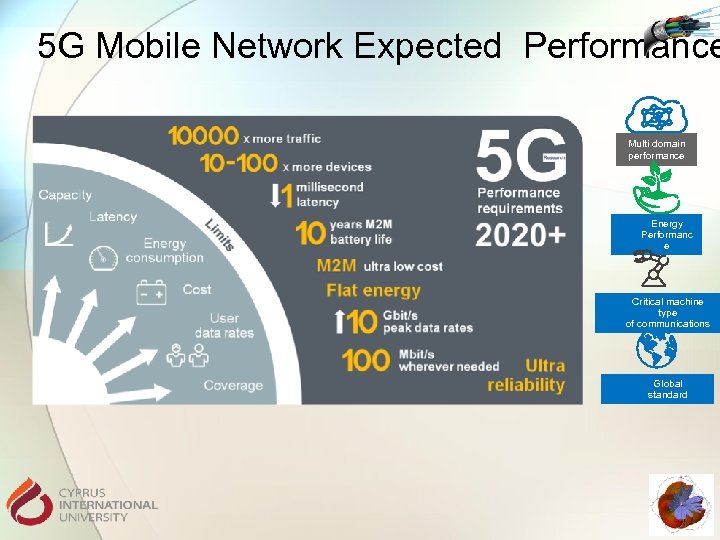
5 G Mobile Network Expected Performance Multi domain performance Energy Performanc e Critical machine type of communications Global standard

5 G Top Use Cases Broadband experience everywhere anytime Massive Machine Type Communication Critical Machine Type Communication Mass market personalized TV
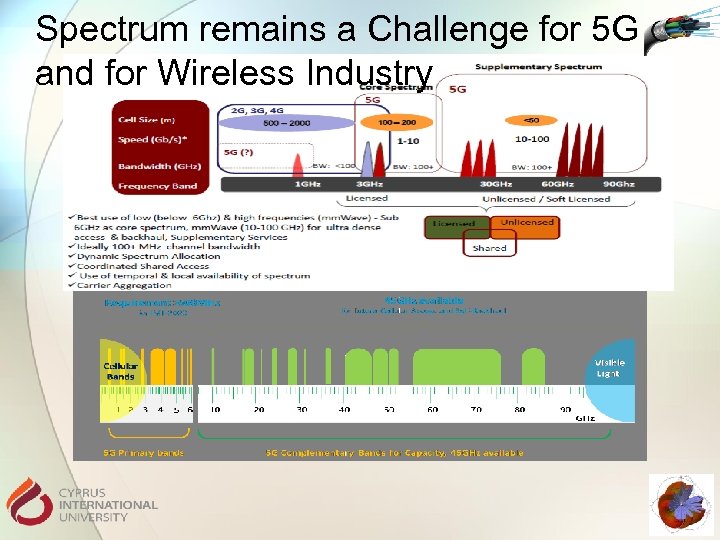
Spectrum remains a Challenge for 5 G and for Wireless Industry
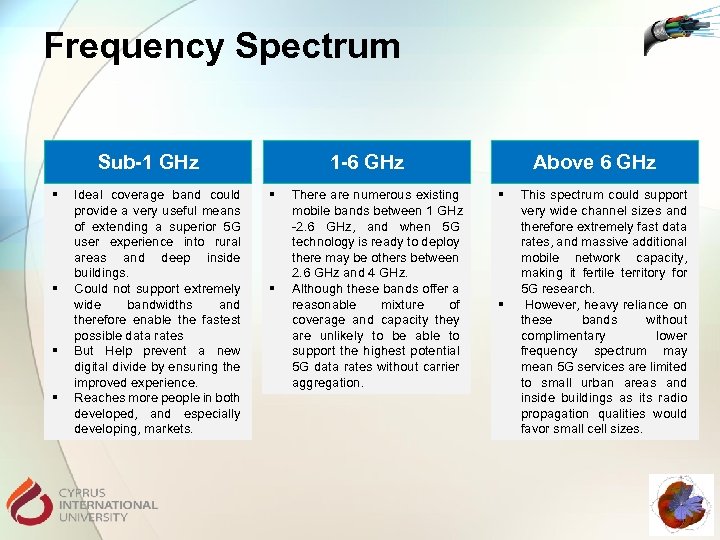
Frequency Spectrum Sub-1 GHz § § Ideal coverage band could provide a very useful means of extending a superior 5 G user experience into rural areas and deep inside buildings. Could not support extremely wide bandwidths and therefore enable the fastest possible data rates But Help prevent a new digital divide by ensuring the improved experience. Reaches more people in both developed, and especially developing, markets. 1 -6 GHz § § There are numerous existing mobile bands between 1 GHz -2. 6 GHz, and when 5 G technology is ready to deploy there may be others between 2. 6 GHz and 4 GHz. Although these bands offer a reasonable mixture of coverage and capacity they are unlikely to be able to support the highest potential 5 G data rates without carrier aggregation. Above 6 GHz § § This spectrum could support very wide channel sizes and therefore extremely fast data rates, and massive additional mobile network capacity, making it fertile territory for 5 G research. However, heavy reliance on these bands without complimentary lower frequency spectrum may mean 5 G services are limited to small urban areas and inside buildings as its radio propagation qualities would favor small cell sizes.
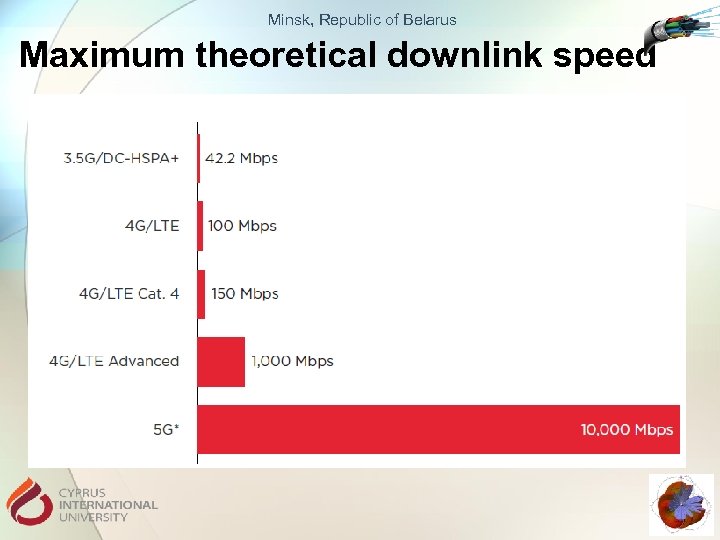
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Maximum theoretical downlink speed
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Necessary breakthroughs
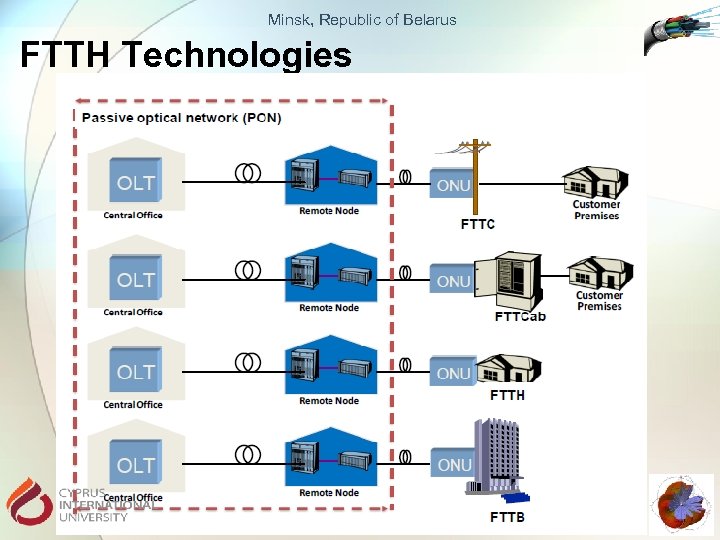
Minsk, Republic of Belarus FTTH Technologies
![Minsk, Republic of Belarus Dedicated Speed [Mb/s] Core Network - PON Trends PON: 32 Minsk, Republic of Belarus Dedicated Speed [Mb/s] Core Network - PON Trends PON: 32](https://present5.com/presentation/a0e9475fcef997242642e5d9eff40039/image-29.jpg)
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Dedicated Speed [Mb/s] Core Network - PON Trends PON: 32 split ratio 10, 000 WDM-PON 10 Gb/s 1, 000 1 Gb/s WDM-PON 10 G-PON 312 Mb/s 100 Mb/s 78 Mb/s Shared line rate 10 10 Mb/s A-PON Ethernet(2. 94 M) 1970 A-PON 1 Mb/s ALOHA WDM-PON G-PON 1980 1990 E-PON 30 Mb/s B-PON 19. 4 Mb/s 4. 8 Mb/s 1. 7 Mb/s 2000 2010 Source: C. Lee, JLT, Dec. 2006 29
Minsk, Republic of Belarus Virtualized architectures • Radio access infrastructures based on cloud architecture technologies will provide on-demand resource processing, storage and network capacity wherever needed. Softwaredefined air interface technologies will be seamlessly integrated into 5 G wireless access network architectures. The evolution of RAN sites will develop toward a “hyper transceiver” approach to mobile access, and will help realize the joint-layer optimization of how radio resources are efficiently utilized. • Core network evolution will revolve around how to enable more flexibility for the creation of new services and new applications. Cloud computing will become the foundation of core networks, and will open the network to allow the leveraging of innovations as they are developed. 5 G core networks will also be equipped to seamlessly integrate with
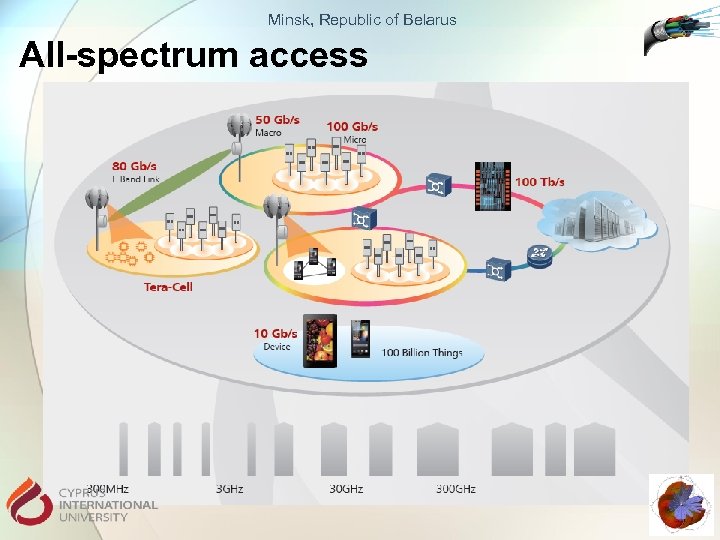
Minsk, Republic of Belarus All-spectrum access
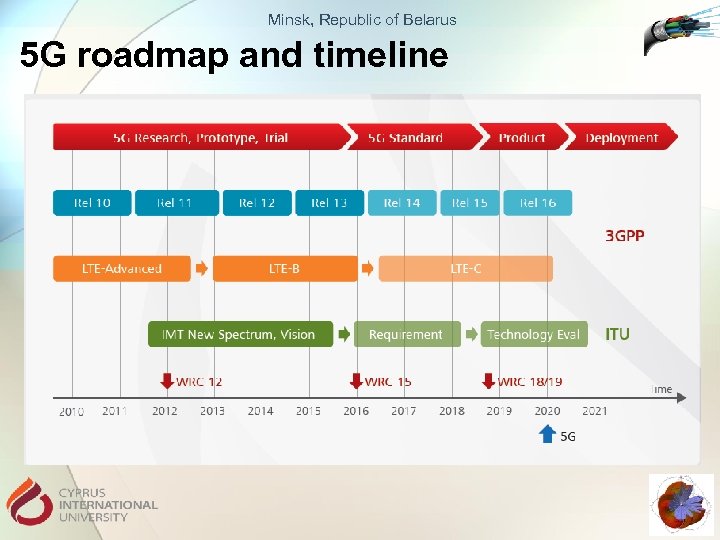
Minsk, Republic of Belarus 5 G roadmap and timeline

Minsk, • The next Republic of Belarus decade promises breakthrough Discussiondevelopments in several fundamental RAN technologies that will be required for implementing commercial-ready 5 G network solutions: • Multiple access and advanced waveform technologies combined with coding and modulation algorithms • Interference management • Access protocols • Service delivery architecture • Mass-scale MIMO • Single frequency full duplex radio technologies • 5 G devices • Virtualized and cloud-based radio access infrastructure • 5 G success depends on the entire ICT

Sonuç As long as wireless communication evolves, convenient, easily accessible and efficient means of utilising the available resources will always be in demand.

Minsk, Republic of Belarus Thanks for your attention. . .
a0e9475fcef997242642e5d9eff40039.ppt