279572d33ad07a1d64ca043974f39b5b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Advances in Capillary Columns For Gas Chromatographic Applications Shawn Reese, Roy Lautamo, Chris Cox Gianna Barlupi, Rick Morehead, Jason Thomas, Gary Stidsen, and Frank Dorman
Advances in Capillary Columns For Gas Chromatographic Applications Shawn Reese, Roy Lautamo, Chris Cox Gianna Barlupi, Rick Morehead, Jason Thomas, Gary Stidsen, and Frank Dorman
 Old Technology? • Gas Chromatography is 50 years old! Like wine and cheese it seems to keep getting better!! • Packed columns (over 100 different phases) • Capillary debut commercially in 1970’s • Phase development parallels some packed column phases
Old Technology? • Gas Chromatography is 50 years old! Like wine and cheese it seems to keep getting better!! • Packed columns (over 100 different phases) • Capillary debut commercially in 1970’s • Phase development parallels some packed column phases
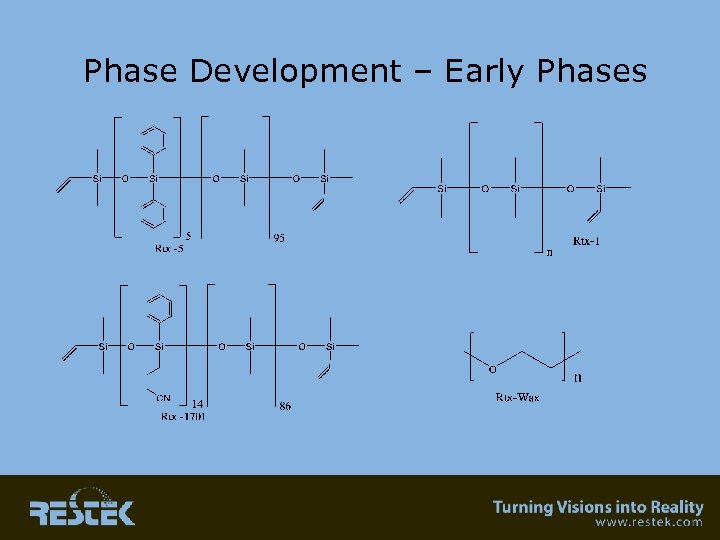 Phase Development – Early Phases
Phase Development – Early Phases
 Capillary Phase Technology • Pendant siloxanes do not show large viscosity changes with temperature (from -40 to 400 o. C) • High polarity applications require a wax phase which has a high temperature limit of 260 • Deactivation technology varies from manufacturer and can be a limiting factor on what is possible • Pendant phases are fairly similar from manufacturer to manufacturer
Capillary Phase Technology • Pendant siloxanes do not show large viscosity changes with temperature (from -40 to 400 o. C) • High polarity applications require a wax phase which has a high temperature limit of 260 • Deactivation technology varies from manufacturer and can be a limiting factor on what is possible • Pendant phases are fairly similar from manufacturer to manufacturer
 What Does the Industry Need? • Low Bleed? – What is bleed? Can it be stopped? • “MS” Phases? – Application of low-bleed technology? • Reproducible columns? – Why do our manufacturing profiles matter to you? • Inertness – Professor Walt Jennings, Riva 2004 • Selectivity-specific applications – PCB’s, Dioxins, PBDPE’s, pesticides
What Does the Industry Need? • Low Bleed? – What is bleed? Can it be stopped? • “MS” Phases? – Application of low-bleed technology? • Reproducible columns? – Why do our manufacturing profiles matter to you? • Inertness – Professor Walt Jennings, Riva 2004 • Selectivity-specific applications – PCB’s, Dioxins, PBDPE’s, pesticides
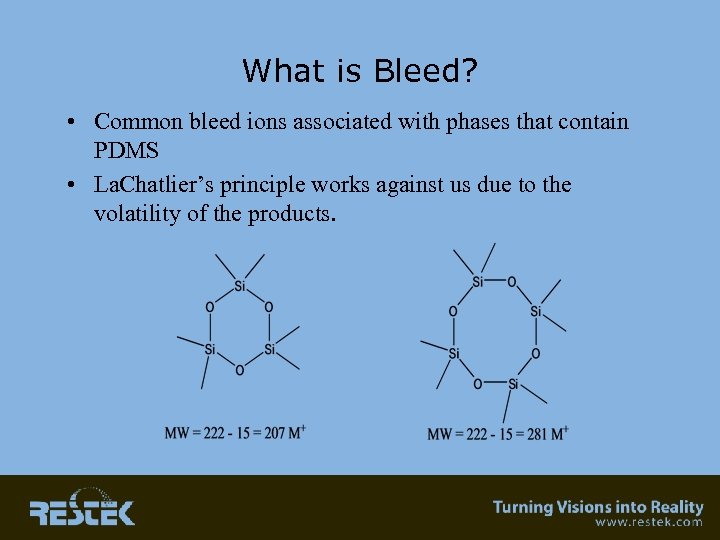 What is Bleed? • Common bleed ions associated with phases that contain PDMS • La. Chatlier’s principle works against us due to the volatility of the products.
What is Bleed? • Common bleed ions associated with phases that contain PDMS • La. Chatlier’s principle works against us due to the volatility of the products.
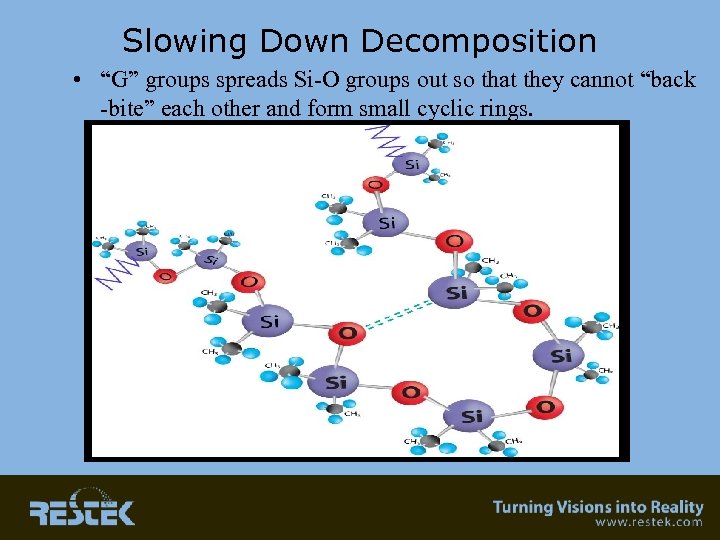 Slowing Down Decomposition • “G” groups spreads Si-O groups out so that they cannot “back -bite” each other and form small cyclic rings.
Slowing Down Decomposition • “G” groups spreads Si-O groups out so that they cannot “back -bite” each other and form small cyclic rings.
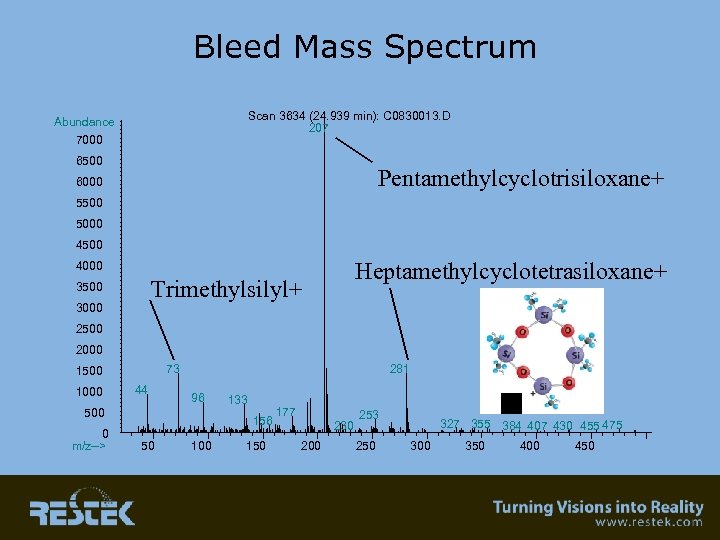 Bleed Mass Spectrum Scan 3634 (24. 939 min): C 0830013. D 207 Abundance 7000 6500 Pentamethylcyclotrisiloxane+ 6000 5500 5000 4500 Heptamethylcyclotetrasiloxane+ 4000 Trimethylsilyl+ 3500 3000 2500 2000 73 1500 1000 44 281 96 500 0 m/z--> 133 156 50 100 150 177 230 200 253 250 327 355 384 407 430 455 475 300 350 400 450
Bleed Mass Spectrum Scan 3634 (24. 939 min): C 0830013. D 207 Abundance 7000 6500 Pentamethylcyclotrisiloxane+ 6000 5500 5000 4500 Heptamethylcyclotetrasiloxane+ 4000 Trimethylsilyl+ 3500 3000 2500 2000 73 1500 1000 44 281 96 500 0 m/z--> 133 156 50 100 150 177 230 200 253 250 327 355 384 407 430 455 475 300 350 400 450
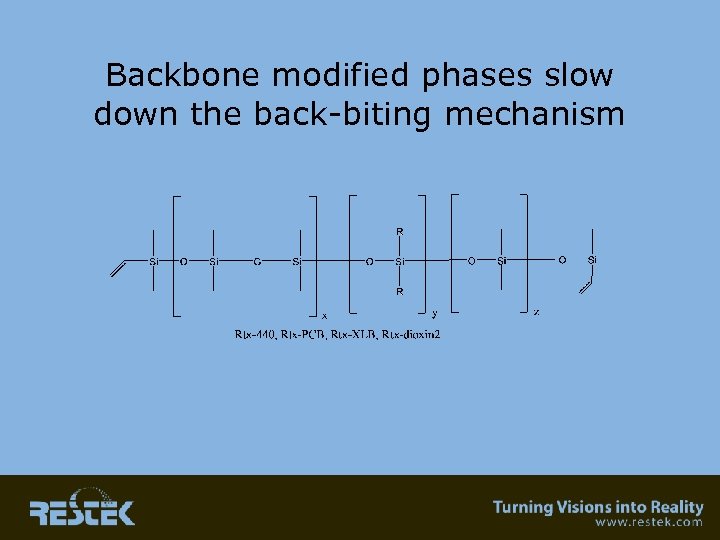 Backbone modified phases slow down the back-biting mechanism
Backbone modified phases slow down the back-biting mechanism
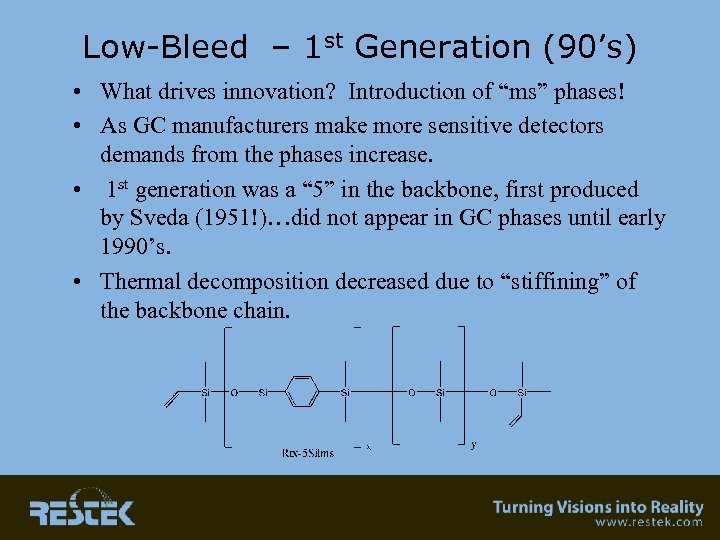 Low-Bleed – 1 st Generation (90’s) • What drives innovation? Introduction of “ms” phases! • As GC manufacturers make more sensitive detectors demands from the phases increase. • 1 st generation was a “ 5” in the backbone, first produced by Sveda (1951!)…did not appear in GC phases until early 1990’s. • Thermal decomposition decreased due to “stiffining” of the backbone chain.
Low-Bleed – 1 st Generation (90’s) • What drives innovation? Introduction of “ms” phases! • As GC manufacturers make more sensitive detectors demands from the phases increase. • 1 st generation was a “ 5” in the backbone, first produced by Sveda (1951!)…did not appear in GC phases until early 1990’s. • Thermal decomposition decreased due to “stiffining” of the backbone chain.
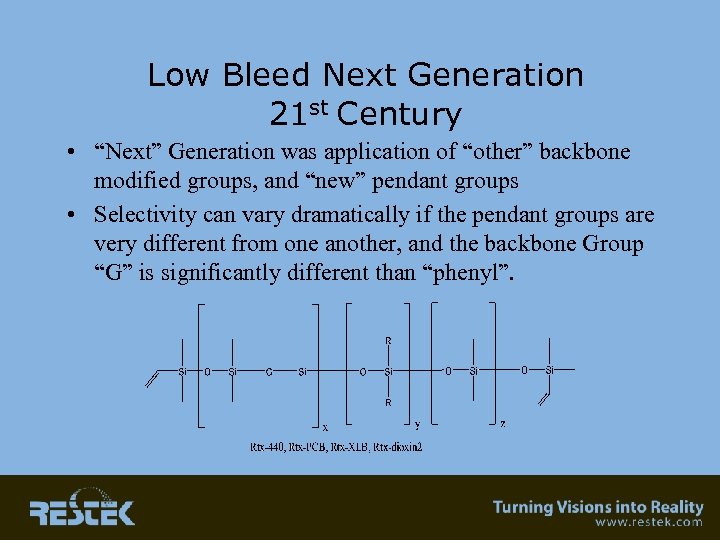 Low Bleed Next Generation 21 st Century • “Next” Generation was application of “other” backbone modified groups, and “new” pendant groups • Selectivity can vary dramatically if the pendant groups are very different from one another, and the backbone Group “G” is significantly different than “phenyl”.
Low Bleed Next Generation 21 st Century • “Next” Generation was application of “other” backbone modified groups, and “new” pendant groups • Selectivity can vary dramatically if the pendant groups are very different from one another, and the backbone Group “G” is significantly different than “phenyl”.
 What “G” groups have been used? • Literature reports the following groups:
What “G” groups have been used? • Literature reports the following groups:
 Deactivations – A new problem? • Bench-top mass spectrometers in the early 90’s had sensitivity similar to the standard FID • Today, sensitivity of bench-top mass spectrometers are better than the standard FID, and the column can interfere with detection. • Inertness is a more serious issue now with detection below nanogram levels on MS.
Deactivations – A new problem? • Bench-top mass spectrometers in the early 90’s had sensitivity similar to the standard FID • Today, sensitivity of bench-top mass spectrometers are better than the standard FID, and the column can interfere with detection. • Inertness is a more serious issue now with detection below nanogram levels on MS.
 What else can we do? • As the mechanism on the previous slide implies, chemically inert polymers demand the most stringent synthetic conditions • We have devised “systems” that limit the polymers ability to “find” proton sources during phase procurement through deactivation techniques and through new, proprietary syntheses.
What else can we do? • As the mechanism on the previous slide implies, chemically inert polymers demand the most stringent synthetic conditions • We have devised “systems” that limit the polymers ability to “find” proton sources during phase procurement through deactivation techniques and through new, proprietary syntheses.
 Restek’s Exceptionally Inert GC Columns (Rxi) • New column technology developed by Chemists at Restek and new research lab, Restek West • Rxi-1 ms, Rxi-5 ms • New deactivation chemistry, new polymer chemistry, new manufacturing process • Results in columns that are: – Highly Inert – Reproducible – Low bleed
Restek’s Exceptionally Inert GC Columns (Rxi) • New column technology developed by Chemists at Restek and new research lab, Restek West • Rxi-1 ms, Rxi-5 ms • New deactivation chemistry, new polymer chemistry, new manufacturing process • Results in columns that are: – Highly Inert – Reproducible – Low bleed
 Reproducibility = Reliablity for the user! • In-house QC results • Comparison between manufacturers • What do you need?
Reproducibility = Reliablity for the user! • In-house QC results • Comparison between manufacturers • What do you need?
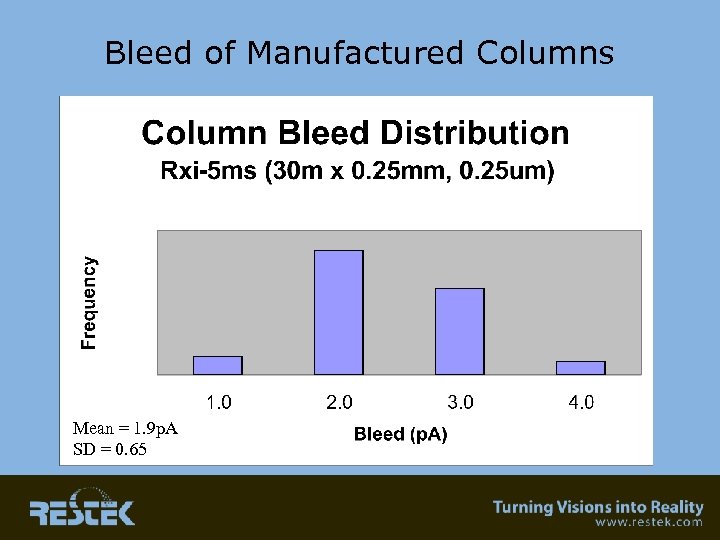 Bleed of Manufactured Columns Mean = 1. 9 p. A SD = 0. 65
Bleed of Manufactured Columns Mean = 1. 9 p. A SD = 0. 65
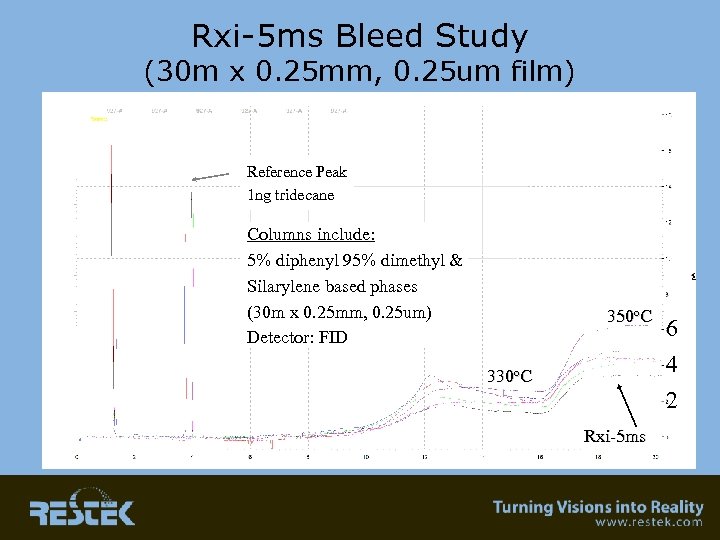 Rxi-5 ms Bleed Study (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um film) Reference Peak 1 ng tridecane Columns include: 5% diphenyl 95% dimethyl & Silarylene based phases (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um) Detector: FID 350 o. C 330 o. C Rxi-5 ms 6 4 2
Rxi-5 ms Bleed Study (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um film) Reference Peak 1 ng tridecane Columns include: 5% diphenyl 95% dimethyl & Silarylene based phases (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um) Detector: FID 350 o. C 330 o. C Rxi-5 ms 6 4 2
 Retention Time “Windows” Ultimate Reproducibility Column-to-Column • Exact Length – Is this important? • Isothermal testing – Comparison of batch to batch reproducibility • In-house QC results – Film thickness – Coating efficiency – Selectivity
Retention Time “Windows” Ultimate Reproducibility Column-to-Column • Exact Length – Is this important? • Isothermal testing – Comparison of batch to batch reproducibility • In-house QC results – Film thickness – Coating efficiency – Selectivity
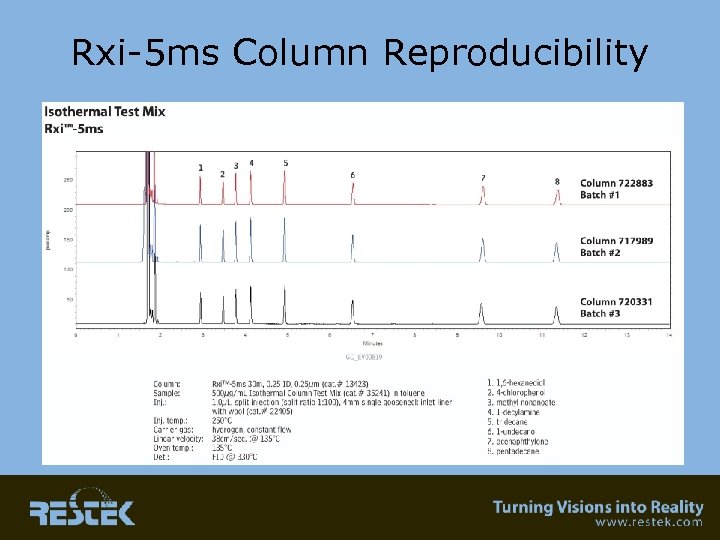 Rxi-5 ms Column Reproducibility
Rxi-5 ms Column Reproducibility
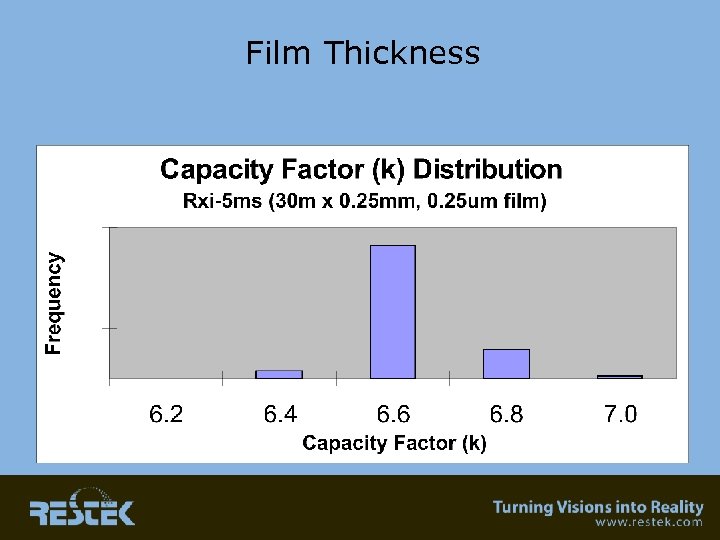 Film Thickness
Film Thickness
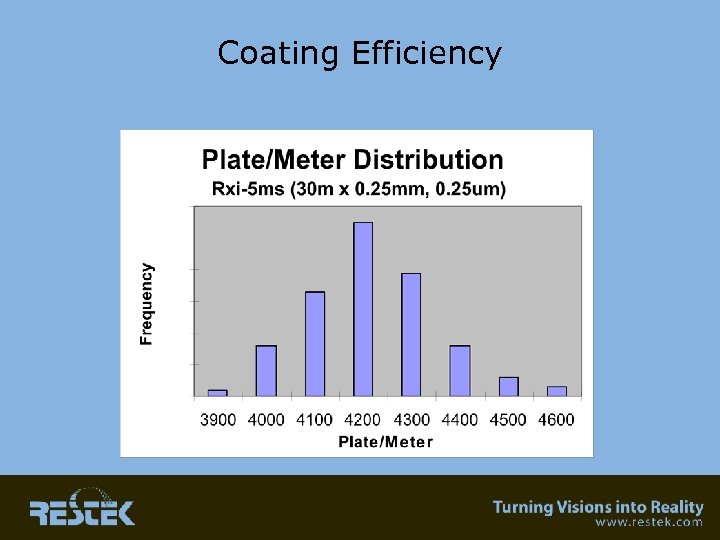 Coating Efficiency
Coating Efficiency
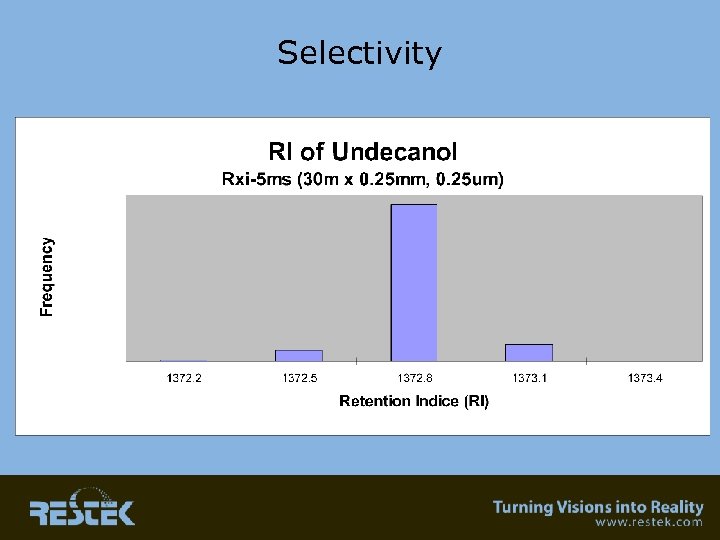 Selectivity
Selectivity
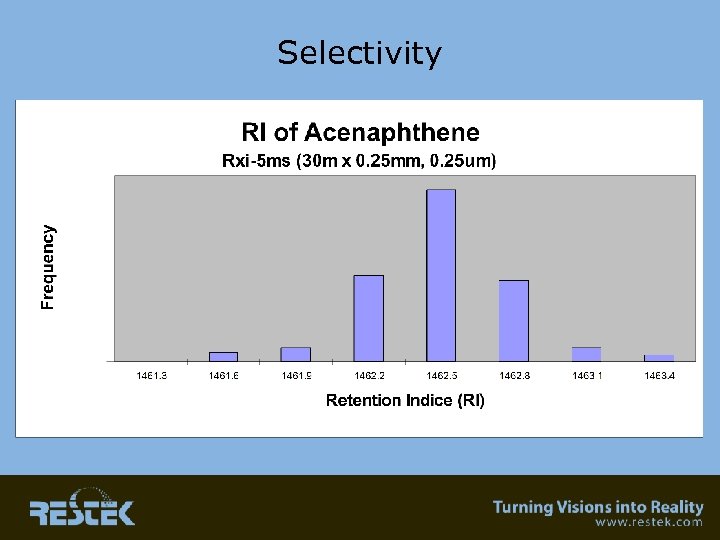 Selectivity
Selectivity
 Inertness • 0. 5 ng on-column concentration – Basic compound – Acidic compound • 2 ng on-column comparison between manufacturers – Chromatographic peaks of pyridine – Response factor • This is the area that is a “WIP”…. we have come a long way…. . can it get better? We’ll show Rxi as an example of what all columns should be like!
Inertness • 0. 5 ng on-column concentration – Basic compound – Acidic compound • 2 ng on-column comparison between manufacturers – Chromatographic peaks of pyridine – Response factor • This is the area that is a “WIP”…. we have come a long way…. . can it get better? We’ll show Rxi as an example of what all columns should be like!
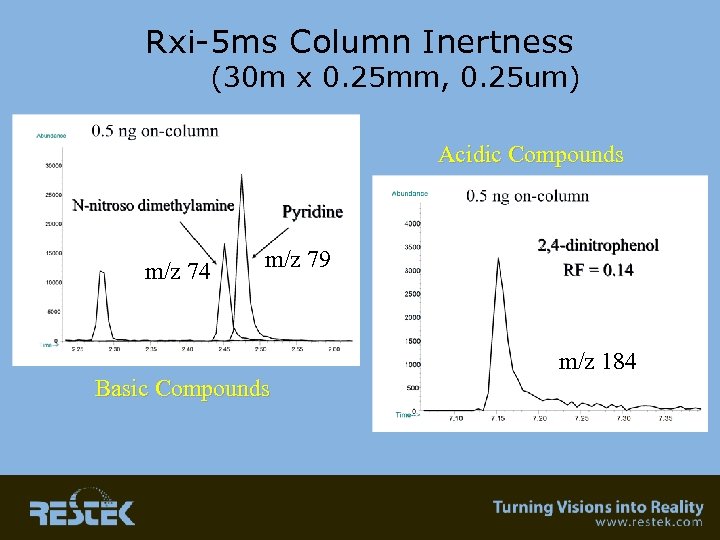 Rxi-5 ms Column Inertness (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um) Acidic Compounds m/z 74 m/z 79 m/z 184 Basic Compounds
Rxi-5 ms Column Inertness (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um) Acidic Compounds m/z 74 m/z 79 m/z 184 Basic Compounds
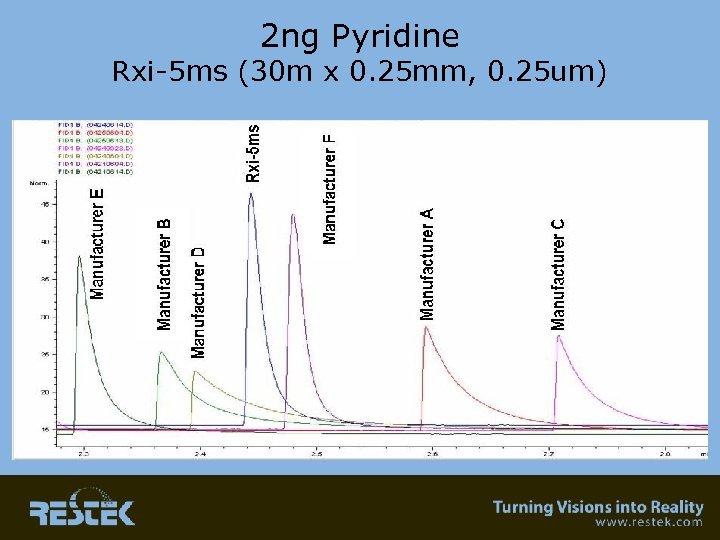 2 ng Pyridine Rxi-5 ms (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um)
2 ng Pyridine Rxi-5 ms (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um)
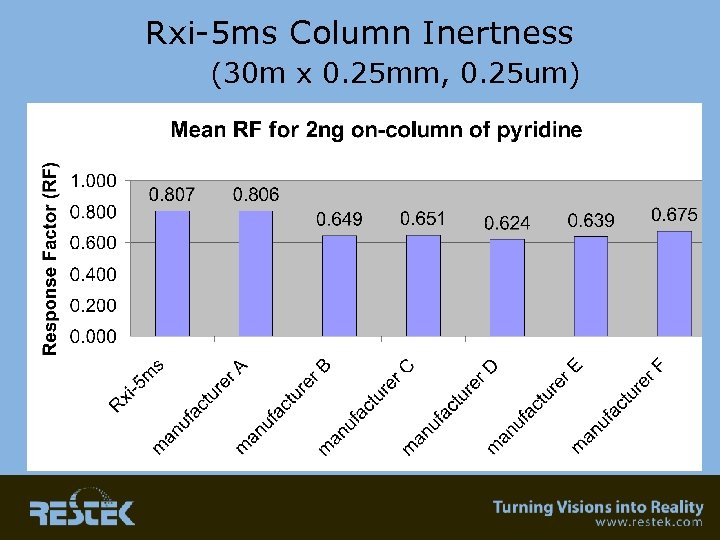 Rxi-5 ms Column Inertness (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um)
Rxi-5 ms Column Inertness (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um)
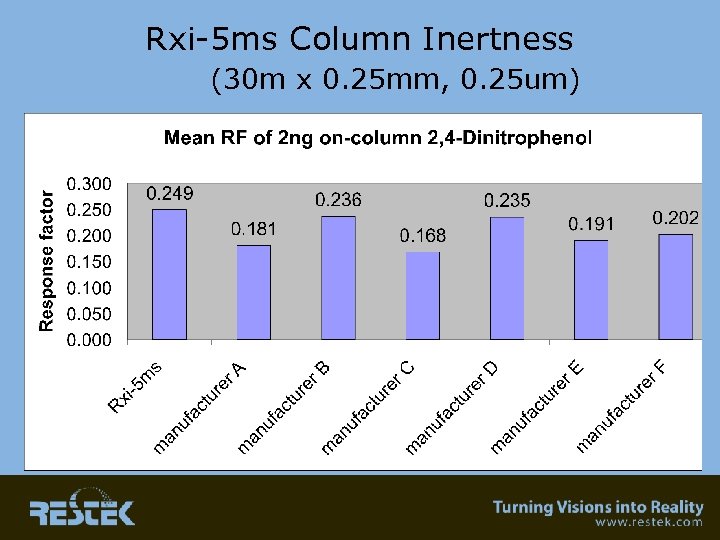 Rxi-5 ms Column Inertness (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um)
Rxi-5 ms Column Inertness (30 m x 0. 25 mm, 0. 25 um)
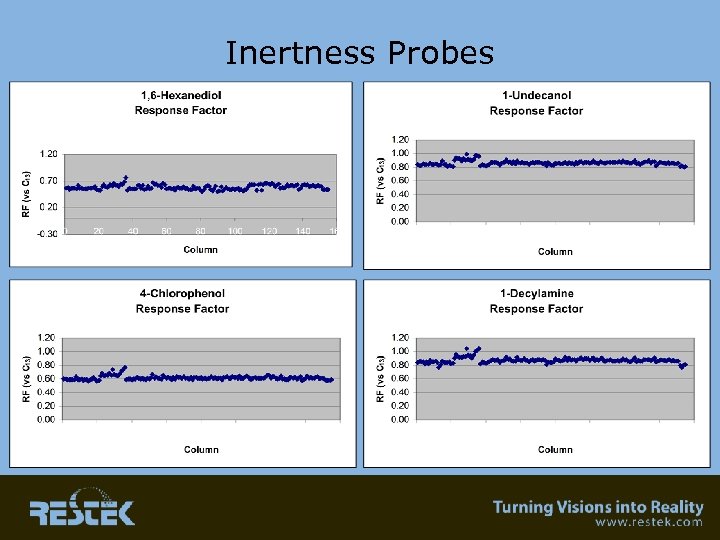 Inertness Probes
Inertness Probes
 Applications • Environmental – Semivolatile analysis • Clinical – Acidic and basic drugs
Applications • Environmental – Semivolatile analysis • Clinical – Acidic and basic drugs
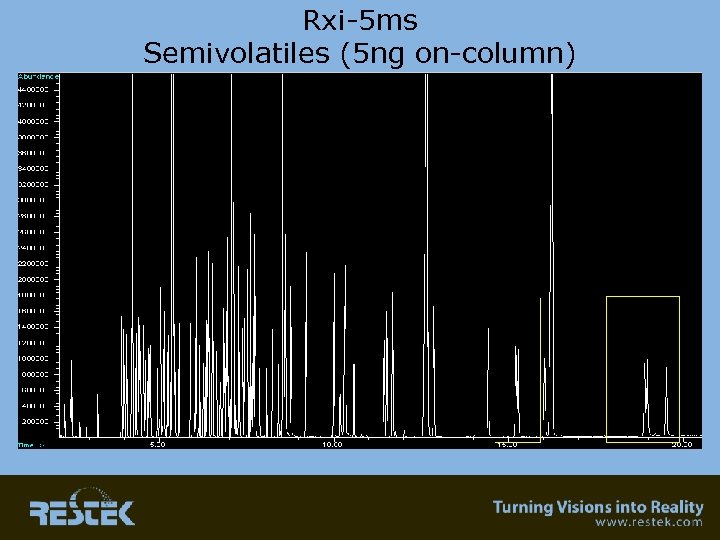 Rxi-5 ms Semivolatiles (5 ng on-column)
Rxi-5 ms Semivolatiles (5 ng on-column)
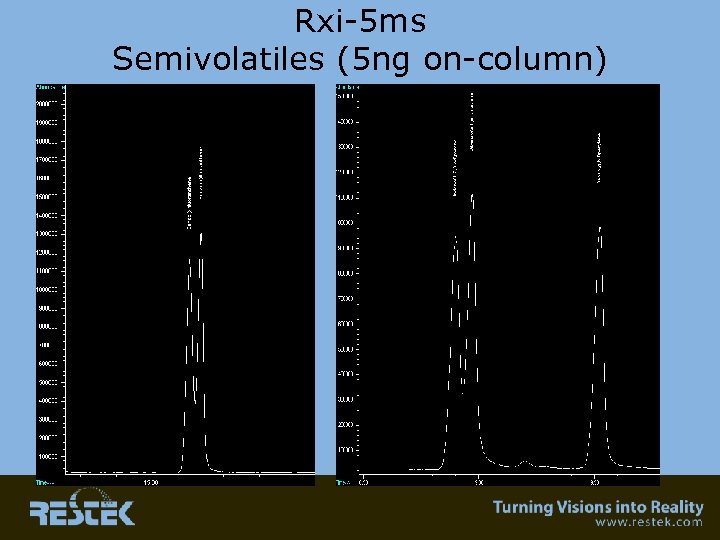 Rxi-5 ms Semivolatiles (5 ng on-column)
Rxi-5 ms Semivolatiles (5 ng on-column)
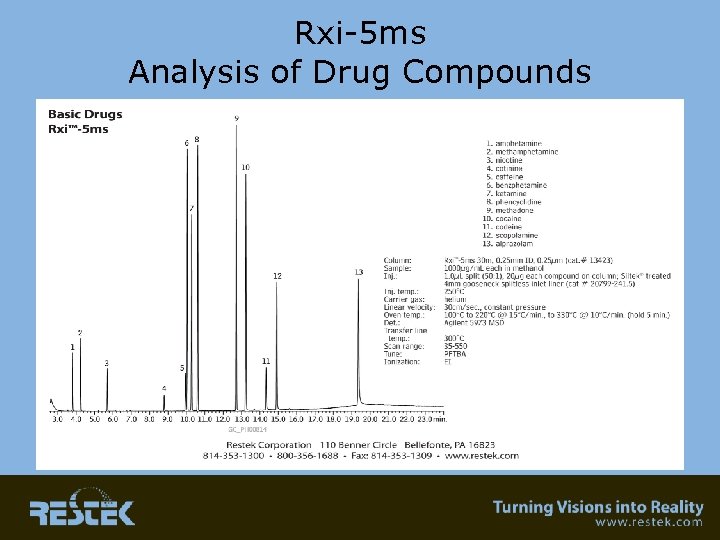 Rxi-5 ms Analysis of Drug Compounds
Rxi-5 ms Analysis of Drug Compounds
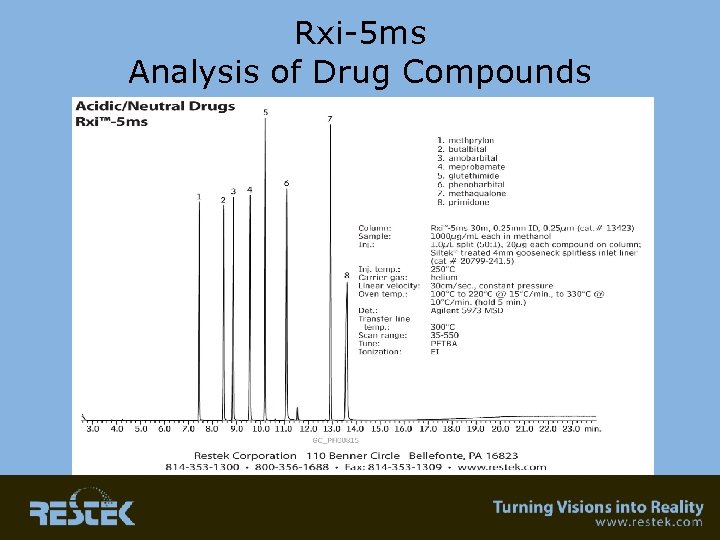 Rxi-5 ms Analysis of Drug Compounds
Rxi-5 ms Analysis of Drug Compounds
 Summary of Rxi Columns • Unsurpassed inertness for active compounds • Low bleed • Excellent column to column manufacturing • Excellent overall performance due to combination of inertness, low bleed, and reproducible manufacturing process
Summary of Rxi Columns • Unsurpassed inertness for active compounds • Low bleed • Excellent column to column manufacturing • Excellent overall performance due to combination of inertness, low bleed, and reproducible manufacturing process
 Special Selectivity? • Application specific – not everyone is doing congener specific PCB analysis • Utilizes low-bleed technology, and incorporates many manufacturing techniques as our Rxi process • These polymers are Restek specific; cannot be found from other manufacturers
Special Selectivity? • Application specific – not everyone is doing congener specific PCB analysis • Utilizes low-bleed technology, and incorporates many manufacturing techniques as our Rxi process • These polymers are Restek specific; cannot be found from other manufacturers
 Rtx-Dioxin 2 • New phase that is specially “tuned” for dioxin analysis
Rtx-Dioxin 2 • New phase that is specially “tuned” for dioxin analysis
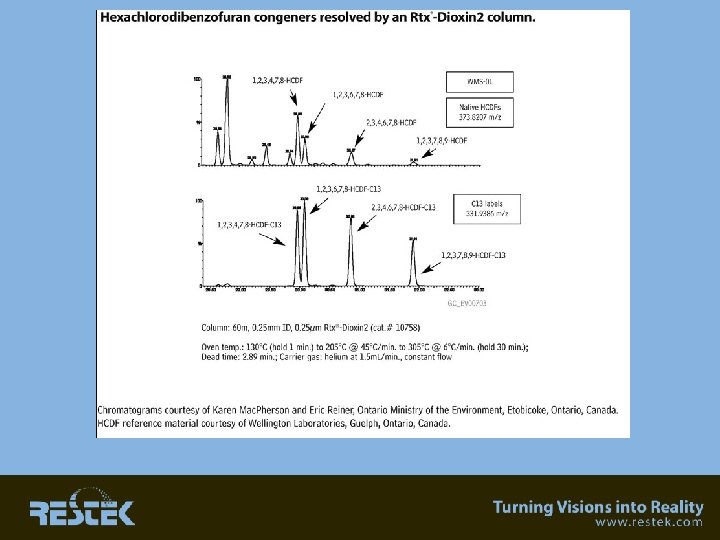 Rtx-Dioxin 2
Rtx-Dioxin 2
 Rtx-PCB Congener Specific Analysis • Resolves most PCB’s into absolute separation or “MS-resolvable” separations (differing Cl numbers). • A low bleed phase – will allow for high temperature applications for “dirty” samples.
Rtx-PCB Congener Specific Analysis • Resolves most PCB’s into absolute separation or “MS-resolvable” separations (differing Cl numbers). • A low bleed phase – will allow for high temperature applications for “dirty” samples.
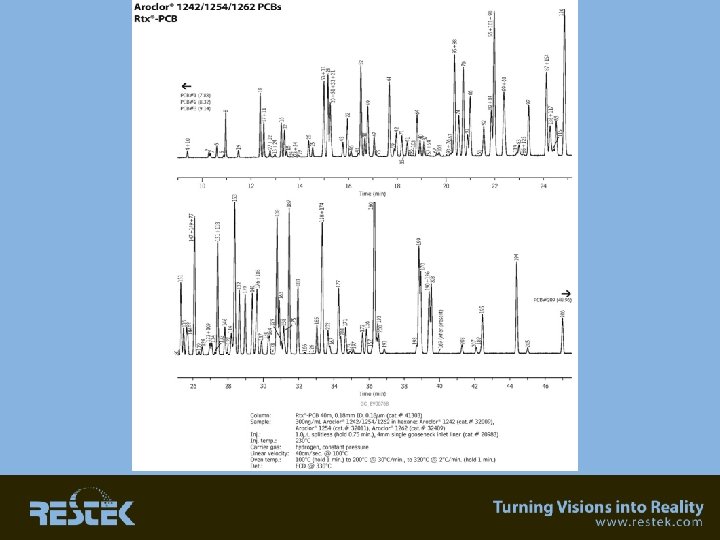 Rtx-PCB place picture here
Rtx-PCB place picture here
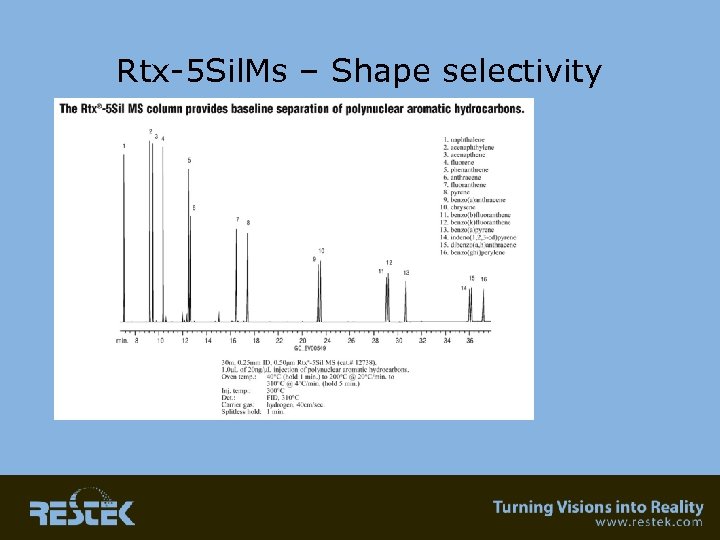 Rtx-5 Sil. Ms – Shape selectivity
Rtx-5 Sil. Ms – Shape selectivity
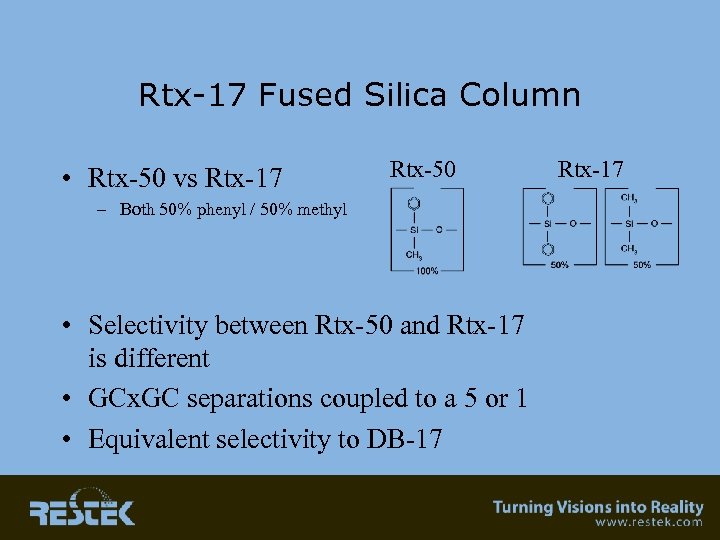 Rtx-17 Fused Silica Column • Rtx-50 vs Rtx-17 Rtx-50 – Both 50% phenyl / 50% methyl • Selectivity between Rtx-50 and Rtx-17 is different • GCx. GC separations coupled to a 5 or 1 • Equivalent selectivity to DB-17 Rtx-17
Rtx-17 Fused Silica Column • Rtx-50 vs Rtx-17 Rtx-50 – Both 50% phenyl / 50% methyl • Selectivity between Rtx-50 and Rtx-17 is different • GCx. GC separations coupled to a 5 or 1 • Equivalent selectivity to DB-17 Rtx-17
 Acknowledgements • Chris English and innovations group for applications • Roy Lautamo for suggestions on how to proceed • Shimadzu for kind invitation and providing support for this trip!!
Acknowledgements • Chris English and innovations group for applications • Roy Lautamo for suggestions on how to proceed • Shimadzu for kind invitation and providing support for this trip!!


