14d12052a23b7bfb0c3b35b095917c2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Advanced Weather Interactive Processing System (AWIPS II) Overview for Development Collaboration Workshop September 29, 2010 Ed Mandel, Steve Schotz, & Jim Calkins NWS – Office of Science and Technology
Advanced Weather Interactive Processing System (AWIPS II) Overview for Development Collaboration Workshop September 29, 2010 Ed Mandel, Steve Schotz, & Jim Calkins NWS – Office of Science and Technology
 AGENDA • AWIPS II Technology Infusion Scope and Milestones • AWIPS II Migration – Approach, Status and Latest Schedule • AWIPS II Architecture Overview – Major Software Components – Communications Interfaces – Standards and Formats • AWIPS II Extended Projects • AWIPS II Software Development Strategy in the AWIPS II Era
AGENDA • AWIPS II Technology Infusion Scope and Milestones • AWIPS II Migration – Approach, Status and Latest Schedule • AWIPS II Architecture Overview – Major Software Components – Communications Interfaces – Standards and Formats • AWIPS II Extended Projects • AWIPS II Software Development Strategy in the AWIPS II Era
 AWIPS II Technology Infusion Scope AWIPS II Technology Infusion (FY 2005 – FY 2015) – A long-term project which delivers a modern, robust software infrastructure that provides the foundation for future system level enhancements for the entire NWS enterprise • Phase 1: (FY 2006 -FY 2011) – Migration of WFO/RFC AWIPS (AWIPS I) to a modern Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) infrastructure executed incrementally through a series of task orders • Phase II: (FY 2009 -FY 2013) – AWIPS SOA Extension – Creation of a seamless weather enterprise spanning NWS operations • Migration of NAWIPS into the AWIPS ISOA • Delivery of thin client to support for the Weather Service Offices, Center Weather Support Units, Incident Meteorologists, (e. g. , Fire Weather, backup support for RFCs and National Centers) • Integration of Weather Event Simulator) • CHPS Integration into AWIPS SOA • Phase III: (FY 2009 – FY 2015) – Enterprise Level Enhancements • • Data delivery enhancements: “Smart push-smart pull” data access Integrated visual collaboration Information generation enhancements Visualization enhancements
AWIPS II Technology Infusion Scope AWIPS II Technology Infusion (FY 2005 – FY 2015) – A long-term project which delivers a modern, robust software infrastructure that provides the foundation for future system level enhancements for the entire NWS enterprise • Phase 1: (FY 2006 -FY 2011) – Migration of WFO/RFC AWIPS (AWIPS I) to a modern Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) infrastructure executed incrementally through a series of task orders • Phase II: (FY 2009 -FY 2013) – AWIPS SOA Extension – Creation of a seamless weather enterprise spanning NWS operations • Migration of NAWIPS into the AWIPS ISOA • Delivery of thin client to support for the Weather Service Offices, Center Weather Support Units, Incident Meteorologists, (e. g. , Fire Weather, backup support for RFCs and National Centers) • Integration of Weather Event Simulator) • CHPS Integration into AWIPS SOA • Phase III: (FY 2009 – FY 2015) – Enterprise Level Enhancements • • Data delivery enhancements: “Smart push-smart pull” data access Integrated visual collaboration Information generation enhancements Visualization enhancements
 AWIPS II Migration Re-Architecture Approach • Perform “black-box” conversion – Preserve existing functionality, look and feel on top of new infrastructure • Thorough field validation and acceptance before deployment • No loss of functionality – Deployed system current with deployed AWIPS capability (i. e. , OB 9) • Use open source projects - No proprietary code • Objective is to make AWIPS II available for collaborative development
AWIPS II Migration Re-Architecture Approach • Perform “black-box” conversion – Preserve existing functionality, look and feel on top of new infrastructure • Thorough field validation and acceptance before deployment • No loss of functionality – Deployed system current with deployed AWIPS capability (i. e. , OB 9) • Use open source projects - No proprietary code • Objective is to make AWIPS II available for collaborative development
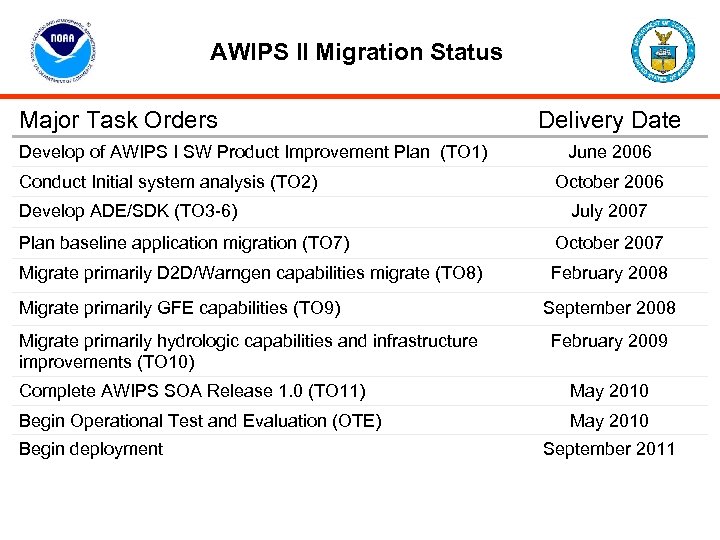 AWIPS II Migration Status Major Task Orders Develop of AWIPS I SW Product Improvement Plan (TO 1) Conduct Initial system analysis (TO 2) Develop ADE/SDK (TO 3 -6) Delivery Date June 2006 October 2006 July 2007 Plan baseline application migration (TO 7) October 2007 Migrate primarily D 2 D/Warngen capabilities migrate (TO 8) February 2008 Migrate primarily GFE capabilities (TO 9) Migrate primarily hydrologic capabilities and infrastructure improvements (TO 10) September 2008 February 2009 Complete AWIPS SOA Release 1. 0 (TO 11) May 2010 Begin Operational Test and Evaluation (OTE) May 2010 Begin deployment September 2011
AWIPS II Migration Status Major Task Orders Develop of AWIPS I SW Product Improvement Plan (TO 1) Conduct Initial system analysis (TO 2) Develop ADE/SDK (TO 3 -6) Delivery Date June 2006 October 2006 July 2007 Plan baseline application migration (TO 7) October 2007 Migrate primarily D 2 D/Warngen capabilities migrate (TO 8) February 2008 Migrate primarily GFE capabilities (TO 9) Migrate primarily hydrologic capabilities and infrastructure improvements (TO 10) September 2008 February 2009 Complete AWIPS SOA Release 1. 0 (TO 11) May 2010 Begin Operational Test and Evaluation (OTE) May 2010 Begin deployment September 2011
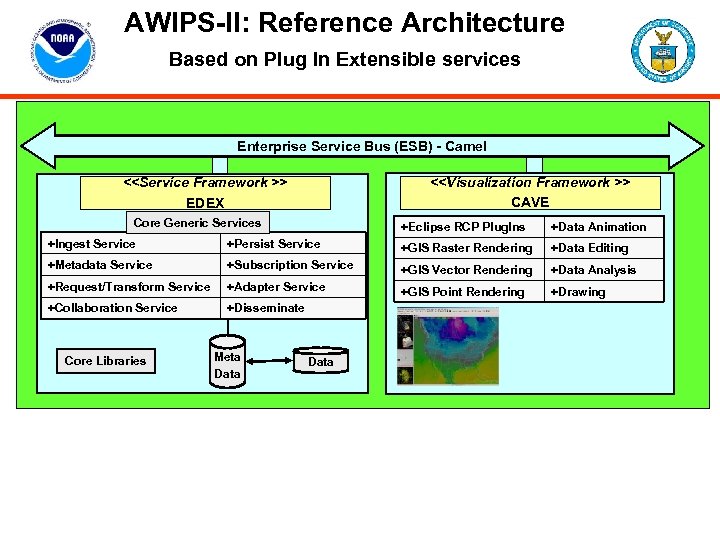 AWIPS-II: Reference Architecture Based on Plug In Extensible services AWIPS-II Reference Architecture Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) - Camel <
AWIPS-II: Reference Architecture Based on Plug In Extensible services AWIPS-II Reference Architecture Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) - Camel <
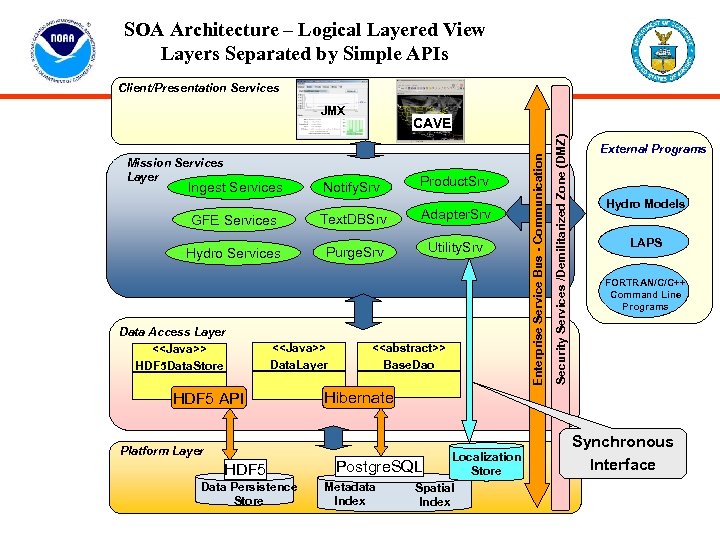 SOA Architecture – Logical Layered View Layers Separated by Simple APIs Client/Presentation Services JMX Notify. Srv Product. Srv GFE Services Text. DBSrv Adapter. Srv Hydro Services Purge. Srv Utility. Srv Data Access Layer <
SOA Architecture – Logical Layered View Layers Separated by Simple APIs Client/Presentation Services JMX Notify. Srv Product. Srv GFE Services Text. DBSrv Adapter. Srv Hydro Services Purge. Srv Utility. Srv Data Access Layer <
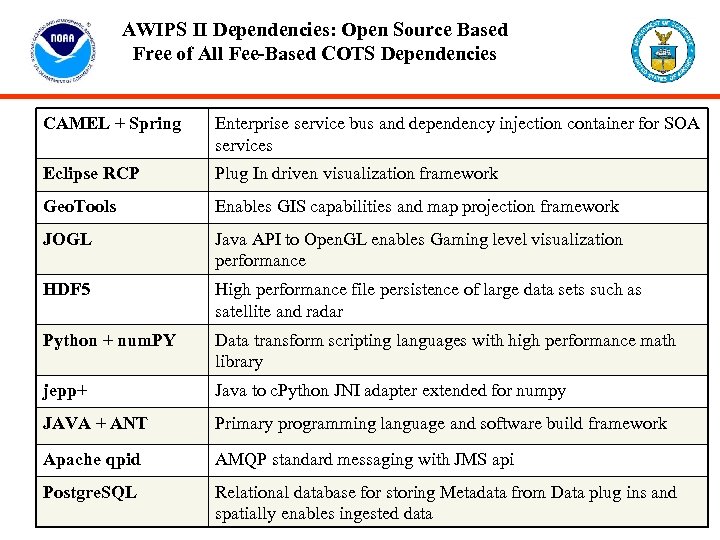 AWIPS II Dependencies: Open Source Based Free of All Fee-Based COTS Dependencies CAMEL + Spring Enterprise service bus and dependency injection container for SOA services Eclipse RCP Plug In driven visualization framework Geo. Tools Enables GIS capabilities and map projection framework JOGL Java API to Open. GL enables Gaming level visualization performance HDF 5 High performance file persistence of large data sets such as satellite and radar Python + num. PY Data transform scripting languages with high performance math library jepp+ Java to c. Python JNI adapter extended for numpy JAVA + ANT Primary programming language and software build framework Apache qpid AMQP standard messaging with JMS api Postgre. SQL Relational database for storing Metadata from Data plug ins and spatially enables ingested data
AWIPS II Dependencies: Open Source Based Free of All Fee-Based COTS Dependencies CAMEL + Spring Enterprise service bus and dependency injection container for SOA services Eclipse RCP Plug In driven visualization framework Geo. Tools Enables GIS capabilities and map projection framework JOGL Java API to Open. GL enables Gaming level visualization performance HDF 5 High performance file persistence of large data sets such as satellite and radar Python + num. PY Data transform scripting languages with high performance math library jepp+ Java to c. Python JNI adapter extended for numpy JAVA + ANT Primary programming language and software build framework Apache qpid AMQP standard messaging with JMS api Postgre. SQL Relational database for storing Metadata from Data plug ins and spatially enables ingested data
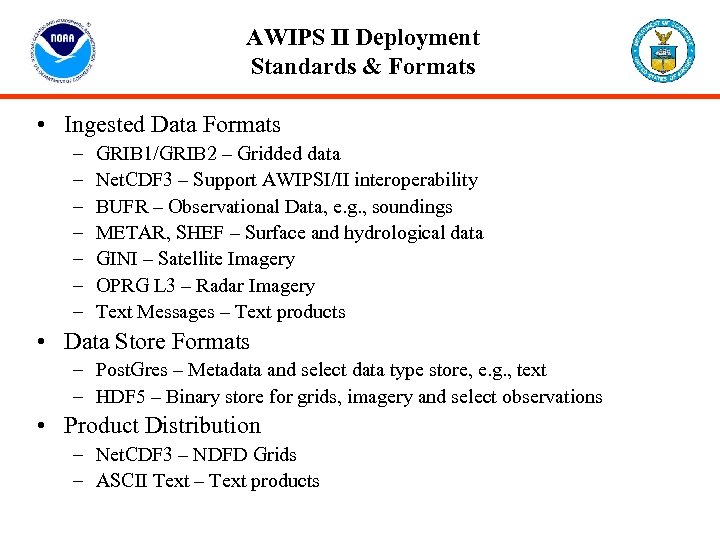 AWIPS II Deployment Standards & Formats • Ingested Data Formats – – – – GRIB 1/GRIB 2 – Gridded data Net. CDF 3 – Support AWIPSI/II interoperability BUFR – Observational Data, e. g. , soundings METAR, SHEF – Surface and hydrological data GINI – Satellite Imagery OPRG L 3 – Radar Imagery Text Messages – Text products • Data Store Formats – Post. Gres – Metadata and select data type store, e. g. , text – HDF 5 – Binary store for grids, imagery and select observations • Product Distribution – Net. CDF 3 – NDFD Grids – ASCII Text – Text products
AWIPS II Deployment Standards & Formats • Ingested Data Formats – – – – GRIB 1/GRIB 2 – Gridded data Net. CDF 3 – Support AWIPSI/II interoperability BUFR – Observational Data, e. g. , soundings METAR, SHEF – Surface and hydrological data GINI – Satellite Imagery OPRG L 3 – Radar Imagery Text Messages – Text products • Data Store Formats – Post. Gres – Metadata and select data type store, e. g. , text – HDF 5 – Binary store for grids, imagery and select observations • Product Distribution – Net. CDF 3 – NDFD Grids – ASCII Text – Text products
 AWIPS II Extended
AWIPS II Extended
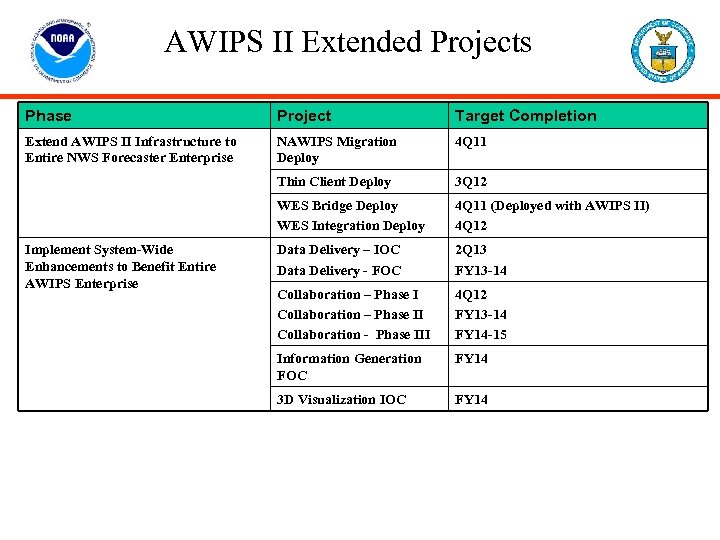 AWIPS II Extended Projects Phase Project Target Completion Extend AWIPS II Infrastructure to Entire NWS Forecaster Enterprise NAWIPS Migration Deploy 4 Q 11 Thin Client Deploy 3 Q 12 WES Bridge Deploy WES Integration Deploy 4 Q 11 (Deployed with AWIPS II) 4 Q 12 Data Delivery – IOC Data Delivery - FOC 2 Q 13 FY 13 -14 Collaboration – Phase II Collaboration - Phase III 4 Q 12 FY 13 -14 FY 14 -15 Information Generation FOC FY 14 3 D Visualization IOC FY 14 Implement System-Wide Enhancements to Benefit Entire AWIPS Enterprise
AWIPS II Extended Projects Phase Project Target Completion Extend AWIPS II Infrastructure to Entire NWS Forecaster Enterprise NAWIPS Migration Deploy 4 Q 11 Thin Client Deploy 3 Q 12 WES Bridge Deploy WES Integration Deploy 4 Q 11 (Deployed with AWIPS II) 4 Q 12 Data Delivery – IOC Data Delivery - FOC 2 Q 13 FY 13 -14 Collaboration – Phase II Collaboration - Phase III 4 Q 12 FY 13 -14 FY 14 -15 Information Generation FOC FY 14 3 D Visualization IOC FY 14 Implement System-Wide Enhancements to Benefit Entire AWIPS Enterprise
 AWIPS II Extended - NAWIPS Migration • Objectives – Incorporate NAWIPS capabilities into AWIPS SOA • Key Benefits – Enables more cost-effective software development environment for common requirements across the NWS enterprise; Helps enable software agility – Lays ground work for more effective collaboration and seamless products across NWS enterprise (NCs, WFOs, RFCs, CWSUs) by providing common infrastructure – Strengthens NWS partnership with University Community by providing entire suite of AWIPS capabilities – Helps enable more efficient R to O and O to R – Improves support for OCONUS Regions by providing common software infrastructure for NAWIPS and AWIPS functionality • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – Provides opportunities to leverage/share NAWIPS capabilities with broader AWIPS user customer base • Grid/Ensemble diagnostics • Drawing/Product generation tools to support collaboration requirements
AWIPS II Extended - NAWIPS Migration • Objectives – Incorporate NAWIPS capabilities into AWIPS SOA • Key Benefits – Enables more cost-effective software development environment for common requirements across the NWS enterprise; Helps enable software agility – Lays ground work for more effective collaboration and seamless products across NWS enterprise (NCs, WFOs, RFCs, CWSUs) by providing common infrastructure – Strengthens NWS partnership with University Community by providing entire suite of AWIPS capabilities – Helps enable more efficient R to O and O to R – Improves support for OCONUS Regions by providing common software infrastructure for NAWIPS and AWIPS functionality • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – Provides opportunities to leverage/share NAWIPS capabilities with broader AWIPS user customer base • Grid/Ensemble diagnostics • Drawing/Product generation tools to support collaboration requirements
 AWIPS II Extended - AWIPS II Thin Client • Objectives – Develop enterprise solution for remote access to AWIPS capabilities • Key Benefits – Incorporate FX-Net capabilities into baseline – Provides common solution to address remote access requirements to support Incident Meteorologists, e. g. , Fire Wx, Weather Service Offices, etc. – Allows remote users to have access to latest set of AWIPS capabilities – Provides partial solution for COOP scenarios at NCs and RFCs – In combination with Data Delivery Project, allows us to begin to analyze future opportunities for utilizing cloud computing
AWIPS II Extended - AWIPS II Thin Client • Objectives – Develop enterprise solution for remote access to AWIPS capabilities • Key Benefits – Incorporate FX-Net capabilities into baseline – Provides common solution to address remote access requirements to support Incident Meteorologists, e. g. , Fire Wx, Weather Service Offices, etc. – Allows remote users to have access to latest set of AWIPS capabilities – Provides partial solution for COOP scenarios at NCs and RFCs – In combination with Data Delivery Project, allows us to begin to analyze future opportunities for utilizing cloud computing
 AWIPS II Extended - Weather Event Simulator (WES) • Objectives – Develop enterprise solution to support NWS training requirements • Phase I: Provide bridge for current WES capability into AWIPS II. Also serves as a pathfinder for Phase II • Phase II: Develop integrated solution for AWIPS enterprise • Key Benefits – Provides robust, sustainable baseline solution to support NWS training requirements – Allows training users to have access to latest built set of AWIPS capabilities – Provides training solution for all AWIPS applications
AWIPS II Extended - Weather Event Simulator (WES) • Objectives – Develop enterprise solution to support NWS training requirements • Phase I: Provide bridge for current WES capability into AWIPS II. Also serves as a pathfinder for Phase II • Phase II: Develop integrated solution for AWIPS enterprise • Key Benefits – Provides robust, sustainable baseline solution to support NWS training requirements – Allows training users to have access to latest built set of AWIPS capabilities – Provides training solution for all AWIPS applications
 AWIPS II Extended - Data Delivery • Objectives – Develop robust data delivery system within AWIPS II infrastructure that enables efficient access to high volume datasets – Develop operational robust infrastructure to support “intelligent” access to non-local datasets – User defined sub-setting by space, time, and parameter – Subscription or Ad-hoc access methods based on weather events • Key Benefits – Supports high impact based forecast and decision assistance processes by allowing users to access just the data they need by space, time, parameter; Enables more efficient data mining – Enables effective on-demand access to Weather Information Database – Enables synergy and interoperability with Next. Gen technologies, e. g. , data discovery services, data access services and data providers. – Mitigates high growth in data volume e. g. ensembles, high-resolution models • Multi-Phase Implementation – IOC Focus – NWS data providers, e. g. , NOMADS, MADIS, possibly with basic services only, discovery, sub-setting – Target FY 13
AWIPS II Extended - Data Delivery • Objectives – Develop robust data delivery system within AWIPS II infrastructure that enables efficient access to high volume datasets – Develop operational robust infrastructure to support “intelligent” access to non-local datasets – User defined sub-setting by space, time, and parameter – Subscription or Ad-hoc access methods based on weather events • Key Benefits – Supports high impact based forecast and decision assistance processes by allowing users to access just the data they need by space, time, parameter; Enables more efficient data mining – Enables effective on-demand access to Weather Information Database – Enables synergy and interoperability with Next. Gen technologies, e. g. , data discovery services, data access services and data providers. – Mitigates high growth in data volume e. g. ensembles, high-resolution models • Multi-Phase Implementation – IOC Focus – NWS data providers, e. g. , NOMADS, MADIS, possibly with basic services only, discovery, sub-setting – Target FY 13
 AWIPS II Extended Data Delivery Overview -Continued • Synergies with Next. Gen (4 -D Cube) – Data registry and discovery services – “Smart” push/pull technology • Sub-setting by user selectable space, time, and parameter • Complex retrievals, e. g. , derived parameters, coordinate transformations, etc – Ad hoc and subscription services – Operationally robust – supports availability, latency and security requirements for operational users – Plan to leverage Next. Gen services including Reg/Rep, WCS, WFS • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – – IRIS for data access/distribution IHIS for data access/distribution GOES-R and NPP/NDE – Data Provider and data access/distribution services NWS Infrastructure Project – Central Data Server services
AWIPS II Extended Data Delivery Overview -Continued • Synergies with Next. Gen (4 -D Cube) – Data registry and discovery services – “Smart” push/pull technology • Sub-setting by user selectable space, time, and parameter • Complex retrievals, e. g. , derived parameters, coordinate transformations, etc – Ad hoc and subscription services – Operationally robust – supports availability, latency and security requirements for operational users – Plan to leverage Next. Gen services including Reg/Rep, WCS, WFS • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – – IRIS for data access/distribution IHIS for data access/distribution GOES-R and NPP/NDE – Data Provider and data access/distribution services NWS Infrastructure Project – Central Data Server services
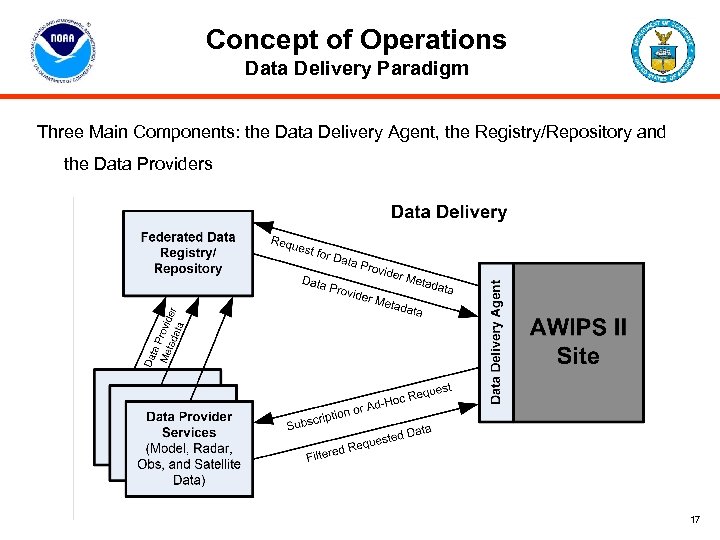 Concept of Operations Data Delivery Paradigm Three Main Components: the Data Delivery Agent, the Registry/Repository and the Data Providers 17
Concept of Operations Data Delivery Paradigm Three Main Components: the Data Delivery Agent, the Registry/Repository and the Data Providers 17
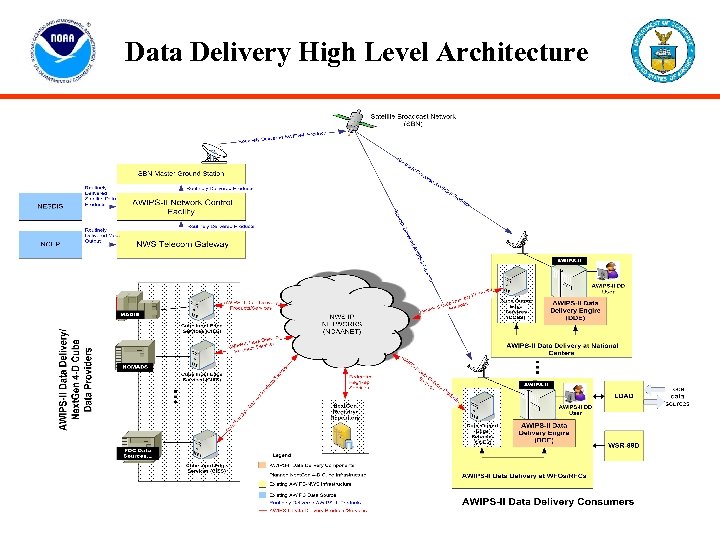 Data Delivery High Level Architecture
Data Delivery High Level Architecture
 AWIPS II Extended Collaboration • Objectives – Develop capabilities to support real-time collaboration – Phase I: Develop/Enhance internal NWS collaboration capabilities – Phase II: Develop/Enhance IOC collaboration capabilities with external partners – Phase III: Improve collaboration capabilities with external partners • Key Benefits – Enables more effective collaboration across all levels of NWS promoting a more coordinated and seamless set of products and services – Fosters consistency of NWS products and services – Enables interoperability between NWS and decision makers, e. g. , emergency managers to support Decision Support Services • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – – IRIS for collaboration with external partners IHIS for collaboration with external partners Canadian Environment Services /NWS Marine Forecast Collaboration Project Weather and Emerg. Management Decision Support (RENCI) Project for collaboration with North Carolina Emergency Managers
AWIPS II Extended Collaboration • Objectives – Develop capabilities to support real-time collaboration – Phase I: Develop/Enhance internal NWS collaboration capabilities – Phase II: Develop/Enhance IOC collaboration capabilities with external partners – Phase III: Improve collaboration capabilities with external partners • Key Benefits – Enables more effective collaboration across all levels of NWS promoting a more coordinated and seamless set of products and services – Fosters consistency of NWS products and services – Enables interoperability between NWS and decision makers, e. g. , emergency managers to support Decision Support Services • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – – IRIS for collaboration with external partners IHIS for collaboration with external partners Canadian Environment Services /NWS Marine Forecast Collaboration Project Weather and Emerg. Management Decision Support (RENCI) Project for collaboration with North Carolina Emergency Managers
 Phase I Collaboration Con. Ops • Data display sharing – This capability will allow participating NWS offices to view each other’s AWIPS data displays during collaboration sessions • Telestrator Functions – Simple line drawing capabilities, that will allow forecasters to draw and erase temporary lines and polygons on their AWIPS displays that can be viewed by participating collaborators. – Telestrator functions will help forecasters identify and discuss specific features of interest, e. g. , satellite and radar storm signatures, etc. • Creation and editing of hydrometeorological objects – Creation, editing and exchange of geo-referenced objects and products such as fronts, areas of severe weather, troughs and ridges, etc. and graphical products such as watches and warnings. – Meteorological objects and products will be displayed and/or exchanged among the participating collaborators allowing participants to import these graphics and display them in AWIPS applications. The display and exchange of meteorological objects and products will allow sites to collaborate in real-time on object or product features such as location, shape, and intensity. – Object and product attributes such as front type, product type, etc; will also be saved so that they are available forecaster access and editing. • An integrated text chat capability that will allow forecasters to chat during the collaboration session.
Phase I Collaboration Con. Ops • Data display sharing – This capability will allow participating NWS offices to view each other’s AWIPS data displays during collaboration sessions • Telestrator Functions – Simple line drawing capabilities, that will allow forecasters to draw and erase temporary lines and polygons on their AWIPS displays that can be viewed by participating collaborators. – Telestrator functions will help forecasters identify and discuss specific features of interest, e. g. , satellite and radar storm signatures, etc. • Creation and editing of hydrometeorological objects – Creation, editing and exchange of geo-referenced objects and products such as fronts, areas of severe weather, troughs and ridges, etc. and graphical products such as watches and warnings. – Meteorological objects and products will be displayed and/or exchanged among the participating collaborators allowing participants to import these graphics and display them in AWIPS applications. The display and exchange of meteorological objects and products will allow sites to collaborate in real-time on object or product features such as location, shape, and intensity. – Object and product attributes such as front type, product type, etc; will also be saved so that they are available forecaster access and editing. • An integrated text chat capability that will allow forecasters to chat during the collaboration session.
 AWIPS II Extended – Information Generation • Objective – Develop infrastructure to support common set of information generation services and tools to support decision assistance • Key Benefits – Enables AWIPS tools and Decision Maker tools for decision support • Streamlines generation of products to support emerging industry standards, e. g. , CAP and GIS • Reduces development time associated with the introduction of new products and services • Enables generation of NWS products from both local data bases and the 4 -D weather Data Cube • Opportunities for synergy with IRIS project • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – IRIS vision is to provide a enterprise solution for information storage for NWS and decisions makers access • Initial Capabilities Encapsulated in IHIS Project
AWIPS II Extended – Information Generation • Objective – Develop infrastructure to support common set of information generation services and tools to support decision assistance • Key Benefits – Enables AWIPS tools and Decision Maker tools for decision support • Streamlines generation of products to support emerging industry standards, e. g. , CAP and GIS • Reduces development time associated with the introduction of new products and services • Enables generation of NWS products from both local data bases and the 4 -D weather Data Cube • Opportunities for synergy with IRIS project • Potential Synergies with Other Projects – IRIS vision is to provide a enterprise solution for information storage for NWS and decisions makers access • Initial Capabilities Encapsulated in IHIS Project
 AWIPS II Extended - Advanced Visualization • Objective – Develop advanced visualizations techniques, e. g. , 3 -D visualization that can be utilized by AWIPS baseline applications • Key Benefits – Enables more effective forecaster visualization of datasets to support forecast and decision making processes. • Methods to improve situational awareness • Methods to improve identification of factors that affect high impact events
AWIPS II Extended - Advanced Visualization • Objective – Develop advanced visualizations techniques, e. g. , 3 -D visualization that can be utilized by AWIPS baseline applications • Key Benefits – Enables more effective forecaster visualization of datasets to support forecast and decision making processes. • Methods to improve situational awareness • Methods to improve identification of factors that affect high impact events
 AWIPS II Software Development Strategy In the AWIPS II Era
AWIPS II Software Development Strategy In the AWIPS II Era
 AWIPS II Software Development Strategy • Vision – – Enable collaborative AWIPS II Environment to effectively incorporate new science and technology into AWIPS II operational baseline from NOAA development organizations, proving grounds and test beds, and academic and research communities. – AWIPS II becomes the premium “Open Source” software platform for the hydrometeorological community • Supporting Objectives – Enable effective user and developer collaboration to support new capability development and enhancements – Enable agile prototyping and development in the AWIPS Development Environment (ADE) to reduce necessary software development time and cost to “productionize” new science and technology into AWIPS baseline – Provide timely and effective feedback to AWIPS program to ensure AWIPS architecture refresh plans keeps pace with new science and technologies
AWIPS II Software Development Strategy • Vision – – Enable collaborative AWIPS II Environment to effectively incorporate new science and technology into AWIPS II operational baseline from NOAA development organizations, proving grounds and test beds, and academic and research communities. – AWIPS II becomes the premium “Open Source” software platform for the hydrometeorological community • Supporting Objectives – Enable effective user and developer collaboration to support new capability development and enhancements – Enable agile prototyping and development in the AWIPS Development Environment (ADE) to reduce necessary software development time and cost to “productionize” new science and technology into AWIPS baseline – Provide timely and effective feedback to AWIPS program to ensure AWIPS architecture refresh plans keeps pace with new science and technologies
 Software Agility Strategy - Continued • Software Agility Requirements – Provide well- defined common libraries and toolkits to support data access, hydrometeorological calculations, visualization, and information generation – Provide well-documented AWIPS Development Environment (ADE) to development community – Provide effective training and developer support to development community – Develop streamlined governance processes balancing software agility needs with necessary software engineering discipline to ensure high quality software infusion into AWIPS baseline – Provide agile AWIPS test environment and methods including regression and automated test tools – Establish OST in-house AWIPS II software development expertise to provide effective guidance on all phases of the software development life cycle to AWIPS stakeholders
Software Agility Strategy - Continued • Software Agility Requirements – Provide well- defined common libraries and toolkits to support data access, hydrometeorological calculations, visualization, and information generation – Provide well-documented AWIPS Development Environment (ADE) to development community – Provide effective training and developer support to development community – Develop streamlined governance processes balancing software agility needs with necessary software engineering discipline to ensure high quality software infusion into AWIPS baseline – Provide agile AWIPS test environment and methods including regression and automated test tools – Establish OST in-house AWIPS II software development expertise to provide effective guidance on all phases of the software development life cycle to AWIPS stakeholders
 Software Development Strategy Near-Term Activities and Plans • Spin-Up OST AWIPS II development team using support contract mechanism – Team will be the kernel of OST AWIPS II software expertise – Government Team chartered - July 2010 – Contractor Team Tasking – October 2010 • Develop AWIPS II software developers documentation, training and support – RTS tasking planned – FY 11 • Improve AWIPS II testing environment – Regression Testing Task – on Contract – Automated Testing Task – FY 11 – Data Pump – FY 11
Software Development Strategy Near-Term Activities and Plans • Spin-Up OST AWIPS II development team using support contract mechanism – Team will be the kernel of OST AWIPS II software expertise – Government Team chartered - July 2010 – Contractor Team Tasking – October 2010 • Develop AWIPS II software developers documentation, training and support – RTS tasking planned – FY 11 • Improve AWIPS II testing environment – Regression Testing Task – on Contract – Automated Testing Task – FY 11 – Data Pump – FY 11
 SEC AWIPS Software Development Team • • Mission - The AWIPS Software Development Team (ASDT) shall serve as the center of expertise for AWIPS II Software for entire AWIPS II enterprise. The ASDT Roles and Responsibilities – – • Leading the evaluation and guidance for all phases of software development life cycle from requirements analysis to testing Managing and/or developing AWIPS II software infrastructure changes and additions Developing select AWIPS applications Facilitating new science and technology infusion into AWIPS operations. Staffing and Resource Plan – – – Government Team of five led by Jim Calkins Contractor Team of five utilizing Chugach contract (Same contractor that supports NCEP) Addition of 6 NCEP contractors ~January 2011
SEC AWIPS Software Development Team • • Mission - The AWIPS Software Development Team (ASDT) shall serve as the center of expertise for AWIPS II Software for entire AWIPS II enterprise. The ASDT Roles and Responsibilities – – • Leading the evaluation and guidance for all phases of software development life cycle from requirements analysis to testing Managing and/or developing AWIPS II software infrastructure changes and additions Developing select AWIPS applications Facilitating new science and technology infusion into AWIPS operations. Staffing and Resource Plan – – – Government Team of five led by Jim Calkins Contractor Team of five utilizing Chugach contract (Same contractor that supports NCEP) Addition of 6 NCEP contractors ~January 2011
 ASDT Near-Term Activities • Team Activities – Establishing AWIPS II development environment patterned after RTS Omaha and NCEP development environments • Subversion – CM/Version Control • TRAC – Task tracking and management • Hudson – Software build support – Drafting AWIPS II development life cycle processes – Initial focus on supporting local application migration
ASDT Near-Term Activities • Team Activities – Establishing AWIPS II development environment patterned after RTS Omaha and NCEP development environments • Subversion – CM/Version Control • TRAC – Task tracking and management • Hudson – Software build support – Drafting AWIPS II development life cycle processes – Initial focus on supporting local application migration
 QUESTIONS ? ?
QUESTIONS ? ?


