e20295dadb93986659f649254d1e52b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Advanced Use Case Modeling ECE 621
Advanced Use Case Modeling ECE 621
 Association Relationship • Association relationships only show which actors interact with the system to perform a given use case • Association relationship DO NOT model the flow of data between the actor and the system • A directed association relationship only shows if the system or the actor initiates the connection
Association Relationship • Association relationships only show which actors interact with the system to perform a given use case • Association relationship DO NOT model the flow of data between the actor and the system • A directed association relationship only shows if the system or the actor initiates the connection
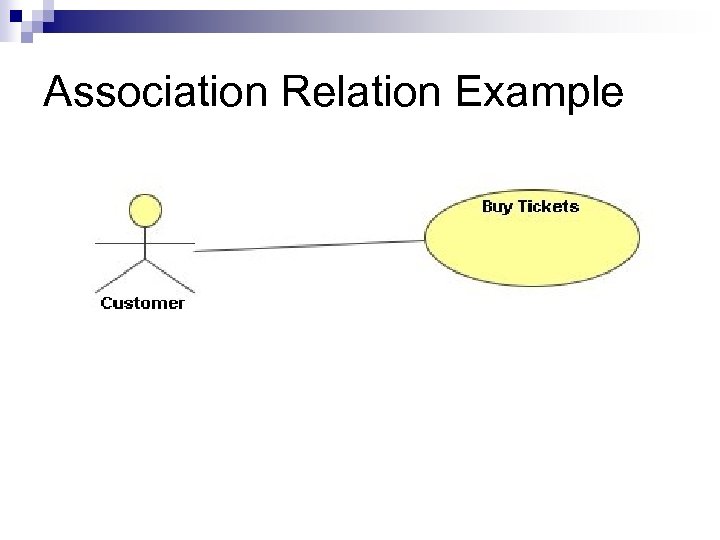 Association Relation Example
Association Relation Example
 Abstract Use Case n n Abstract use cases cannot be performed Abstract use cases only provide partial behavior and thus they need to be implemented
Abstract Use Case n n Abstract use cases cannot be performed Abstract use cases only provide partial behavior and thus they need to be implemented
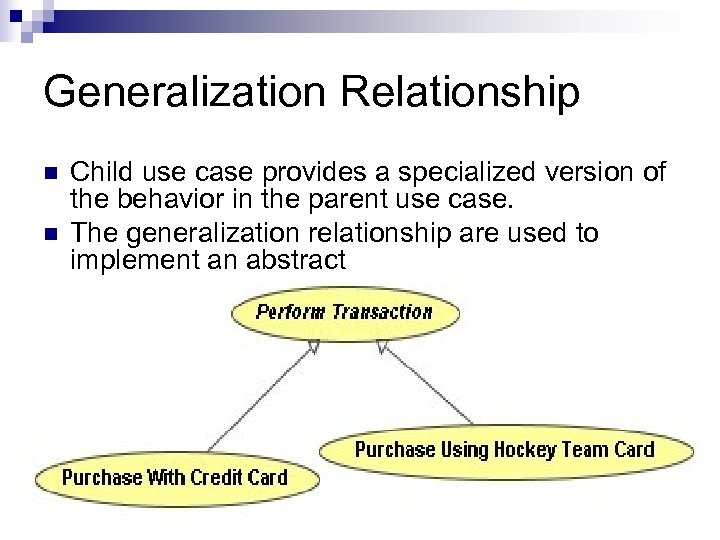 Generalization Relationship n n Child use case provides a specialized version of the behavior in the parent use case. The generalization relationship are used to implement an abstract
Generalization Relationship n n Child use case provides a specialized version of the behavior in the parent use case. The generalization relationship are used to implement an abstract
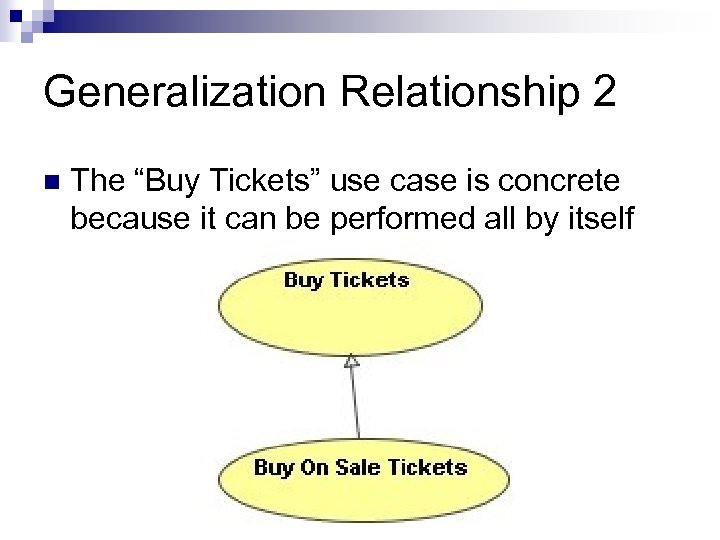 Generalization Relationship 2 n The “Buy Tickets” use case is concrete because it can be performed all by itself
Generalization Relationship 2 n The “Buy Tickets” use case is concrete because it can be performed all by itself
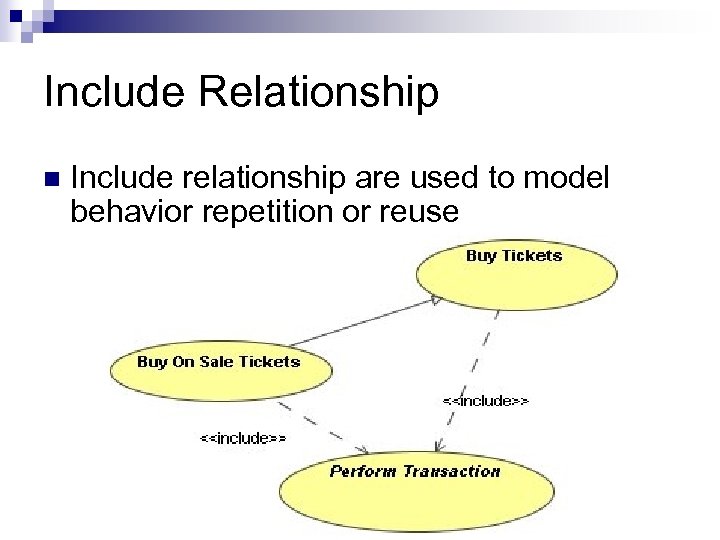 Include Relationship n Include relationship are used to model behavior repetition or reuse
Include Relationship n Include relationship are used to model behavior repetition or reuse
 Extend Relationship Extension use cases usually contain behavior that it optional or exceptional n Extension use cases are usually performed upon a condition being satisfied n
Extend Relationship Extension use cases usually contain behavior that it optional or exceptional n Extension use cases are usually performed upon a condition being satisfied n
 Extension Points n Extension points state where the behavior in the extension use case is inserted into the base use case.
Extension Points n Extension points state where the behavior in the extension use case is inserted into the base use case.
 Use Case Descriptions Usually is used in a template n There must be one use case description for every use case shown in the diagram n There must be one actor description for every actor shown in the diagram n
Use Case Descriptions Usually is used in a template n There must be one use case description for every use case shown in the diagram n There must be one actor description for every actor shown in the diagram n
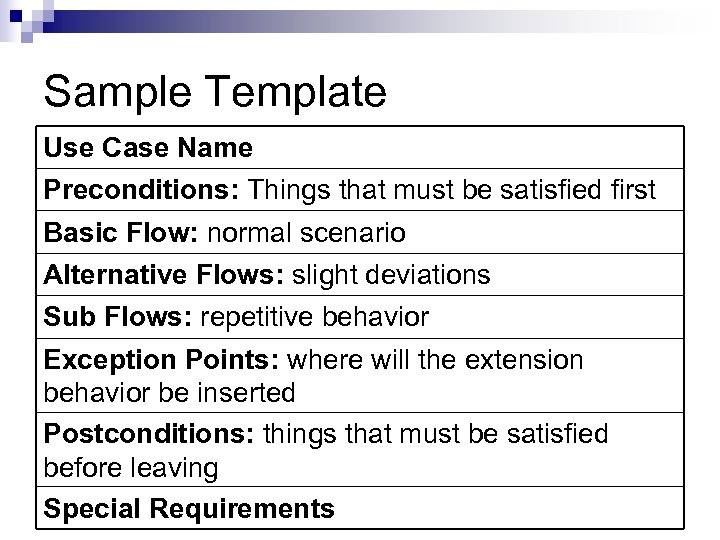 Sample Template Use Case Name Preconditions: Things that must be satisfied first Basic Flow: normal scenario Alternative Flows: slight deviations Sub Flows: repetitive behavior Exception Points: where will the extension behavior be inserted Postconditions: things that must be satisfied before leaving Special Requirements
Sample Template Use Case Name Preconditions: Things that must be satisfied first Basic Flow: normal scenario Alternative Flows: slight deviations Sub Flows: repetitive behavior Exception Points: where will the extension behavior be inserted Postconditions: things that must be satisfied before leaving Special Requirements
 Buy Tickets – Basic Flow The system displays to the customer a calendar for all season games. The Customer then chooses the game he/she would like to attend. The Customer then specifies the section in which he/she would like the tickets to be located. The System checks whether the requested tickets are available or not. If they are available, the System offers these tickets to the Customer. The Customer chooses to accept or reject the tickets. If the Customer accepts the tickets, the Customer is offered the option to pay either by a credit card or using the hockey team card. Upon, verification of payment information, the tickets are issued.
Buy Tickets – Basic Flow The system displays to the customer a calendar for all season games. The Customer then chooses the game he/she would like to attend. The Customer then specifies the section in which he/she would like the tickets to be located. The System checks whether the requested tickets are available or not. If they are available, the System offers these tickets to the Customer. The Customer chooses to accept or reject the tickets. If the Customer accepts the tickets, the Customer is offered the option to pay either by a credit card or using the hockey team card. Upon, verification of payment information, the tickets are issued.
 Buy Tickets - Alternative Flows n n n If the System cannot find the required seats, then Customer is notified and the use case ends If the Customer rejects the offered tickets, the use case ends If the Customer’s payment information cannot be verified, the Customer is notified to contact customer service and then the use case ends
Buy Tickets - Alternative Flows n n n If the System cannot find the required seats, then Customer is notified and the use case ends If the Customer rejects the offered tickets, the use case ends If the Customer’s payment information cannot be verified, the Customer is notified to contact customer service and then the use case ends
 Buy Ticket - Subflows n After the Customer enters the information regarding the requested seats; the systems first checks to see if there any tickets in the given section; then the system checks if there any consecutive seats as there is the required number of tickets.
Buy Ticket - Subflows n After the Customer enters the information regarding the requested seats; the systems first checks to see if there any tickets in the given section; then the system checks if there any consecutive seats as there is the required number of tickets.
 Buy Team Merchandise – Extension Points n Extension Points: Whenever team merchandise is purchased and a ticket is entered for a chance to win
Buy Team Merchandise – Extension Points n Extension Points: Whenever team merchandise is purchased and a ticket is entered for a chance to win


