 Advanced Real-time Post-Processing using GPGPU techniques
Advanced Real-time Post-Processing using GPGPU techniques
 Presentation overview ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ Problem description and objectives Depth of field Methods GPGPU programming Results Conclusion Questions
Presentation overview ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ Problem description and objectives Depth of field Methods GPGPU programming Results Conclusion Questions
 Problem description and objectives ∙ Post processing filters ∙ Different depth of field algorithms ∙ Visual quality ∙ Implement using HLSL and CUDA ∙ Performance ∙ Usability
Problem description and objectives ∙ Post processing filters ∙ Different depth of field algorithms ∙ Visual quality ∙ Implement using HLSL and CUDA ∙ Performance ∙ Usability
 Depth of field ∙ Depth cue ∙ Focus plane ∙ Focus in area in front of and beyond ∙ Different blurriness
Depth of field ∙ Depth cue ∙ Focus plane ∙ Focus in area in front of and beyond ∙ Different blurriness
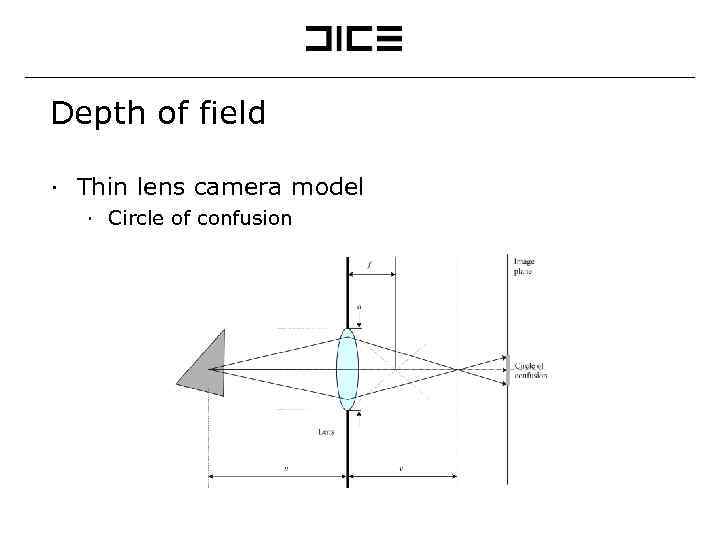 Depth of field ∙ Thin lens camera model ∙ Circle of confusion
Depth of field ∙ Thin lens camera model ∙ Circle of confusion
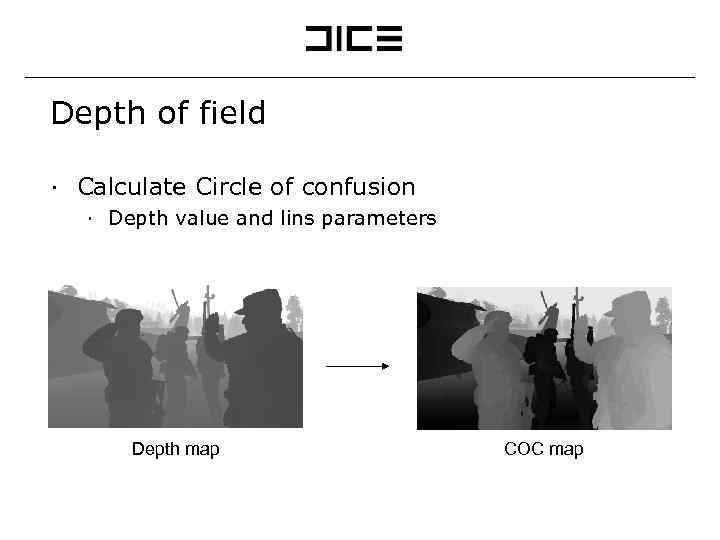 Depth of field ∙ Calculate Circle of confusion ∙ Depth value and lins parameters Depth map COC map
Depth of field ∙ Calculate Circle of confusion ∙ Depth value and lins parameters Depth map COC map
 Methods ∙ ∙ Poisson disc blur Multi-passed diffusion Separable diffusion Summed-area table
Methods ∙ ∙ Poisson disc blur Multi-passed diffusion Separable diffusion Summed-area table
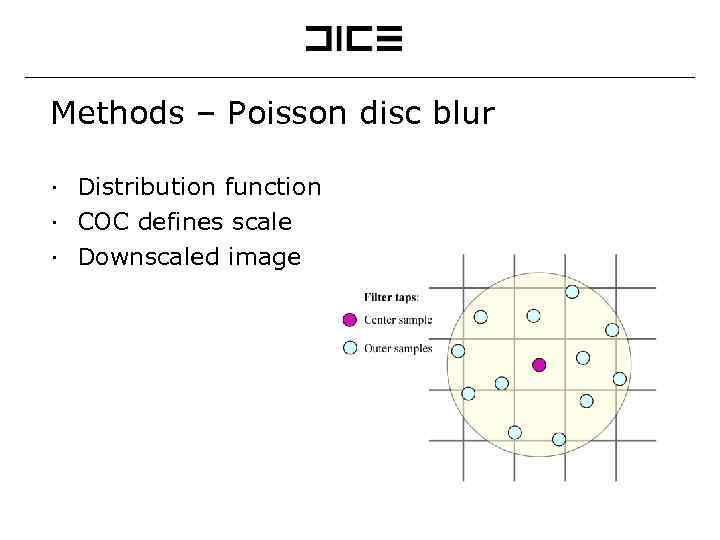 Methods – Poisson disc blur ∙ Distribution function ∙ COC defines scale ∙ Downscaled image
Methods – Poisson disc blur ∙ Distribution function ∙ COC defines scale ∙ Downscaled image
 Methods – Poisson disc blur ∙ Calculate values and interpolate depending on COC
Methods – Poisson disc blur ∙ Calculate values and interpolate depending on COC
 Methods – Multi-passed diffusion ∙ Every pixel gets new value depending on the COC gradient Iterations
Methods – Multi-passed diffusion ∙ Every pixel gets new value depending on the COC gradient Iterations
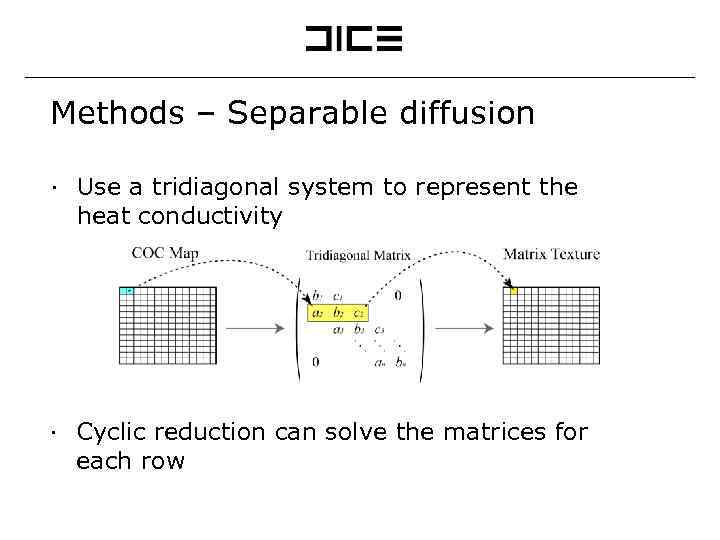 Methods – Separable diffusion ∙ Use a tridiagonal system to represent the heat conductivity ∙ Cyclic reduction can solve the matrices for each row
Methods – Separable diffusion ∙ Use a tridiagonal system to represent the heat conductivity ∙ Cyclic reduction can solve the matrices for each row
 Methods – Separable diffusion ∙ Each row is solved independently ∙ In each step a reduced tridiagonal matrix is calculated (and output value) until the system is solved
Methods – Separable diffusion ∙ Each row is solved independently ∙ In each step a reduced tridiagonal matrix is calculated (and output value) until the system is solved
 GPGPU programming ∙ General ∙ Better flexibility ∙ Potential advantages ∙ CUDA ∙ Extension of C ∙ Large community
GPGPU programming ∙ General ∙ Better flexibility ∙ Potential advantages ∙ CUDA ∙ Extension of C ∙ Large community
 GPGPU programming ∙ Executes in chunks of threads ∙ User specified blocks ∙ Several memory types ∙ ∙ Global Texture Shared Constant ∙ More choices and possibilities ∙ Hardware specific limits ∙ Great potential
GPGPU programming ∙ Executes in chunks of threads ∙ User specified blocks ∙ Several memory types ∙ ∙ Global Texture Shared Constant ∙ More choices and possibilities ∙ Hardware specific limits ∙ Great potential
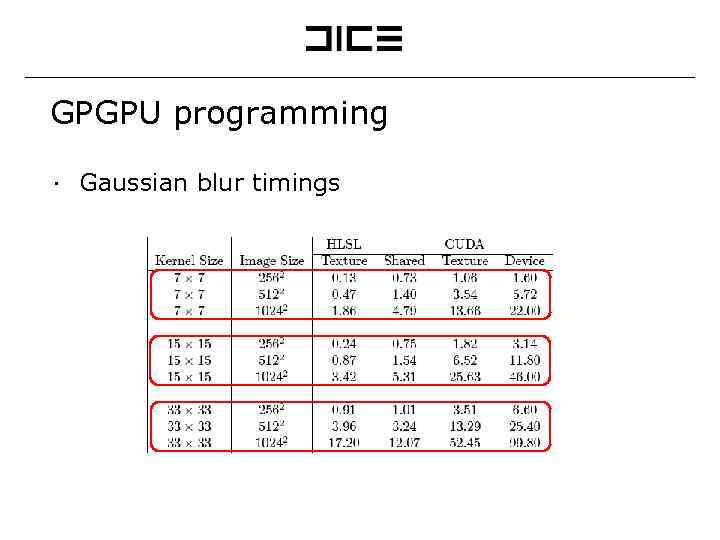 GPGPU programming ∙ Gaussian blur timings
GPGPU programming ∙ Gaussian blur timings
 GPGPU programming ∙ Implementation impact using CUDA ∙ + ∙ ∙ Easy to get started (C) Memory indexing (no more floating point texture indices) Good support for timing on the GPU Good control over computations (threads and memory) ∙ ∙ A lot of ”rules” (amount of threads, occupancy, etc) ∙ Hard to optimize ∙ Beta problems (lack of interop, slow operations)
GPGPU programming ∙ Implementation impact using CUDA ∙ + ∙ ∙ Easy to get started (C) Memory indexing (no more floating point texture indices) Good support for timing on the GPU Good control over computations (threads and memory) ∙ ∙ A lot of ”rules” (amount of threads, occupancy, etc) ∙ Hard to optimize ∙ Beta problems (lack of interop, slow operations)
 Results ∙ HLSL and CUDA for most methods ∙ Exceptions ∙ Poisson disc (HLSL only) ∙ Summed Area-Table (CUDA only) ∙ Timings in runs of 100 on recent hardware
Results ∙ HLSL and CUDA for most methods ∙ Exceptions ∙ Poisson disc (HLSL only) ∙ Summed Area-Table (CUDA only) ∙ Timings in runs of 100 on recent hardware
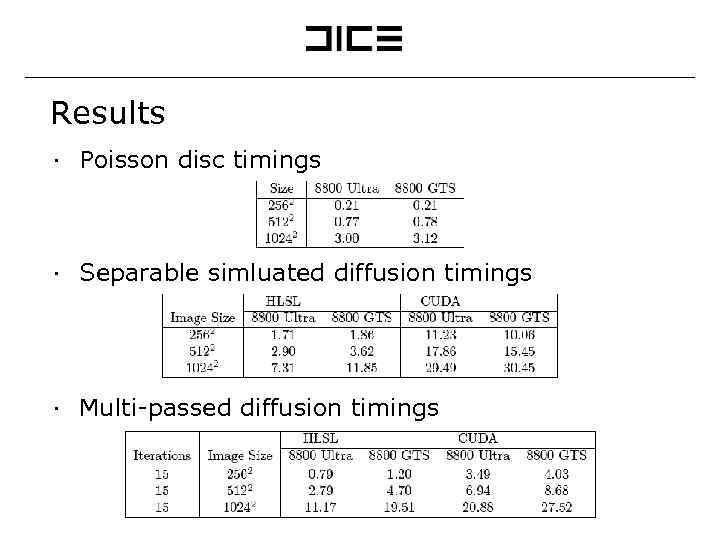 Results ∙ Poisson disc timings ∙ Separable simluated diffusion timings ∙ Multi-passed diffusion timings
Results ∙ Poisson disc timings ∙ Separable simluated diffusion timings ∙ Multi-passed diffusion timings
 Results ∙ Artifacts ∙ Color leaking ∙ Sharp edges
Results ∙ Artifacts ∙ Color leaking ∙ Sharp edges
 Results ∙ Input data
Results ∙ Input data
 Results Multi-passed ∙ Poisson disc diffusion Separable simulated diffusion
Results Multi-passed ∙ Poisson disc diffusion Separable simulated diffusion
 Results ∙ Multi-passed diffusion Poisson disc Separable simulated diffusion
Results ∙ Multi-passed diffusion Poisson disc Separable simulated diffusion
 Results ∙ Lens parameter settings
Results ∙ Lens parameter settings
 Conclusions ∙ Current depth of field filters are good enough ∙ Not really, but better is too expensive ∙ Cut scenes do get time for more computations ∙ GPGPU techniques have great potential ∙ Not mature enough (hardware support etc. ) ∙ Maybe better for other things than image processing ∙ Future work ∙ Diffusion based approach offers best visual quality ∙ Compute shaders anyone?
Conclusions ∙ Current depth of field filters are good enough ∙ Not really, but better is too expensive ∙ Cut scenes do get time for more computations ∙ GPGPU techniques have great potential ∙ Not mature enough (hardware support etc. ) ∙ Maybe better for other things than image processing ∙ Future work ∙ Diffusion based approach offers best visual quality ∙ Compute shaders anyone?
 Videos
Videos
 End
End