11d171af20c37ffd59649f4bbc60c087.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Advanced Microeconomics ECH-51806 Part 1: Consumer Theory and Theory of the Firm Dušan Drabik de Leeuwenborch 2105 Dusan. Drabik@wur. nl The material contained in these slides draws heavily on: Geoffrey A. Jehle and Philip J. Reny (2011). Advanced Microeconomic Theory (3 rd Edition). Prentice Hall, 672 p.
Advanced Microeconomics ECH-51806 Part 1: Consumer Theory and Theory of the Firm Dušan Drabik de Leeuwenborch 2105 Dusan. Drabik@wur. nl The material contained in these slides draws heavily on: Geoffrey A. Jehle and Philip J. Reny (2011). Advanced Microeconomic Theory (3 rd Edition). Prentice Hall, 672 p.
 Disclaimer These slides are not meant to be your sole study material. They are just a (incomplete) summary of what will be covered in Part 1 of the course. 2
Disclaimer These slides are not meant to be your sole study material. They are just a (incomplete) summary of what will be covered in Part 1 of the course. 2
 Quotes to live by “You've got to be very careful if you don't know where you are going, because you might not get there. ” “I'm not going to buy my kids an encyclopedia. Let them walk to school like I did. ” - Yogi Berra 3
Quotes to live by “You've got to be very careful if you don't know where you are going, because you might not get there. ” “I'm not going to buy my kids an encyclopedia. Let them walk to school like I did. ” - Yogi Berra 3
 General Information • Advance level course (abstraction, mathematically oriented, but fun) • All relevant information (e. g. , problem sets, home assignments, tests) here: http: //home. deds. nl/~pvmouche/advmicro. html Textbook Recommended supplemental reading 4
General Information • Advance level course (abstraction, mathematically oriented, but fun) • All relevant information (e. g. , problem sets, home assignments, tests) here: http: //home. deds. nl/~pvmouche/advmicro. html Textbook Recommended supplemental reading 4
 General Information • Exercises to be solved at home and discussed in class (not graded) • Home assignment for Part 1 due on or before September 18, 2017 in room 2105 (hand-written is fine) (graded) • No official office hours for Part 1. Write me an e-mail or stop by 5
General Information • Exercises to be solved at home and discussed in class (not graded) • Home assignment for Part 1 due on or before September 18, 2017 in room 2105 (hand-written is fine) (graded) • No official office hours for Part 1. Write me an e-mail or stop by 5
 Consumer Theory 6
Consumer Theory 6
 Primitive notions Four building blocks: • • Consumption (choice) set Consumption bundle (plan) Preference relation Behavioral assumption 7
Primitive notions Four building blocks: • • Consumption (choice) set Consumption bundle (plan) Preference relation Behavioral assumption 7
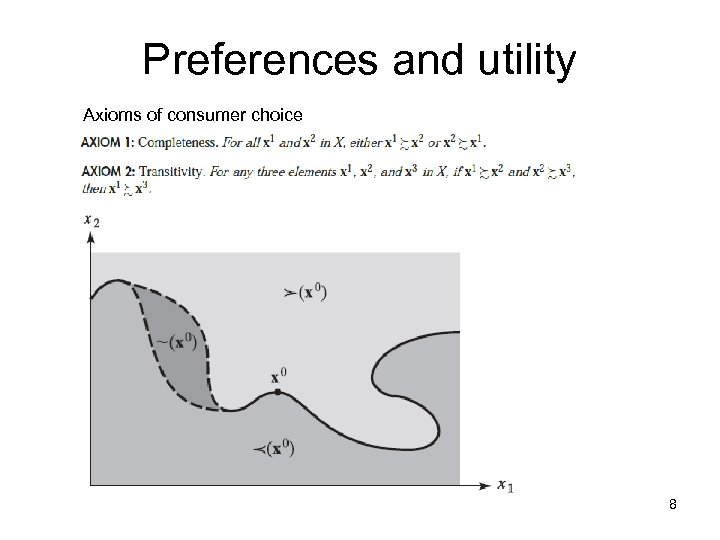 Preferences and utility Axioms of consumer choice 8
Preferences and utility Axioms of consumer choice 8
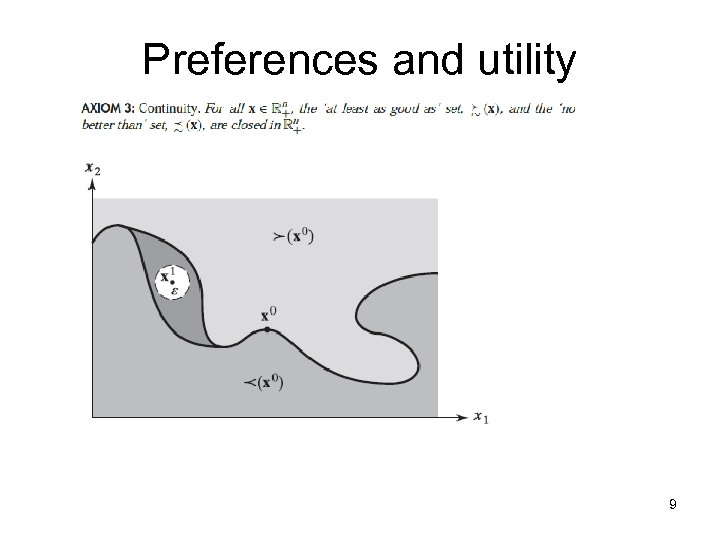 Preferences and utility 9
Preferences and utility 9
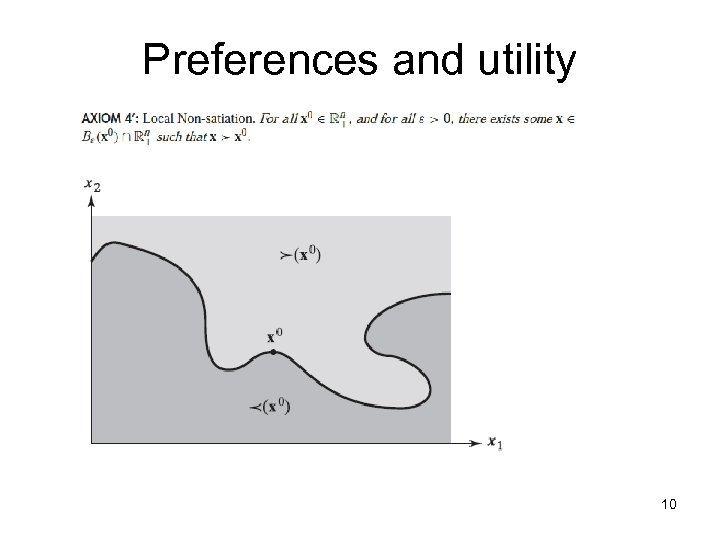 Preferences and utility 10
Preferences and utility 10
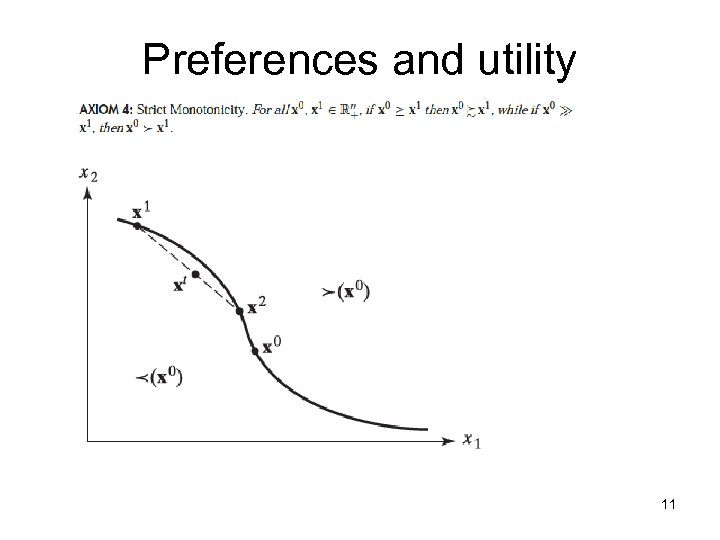 Preferences and utility 11
Preferences and utility 11
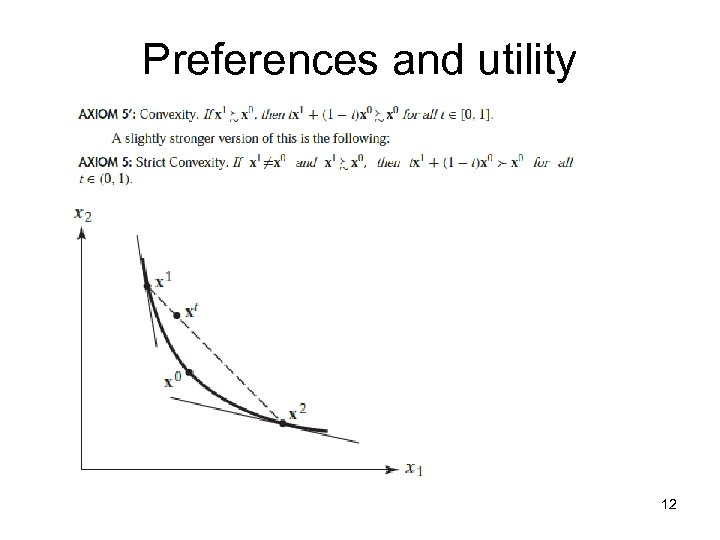 Preferences and utility 12
Preferences and utility 12
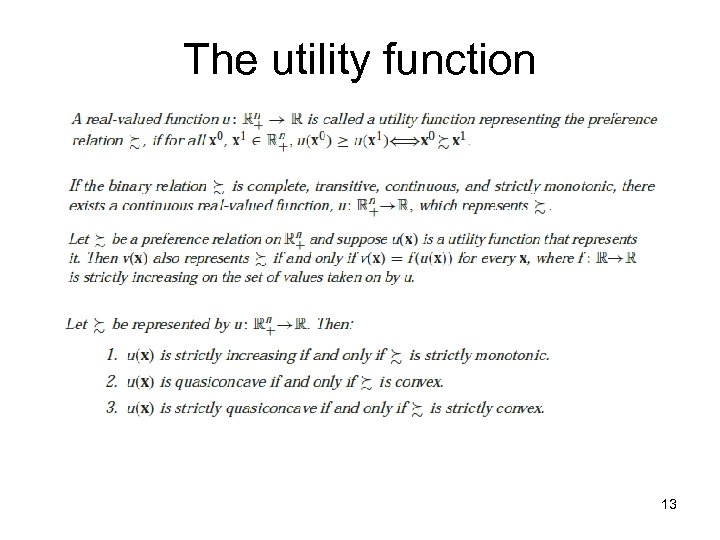 The utility function 13
The utility function 13
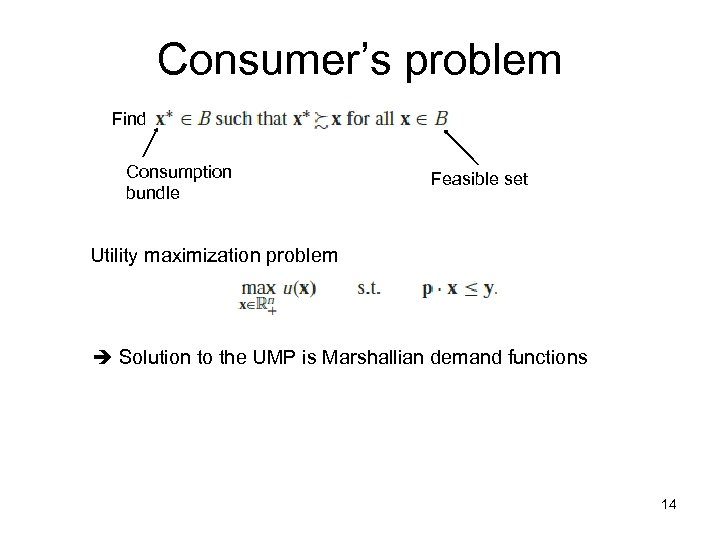 Consumer’s problem Find Consumption bundle Feasible set Utility maximization problem Solution to the UMP is Marshallian demand functions 14
Consumer’s problem Find Consumption bundle Feasible set Utility maximization problem Solution to the UMP is Marshallian demand functions 14
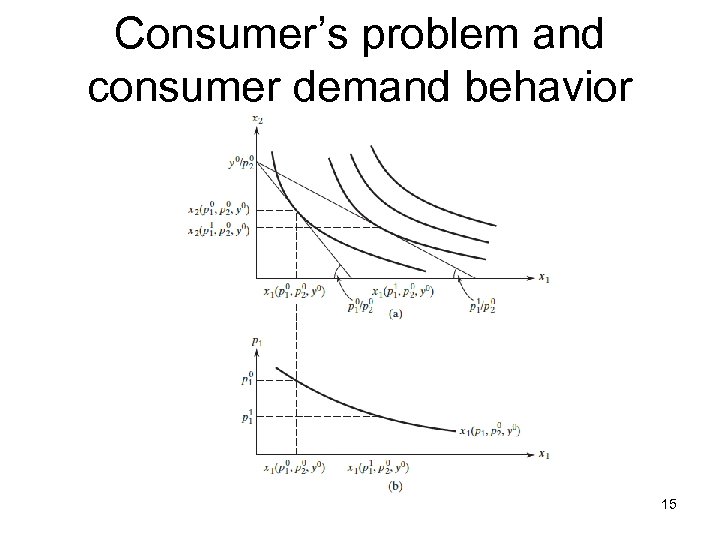 Consumer’s problem and consumer demand behavior 15
Consumer’s problem and consumer demand behavior 15
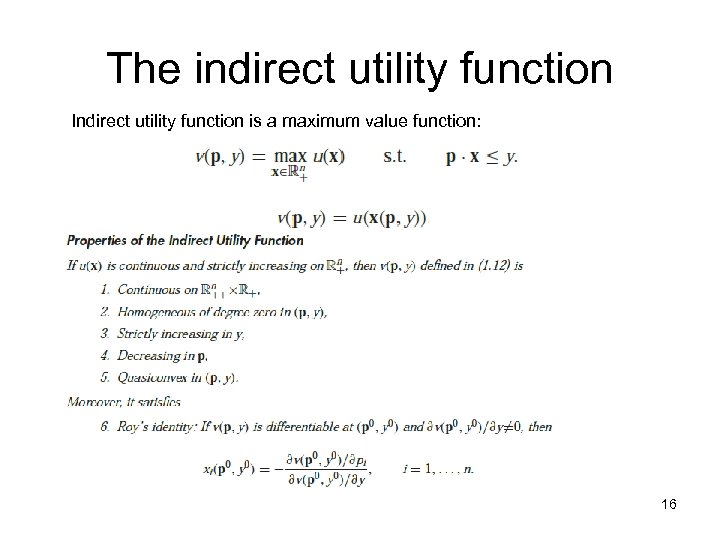 The indirect utility function Indirect utility function is a maximum value function: 16
The indirect utility function Indirect utility function is a maximum value function: 16
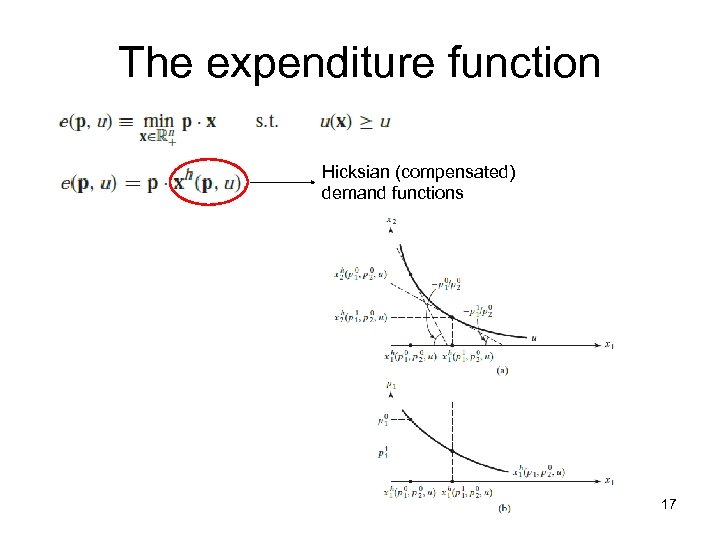 The expenditure function Hicksian (compensated) demand functions 17
The expenditure function Hicksian (compensated) demand functions 17
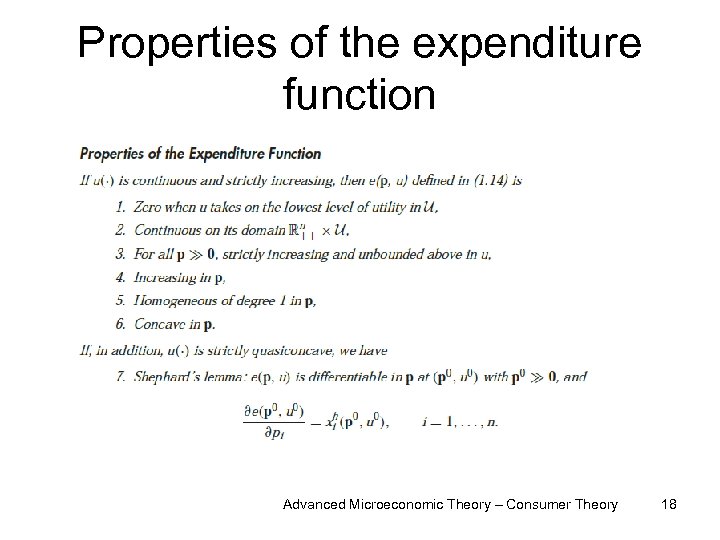 Properties of the expenditure function Advanced Microeconomic Theory – Consumer Theory 18
Properties of the expenditure function Advanced Microeconomic Theory – Consumer Theory 18
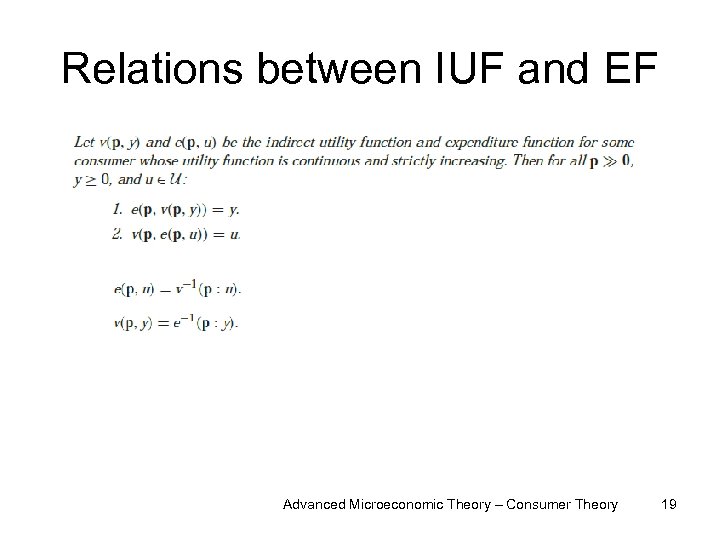 Relations between IUF and EF Advanced Microeconomic Theory – Consumer Theory 19
Relations between IUF and EF Advanced Microeconomic Theory – Consumer Theory 19
 Duality between Marshallian and Hicksian demand functions Advanced Microeconomic Theory – Consumer Theory 20
Duality between Marshallian and Hicksian demand functions Advanced Microeconomic Theory – Consumer Theory 20
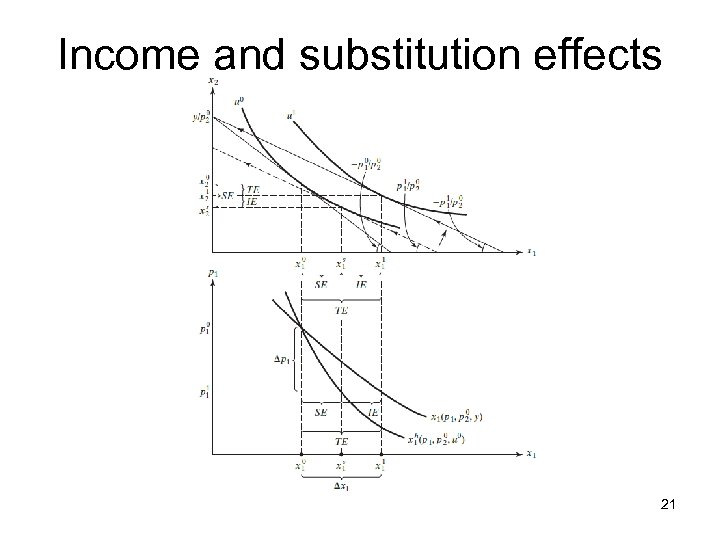 Income and substitution effects 21
Income and substitution effects 21
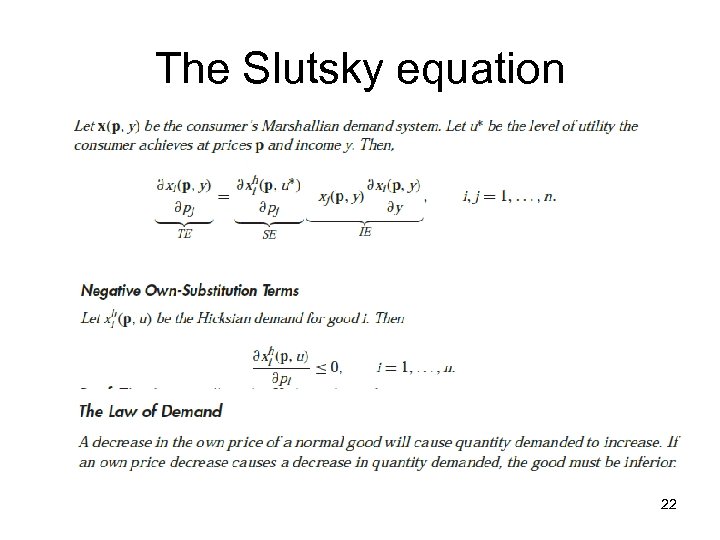 The Slutsky equation 22
The Slutsky equation 22
 23
23
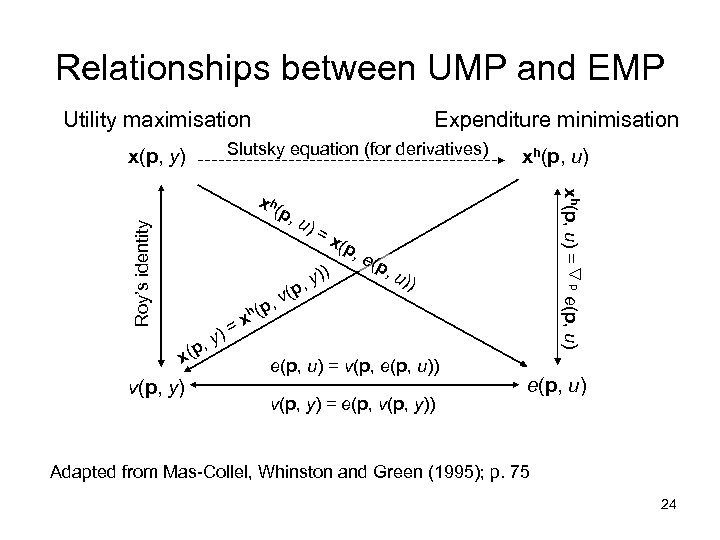 Relationships between UMP and EMP Utility maximisation Expenditure minimisation Slutsky equation (for derivatives) x(p, y) Roy’s identity v(p, y) v(p , =x )) , y (p , e (p , u )) e(p, u) = v(p, e(p, u)) v(p, y) = e(p, v(p, y)) e(p, u) x u) p ) y (p , h p x( = p, xh(p, u) = x h( xh(p, u) e(p, u) Adapted from Mas-Collel, Whinston and Green (1995); p. 75 24
Relationships between UMP and EMP Utility maximisation Expenditure minimisation Slutsky equation (for derivatives) x(p, y) Roy’s identity v(p, y) v(p , =x )) , y (p , e (p , u )) e(p, u) = v(p, e(p, u)) v(p, y) = e(p, v(p, y)) e(p, u) x u) p ) y (p , h p x( = p, xh(p, u) = x h( xh(p, u) e(p, u) Adapted from Mas-Collel, Whinston and Green (1995); p. 75 24
 Theory of the Firm 25
Theory of the Firm 25
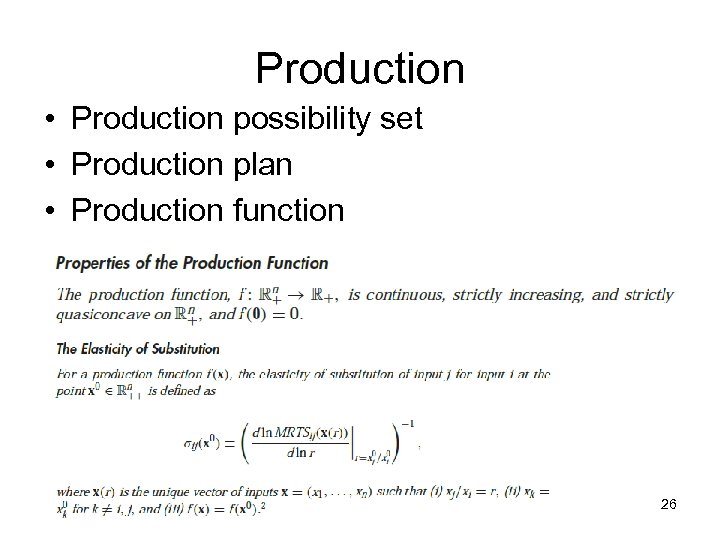 Production • Production possibility set • Production plan • Production function 26
Production • Production possibility set • Production plan • Production function 26
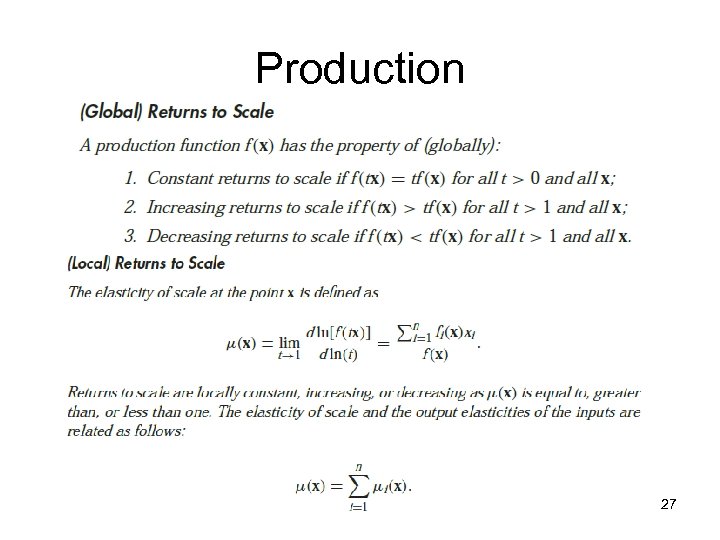 Production 27
Production 27
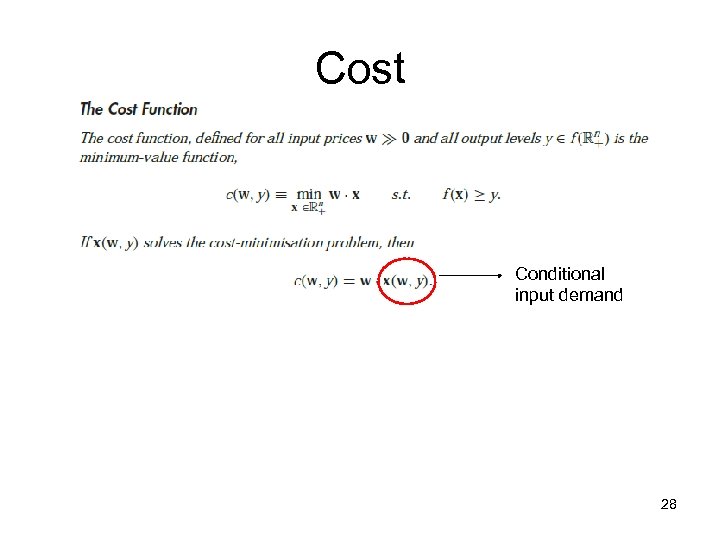 Cost Conditional input demand 28
Cost Conditional input demand 28
 Properties of the cost function 29
Properties of the cost function 29
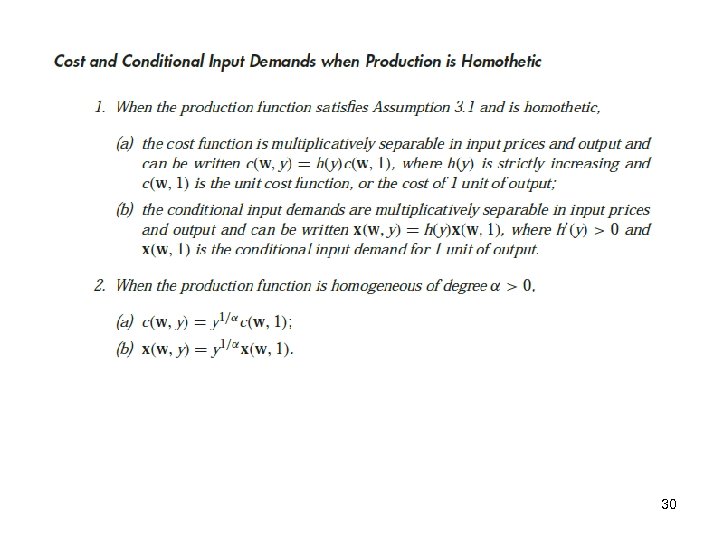 30
30
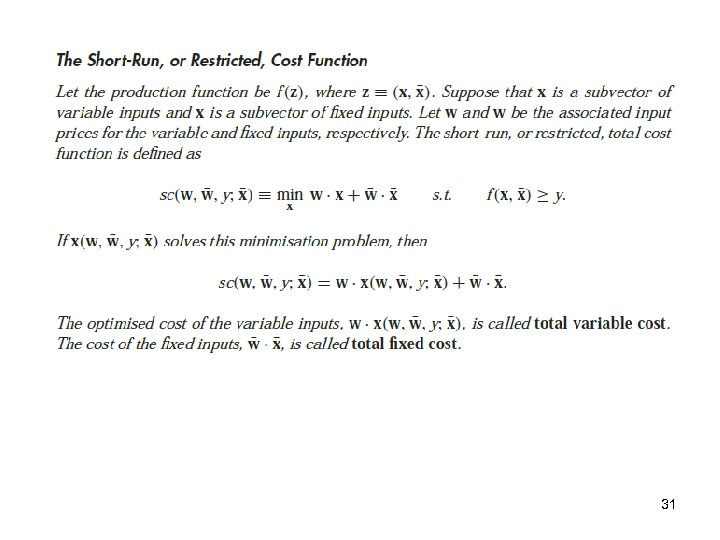 31
31
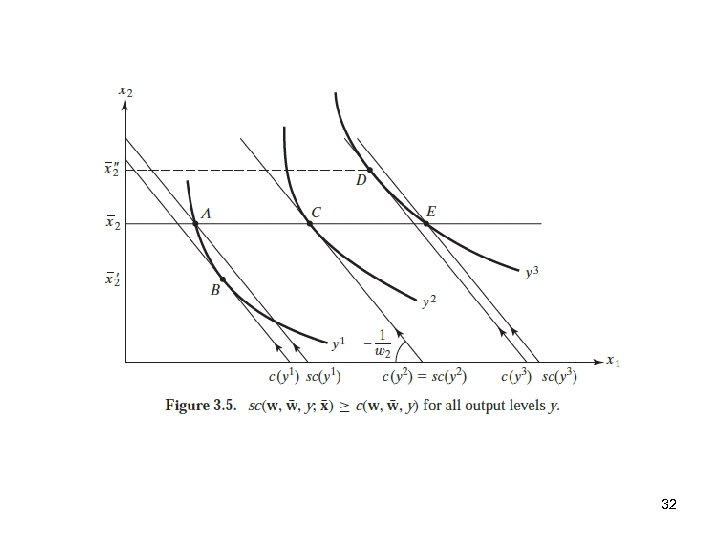 32
32
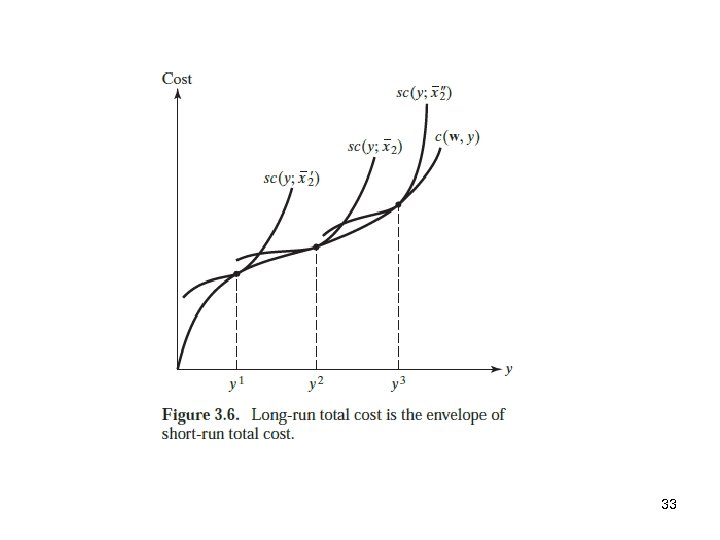 33
33
 The competitive firm Profit maximization . . . or Cost function 34
The competitive firm Profit maximization . . . or Cost function 34
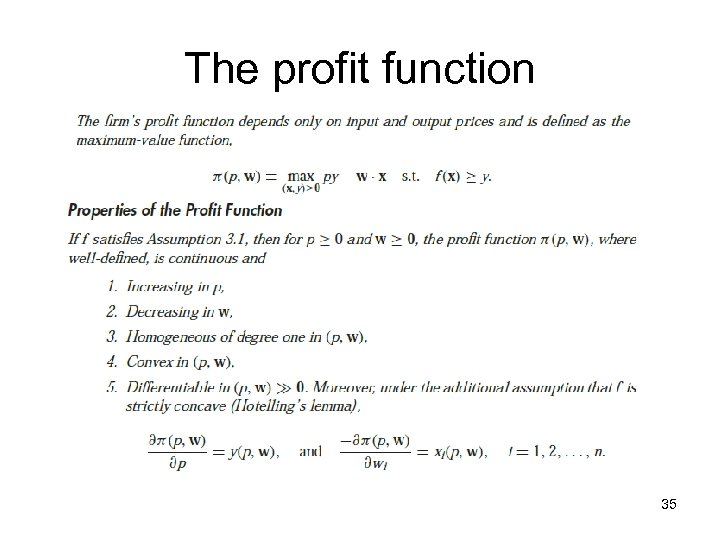 The profit function 35
The profit function 35
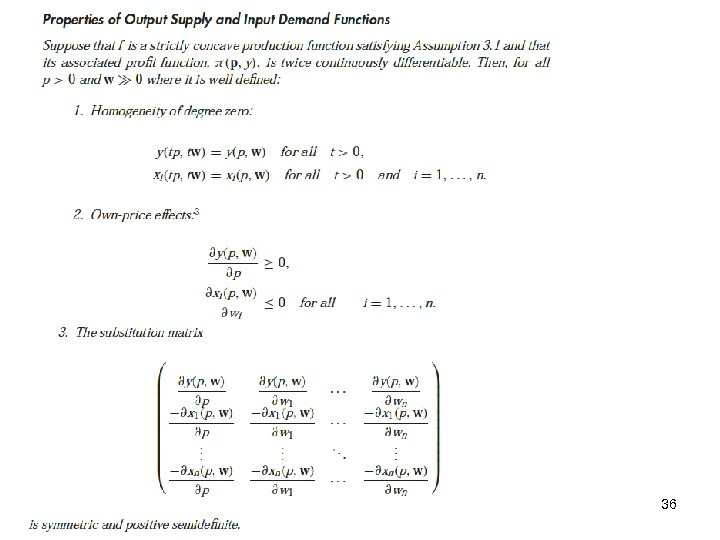 36
36


