e84fa93c78dd11aaa71ea4286f462ce3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) Project Update Mark Heintzelman June 2010
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) Project Update Mark Heintzelman June 2010
 AMI System Requirements Demonstrated Ability @ Scale • Retrieve hourly energy consumption from all (480, 000) endpoints • Two-way communications to reset displayed Peak Demand or k. W, on command • Two-way communications to support direct load control – Meet NIST – Critical Infrastructure Protection requirements • Provide outage management process enhancements • Reduce operational costs related to meter reading and customer movement processes
AMI System Requirements Demonstrated Ability @ Scale • Retrieve hourly energy consumption from all (480, 000) endpoints • Two-way communications to reset displayed Peak Demand or k. W, on command • Two-way communications to support direct load control – Meet NIST – Critical Infrastructure Protection requirements • Provide outage management process enhancements • Reduce operational costs related to meter reading and customer movement processes
 AMI Phased Approach • Phase I – Test the AMI technology – 2004 -2008 – Test hourly data retrieval – Pilot Data Management & time variant pricing – Develop a business case • Phase II – AMI Infrastructure Installation 2009 - 2011 – – Strategic Sourcing Regulatory Filing Infrastructure deployment O&M cost reduction • Phase III – AMI Full Implementation 2012 – Full data and system integration – System optimization – Additional Systems
AMI Phased Approach • Phase I – Test the AMI technology – 2004 -2008 – Test hourly data retrieval – Pilot Data Management & time variant pricing – Develop a business case • Phase II – AMI Infrastructure Installation 2009 - 2011 – – Strategic Sourcing Regulatory Filing Infrastructure deployment O&M cost reduction • Phase III – AMI Full Implementation 2012 – Full data and system integration – System optimization – Additional Systems
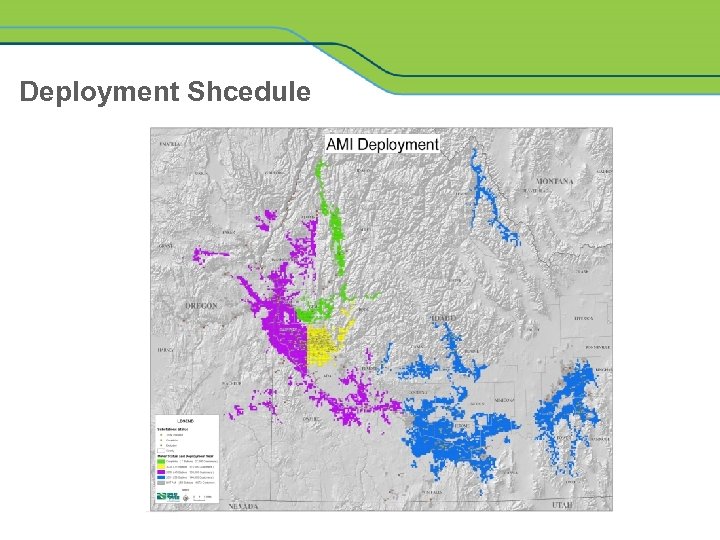 Deployment Shcedule
Deployment Shcedule
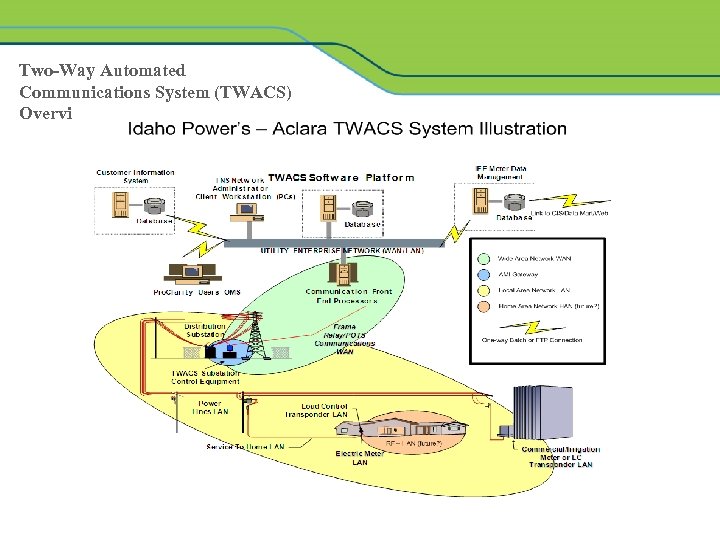 Two-Way Automated Communications System (TWACS) Overview
Two-Way Automated Communications System (TWACS) Overview
 Substation Control Equipment
Substation Control Equipment
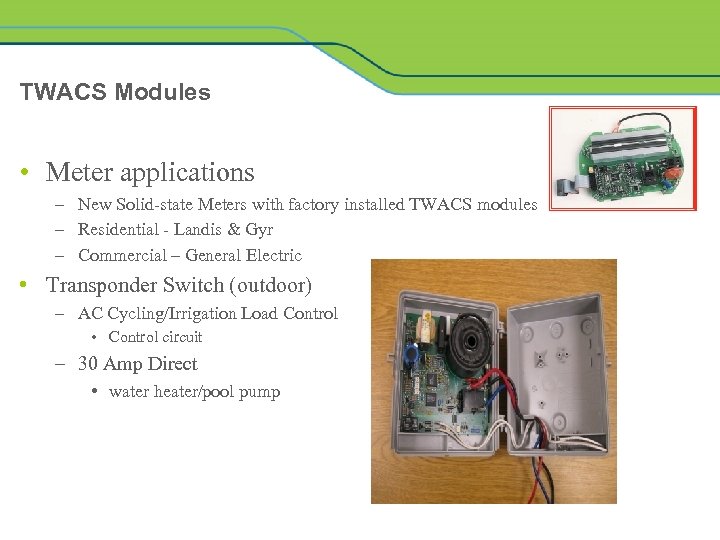 TWACS Modules • Meter applications – New Solid-state Meters with factory installed TWACS modules – Residential - Landis & Gyr – Commercial – General Electric • Transponder Switch (outdoor) – AC Cycling/Irrigation Load Control • Control circuit – 30 Amp Direct • water heater/pool pump
TWACS Modules • Meter applications – New Solid-state Meters with factory installed TWACS modules – Residential - Landis & Gyr – Commercial – General Electric • Transponder Switch (outdoor) – AC Cycling/Irrigation Load Control • Control circuit – 30 Amp Direct • water heater/pool pump
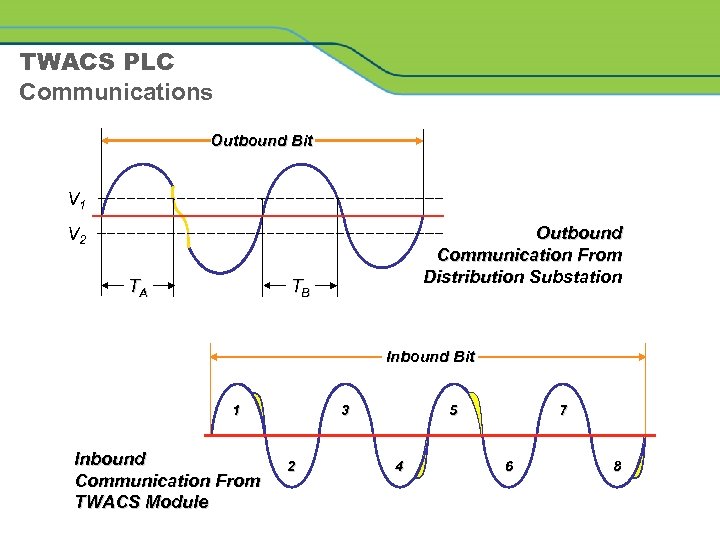 TWACS PLC Communications Outbound Bit V 1 Outbound Communication From Distribution Substation V 2 TA TB Inbound Bit 1 Inbound Communication From TWACS Module 3 2 5 4 7 6 8
TWACS PLC Communications Outbound Bit V 1 Outbound Communication From Distribution Substation V 2 TA TB Inbound Bit 1 Inbound Communication From TWACS Module 3 2 5 4 7 6 8
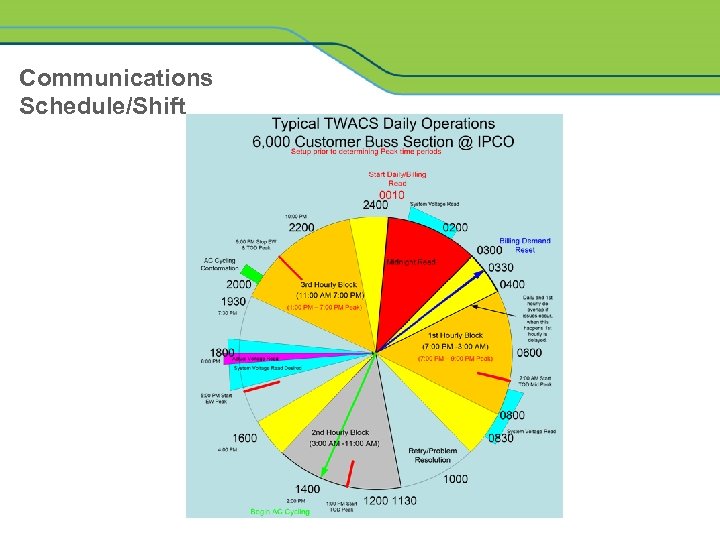 Communications Schedule/Shift
Communications Schedule/Shift
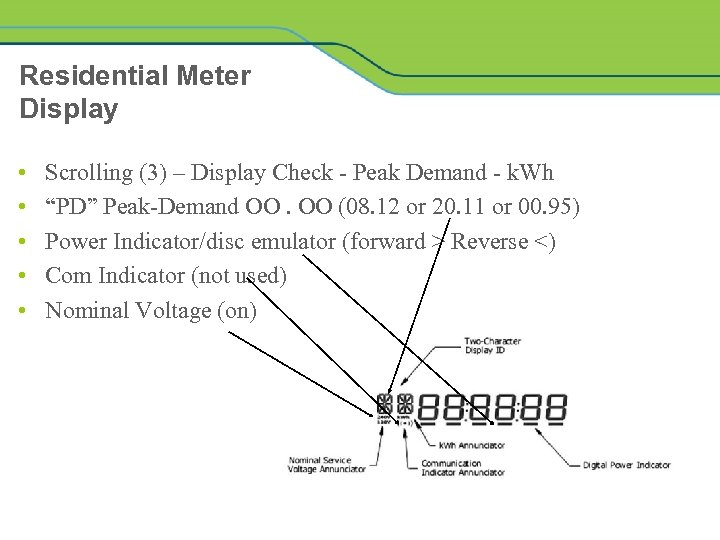 Residential Meter Display • • • Scrolling (3) – Display Check - Peak Demand - k. Wh “PD” Peak-Demand OO. OO (08. 12 or 20. 11 or 00. 95) Power Indicator/disc emulator (forward > Reverse <) Com Indicator (not used) Nominal Voltage (on)
Residential Meter Display • • • Scrolling (3) – Display Check - Peak Demand - k. Wh “PD” Peak-Demand OO. OO (08. 12 or 20. 11 or 00. 95) Power Indicator/disc emulator (forward > Reverse <) Com Indicator (not used) Nominal Voltage (on)
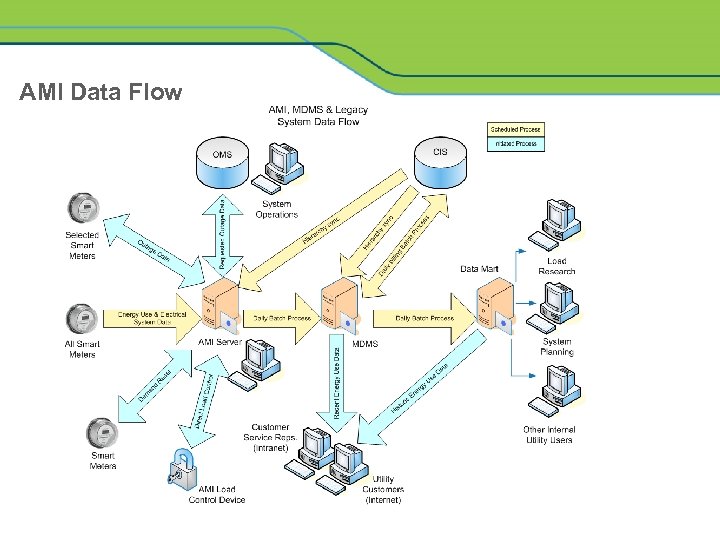 AMI Data Flow
AMI Data Flow
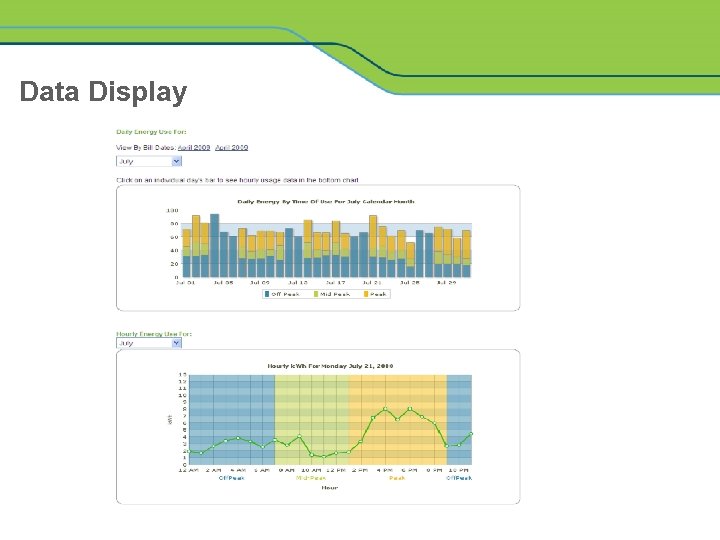 Data Display
Data Display
 Deployment Status • • • 60+ Sub Stations Complete 260, 000 meters exchanged – 750 -1, 000 per day MDMS IEE 5. 3 in production On Schedule On Budget PUC Actions – Certificate of Necessity & Convenience (Dec 2008) – Recovery on investment (June 2009 – June 2012) • DOE Stimulus Grant $47 M for Phase III
Deployment Status • • • 60+ Sub Stations Complete 260, 000 meters exchanged – 750 -1, 000 per day MDMS IEE 5. 3 in production On Schedule On Budget PUC Actions – Certificate of Necessity & Convenience (Dec 2008) – Recovery on investment (June 2009 – June 2012) • DOE Stimulus Grant $47 M for Phase III
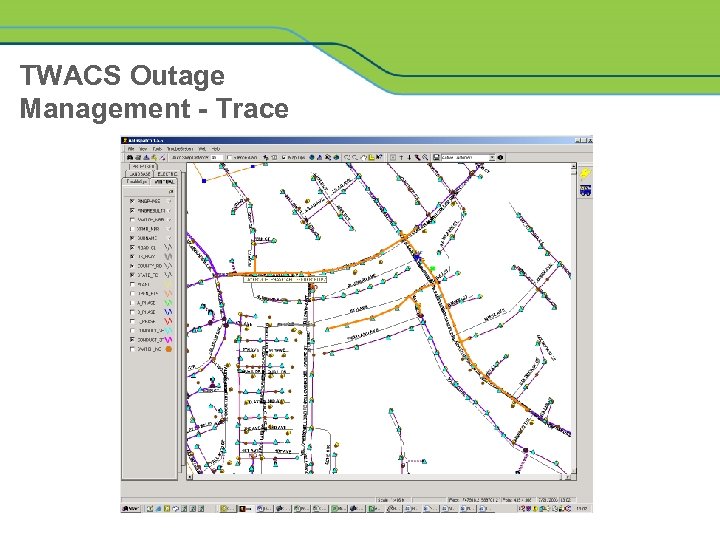 TWACS Outage Management - Trace
TWACS Outage Management - Trace
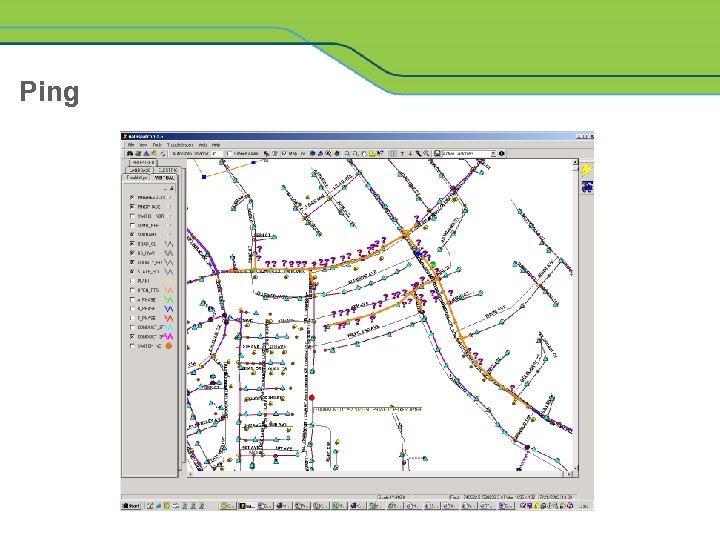 Ping
Ping
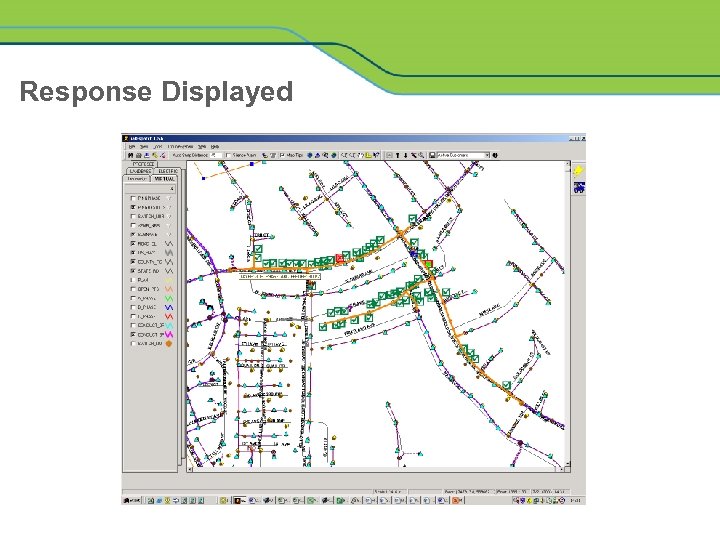 Response Displayed
Response Displayed
 Added Value • Billing Error & High Bill complaint reductions • Customer Satisfaction • Access issues, Digital meters, Data availability - Web • Enhance DSM (Green) • Enable Time Variant Rates (Green) • Enhanced C 2 T/GIS/OMS data • Reduction In Vehicle Use (Green) • Distribution Control? – Capacitors? • System Monitoring & Reporting/Data Acquisition • Voltage, Load, PQ, Energy use, Outage, Electrical location
Added Value • Billing Error & High Bill complaint reductions • Customer Satisfaction • Access issues, Digital meters, Data availability - Web • Enhance DSM (Green) • Enable Time Variant Rates (Green) • Enhanced C 2 T/GIS/OMS data • Reduction In Vehicle Use (Green) • Distribution Control? – Capacitors? • System Monitoring & Reporting/Data Acquisition • Voltage, Load, PQ, Energy use, Outage, Electrical location
 Data Volume • Monthly reading of 500, 000 meters X 12 months = 6, 000 meter reads annually • 250, 000 AMI meters X 26 reads daily = 6, 500, 000 meter reads daily (24 hourly reads + daily k. Wh & k. W reads = 26 reads daily) • 500, 000 AMI meters X 26 reads daily = 13, 000 meter reads daily • 13, 000 daily reads X 365 = 4, 745, 000 meter reads annually • Additional reads (future) – Voltage – Power Quality – Transponder cycle counts • Meter Data Management System (MDMS) – Bleeding edge
Data Volume • Monthly reading of 500, 000 meters X 12 months = 6, 000 meter reads annually • 250, 000 AMI meters X 26 reads daily = 6, 500, 000 meter reads daily (24 hourly reads + daily k. Wh & k. W reads = 26 reads daily) • 500, 000 AMI meters X 26 reads daily = 13, 000 meter reads daily • 13, 000 daily reads X 365 = 4, 745, 000 meter reads annually • Additional reads (future) – Voltage – Power Quality – Transponder cycle counts • Meter Data Management System (MDMS) – Bleeding edge
 Hard AMI Cost Reductions (the business case) • 99% of Meter Reading Costs ($5. 5 M annually) • 90% of Customer Movement Costs ($1. 5 M annually) • Reduction in outage scoping & restoration conformation costs ($363 k annually)
Hard AMI Cost Reductions (the business case) • 99% of Meter Reading Costs ($5. 5 M annually) • 90% of Customer Movement Costs ($1. 5 M annually) • Reduction in outage scoping & restoration conformation costs ($363 k annually)
 Approximate Cost • 3 Years • $74, 000 – $1. 2 M - IT – Systems & Interfaces – $13. 3 M - 142 Station + growth & Communications Equipment Installed – $55. 5 M – 500, 000 Meters Exchanged or installed – 10% contingency and loading • $126 to $140 per endpoint
Approximate Cost • 3 Years • $74, 000 – $1. 2 M - IT – Systems & Interfaces – $13. 3 M - 142 Station + growth & Communications Equipment Installed – $55. 5 M – 500, 000 Meters Exchanged or installed – 10% contingency and loading • $126 to $140 per endpoint
 AMI Phase III (2012) • Implementation of “Mass” Time-Variant-Rates, this will require additional investment (CIS) (stimulus) • DSM Implementation (stimulus) – Direct load control – Indirect load reduction – price signals - TOU – Data analysis • Other Value Added Services (stimulus) – Monitoring – Reporting – Control
AMI Phase III (2012) • Implementation of “Mass” Time-Variant-Rates, this will require additional investment (CIS) (stimulus) • DSM Implementation (stimulus) – Direct load control – Indirect load reduction – price signals - TOU – Data analysis • Other Value Added Services (stimulus) – Monitoring – Reporting – Control
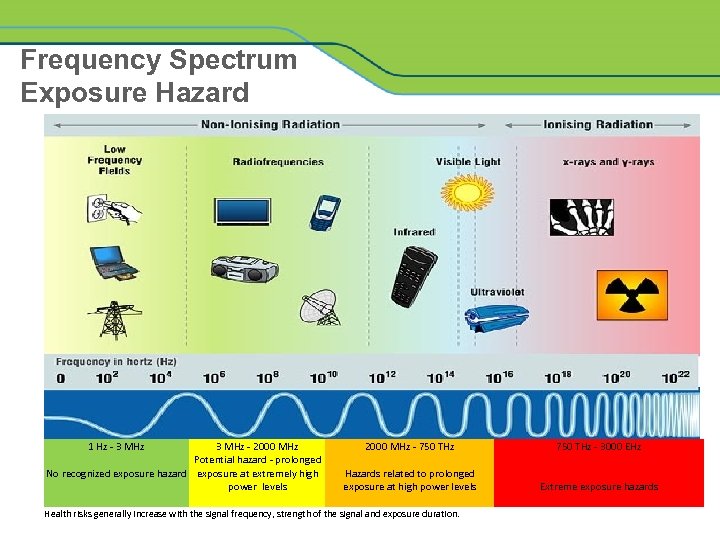 Frequency Spectrum Exposure Hazard 1 Hz - 3 MHz - 2000 MHz Potential hazard - prolonged No recognized exposure hazard exposure at extremely high power levels 2000 MHz - 750 THz - 3000 EHz Hazards related to prolonged exposure at high power levels Extreme exposure hazards Health risks generally increase with the signal frequency, strength of the signal and exposure duration.
Frequency Spectrum Exposure Hazard 1 Hz - 3 MHz - 2000 MHz Potential hazard - prolonged No recognized exposure hazard exposure at extremely high power levels 2000 MHz - 750 THz - 3000 EHz Hazards related to prolonged exposure at high power levels Extreme exposure hazards Health risks generally increase with the signal frequency, strength of the signal and exposure duration.
 Questions
Questions


