971720062eed86476d32ef8988e02503.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Advanced Ch. IPseq Identification of consensus binding sites for the LEAFY transcription factor

Advanced Ch. IPseq Identification of consensus binding sites for the LEAFY transcription factor

Scientific Objective The LEAFY transcription factor has been shown (Moyroud et al. 2011) to bind a dimer of the motif CCANTG[G/T] We will use data from a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay on the LEAFY protein to attempt to confirm this finding https: //pods. iplantcollaborative. org/wiki/x/l. Qi
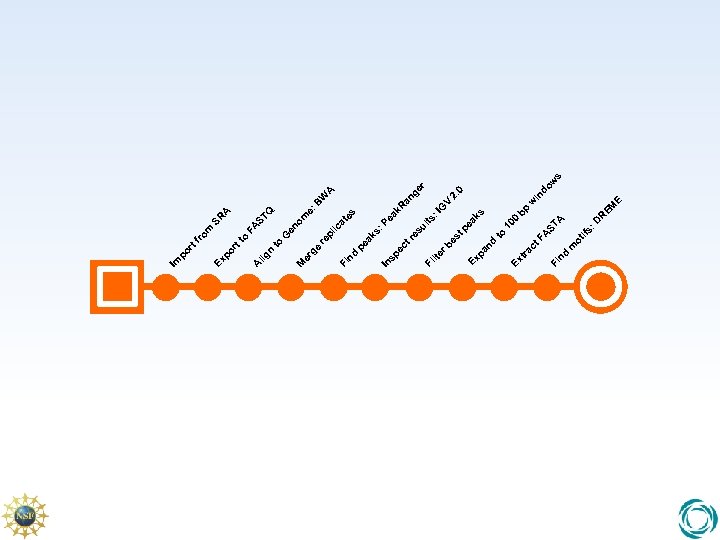
bp E s w do 2. 0 in w R EM : D ifs A 10 0 ea ks ST FA to ot m ac t nd Fi tr Ex nd pa Ex V ge r W A R an : I G lts re su ea k : P es tp lte rb Fi sp ec t In ak s pe ic at es pl e: B om en ST Q A SR FA G re to ge n nd Fi M er lig A to m ro tf rt po Ex po r Im
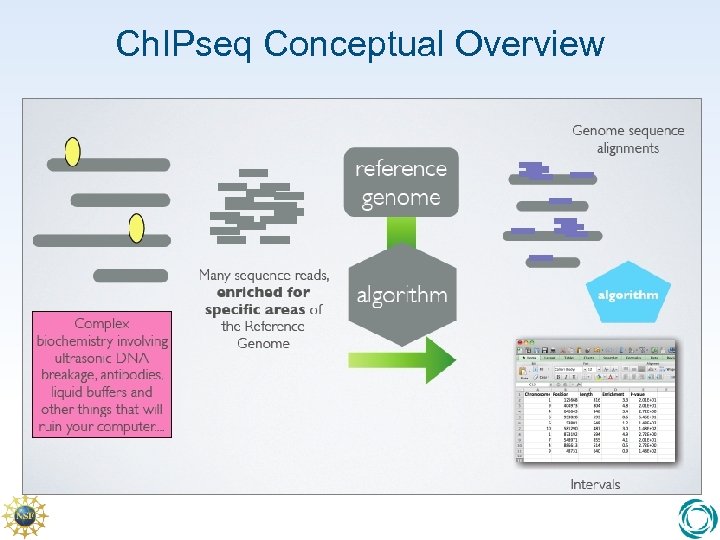
Ch. IPseq Conceptual Overview

The NCBI SRA • NCBI SRA is a repository for NGS sequence reads • Data is stored in association with basic metadata explaining experimental technique and inter-sample relationships • Data format is NCBI-specific SRA and SRA-lite format. “Universal” lossless format. • Upload and download is offered via FTP and HTTP but also via Aspera ASCP – Fast, parallel protocol similar in performance to i. RODS iput/iget commands used in i. Plant Data Store • Use NCBI SRA Import to rapidly copy SRA accession SRP 003928 over ASCP into the i. Plant Data Store.

NCBI SRA Toolkit • SRA data format is a universal format, but no downstream apps can accept it natively. • Need to export SRA to FASTQ, SFF, etc. • These are the standard file formats for representing sequence. • Use the NCBI SRA Toolkit fastq-dump to export FASTQ sequence files from SRA files so we can process them
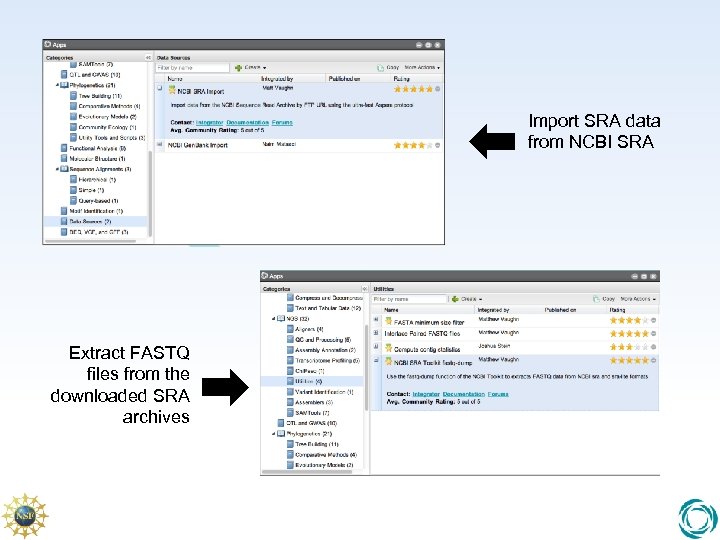
Import SRA data from NCBI SRA Extract FASTQ files from the downloaded SRA archives

BWA • BWA is one of many applications whose objective is to efficiently align short sequence reads to a reference genome sequence • Other alternatives are BOWTIE, MAQ, Top. Hat, Stampy, Novoalign, etc. • BWA is used by the Human 1000 genomes project due to its speed and accuracy.
Outputs from BWA • BWA emits alignments in the SAM format • SAM is a universal system for describing next-gen sequences and their corresponding genome alignments • SAMTools is a suite of applications for manipulating SAM files – Sort, Merge, Index, and more – Emit as binary BAM file
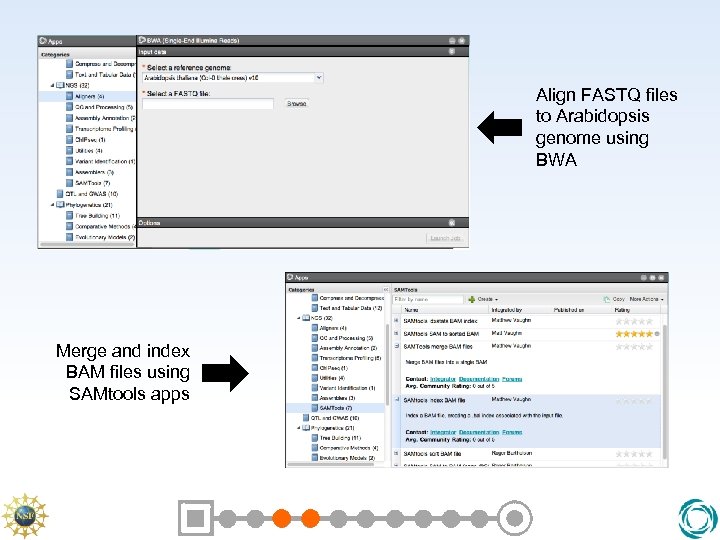
Align FASTQ files to Arabidopsis genome using BWA Merge and index BAM files using SAMtools apps

Peak. Ranger • Peak. Ranger is a fast, optimized algorithm for detecting enrichment peaks in Ch. IPseq data sets • Peak. Ranger was developed at OICR in partnership between mod. ENCODE and i. Plant and is now maintained at UTSW • It’s not the only option for peak finding: – – MACS Ch. IPseq Peak Finder Cis. Genome Find. Peaks http: //ranger. sourceforge. net/
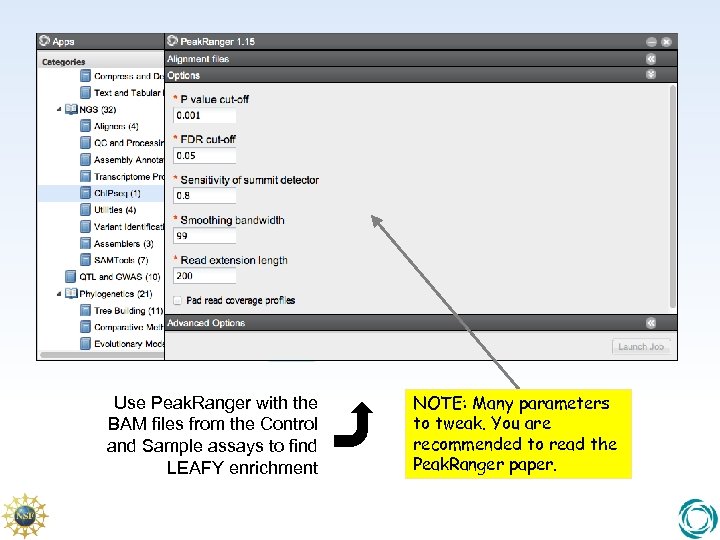
Use Peak. Ranger with the BAM files from the Control and Sample assays to find LEAFY enrichment NOTE: Many parameters to tweak. You are recommended to read the Peak. Ranger paper.
Outputs from Peak. Ranger • Wiggle (. wig) files: Density map of sequence reads across the reference genome for control and sample BAM alignments • Region (. bed) file: Feature file containing the significantly enriched domains in the genome • Summit (. bed) file: Feature file containing the single base maximum of each peak
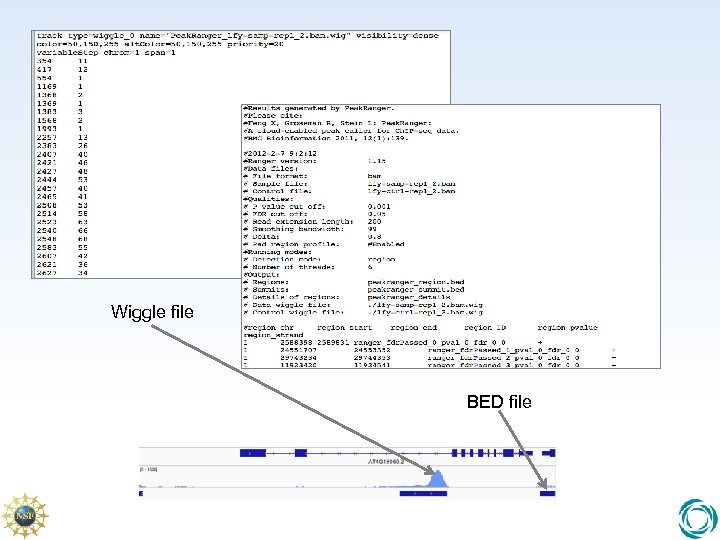
Wiggle file BED file
Integrative Genomics Viewer The Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) is a high-performance visualization tool for interactive exploration of large, integrated genomic datasets. It supports a wide variety of data types, including array-based and next-generation sequence data, and genomic annotations. http: //www. broadinstitute. org/igv/ Use IGV to inspect outputs from Peak. Ranger
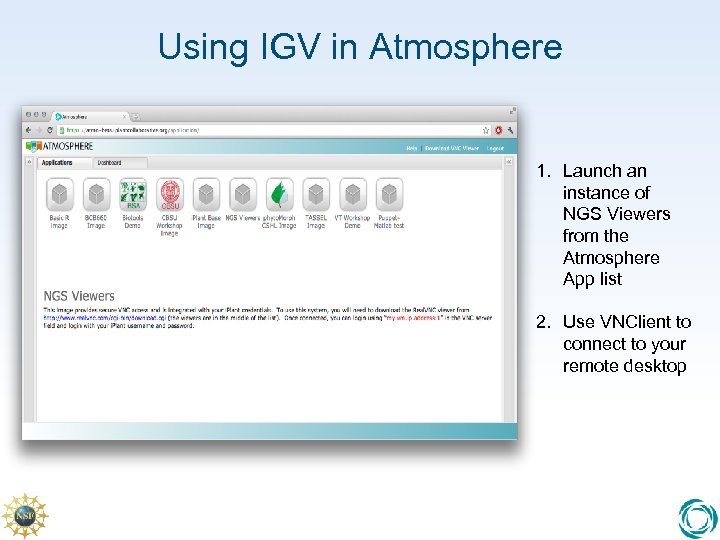
Using IGV in Atmosphere 1. Launch an instance of NGS Viewers from the Atmosphere App list 2. Use VNClient to connect to your remote desktop
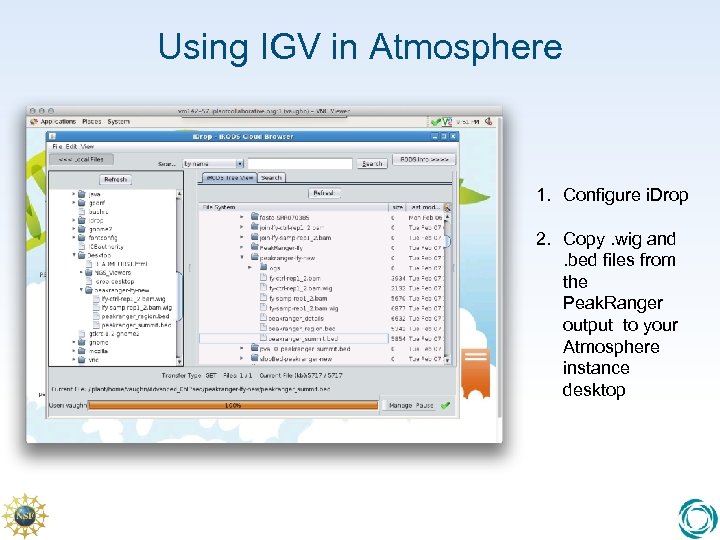
Using IGV in Atmosphere 1. Configure i. Drop 2. Copy. wig and. bed files from the Peak. Ranger output to your Atmosphere instance desktop

Using IGV in Atmosphere 1. Launch IGV (Integrative Genomics Viewer) 2. Change the current genome to A. thaliana (TAIR 10)
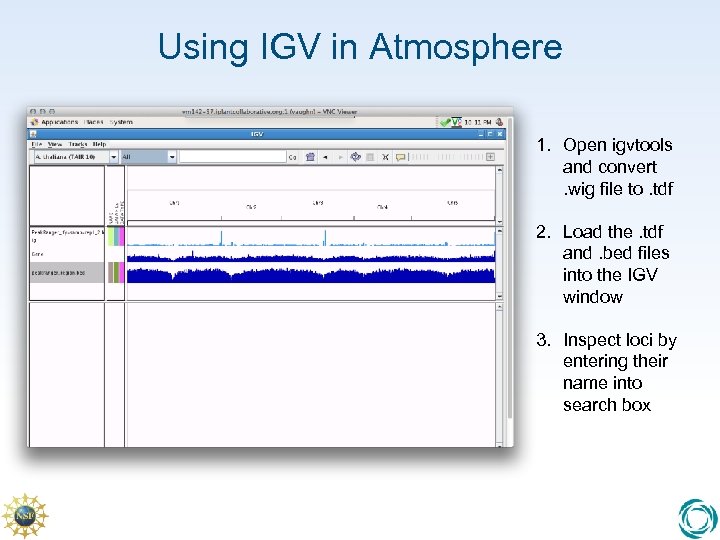
Using IGV in Atmosphere 1. Open igvtools and convert. wig file to. tdf 2. Load the. tdf and. bed files into the IGV window 3. Inspect loci by entering their name into search box
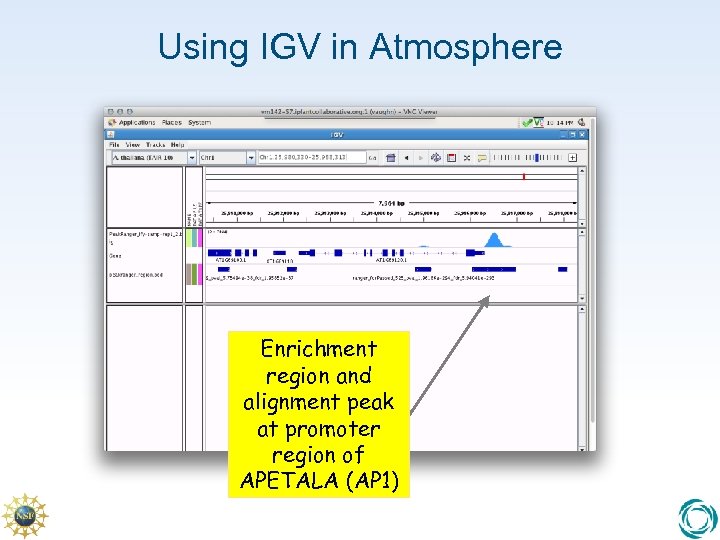
Using IGV in Atmosphere Enrichment region and alignment peak at promoter region of APETALA (AP 1)
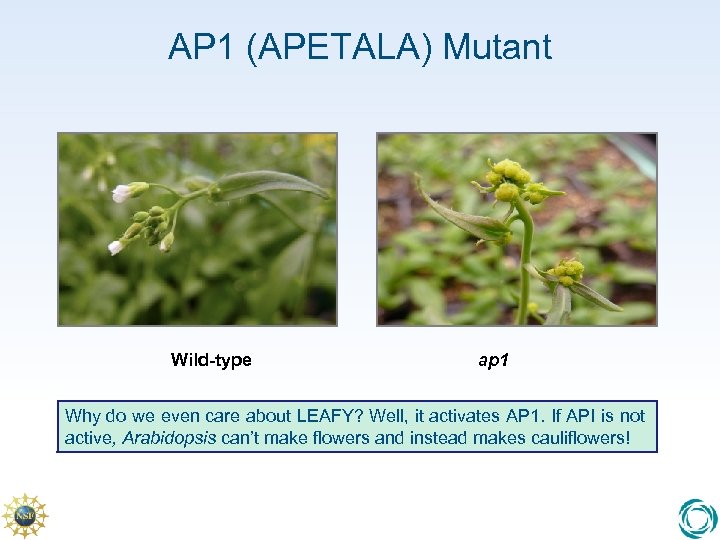
AP 1 (APETALA) Mutant Wild-type ap 1 Why do we even care about LEAFY? Well, it activates AP 1. If API is not active, Arabidopsis can’t make flowers and instead makes cauliflowers!
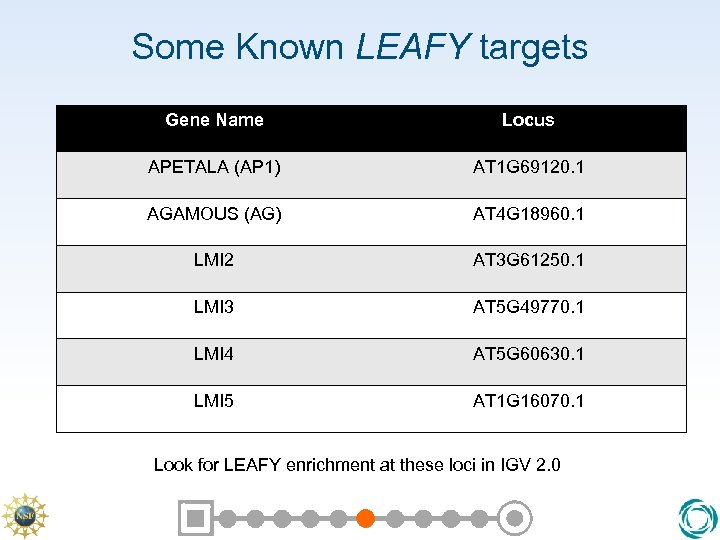
Some Known LEAFY targets Gene Name Locus APETALA (AP 1) AT 1 G 69120. 1 AGAMOUS (AG) AT 4 G 18960. 1 LMI 2 AT 3 G 61250. 1 LMI 3 AT 5 G 49770. 1 LMI 4 AT 5 G 60630. 1 LMI 5 AT 1 G 16070. 1 Look for LEAFY enrichment at these loci in IGV 2. 0

Filtering the Peak. Ranger summits file The statiscally best summits from Peak. Ranger have P-values of Zero. If you look at the summits. bed file you can see this is embedded in the name of the features. So, if we filter the summits. bed for only lines matching pval_0, we will generate a BED file containing summits most likely to be near true LEAFY binding sites. This identical to running egrep “pval_0” peakranger_summit. bed > peakranger_summit_best. bed on a command line Find Lines Matching a Regular Expression
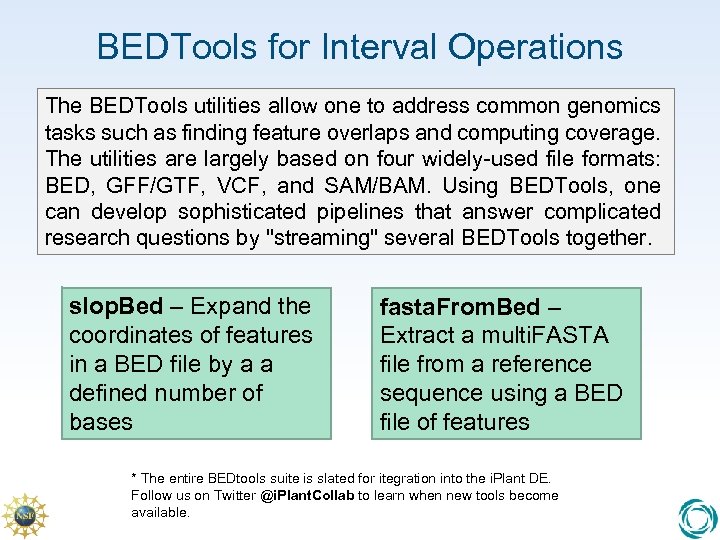
BEDTools for Interval Operations The BEDTools utilities allow one to address common genomics tasks such as finding feature overlaps and computing coverage. The utilities are largely based on four widely-used file formats: BED, GFF/GTF, VCF, and SAM/BAM. Using BEDTools, one can develop sophisticated pipelines that answer complicated research questions by "streaming" several BEDTools together. slop. Bed – Expand the coordinates of features in a BED file by a a defined number of bases fasta. From. Bed – Extract a multi. FASTA file from a reference sequence using a BED file of features * The entire BEDtools suite is slated for itegration into the i. Plant DE. Follow us on Twitter @i. Plant. Collab to learn when new tools become available.
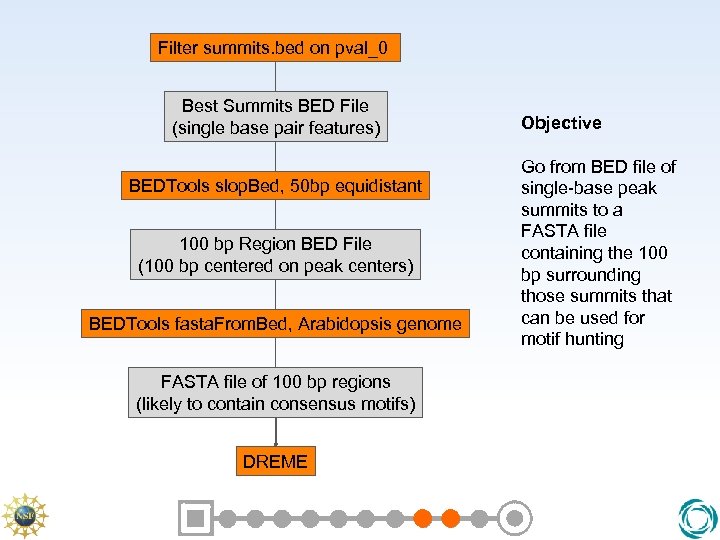
Filter summits. bed on pval_0 Best Summits BED File (single base pair features) BEDTools slop. Bed, 50 bp equidistant 100 bp Region BED File (100 bp centered on peak centers) BEDTools fasta. From. Bed, Arabidopsis genome FASTA file of 100 bp regions (likely to contain consensus motifs) DREME Objective Go from BED file of single-base peak summits to a FASTA file containing the 100 bp surrounding those summits that can be used for motif hunting

DREME • Run DREME on 100 bp windows surrounding LEAFY peaks • Download results
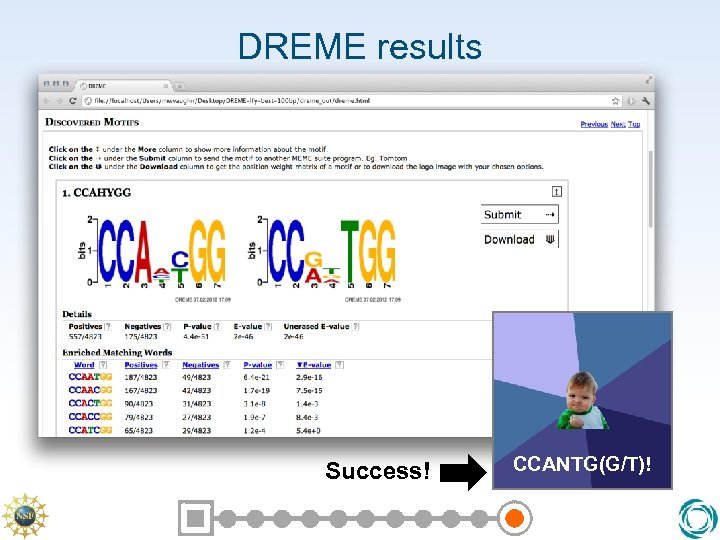
DREME results Success! CCANTG(G/T)!

Potential Next Steps • Identify all consensus LEAFY sites in the genome that fall in promoters • Extract all the promoters where LEAFY has significant binding and associate them with genes. • Generate a simple gene list and run Ontology Term enrichment analysis to find classes of genes influenced by LEAFY
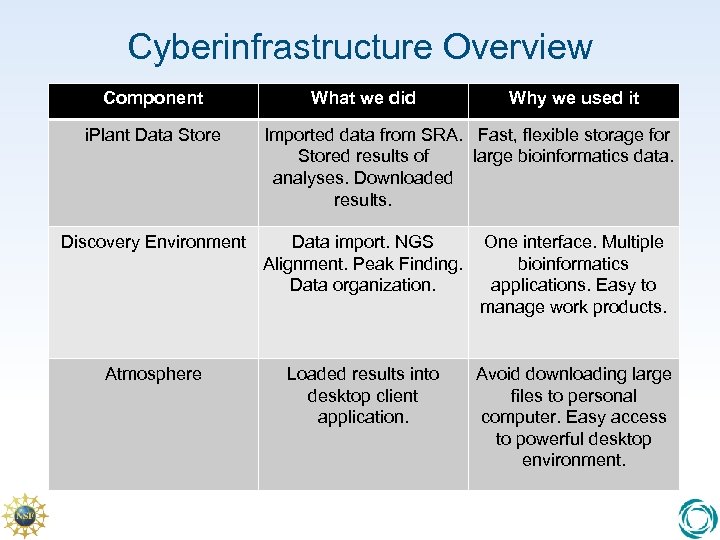
Cyberinfrastructure Overview Component i. Plant Data Store What we did Why we used it Imported data from SRA. Fast, flexible storage for Stored results of large bioinformatics data. analyses. Downloaded results. Discovery Environment Data import. NGS Alignment. Peak Finding. Data organization. One interface. Multiple bioinformatics applications. Easy to manage work products. Atmosphere Loaded results into desktop client application. Avoid downloading large files to personal computer. Easy access to powerful desktop environment.

Questions?
SAMTools

971720062eed86476d32ef8988e02503.ppt