e7117fbaf3dbd58fca4dff098d4b3811.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Advanced Algorithms Minimum spanning tree Generic algorithm Kruskal’s algorithm Prim’s algorithm CSE 780 Algorithms
Advanced Algorithms Minimum spanning tree Generic algorithm Kruskal’s algorithm Prim’s algorithm CSE 780 Algorithms
 Minimum Spanning Tree Learning outcomes: You should be able to: Write Kruskal’s and Prim’s algorithms Run both algorithms on given graphs Analyze both algorithms CSE 780 Algorithms
Minimum Spanning Tree Learning outcomes: You should be able to: Write Kruskal’s and Prim’s algorithms Run both algorithms on given graphs Analyze both algorithms CSE 780 Algorithms
 Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads A road connects 2 and only 2 houses A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: repair enough roads such that 1. every house is connected 2. total repair cost is minimum CSE 780 Algorithms
Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads A road connects 2 and only 2 houses A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: repair enough roads such that 1. every house is connected 2. total repair cost is minimum CSE 780 Algorithms
 Definition Given a connected graph G = (V, E), with weight function w : E --> R Find min-weight connected subgraph Spanning tree T: A tree that includes all nodes from V T = (V, E’), where E’ E Weight of T: W( T ) = w(e) Minimum spanning tree (MST): A tree with minimum weight among all spanning trees CSE 780 Algorithms
Definition Given a connected graph G = (V, E), with weight function w : E --> R Find min-weight connected subgraph Spanning tree T: A tree that includes all nodes from V T = (V, E’), where E’ E Weight of T: W( T ) = w(e) Minimum spanning tree (MST): A tree with minimum weight among all spanning trees CSE 780 Algorithms
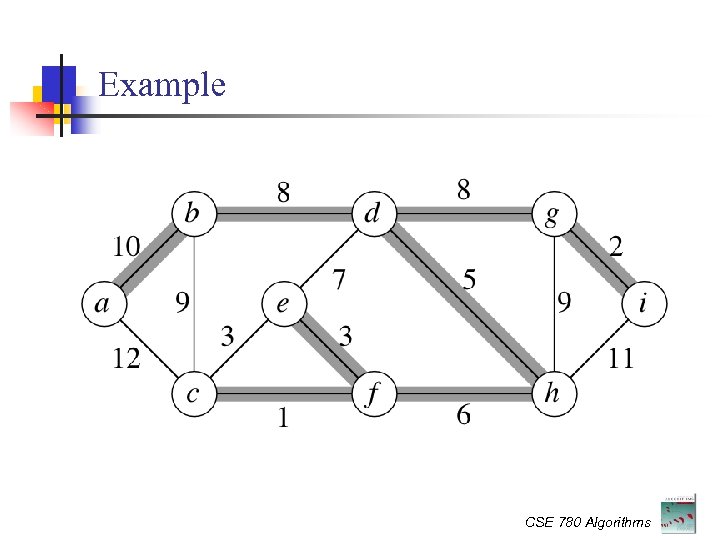 Example CSE 780 Algorithms
Example CSE 780 Algorithms
 MST for given G may not be unique Since MST is a spanning tree: # edges : |V| - 1 If the graph is unweighted: All spanning trees have same weight CSE 780 Algorithms
MST for given G may not be unique Since MST is a spanning tree: # edges : |V| - 1 If the graph is unweighted: All spanning trees have same weight CSE 780 Algorithms
 Generic Algorithm Framework for G = (V, E) : Goal: build a set of edges A E Start with A empty Add edge into A one by one At any moment, A is a subset of some MST for G CSE 780 Algorithms
Generic Algorithm Framework for G = (V, E) : Goal: build a set of edges A E Start with A empty Add edge into A one by one At any moment, A is a subset of some MST for G CSE 780 Algorithms
 Finding Safe Edges When A is empty, example of safe edges? The edge with smallest weight Intuition: Suppose S V, --- a cut (S, V-S) – a partition of vertices into sets S and V-S should be connected By the crossing edge with the smallest weight ! That edge also called a light edge crossing the cut (S, V-S) A cut (S, V-S) respects set A of edges If no edges from A crosses the cut (S, V-S) CSE 780 Algorithms
Finding Safe Edges When A is empty, example of safe edges? The edge with smallest weight Intuition: Suppose S V, --- a cut (S, V-S) – a partition of vertices into sets S and V-S should be connected By the crossing edge with the smallest weight ! That edge also called a light edge crossing the cut (S, V-S) A cut (S, V-S) respects set A of edges If no edges from A crosses the cut (S, V-S) CSE 780 Algorithms
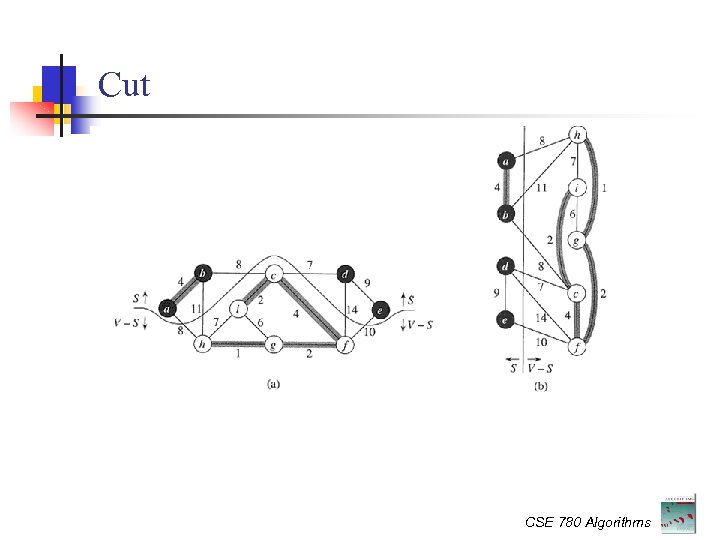 Cut CSE 780 Algorithms
Cut CSE 780 Algorithms
 Safe-Edge Theorem: Let A be a subset of some MST, (S, V-S) be a cut that respects A, and (u, v) be a light edge crossing (S, V-S). Then (u, v) is safe for A. Proof Greedy Approach: Based on the Corollary: generic algorithm and the corollary, to compute MST we only need a way to find Let C = (Vc , Ec ) be a connected component in the graph a = (V, A). at each is a light (forest) G safe edge If (u, v) moment. edge connecting C A to some other component in GA , then (u, v) is safe for A. CSE 780 Algorithms
Safe-Edge Theorem: Let A be a subset of some MST, (S, V-S) be a cut that respects A, and (u, v) be a light edge crossing (S, V-S). Then (u, v) is safe for A. Proof Greedy Approach: Based on the Corollary: generic algorithm and the corollary, to compute MST we only need a way to find Let C = (Vc , Ec ) be a connected component in the graph a = (V, A). at each is a light (forest) G safe edge If (u, v) moment. edge connecting C A to some other component in GA , then (u, v) is safe for A. CSE 780 Algorithms
 Kruskal’s Algorithm Start with A empty, and each vertex being its own connected component Repeatedly merge two components by connecting them with a light edge crossing them Two issues: Maintain sets of components Choose light edges CSE 780 Algorithms
Kruskal’s Algorithm Start with A empty, and each vertex being its own connected component Repeatedly merge two components by connecting them with a light edge crossing them Two issues: Maintain sets of components Choose light edges CSE 780 Algorithms
 Pseudo-code CSE 780 Algorithms
Pseudo-code CSE 780 Algorithms
 Disjoint Set Operations Disjoint set data structure maintains a collection S = {S 1, S 2, …, Sk} of disjoint dynamic sets where each set is identified by a representative (member) of the set. MAKE-SET(x): create a new set whose only member (and representative) is pointed at by x. UNION(x, y): unites dynamic sets containing x and y, Sx and Sy, eliminating Sx and Sy from S. FIND-SET(x): returns a pointer to the representative of the set containing x. CSE 780 Algorithms
Disjoint Set Operations Disjoint set data structure maintains a collection S = {S 1, S 2, …, Sk} of disjoint dynamic sets where each set is identified by a representative (member) of the set. MAKE-SET(x): create a new set whose only member (and representative) is pointed at by x. UNION(x, y): unites dynamic sets containing x and y, Sx and Sy, eliminating Sx and Sy from S. FIND-SET(x): returns a pointer to the representative of the set containing x. CSE 780 Algorithms
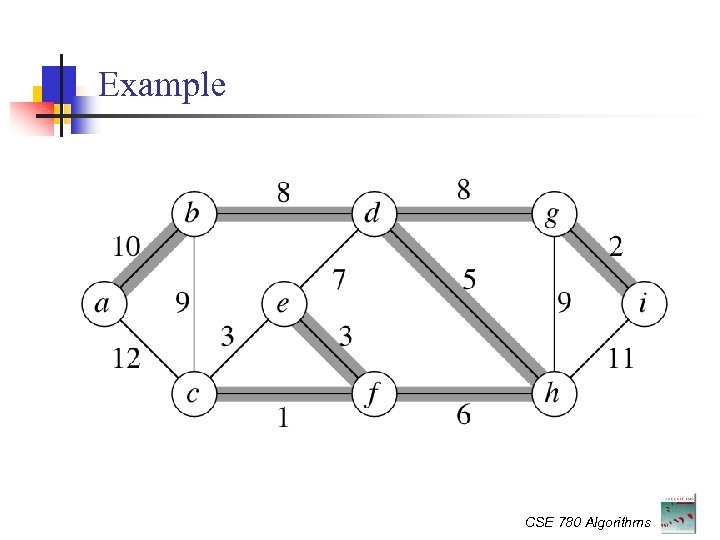 Example CSE 780 Algorithms
Example CSE 780 Algorithms
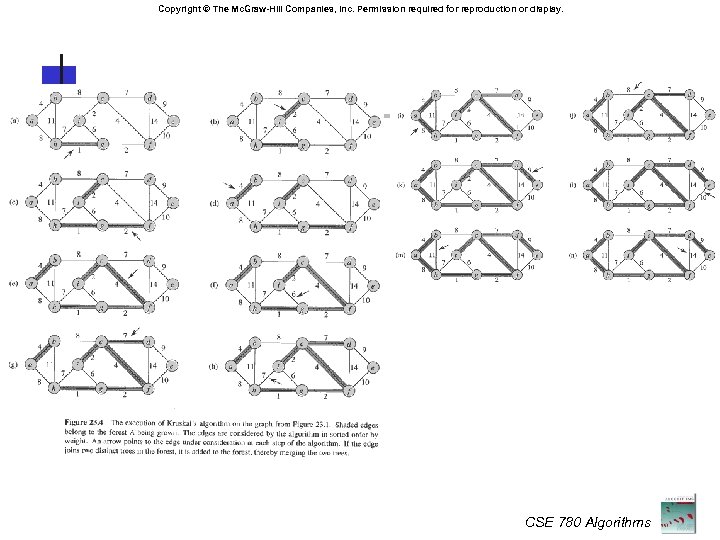 Copyright © The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CSE 780 Algorithms
Copyright © The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CSE 780 Algorithms
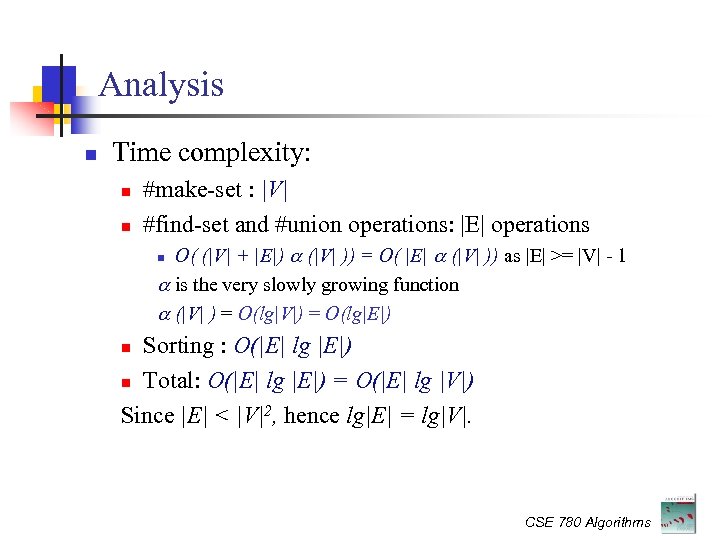 Analysis Time complexity: #make-set : |V| #find-set and #union operations: |E| operations O( (|V| + |E|) (|V| )) = O( |E| (|V| )) as |E| >= |V| - 1 is the very slowly growing function (|V| ) = O(lg|V|) = O(lg|E|) Sorting : O(|E| lg |E|) Total: O(|E| lg |E|) = O(|E| lg |V|) Since |E| < |V|2, hence lg|E| = lg|V|. CSE 780 Algorithms
Analysis Time complexity: #make-set : |V| #find-set and #union operations: |E| operations O( (|V| + |E|) (|V| )) = O( |E| (|V| )) as |E| >= |V| - 1 is the very slowly growing function (|V| ) = O(lg|V|) = O(lg|E|) Sorting : O(|E| lg |E|) Total: O(|E| lg |E|) = O(|E| lg |V|) Since |E| < |V|2, hence lg|E| = lg|V|. CSE 780 Algorithms
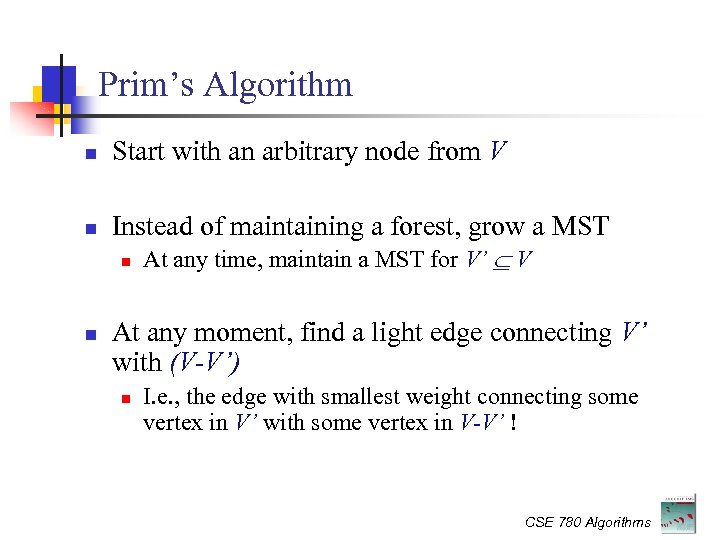 Prim’s Algorithm Start with an arbitrary node from V Instead of maintaining a forest, grow a MST At any time, maintain a MST for V’ V At any moment, find a light edge connecting V’ with (V-V’) I. e. , the edge with smallest weight connecting some vertex in V’ with some vertex in V-V’ ! CSE 780 Algorithms
Prim’s Algorithm Start with an arbitrary node from V Instead of maintaining a forest, grow a MST At any time, maintain a MST for V’ V At any moment, find a light edge connecting V’ with (V-V’) I. e. , the edge with smallest weight connecting some vertex in V’ with some vertex in V-V’ ! CSE 780 Algorithms
 Prim’s Algorithm cont. Again two issues: Maintain the tree already build at any moment Easy: simply a tree rooted at r : the starting node Find the next light edge efficiently For v V - V’, define key(v) = the min distance between v and some node from V’ (current MST) At any moment, find the node with min key. Use a priority queue ! CSE 780 Algorithms
Prim’s Algorithm cont. Again two issues: Maintain the tree already build at any moment Easy: simply a tree rooted at r : the starting node Find the next light edge efficiently For v V - V’, define key(v) = the min distance between v and some node from V’ (current MST) At any moment, find the node with min key. Use a priority queue ! CSE 780 Algorithms
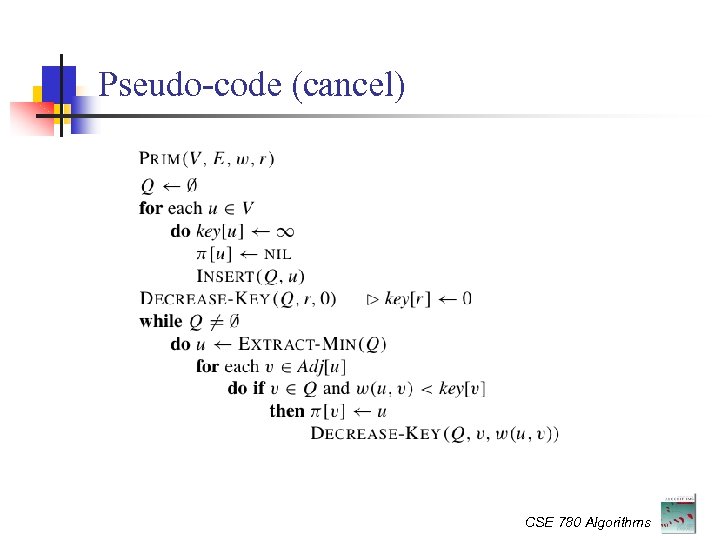 Pseudo-code (cancel) CSE 780 Algorithms
Pseudo-code (cancel) CSE 780 Algorithms
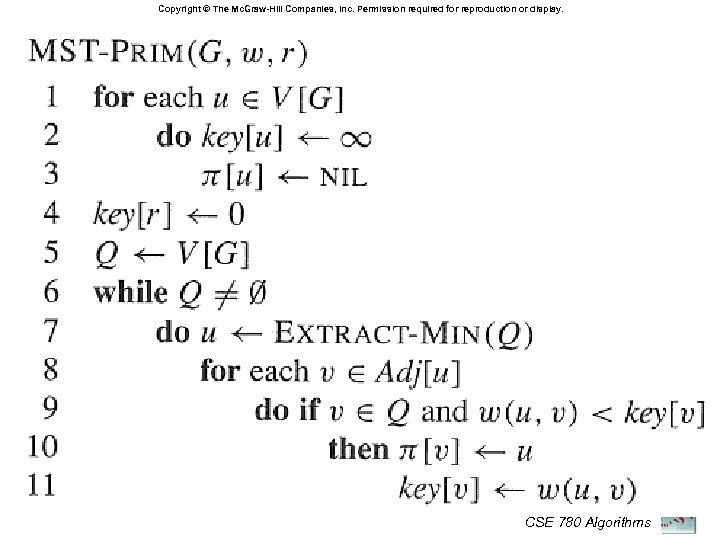 Copyright © The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CSE 780 Algorithms
Copyright © The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CSE 780 Algorithms
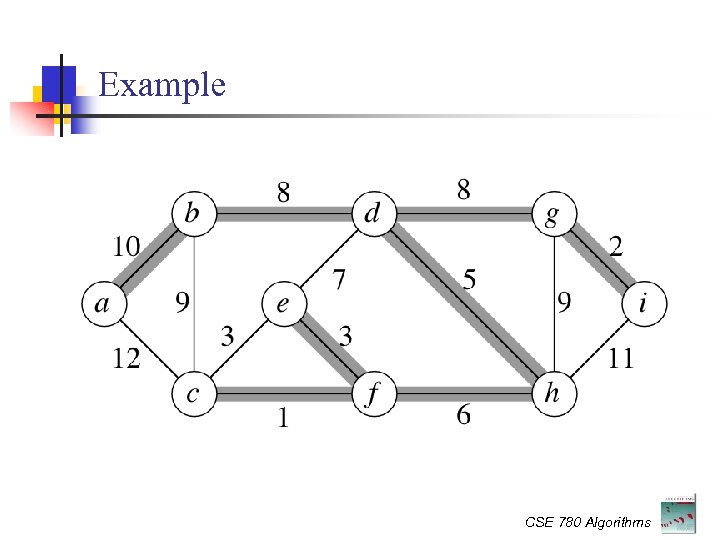 Example CSE 780 Algorithms
Example CSE 780 Algorithms
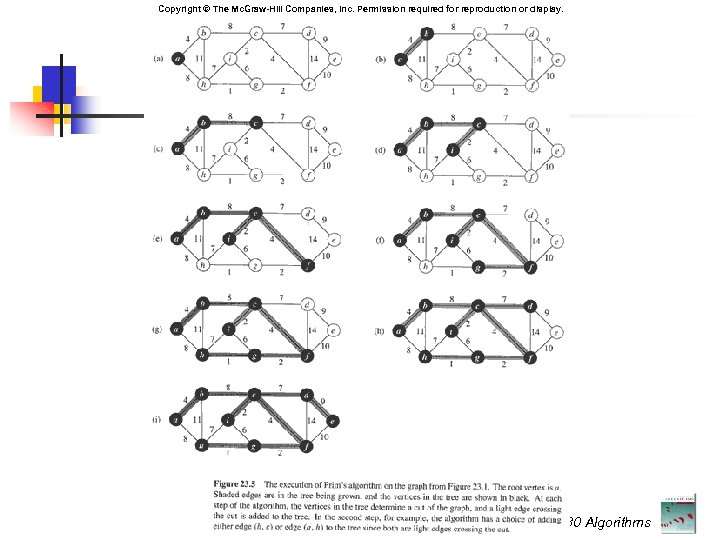 Copyright © The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CSE 780 Algorithms
Copyright © The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CSE 780 Algorithms
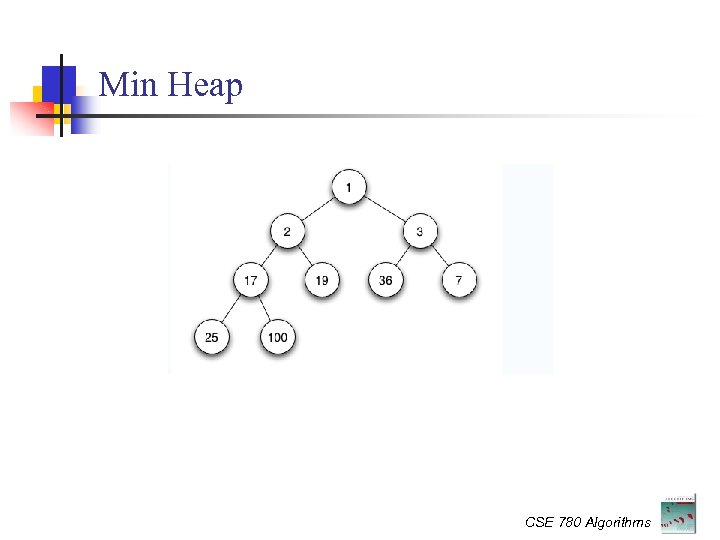 Min Heap CSE 780 Algorithms
Min Heap CSE 780 Algorithms
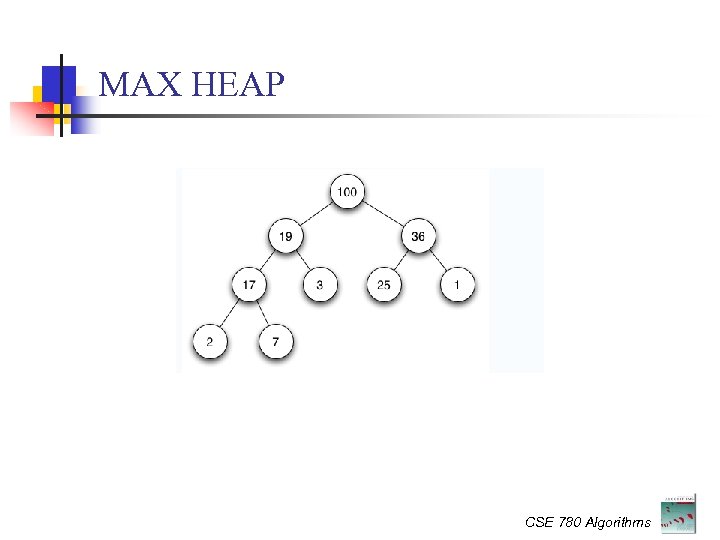 MAX HEAP CSE 780 Algorithms
MAX HEAP CSE 780 Algorithms
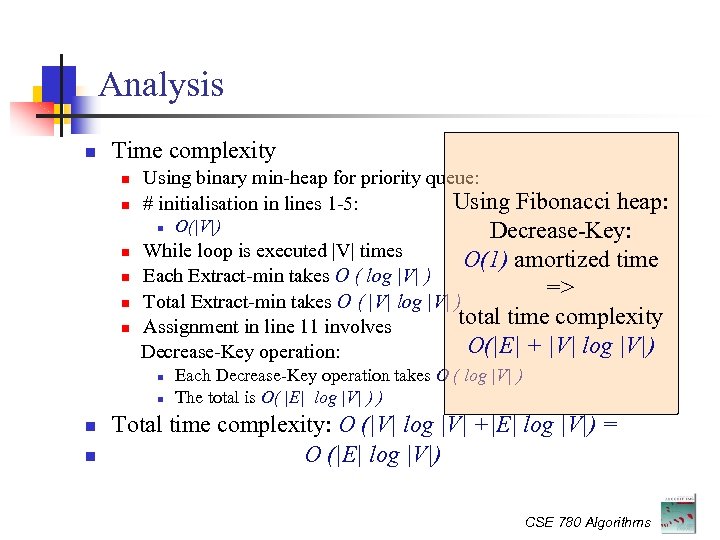 Analysis Time complexity Using binary min-heap for priority queue: Using # initialisation in lines 1 -5: Fibonacci heap: O(|V|) Decrease-Key: While loop is executed |V| times O(1) amortized time Each Extract-min takes O ( log |V| ) => Total Extract-min takes O ( |V| log |V| ) total time complexity Assignment in line 11 involves O(|E| + |V| log |V|) Decrease-Key operation: Each Decrease-Key operation takes O ( log |V| ) The total is O( |E| log |V| ) ) Total time complexity: O (|V| log |V| +|E| log |V|) = O (|E| log |V|) CSE 780 Algorithms
Analysis Time complexity Using binary min-heap for priority queue: Using # initialisation in lines 1 -5: Fibonacci heap: O(|V|) Decrease-Key: While loop is executed |V| times O(1) amortized time Each Extract-min takes O ( log |V| ) => Total Extract-min takes O ( |V| log |V| ) total time complexity Assignment in line 11 involves O(|E| + |V| log |V|) Decrease-Key operation: Each Decrease-Key operation takes O ( log |V| ) The total is O( |E| log |V| ) ) Total time complexity: O (|V| log |V| +|E| log |V|) = O (|E| log |V|) CSE 780 Algorithms
 Applications Clustering Euclidean traveling salesman problem CSE 780 Algorithms
Applications Clustering Euclidean traveling salesman problem CSE 780 Algorithms


