6c44439d7b364a952bc4b4fe74178884.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 ADSL Systems - An Overview Praveen Reguraman Inter. Operability Lab University of New Hampshire 1999
ADSL Systems - An Overview Praveen Reguraman Inter. Operability Lab University of New Hampshire 1999
 Contents • • ADSL - An Overview ADSL Network Architecture ADSL Protocol Architecture Typical ADSL Implementations RFC 1483 PPP Over ATM Over ADSL PPP over Ethernet.
Contents • • ADSL - An Overview ADSL Network Architecture ADSL Protocol Architecture Typical ADSL Implementations RFC 1483 PPP Over ATM Over ADSL PPP over Ethernet.
 ADSL An Overview
ADSL An Overview
 ADSL • ADSL - Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line • Copper based High speed network access technology • rapidly growing broadband access solution for home networking and small business systems • uses multi-carrier modulation over unused frequency bands in phone lines • supports data rates up to 6144 Kbps downstream and 640 Kbps upstream
ADSL • ADSL - Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line • Copper based High speed network access technology • rapidly growing broadband access solution for home networking and small business systems • uses multi-carrier modulation over unused frequency bands in phone lines • supports data rates up to 6144 Kbps downstream and 640 Kbps upstream
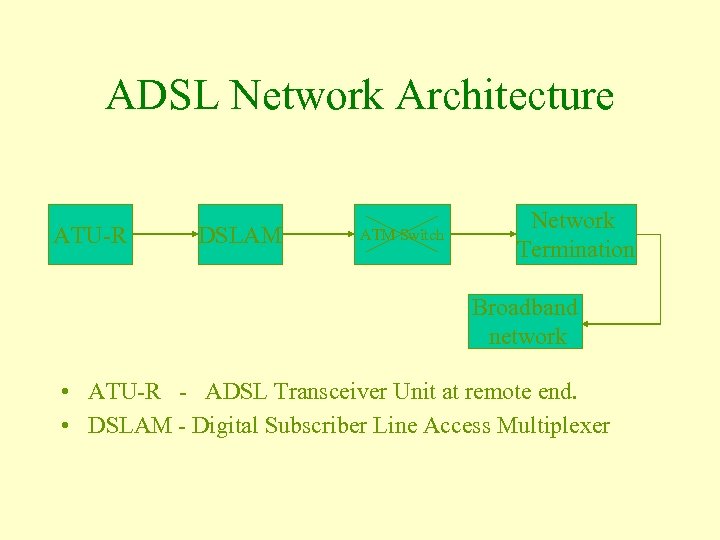 ADSL Network Architecture ATU-R DSLAM ATM Switch Network Termination Broadband network • ATU-R - ADSL Transceiver Unit at remote end. • DSLAM - Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer
ADSL Network Architecture ATU-R DSLAM ATM Switch Network Termination Broadband network • ATU-R - ADSL Transceiver Unit at remote end. • DSLAM - Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer
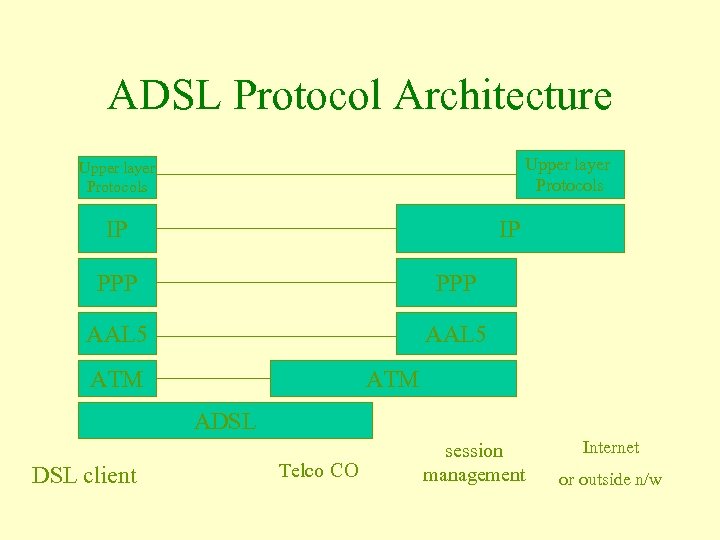 ADSL Protocol Architecture Upper layer Protocols IP IP PPP AAL 5 ATM ADSL client Telco CO session management Internet or outside n/w
ADSL Protocol Architecture Upper layer Protocols IP IP PPP AAL 5 ATM ADSL client Telco CO session management Internet or outside n/w
 ADSL Implementations • RFC 1483 • PPP Over ATM Over ADSL • PPP Over Ethernet
ADSL Implementations • RFC 1483 • PPP Over ATM Over ADSL • PPP Over Ethernet
 RFC 1483 • RFC 1483 - Multi-Protocol Over AAL 5 • creation and use of PVCs for data transfer. • uses LLC/SNAP Encapsulation for routed/bridged PDUs. • Supports IEEE 802. 3/802. 2, Ethernet II Bridged PDUs and PPP protocol units for ADSL.
RFC 1483 • RFC 1483 - Multi-Protocol Over AAL 5 • creation and use of PVCs for data transfer. • uses LLC/SNAP Encapsulation for routed/bridged PDUs. • Supports IEEE 802. 3/802. 2, Ethernet II Bridged PDUs and PPP protocol units for ADSL.
 LLC/SNAP Encapsulation A Brief overview
LLC/SNAP Encapsulation A Brief overview
 Payload format for routed ISO PDUS LLC 0 x. FE-FE-03 ISO PDUs • • • The routed/bridged PDUs are encapsulated in the IEEE 802. 2 LLC header. The value 0 x. FE-FE-03 indicates a routed ISO PDU. Routed ISO protocol is identified by one octet NLPID field which is a part of protocol data IP, though has a defined NLPID, should be encapsulated using SNAP. LLC Header is followed by a SNAP header for all non-ISO protocols and for bridged PDUs.
Payload format for routed ISO PDUS LLC 0 x. FE-FE-03 ISO PDUs • • • The routed/bridged PDUs are encapsulated in the IEEE 802. 2 LLC header. The value 0 x. FE-FE-03 indicates a routed ISO PDU. Routed ISO protocol is identified by one octet NLPID field which is a part of protocol data IP, though has a defined NLPID, should be encapsulated using SNAP. LLC Header is followed by a SNAP header for all non-ISO protocols and for bridged PDUs.
 SNAP Header OUI PID • The Value 0 x. AA-AA-03 in LLC header indicates the presence of a SNAP header. • OUI - Organizationally Unique Identifier ( 3 octets) identifies an organization which administers the protocol encapsulated. • PID - Protocol Identifier ( 2 octets) identifies the protocol encapsulated.
SNAP Header OUI PID • The Value 0 x. AA-AA-03 in LLC header indicates the presence of a SNAP header. • OUI - Organizationally Unique Identifier ( 3 octets) identifies an organization which administers the protocol encapsulated. • PID - Protocol Identifier ( 2 octets) identifies the protocol encapsulated.
 Payload format for Routed Non-ISO PDUs LLC 0 x. AA-AA-03 OUI Ether. Type (2 octets) Non-ISO PDU • The OUI Value 0 x 00 -00 -00 indicates that the following PID is an Ether. Type. • The Ether. Type value is 0 x 08 -00 for IP.
Payload format for Routed Non-ISO PDUs LLC 0 x. AA-AA-03 OUI Ether. Type (2 octets) Non-ISO PDU • The OUI Value 0 x 00 -00 -00 indicates that the following PID is an Ether. Type. • The Ether. Type value is 0 x 08 -00 for IP.
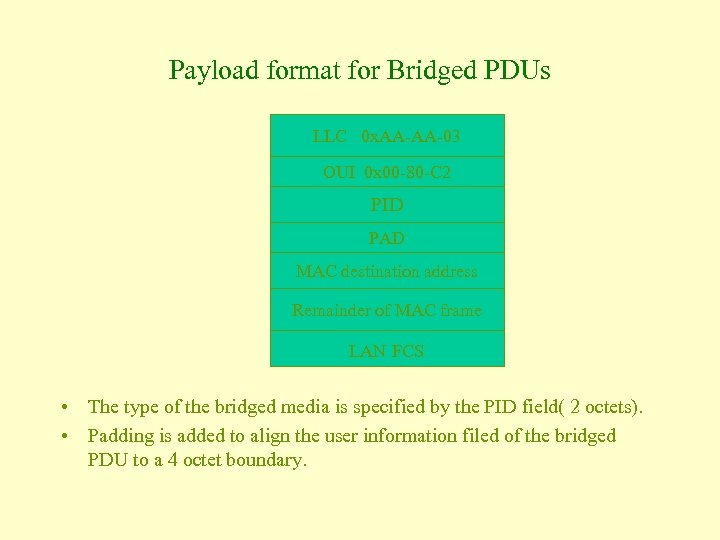 Payload format for Bridged PDUs LLC 0 x. AA-AA-03 OUI 0 x 00 -80 -C 2 PID PAD MAC destination address Remainder of MAC frame LAN FCS • The type of the bridged media is specified by the PID field( 2 octets). • Padding is added to align the user information filed of the bridged PDU to a 4 octet boundary.
Payload format for Bridged PDUs LLC 0 x. AA-AA-03 OUI 0 x 00 -80 -C 2 PID PAD MAC destination address Remainder of MAC frame LAN FCS • The type of the bridged media is specified by the PID field( 2 octets). • Padding is added to align the user information filed of the bridged PDU to a 4 octet boundary.
 VC Multiplexing • VC Multiplexing is an alternative approach to LLC/SNAP encapsulation. • VC Multiplexing is used when a large number of VCs could be dynamically created and used. • VC Multiplexing assigns a particular VC for a particular protocol and all PDUs of that protocol use the assigned VC. • VC multiplexing is preferred in a SVC environment and LLC/SNAP is used for PVCs.
VC Multiplexing • VC Multiplexing is an alternative approach to LLC/SNAP encapsulation. • VC Multiplexing is used when a large number of VCs could be dynamically created and used. • VC Multiplexing assigns a particular VC for a particular protocol and all PDUs of that protocol use the assigned VC. • VC multiplexing is preferred in a SVC environment and LLC/SNAP is used for PVCs.
 PPP over ATM over ADSL
PPP over ATM over ADSL
 PPP Over AAL 5 • Uses LLC/SNAP encapsulation for PPP PDUs. • The NLPID value is 0 x. CF for PPP. • The PPP PDU contains the PPP -Protocol Identifier followed by information and the padding.
PPP Over AAL 5 • Uses LLC/SNAP encapsulation for PPP PDUs. • The NLPID value is 0 x. CF for PPP. • The PPP PDU contains the PPP -Protocol Identifier followed by information and the padding.
 PPP - An Introduction
PPP - An Introduction
 Protocol summary • PPP -designed for simple links to transport packets between two peers. • PPP encapsulation provides for multiplexing of different network-layer protocols simultaneously over the same link. • PPP provides a Link Control Protocol (LCP) which negotiates the establishment and termination of a PPP link. • LCP also negotiates the options for encapsulation format, authentication and link quality monitoring. • The network layer protocols that are supported by the PPP link are managed by a family of network control protocols defined.
Protocol summary • PPP -designed for simple links to transport packets between two peers. • PPP encapsulation provides for multiplexing of different network-layer protocols simultaneously over the same link. • PPP provides a Link Control Protocol (LCP) which negotiates the establishment and termination of a PPP link. • LCP also negotiates the options for encapsulation format, authentication and link quality monitoring. • The network layer protocols that are supported by the PPP link are managed by a family of network control protocols defined.
 PPP Encapsulation Protocol Information (8/16 bits) Padding • The Protocol field identifies the datagram encapsulated in the information field. • Information filed contains the datagram and could be zero or more octets up to a Maximum Receive Unit (MRU). • The default MRU value is 1500 octets , though it could vary by negotiation. • The Information field may be padded up to the MRU number of octets.
PPP Encapsulation Protocol Information (8/16 bits) Padding • The Protocol field identifies the datagram encapsulated in the information field. • Information filed contains the datagram and could be zero or more octets up to a Maximum Receive Unit (MRU). • The default MRU value is 1500 octets , though it could vary by negotiation. • The Information field may be padded up to the MRU number of octets.
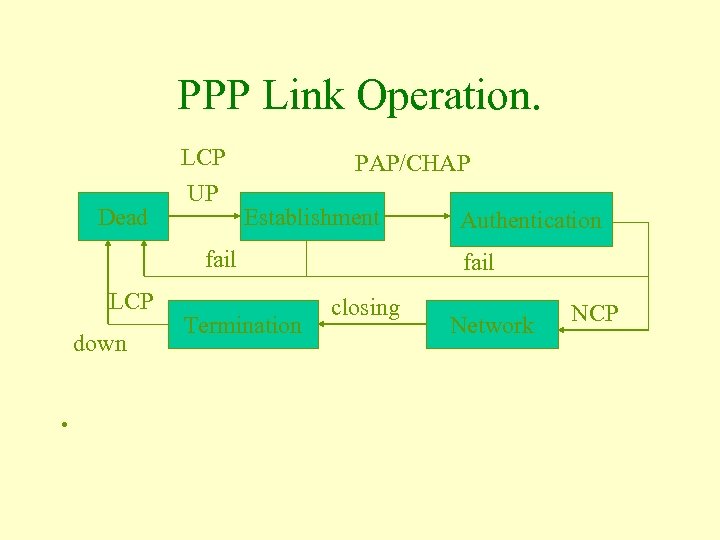 PPP Link Operation. Dead LCP UP PAP/CHAP Establishment fail LCP down • Termination Authentication fail closing Network NCP
PPP Link Operation. Dead LCP UP PAP/CHAP Establishment fail LCP down • Termination Authentication fail closing Network NCP
 Link Establishment • Link establishment phase uses the Link control protocol. • Link Configuration Options - the Maximum Receive Unit size. - Authentication and protocol to be used for authentication - Protocol Field Compression. - Link quality monitoring - Magic number option for detecting looped back links. - Address and Control field compression.
Link Establishment • Link establishment phase uses the Link control protocol. • Link Configuration Options - the Maximum Receive Unit size. - Authentication and protocol to be used for authentication - Protocol Field Compression. - Link quality monitoring - Magic number option for detecting looped back links. - Address and Control field compression.
 Link Establishment Process Configure request Peer Configure Ack/Nak Peer • The configure-request message is sent to request a link establishment and it contains the various options requested. • This request is responded with a Configure-Ack if the negotiation is accepted. • A Configure-Nak is sent if the negotiation is not acceptable and it suggests an acceptable negotiation.
Link Establishment Process Configure request Peer Configure Ack/Nak Peer • The configure-request message is sent to request a link establishment and it contains the various options requested. • This request is responded with a Configure-Ack if the negotiation is accepted. • A Configure-Nak is sent if the negotiation is not acceptable and it suggests an acceptable negotiation.
 Authentication • Authentication Option uses Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) or Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). • The protocol used depends on negotiation. • CHAP uses a one-way hashing algorithm which is known only to the user, to respond to a challenge sent by the authenticator. • CHAP is more secure than PAP.
Authentication • Authentication Option uses Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) or Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). • The protocol used depends on negotiation. • CHAP uses a one-way hashing algorithm which is known only to the user, to respond to a challenge sent by the authenticator. • CHAP is more secure than PAP.
 Magic Number • This option detects looped back links. • The magic number is a unique number chosen in the most random way possible. • This number enabled in a configure request is compared with the last request sent and if equal indicate a looped back link. • Link quality monitoring also uses this option to verify proper link communication.
Magic Number • This option detects looped back links. • The magic number is a unique number chosen in the most random way possible. • This number enabled in a configure request is compared with the last request sent and if equal indicate a looped back link. • Link quality monitoring also uses this option to verify proper link communication.
 PPP Over Ethernet A Brief Introduction.
PPP Over Ethernet A Brief Introduction.
 PPPo. E - How it works • PPPo. E - enables establishing PPP sessions and encapsulating PPP packets over Ethernet. • It has two distinct stages - A discovery stage and a Session stage. • The discovery stage identifies the Ethernet MAC address of the peer with which the PPP session is to be established. • The session stage gets a PPPo. E session ID for the PPP session and encapsulates PPP packets.
PPPo. E - How it works • PPPo. E - enables establishing PPP sessions and encapsulating PPP packets over Ethernet. • It has two distinct stages - A discovery stage and a Session stage. • The discovery stage identifies the Ethernet MAC address of the peer with which the PPP session is to be established. • The session stage gets a PPPo. E session ID for the PPP session and encapsulates PPP packets.
 Discovery stage • The discovery stage works similar to the ARP (Address resolution) request-response mechanism. • The host which is required to establish a PPP session broadcasts a session Initiation packet. • The Initiation packet is responded with offer packets from the Access Concentrators accepting the request. • The host follows with a unicast session request packet to a particular Access concentrator. • The Access concentrator replies with a confirmation and a session ID is obtained and the session established.
Discovery stage • The discovery stage works similar to the ARP (Address resolution) request-response mechanism. • The host which is required to establish a PPP session broadcasts a session Initiation packet. • The Initiation packet is responded with offer packets from the Access Concentrators accepting the request. • The host follows with a unicast session request packet to a particular Access concentrator. • The Access concentrator replies with a confirmation and a session ID is obtained and the session established.
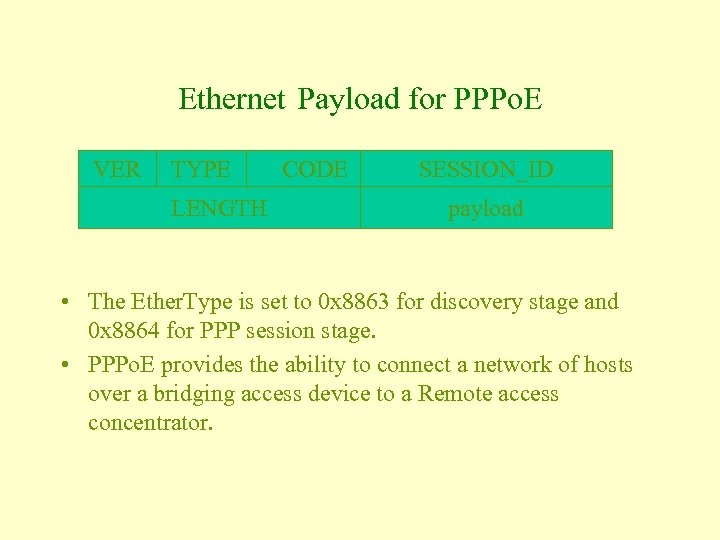 Ethernet Payload for PPPo. E VER TYPE LENGTH CODE SESSION_ID payload • The Ether. Type is set to 0 x 8863 for discovery stage and 0 x 8864 for PPP session stage. • PPPo. E provides the ability to connect a network of hosts over a bridging access device to a Remote access concentrator.
Ethernet Payload for PPPo. E VER TYPE LENGTH CODE SESSION_ID payload • The Ether. Type is set to 0 x 8863 for discovery stage and 0 x 8864 for PPP session stage. • PPPo. E provides the ability to connect a network of hosts over a bridging access device to a Remote access concentrator.
 Conclusion • ADSL is rapidly gaining widespread attention due to its low cost broadband access solution. • Various methods are developed to enable the mass deployment of ADSL systems. • With Qo. S metrics gaining more attention day by day, the impact of Qo. S implementations on the cost effectiveness of ADSL solutions is an interesting thought. • How the existing solutions adapt themselves to Qo. S metrics or how they should be modified will lead to interesting research.
Conclusion • ADSL is rapidly gaining widespread attention due to its low cost broadband access solution. • Various methods are developed to enable the mass deployment of ADSL systems. • With Qo. S metrics gaining more attention day by day, the impact of Qo. S implementations on the cost effectiveness of ADSL solutions is an interesting thought. • How the existing solutions adapt themselves to Qo. S metrics or how they should be modified will lead to interesting research.


