dd6346ce8e87b023c373364d13425c14.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88
 ADRs: Past, present and future And a trip down memory lane
ADRs: Past, present and future And a trip down memory lane
 Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) It’s all about drug safety (or an understanding of risk)
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) It’s all about drug safety (or an understanding of risk)
 RISK Something financial advisors ignore n Medicine is all about balancing benefits and risks n Particularly so for prescribing n ADRs remind us of risks n ADR awareness strengthens the balance n
RISK Something financial advisors ignore n Medicine is all about balancing benefits and risks n Particularly so for prescribing n ADRs remind us of risks n ADR awareness strengthens the balance n
 Overview n n n n The past: Woeful drug regulation and safety Some milestones ADRAC Pharmacovigilance ADR reporting International perspective/more on national reporting Some personal perspectives
Overview n n n n The past: Woeful drug regulation and safety Some milestones ADRAC Pharmacovigilance ADR reporting International perspective/more on national reporting Some personal perspectives
 The present: n Current concerns n Increasing prominence of pharmacovigilance n ACSOM/RMPs n IOM recommendations n n The future
The present: n Current concerns n Increasing prominence of pharmacovigilance n ACSOM/RMPs n IOM recommendations n n The future
 The beginning
The beginning
 Thalidomide n n n The only non-barbiturate sedative known in the late 1950’s “Completely safe, even during pregnancy” Developers “could not find a dose high enough to kill a rat” By 1960, thalidomide was marketed in 46 countries Australian obstetrician William Mc. Bride discovered it also alleviated morning sickness
Thalidomide n n n The only non-barbiturate sedative known in the late 1950’s “Completely safe, even during pregnancy” Developers “could not find a dose high enough to kill a rat” By 1960, thalidomide was marketed in 46 countries Australian obstetrician William Mc. Bride discovered it also alleviated morning sickness
 Not so safe He started recommending off-label use of the drug to his pregnant patients, setting a worldwide trend n In 1961, Mc. Bride began to associate thalidomide severe birth defects in the babies he delivered n Phocomelia, resulting in shortened, absent, or flipper-like limbs n
Not so safe He started recommending off-label use of the drug to his pregnant patients, setting a worldwide trend n In 1961, Mc. Bride began to associate thalidomide severe birth defects in the babies he delivered n Phocomelia, resulting in shortened, absent, or flipper-like limbs n
 The disaster Estimated 10, 000 babies born with phocomelia worldwide n by March 1962, the drug was banned in most countries n Identified gross deficiencies in drug regulation (both approval process and pharmacovigilance) n Catalyzed the beginnings of the rigorous drug approval and monitoring systems n
The disaster Estimated 10, 000 babies born with phocomelia worldwide n by March 1962, the drug was banned in most countries n Identified gross deficiencies in drug regulation (both approval process and pharmacovigilance) n Catalyzed the beginnings of the rigorous drug approval and monitoring systems n
 Not in the USA n n n FDA decision to hold the approval of thalidomide was not because of the birth defects but because of concerns about peripheral neuropathy Dr Frances Kelsey of the U. S. FDA, was recognized by President John F. Kennedy as a recipient of the Gold Medal Award for Distinguished Civilian Service
Not in the USA n n n FDA decision to hold the approval of thalidomide was not because of the birth defects but because of concerns about peripheral neuropathy Dr Frances Kelsey of the U. S. FDA, was recognized by President John F. Kennedy as a recipient of the Gold Medal Award for Distinguished Civilian Service

 Analgesic nephropathy n n n Consequence of daily use for many years of mixtures containing at least two antipyretic analgesics and usually caffeine or codeine (or both) Characterized by renal papillary necrosis and chronic interstitial nephritis Insidious progression to renal failure In Australia 25% of cases of end-stage renal failure due to analgesic nephropathy in the early 1970 s Virtually eliminated by control of the ingredients of and numbers of analgesics available OTC
Analgesic nephropathy n n n Consequence of daily use for many years of mixtures containing at least two antipyretic analgesics and usually caffeine or codeine (or both) Characterized by renal papillary necrosis and chronic interstitial nephritis Insidious progression to renal failure In Australia 25% of cases of end-stage renal failure due to analgesic nephropathy in the early 1970 s Virtually eliminated by control of the ingredients of and numbers of analgesics available OTC
 An Australian Epidemic n n n Powerful advertising encouraged frequent use In the 1950’s it was common practice for housewives to purchase a gross (144) powders of aspirin, phenacetin and caffeine (APC) with the weekly groceries Autopsy prevalence of renal papillary necrosis was 21. 4%, much higher than that in other countries Between 1959 and 1961 Kincaid Smith “did several hundred autopsies” in patients with papillary necrosis Presented her data at Prague in 1963 and “I was absolutely howled down by the European pathologists. They said it’s a lot of rubbish”
An Australian Epidemic n n n Powerful advertising encouraged frequent use In the 1950’s it was common practice for housewives to purchase a gross (144) powders of aspirin, phenacetin and caffeine (APC) with the weekly groceries Autopsy prevalence of renal papillary necrosis was 21. 4%, much higher than that in other countries Between 1959 and 1961 Kincaid Smith “did several hundred autopsies” in patients with papillary necrosis Presented her data at Prague in 1963 and “I was absolutely howled down by the European pathologists. They said it’s a lot of rubbish”
 Benoxaprofen (1980) More than 2, 000 arthritis patients were administered the drug in premarketing n In 1980 the drug was released for marketing in the UK n Heavily promoted and widely used n 61 deaths (hepatitis) in the UK, most in elderly people n Marketing suspended August 1982 n
Benoxaprofen (1980) More than 2, 000 arthritis patients were administered the drug in premarketing n In 1980 the drug was released for marketing in the UK n Heavily promoted and widely used n 61 deaths (hepatitis) in the UK, most in elderly people n Marketing suspended August 1982 n



 Chinese herb nephropathy Rapidly progressive interstitial nephropathy n Reported after the introduction of Chinese herbs in a slimming regimen for young Belgian women n Interstitial fibrosis associated with tubular atrophy and global sclerosis of glomeruli n Urothelial malignancy of the upper urinary tract develops subsequently in almost half of the patients n
Chinese herb nephropathy Rapidly progressive interstitial nephropathy n Reported after the introduction of Chinese herbs in a slimming regimen for young Belgian women n Interstitial fibrosis associated with tubular atrophy and global sclerosis of glomeruli n Urothelial malignancy of the upper urinary tract develops subsequently in almost half of the patients n
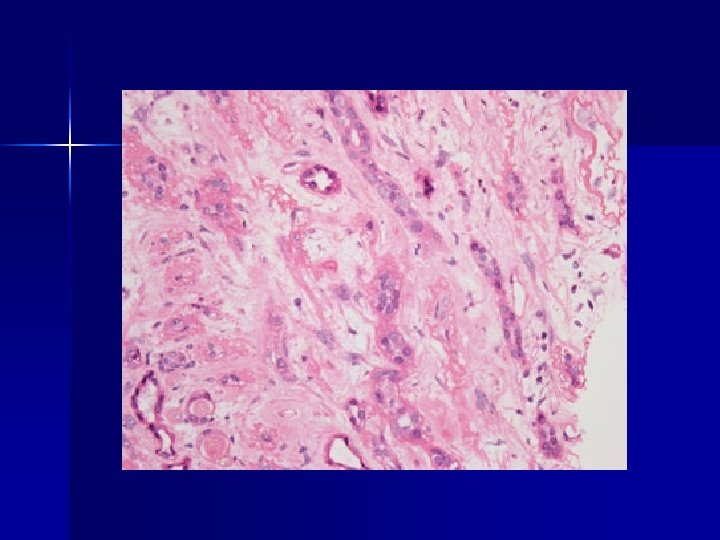
 Herbal hell n n In the 1990 s >100 Belgian women took Chinese herbs as part of a weight loss regimen and developed ESRF Almost all progressed to dialysis, transplantation or malignancy Due to nephrotoxic and carcinogenic aristolochic acid extracted from species of Aristolochia Stephania tetrandra (‘Han Fang-ji’), was inadvertently substituted by Aristolochia fangchi
Herbal hell n n In the 1990 s >100 Belgian women took Chinese herbs as part of a weight loss regimen and developed ESRF Almost all progressed to dialysis, transplantation or malignancy Due to nephrotoxic and carcinogenic aristolochic acid extracted from species of Aristolochia Stephania tetrandra (‘Han Fang-ji’), was inadvertently substituted by Aristolochia fangchi
 A recent Australian case n Nephropathy associated with use of a Chinese herbal product containing aristolochic acid. Med J Aust 2011; 194 (7): 367 -368.
A recent Australian case n Nephropathy associated with use of a Chinese herbal product containing aristolochic acid. Med J Aust 2011; 194 (7): 367 -368.
 n The past was punctuated by protracted periods before identification n Has pharmacovigilance resulted in quicker identification and action?
n The past was punctuated by protracted periods before identification n Has pharmacovigilance resulted in quicker identification and action?
 Lumiracoxib (2007) International launch July 2005 n 100 mg daily approved for OA in > 50 countries, including EU, Canada, Latin America. n 200 mg dose registered by TGA April 2004 n PBS funded (200 mg) August 2006 n Estimated 60, 000 patients treated in Australia n
Lumiracoxib (2007) International launch July 2005 n 100 mg daily approved for OA in > 50 countries, including EU, Canada, Latin America. n 200 mg dose registered by TGA April 2004 n PBS funded (200 mg) August 2006 n Estimated 60, 000 patients treated in Australia n
 Lumiracoxib ADRAC reports May 2007 report of fatal hepatic toxicity in association with lumiracoxib. n Another report of liver failure within weeks n From mid-June to 9 August a further 6 reports of liver failure n Two cases from PAH (one transplanted, one fatal) n
Lumiracoxib ADRAC reports May 2007 report of fatal hepatic toxicity in association with lumiracoxib. n Another report of liver failure within weeks n From mid-June to 9 August a further 6 reports of liver failure n Two cases from PAH (one transplanted, one fatal) n
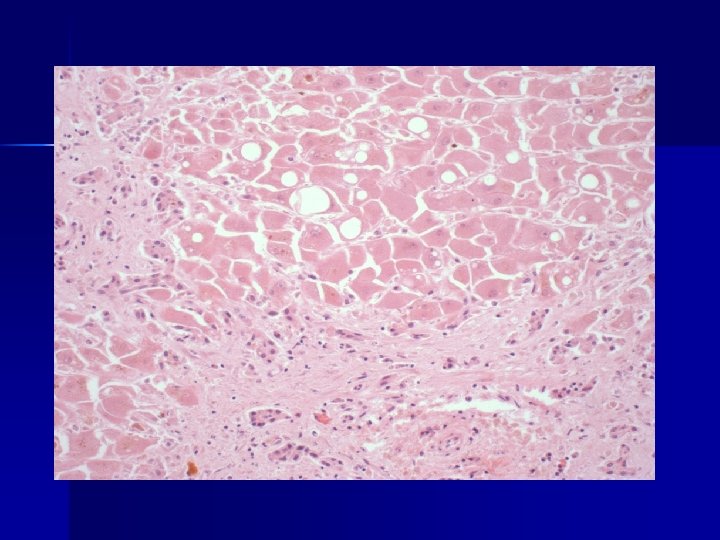
 Priority review conducted by ADRAC on 10 August 2007 n All involved women > 50 years n None had pre-existing liver disease n None had obvious risk factors for liver disease n Onset typically after a few months n Typically associated with doses ≥ 200 mg/day n
Priority review conducted by ADRAC on 10 August 2007 n All involved women > 50 years n None had pre-existing liver disease n None had obvious risk factors for liver disease n Onset typically after a few months n Typically associated with doses ≥ 200 mg/day n
 Serious liver toxicity and other NSAIDS Lumiracoxib 8 (4. 8%) All ADR reports 167 n Celecoxib 15 (0. 38%). 3957 ADR reports n Diclofenac 7 (0. 26%). All reports 1924 n Ibuprofen 6 (0. 61%). All reports 980 n Meloxicam 5 (1. 1%). All reports 454 n Naproxen 3 (0. 21%). All reports 1442 n
Serious liver toxicity and other NSAIDS Lumiracoxib 8 (4. 8%) All ADR reports 167 n Celecoxib 15 (0. 38%). 3957 ADR reports n Diclofenac 7 (0. 26%). All reports 1924 n Ibuprofen 6 (0. 61%). All reports 980 n Meloxicam 5 (1. 1%). All reports 454 n Naproxen 3 (0. 21%). All reports 1442 n

 Reports since Deregistration 4 reports of severe liver injury/liver failure n 11 further reports of hepatitis/abnormal LFT n Total reports: n 11 severe n 15 hepatitis/abnormal LFTs n
Reports since Deregistration 4 reports of severe liver injury/liver failure n 11 further reports of hepatitis/abnormal LFT n Total reports: n 11 severe n 15 hepatitis/abnormal LFTs n
 Detection of ADRs: pharmacovigilance The science related to the detection, assessment, and prevention of ADRs n An observational science to identify and investigate unexpected clinical events after a new drug is in use n Primary function is to evaluate and improve the safety of marketed medicines n
Detection of ADRs: pharmacovigilance The science related to the detection, assessment, and prevention of ADRs n An observational science to identify and investigate unexpected clinical events after a new drug is in use n Primary function is to evaluate and improve the safety of marketed medicines n
 Data derived from many sources n n n Published case reports Spontaneous ADR reports Post-marketing clinical and epidemiological studies Morbidity and mortality databases Prescription event monitoring schemes
Data derived from many sources n n n Published case reports Spontaneous ADR reports Post-marketing clinical and epidemiological studies Morbidity and mortality databases Prescription event monitoring schemes
 The evidence A hierarchy of evidence from n case reports (the lowest level) n through observational studies n to clinical trials and meta-analysis n
The evidence A hierarchy of evidence from n case reports (the lowest level) n through observational studies n to clinical trials and meta-analysis n
 (Voluntary) Reporting n n n n Remains the cornerstone of PMS Has reached a high level of sophistication internationally Limitations are well known: poor quality of some reports significant under-reporting difficulty in calculating rates because of incomplete numerator data along with unreliable denominators limited ability to establish cause and effect
(Voluntary) Reporting n n n n Remains the cornerstone of PMS Has reached a high level of sophistication internationally Limitations are well known: poor quality of some reports significant under-reporting difficulty in calculating rates because of incomplete numerator data along with unreliable denominators limited ability to establish cause and effect
 Limitations n n n Under-reporting can lead to long delays between marketing and detection and regulatory action of an ADR Almost 7 million patients were exposed to fenfluramine before the association with valvular heart disease led to withdrawal from the market Spontaneous reporting systems played no part in the identification of the rofecoxib CV signal (high background incidence of MI in patients with multiple risk factors)
Limitations n n n Under-reporting can lead to long delays between marketing and detection and regulatory action of an ADR Almost 7 million patients were exposed to fenfluramine before the association with valvular heart disease led to withdrawal from the market Spontaneous reporting systems played no part in the identification of the rofecoxib CV signal (high background incidence of MI in patients with multiple risk factors)
 Is there still a role for spontaneous reporting? n n Responsible for the identification of numerous safety signals ADR reporting emphasises the importance of drug safety issues to those involved May detect reactions that might otherwise go unrecorded, because it entails suspicions that clinicians consider potentially important And the reports allow for a qualitative description
Is there still a role for spontaneous reporting? n n Responsible for the identification of numerous safety signals ADR reporting emphasises the importance of drug safety issues to those involved May detect reactions that might otherwise go unrecorded, because it entails suspicions that clinicians consider potentially important And the reports allow for a qualitative description
 A real strength of spontaneous reporting systems Establishment of large national databases n The central repository exposes clusters of like reports n Alerts to a possible signal n Having our own database enables detection of ADRs unique to the country (eg mianserin, lumiracoxib) n
A real strength of spontaneous reporting systems Establishment of large national databases n The central repository exposes clusters of like reports n Alerts to a possible signal n Having our own database enables detection of ADRs unique to the country (eg mianserin, lumiracoxib) n
 Actively soliciting reports Most reporting systems rely on passive data collection n In the UK, reports are actively solicited through the Prescription Event Monitoring system, n Surveys prescribers regarding any adverse experiences among the first 10, 000 patients given a drug n
Actively soliciting reports Most reporting systems rely on passive data collection n In the UK, reports are actively solicited through the Prescription Event Monitoring system, n Surveys prescribers regarding any adverse experiences among the first 10, 000 patients given a drug n
 NZ IMMP The New Zealand Intensive Medicines Monitoring Programme has been in operation for >30 years n Methodology based on establishing cohorts of about 10, 000 patients monitored for a mean of almost 5 years n Collect all adverse events from a combination of prescription follow-up and intensified spontaneous reporting n
NZ IMMP The New Zealand Intensive Medicines Monitoring Programme has been in operation for >30 years n Methodology based on establishing cohorts of about 10, 000 patients monitored for a mean of almost 5 years n Collect all adverse events from a combination of prescription follow-up and intensified spontaneous reporting n
 Fluoxetine and hyponatraemia. Pillans P, Coulter DM. NZ Med J 1994; 107: 86 -7 n Cohort of 5628 patients (3539 female) n 7 patients, 68 -88 years, all female n 3 on thiazides long term n Na 114 -128 n 5 within 19 days of commencement n Reported rate 8. 5/1000 n Recovery after withdrawal in all
Fluoxetine and hyponatraemia. Pillans P, Coulter DM. NZ Med J 1994; 107: 86 -7 n Cohort of 5628 patients (3539 female) n 7 patients, 68 -88 years, all female n 3 on thiazides long term n Na 114 -128 n 5 within 19 days of commencement n Reported rate 8. 5/1000 n Recovery after withdrawal in all
 Fluoxetine hyponatraemia conclusion Significant incidence (1/100) in the elderly n Onset typically in first few weeks n Advisable to monitor electrolytes during first month n Diuretics increase risk n (Unable to confirm SIADH due to limited data) n
Fluoxetine hyponatraemia conclusion Significant incidence (1/100) in the elderly n Onset typically in first few weeks n Advisable to monitor electrolytes during first month n Diuretics increase risk n (Unable to confirm SIADH due to limited data) n
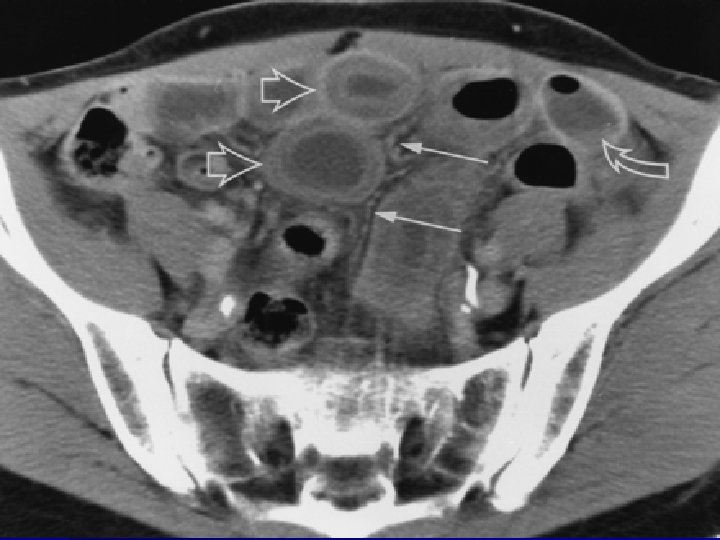
 Angioedema and urticaria with ACE inhibitors. Pillans P, Coulter D, Black. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1996: 51, 123 -6 Captopril, enalapril and lisinopril intensively monitored n Cohorts totalled 53, 263 patients n 63 reports n Reported rate 1. 2/1000 n 47 late onset (3 weeks-4 years) n No deaths n
Angioedema and urticaria with ACE inhibitors. Pillans P, Coulter D, Black. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1996: 51, 123 -6 Captopril, enalapril and lisinopril intensively monitored n Cohorts totalled 53, 263 patients n 63 reports n Reported rate 1. 2/1000 n 47 late onset (3 weeks-4 years) n No deaths n
 ACEI angioedema Severe in 9 with early-onset n Severe in 6 with late onset n 17 patients had up to 12 episodes before diagnosis n May be long symptom free intervals between attacks n 3 associated with an increase in dose n Angioedema may occur with or without urticaria n
ACEI angioedema Severe in 9 with early-onset n Severe in 6 with late onset n 17 patients had up to 12 episodes before diagnosis n May be long symptom free intervals between attacks n 3 associated with an increase in dose n Angioedema may occur with or without urticaria n
 Data mining The WHO, FDA and some government agencies also use statistical methods of data mining to help discern which combinations of drugs and adverse events in their database suggest a causal link n Data mining can trigger additional analysis of individual cases or population-based studies. n
Data mining The WHO, FDA and some government agencies also use statistical methods of data mining to help discern which combinations of drugs and adverse events in their database suggest a causal link n Data mining can trigger additional analysis of individual cases or population-based studies. n
 International perspective n n Bring all the relevant evidence (reports) together in one place WHO international spontaneous reporting database in Sweden PSURs by pharmaceutical companies provide global safety updates, but the emphasis has been on fulfilment of regulatory requirements, rather than the need to gather better evidence of safety
International perspective n n Bring all the relevant evidence (reports) together in one place WHO international spontaneous reporting database in Sweden PSURs by pharmaceutical companies provide global safety updates, but the emphasis has been on fulfilment of regulatory requirements, rather than the need to gather better evidence of safety
 National ADR monitoring schemes n n Many countries have their own spontaneous reporting systems Large databases have been developed which are clearly national assets The Australian and NZ schemes have played important roles internationally Rapport with healthcare professionals and a reporting mindset have been built up over >40 years
National ADR monitoring schemes n n Many countries have their own spontaneous reporting systems Large databases have been developed which are clearly national assets The Australian and NZ schemes have played important roles internationally Rapport with healthcare professionals and a reporting mindset have been built up over >40 years
 ADR data provide a sound foundation for regulatory and educational activities, n as well as a valuable resource for research n Advisory Committees, such as ADRAC, now ACSOM, are an essential component n
ADR data provide a sound foundation for regulatory and educational activities, n as well as a valuable resource for research n Advisory Committees, such as ADRAC, now ACSOM, are an essential component n
 The past-ADRAC n n n ADRAC’s inception May 1970 Tasked to advise TGA on safety of medicines As with the MARC in NZ, helped to build 2 of the best pharmacovigilance systems in the world Role fundamental for advising and reporting on all matters relating to safety of medicines Helped to identify safety concerns and advise on remedial action
The past-ADRAC n n n ADRAC’s inception May 1970 Tasked to advise TGA on safety of medicines As with the MARC in NZ, helped to build 2 of the best pharmacovigilance systems in the world Role fundamental for advising and reporting on all matters relating to safety of medicines Helped to identify safety concerns and advise on remedial action
 MARC/ADRAC Garth Mc. Queen founded NZ CARM in the late 1960’s n Followed by Ralph Edwards (who became Director of WHO center in Sweden n David Coulter founded the IMMP n John Mc. Ewen one of key players in Australia n
MARC/ADRAC Garth Mc. Queen founded NZ CARM in the late 1960’s n Followed by Ralph Edwards (who became Director of WHO center in Sweden n David Coulter founded the IMMP n John Mc. Ewen one of key players in Australia n
 ADRAC/TGA >300, 000 reports in the database n ± 12, 000 ADR reports per year n Founding member of WHO International Drug Monitoring n Australian system has contributed to early recognition of many ADRs n n n helped to define the nature of the adverse reaction in question, and assist in further research
ADRAC/TGA >300, 000 reports in the database n ± 12, 000 ADR reports per year n Founding member of WHO International Drug Monitoring n Australian system has contributed to early recognition of many ADRs n n n helped to define the nature of the adverse reaction in question, and assist in further research
 Example 1 The factors involved in flucloxacillininduced hepatitis n delayed onset, n cholestatic pattern n and delayed recovery n arose from Australian reports n
Example 1 The factors involved in flucloxacillininduced hepatitis n delayed onset, n cholestatic pattern n and delayed recovery n arose from Australian reports n
 Example 2 The large number and detail of ADRAC reports of amoxicillin/clavulanate induced hepatitis n established that many cases have a delayed onset and cholestatic pattern n
Example 2 The large number and detail of ADRAC reports of amoxicillin/clavulanate induced hepatitis n established that many cases have a delayed onset and cholestatic pattern n
 ACSOM n n n Inception 2010 as a statutory expert committee Encompasses ADRAC’s activities, including current collection of spontaneous ADRs, but broader terms of reference A major role is to advise the TGA on the quality and appropriateness of RMPs are designed to characterise and proactively manage drug risks Recommendations can be a condition of recommendation
ACSOM n n n Inception 2010 as a statutory expert committee Encompasses ADRAC’s activities, including current collection of spontaneous ADRs, but broader terms of reference A major role is to advise the TGA on the quality and appropriateness of RMPs are designed to characterise and proactively manage drug risks Recommendations can be a condition of recommendation
 Australian reports contributing to early recognition n n n n Cerivastatin and rhabdomyolysis “Triple Whammy” Tiaprofenic acid and cystitis Mianserin and agranulocytosis Pergolide and cardiac valvulopathy Atypical antipsychotics and hyperglycaemia Leflunomide and pancytopenia and pneumonitis Ticlopidine and TTP
Australian reports contributing to early recognition n n n n Cerivastatin and rhabdomyolysis “Triple Whammy” Tiaprofenic acid and cystitis Mianserin and agranulocytosis Pergolide and cardiac valvulopathy Atypical antipsychotics and hyperglycaemia Leflunomide and pancytopenia and pneumonitis Ticlopidine and TTP
 Early recognition Isotretinoin and depression n Alendronate and oesophageal ulceration n Vigabatrin and visual field defects n Clozapine, olanzapine and NMS n SSRIs and withdrawal reactions n Cisapride and QT prolongation/torsade n Clozapine and myocarditis n Fluoroquinolones and Achilles tendinitis n
Early recognition Isotretinoin and depression n Alendronate and oesophageal ulceration n Vigabatrin and visual field defects n Clozapine, olanzapine and NMS n SSRIs and withdrawal reactions n Cisapride and QT prolongation/torsade n Clozapine and myocarditis n Fluoroquinolones and Achilles tendinitis n
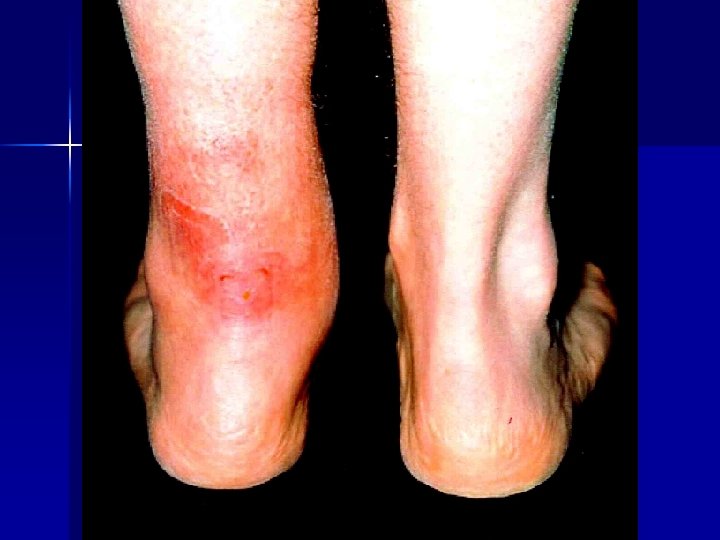
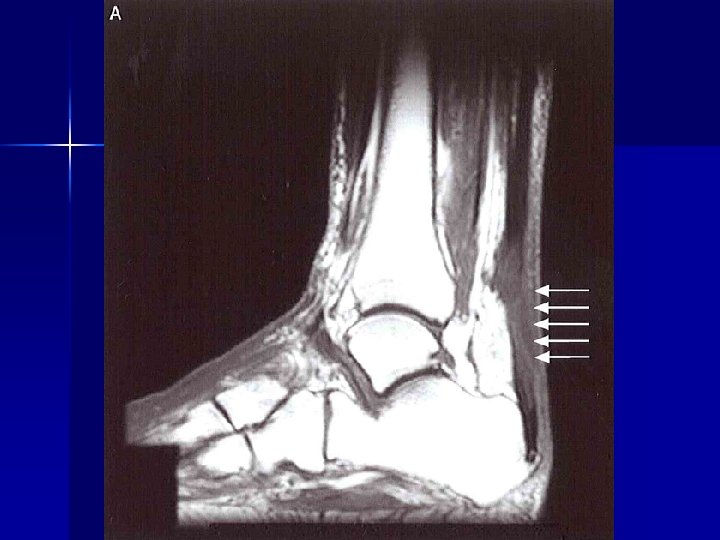
 ADRAC Bulletin The major vehicle for dissemination of information n Including alerting heath professionals to important safety issues n Sent to all practitioners in the country n Now replaced by the TGA’s Medicines Safety Update (included in Australian Prescriber) n
ADRAC Bulletin The major vehicle for dissemination of information n Including alerting heath professionals to important safety issues n Sent to all practitioners in the country n Now replaced by the TGA’s Medicines Safety Update (included in Australian Prescriber) n

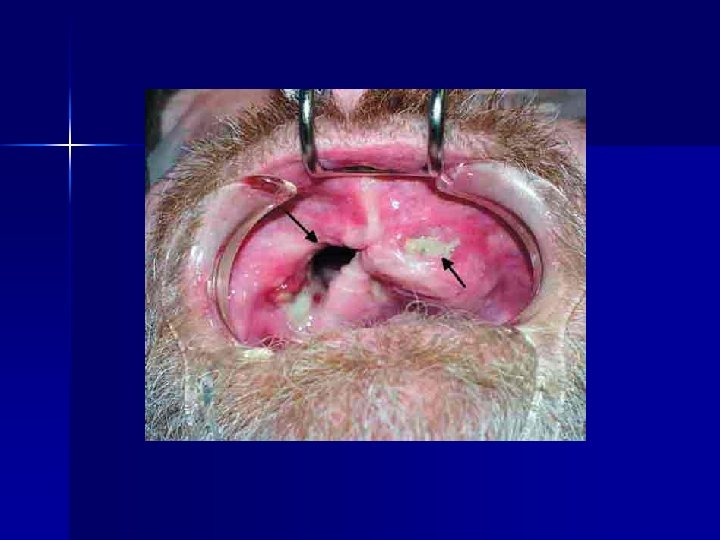
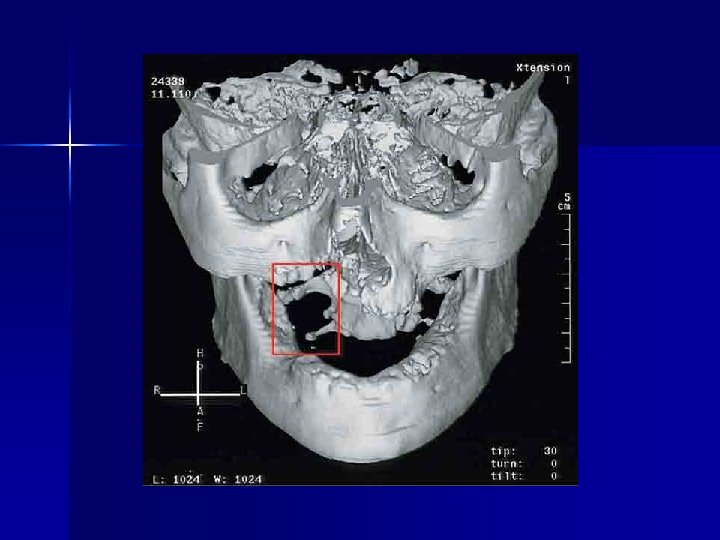

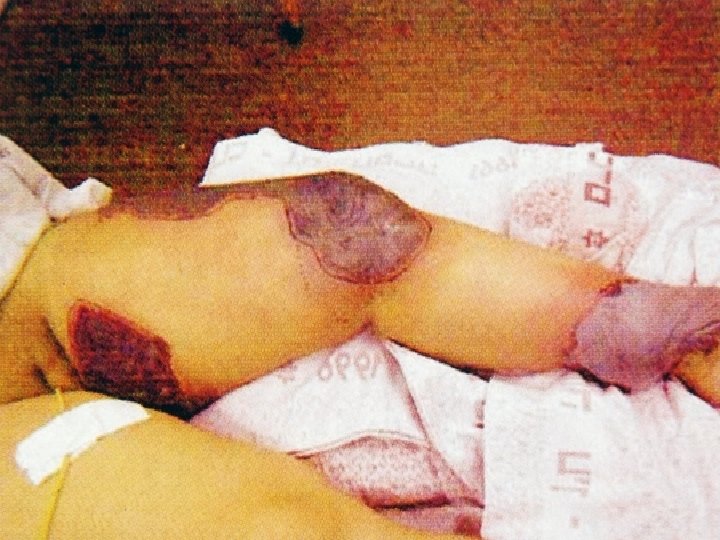
 Some personal perspectives n n n n An interesting component of clinical pharmacology Opportunities to publish Ketoconazole and hyponatraemia (Lancet 1985) Roxithromycin and hepatitis (Drug Safety 1993) Clozapine and myocarditis (1994) Interaction between miconazole oral gel and warfarin (NZ Med J 1996) Paroxetine withdrawal reactions (1997)
Some personal perspectives n n n n An interesting component of clinical pharmacology Opportunities to publish Ketoconazole and hyponatraemia (Lancet 1985) Roxithromycin and hepatitis (Drug Safety 1993) Clozapine and myocarditis (1994) Interaction between miconazole oral gel and warfarin (NZ Med J 1996) Paroxetine withdrawal reactions (1997)
 Chan J, Pillans PI. Leflunomide associated pancytopenia with or without methotrexate. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2004; 38: 1206 -11 5 cases at PAH n 18 cases reported to ADRAC (5 fatal) n Management: n Folinic acid rescue (MTX toxicity) n Cholestyramine (leflunomide toxicity) n G-CSF (neutropenia) n
Chan J, Pillans PI. Leflunomide associated pancytopenia with or without methotrexate. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2004; 38: 1206 -11 5 cases at PAH n 18 cases reported to ADRAC (5 fatal) n Management: n Folinic acid rescue (MTX toxicity) n Cholestyramine (leflunomide toxicity) n G-CSF (neutropenia) n
 HIT: Sturtevant JM, Pillans P, Mackenzie F, Gibbs H. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: recent experience in a large teaching hospital. Int Med J 2006; 36: 431 -436 n n Increasing frequency (and request for HIT screens) 22 cases over 5 years (all on UFH) Thrombosis in 14 of 22 Mean time to HIT screen 14 days
HIT: Sturtevant JM, Pillans P, Mackenzie F, Gibbs H. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: recent experience in a large teaching hospital. Int Med J 2006; 36: 431 -436 n n Increasing frequency (and request for HIT screens) 22 cases over 5 years (all on UFH) Thrombosis in 14 of 22 Mean time to HIT screen 14 days
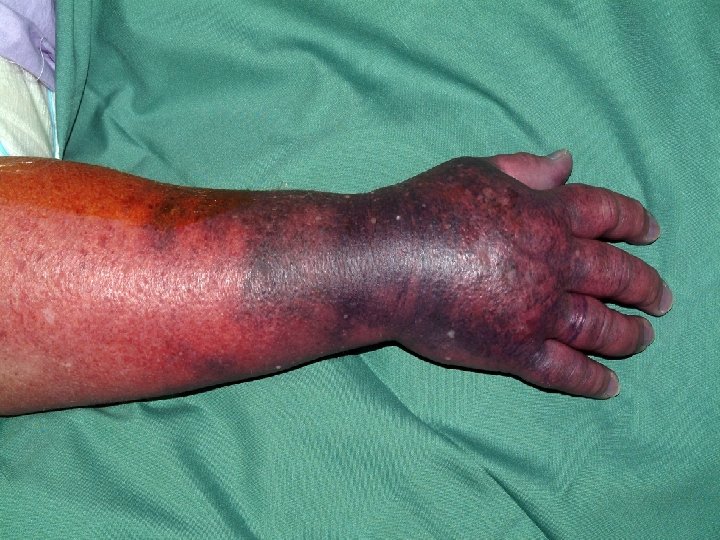
 Chan J, Pillans PI. Leflunomide associated pancytopenia with or without methotrexate. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2004; 38: 1206 -11 5 cases at PAH n 18 cases reported to ADRAC (5 fatal) n Management: n Folinic acid rescue (MTX toxicity) n Cholestyramine (leflunomide toxicity) n G-CSF (neutropenia) n
Chan J, Pillans PI. Leflunomide associated pancytopenia with or without methotrexate. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2004; 38: 1206 -11 5 cases at PAH n 18 cases reported to ADRAC (5 fatal) n Management: n Folinic acid rescue (MTX toxicity) n Cholestyramine (leflunomide toxicity) n G-CSF (neutropenia) n
 The role of the Clinical Pharmacologist An important part of QUM n Strengthen reporting in your hospital n Drug safety education (students, residents, registrars, grand rounds) n Pharmacovigilance research n Publishing n Membership of national committees (MARC, ACSOM) n
The role of the Clinical Pharmacologist An important part of QUM n Strengthen reporting in your hospital n Drug safety education (students, residents, registrars, grand rounds) n Pharmacovigilance research n Publishing n Membership of national committees (MARC, ACSOM) n
 Drug safety-the present Public concern about drug safety n Recalls of high-profile drugs n n Clinical trials and PMS often fail to uncover important ADRs n Criticism of drug regulatory agencies (particularly FDA)
Drug safety-the present Public concern about drug safety n Recalls of high-profile drugs n n Clinical trials and PMS often fail to uncover important ADRs n Criticism of drug regulatory agencies (particularly FDA)
 The present-International Issues n Recommendations to overhaul drug safety monitoring and ensure greater patient protection n Increasing prominence of pharmacovigilance worldwide n Comprehensive review of drug-safety system conducted by Institute of Medicine (IOM)
The present-International Issues n Recommendations to overhaul drug safety monitoring and ensure greater patient protection n Increasing prominence of pharmacovigilance worldwide n Comprehensive review of drug-safety system conducted by Institute of Medicine (IOM)
 Current limitations Speed versus safety n Tight pre-approval regulation vs loose post approval regulation n Active data collection pre-approval vs passive post-approval n Abundance of clinical efficacy data pre-approval vs much less safety data post approval n
Current limitations Speed versus safety n Tight pre-approval regulation vs loose post approval regulation n Active data collection pre-approval vs passive post-approval n Abundance of clinical efficacy data pre-approval vs much less safety data post approval n
 More limitations Most resources allocated to premarketing evaluation n No systematic approach of identifying safety signals and translating into post -marketing studies n No authority to force sponsors to complete post-marketing commitments n No resources to conduct studies in house n
More limitations Most resources allocated to premarketing evaluation n No systematic approach of identifying safety signals and translating into post -marketing studies n No authority to force sponsors to complete post-marketing commitments n No resources to conduct studies in house n
 IOM Recommendations Improved monitoring of drug safety n Shift surveillance from passive/reactive to active/proactive n Take advantage of large databases n Identify safety signals and translate them into high quality studies n Additional resources n New regulatory powers n
IOM Recommendations Improved monitoring of drug safety n Shift surveillance from passive/reactive to active/proactive n Take advantage of large databases n Identify safety signals and translate them into high quality studies n Additional resources n New regulatory powers n
 IOM recommendations n n Period of conditional approval ( ± 2 years) Clear caveat in datasheet: “Drug approval is conditional – this drug has only been studied in a limited number of patients” Moratorium on marketing/advertising during this period Will increase individuals exposed from ± 3000 to 30, 000 – 300, 000
IOM recommendations n n Period of conditional approval ( ± 2 years) Clear caveat in datasheet: “Drug approval is conditional – this drug has only been studied in a limited number of patients” Moratorium on marketing/advertising during this period Will increase individuals exposed from ± 3000 to 30, 000 – 300, 000
 3 Full approval dependent on completion of post-marketing studies, addressing safety issues n Review of risk-benefit status of new drugs after 5 years n New culture of safety where risks and benefits are examined during the entire market life n
3 Full approval dependent on completion of post-marketing studies, addressing safety issues n Review of risk-benefit status of new drugs after 5 years n New culture of safety where risks and benefits are examined during the entire market life n
 The future Build on the present scheme n and assess all available information about the performance of medicines, n Carefully planned post-marketing studies (RMPs) n Regular, systematic and ongoing evaluation using linked observational data n
The future Build on the present scheme n and assess all available information about the performance of medicines, n Carefully planned post-marketing studies (RMPs) n Regular, systematic and ongoing evaluation using linked observational data n
 n n n Establish pharmacoepidemiology data analysis centres Controlled epidemiological studies: observational methods for detecting and quantifying the frequency of adverse drug effects Utilise automated data bases
n n n Establish pharmacoepidemiology data analysis centres Controlled epidemiological studies: observational methods for detecting and quantifying the frequency of adverse drug effects Utilise automated data bases
 UK General Practice Research Database Population coverage >3 million n Collects truly population-based data n Follow up large cohorts of users of specific drugs n Includes both outpatient and inpatient clinical information n
UK General Practice Research Database Population coverage >3 million n Collects truly population-based data n Follow up large cohorts of users of specific drugs n Includes both outpatient and inpatient clinical information n
 Observational health care data can describe the vast majority of healthcare encounters n including doctor visits n medicine dispensing n hospital admissions n deaths n and various disease registries n
Observational health care data can describe the vast majority of healthcare encounters n including doctor visits n medicine dispensing n hospital admissions n deaths n and various disease registries n
 The ultimate aim should be the development of a complete population database n with well-documented exposures to medicines, n outcomes, n and potential risk n
The ultimate aim should be the development of a complete population database n with well-documented exposures to medicines, n outcomes, n and potential risk n
 The future: prevention n n Genetic variation in drug metabolism is a potentially preventable cause of ADRs Use genetic information to individualise drug therapy (pharmacogenomics) Many drugs are metabolised by at least one enzyme with a variant allele known to cause poor metabolism Drug therapy based on an individuals’ genetic make-up may result in a clinically important reduction in ADRs
The future: prevention n n Genetic variation in drug metabolism is a potentially preventable cause of ADRs Use genetic information to individualise drug therapy (pharmacogenomics) Many drugs are metabolised by at least one enzyme with a variant allele known to cause poor metabolism Drug therapy based on an individuals’ genetic make-up may result in a clinically important reduction in ADRs
 ANZTPA 20 June 2011, PMs of Aus an NZ agreed to proceed with a joint scheme for drug regulation n Formation of the Australian NZ Therapeutics Products Agency (ANZTPA) n Plan to include a monitoring communication scheme for products new to the market n
ANZTPA 20 June 2011, PMs of Aus an NZ agreed to proceed with a joint scheme for drug regulation n Formation of the Australian NZ Therapeutics Products Agency (ANZTPA) n Plan to include a monitoring communication scheme for products new to the market n
 Early Warning System Plan to establish a trans-Tasman early warning system n Will advise public of potential safety concerns n Trialled by Medsafe: can stimulate more reports n Lack of reports suggests no signal n
Early Warning System Plan to establish a trans-Tasman early warning system n Will advise public of potential safety concerns n Trialled by Medsafe: can stimulate more reports n Lack of reports suggests no signal n
 Key points ADRs are common n Can mimic almost any disease n Some are preventable n Many are not n Spontaneous reporting remains the cornerstone n Reporting is a professional responsibility n
Key points ADRs are common n Can mimic almost any disease n Some are preventable n Many are not n Spontaneous reporting remains the cornerstone n Reporting is a professional responsibility n
 Key points 2 n n Despite advances in pharmacovigilance, Postmarketing surveillance remains the weakest link in the regulatory process Risk management plans (RMPs) are now essential As is post-marketing, systematic ongoing evaluation
Key points 2 n n Despite advances in pharmacovigilance, Postmarketing surveillance remains the weakest link in the regulatory process Risk management plans (RMPs) are now essential As is post-marketing, systematic ongoing evaluation
 Key points 3 n n n Approach should shift from passive/reactive to active/proactive There are still major challenges to satisfy consumer expectations and realise the benefits of the technological age Remember the risks!
Key points 3 n n n Approach should shift from passive/reactive to active/proactive There are still major challenges to satisfy consumer expectations and realise the benefits of the technological age Remember the risks!



