9231fb34c94b69f46d48b903c80c94a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 ADMINISTRATIVE ENGLISH
ADMINISTRATIVE ENGLISH
 ELECTION
ELECTION
 1. DIFFERENT KINDS OF ELECTION general election – choosing a national parliament local election – choosing a local council
1. DIFFERENT KINDS OF ELECTION general election – choosing a national parliament local election – choosing a local council
 by-election – choosing a new Member of Parliament (when the previous member has resigned or died) referendum – voting on whether to do something or not a referendum on abortion
by-election – choosing a new Member of Parliament (when the previous member has resigned or died) referendum – voting on whether to do something or not a referendum on abortion
 2. PEOPLE WHO WANT TO BE ELECTED candidate stand for / run for - kandydować She’s decided to stand for the European Parliament. He’s running for president.
2. PEOPLE WHO WANT TO BE ELECTED candidate stand for / run for - kandydować She’s decided to stand for the European Parliament. He’s running for president.
 campaign manifesto - ? ? ? slogan
campaign manifesto - ? ? ? slogan
 SOME FAMOUS POLITICAL SLOGANS Yes we can. 2008 U. S. presidential campaign slogan of Barack Obama 2012 ? ? ?
SOME FAMOUS POLITICAL SLOGANS Yes we can. 2008 U. S. presidential campaign slogan of Barack Obama 2012 ? ? ?
 Liberte, Egalite, Fraternite The national motto of France with its origins in the French Revolution
Liberte, Egalite, Fraternite The national motto of France with its origins in the French Revolution
 Workers of the world, unite! A communist slogan from Karl Marx’s „Communist Manifesto”
Workers of the world, unite! A communist slogan from Karl Marx’s „Communist Manifesto”
 Nothing about us without us. Think global, act local.
Nothing about us without us. Think global, act local.
 3. THE PROCESS OF ELECTING vote for /against – głosować za /przeciw a vote – głos voter – wyborca
3. THE PROCESS OF ELECTING vote for /against – głosować za /przeciw a vote – głos voter – wyborca
 the electorate – all the people in a country who have the right to vote in an election constitutency - okręg wyborczy
the electorate – all the people in a country who have the right to vote in an election constitutency - okręg wyborczy
 polling station – lokal wyborczy ballot paper – karta do głosowania ballot box - ? ? ?
polling station – lokal wyborczy ballot paper – karta do głosowania ballot box - ? ? ?
 4. THE RESULT OF AN ELECTION count the votes – liczyć głosy elect – ? ? ? re-elect - ? ? ? get in / into - wejść do His ambition is to get into Parliament.
4. THE RESULT OF AN ELECTION count the votes – liczyć głosy elect – ? ? ? re-elect - ? ? ? get in / into - wejść do His ambition is to get into Parliament.
 5. TYPES OF ELECTORAL SYSTEMS first-past-the-post „pierwszy na mecie”, ordynacja większościowa, dotyczy okręgów jednomandatowych used in: Great Britain, Australia, the USA, Canada, Japan Poland ? ? ?
5. TYPES OF ELECTORAL SYSTEMS first-past-the-post „pierwszy na mecie”, ordynacja większościowa, dotyczy okręgów jednomandatowych used in: Great Britain, Australia, the USA, Canada, Japan Poland ? ? ?
 Poland – since 2011 in election to/of: Ø the Senate, Ø the President of Poland, Ø presidents/mayors of towns, heads of communes (prezydenci/burmistrzowie miast, wójtowie),
Poland – since 2011 in election to/of: Ø the Senate, Ø the President of Poland, Ø presidents/mayors of towns, heads of communes (prezydenci/burmistrzowie miast, wójtowie),
 Ø town councils of non-urban districts (without district rights) rad gmin w gminach nie będących miastami na prawie powiatu (tzw. powiatów grodzkich).
Ø town councils of non-urban districts (without district rights) rad gmin w gminach nie będących miastami na prawie powiatu (tzw. powiatów grodzkich).
 proportional representation ordynacja proporcjonalna Poland – party lists, 5 % threshold
proportional representation ordynacja proporcjonalna Poland – party lists, 5 % threshold
 PARLIAMENT
PARLIAMENT
 1. PARLIAMENTS AND THEIR MEMBERS What is a parliament? q a group of people who discuss and make the laws of a country, q the place where they meet
1. PARLIAMENTS AND THEIR MEMBERS What is a parliament? q a group of people who discuss and make the laws of a country, q the place where they meet
 different countries parliament congress the National Assembly diet different names
different countries parliament congress the National Assembly diet different names
 Which countries do these parliaments come from? Bundestag Knesset Althing – the oldest (930 AD) Saeima Paremata Aotearoa Shura
Which countries do these parliaments come from? Bundestag Knesset Althing – the oldest (930 AD) Saeima Paremata Aotearoa Shura
 Many parliaments consist of two parts: v v a lower house an upper house
Many parliaments consist of two parts: v v a lower house an upper house
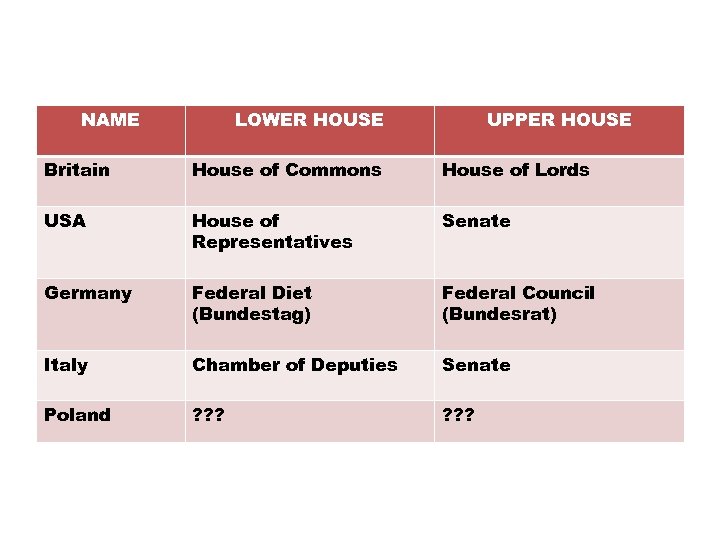 NAME LOWER HOUSE UPPER HOUSE Britain House of Commons House of Lords USA House of Representatives Senate Germany Federal Diet (Bundestag) Federal Council (Bundesrat) Italy Chamber of Deputies Senate Poland ? ? ?
NAME LOWER HOUSE UPPER HOUSE Britain House of Commons House of Lords USA House of Representatives Senate Germany Federal Diet (Bundestag) Federal Council (Bundesrat) Italy Chamber of Deputies Senate Poland ? ? ?
 Member of Parliament (MP) – a person elected to Parliament Member of the European Parliament (MEP)
Member of Parliament (MP) – a person elected to Parliament Member of the European Parliament (MEP)
 Speaker – the person who controls business in parliament seat – a place in parliament won in an election (miejsce, mandat)
Speaker – the person who controls business in parliament seat – a place in parliament won in an election (miejsce, mandat)
 WORKING IN PARLIAMENT sitting – a meeting of parliament an all-night sitting ? ? ? - a series of meetings ? ? ? - formal discussion
WORKING IN PARLIAMENT sitting – a meeting of parliament an all-night sitting ? ? ? - a series of meetings ? ? ? - formal discussion
 legislate – to make a law (uchwalać ustawę) ? ? ? – ustawodawstwo
legislate – to make a law (uchwalać ustawę) ? ? ? – ustawodawstwo
 bill – a plan for a possible new law (projekt ustawy) act – ustawa the 2004 Act on Elections to the European Parliament
bill – a plan for a possible new law (projekt ustawy) act – ustawa the 2004 Act on Elections to the European Parliament
 HOMEWORK
HOMEWORK
 Political promises Political parties often make promises in their election manifestos. Match the verbs and the endings:
Political promises Political parties often make promises in their election manifestos. Match the verbs and the endings:
 We are going to … o o o build create protect reduce, fight reduce, cut provide • crime, unemployment • more houses, schools, hospitals, roads • more jobs • the environment • better education, health care • taxes
We are going to … o o o build create protect reduce, fight reduce, cut provide • crime, unemployment • more houses, schools, hospitals, roads • more jobs • the environment • better education, health care • taxes


