a0e15388eacc7355cdb6ee72356f9de9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 Administering the Kindergarten ACCESS for ELLs ® and MODEL™ Presenter, Affiliation Date © 2011 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, on behalf of the WIDA Consortium www. wida. us
Administering the Kindergarten ACCESS for ELLs ® and MODEL™ Presenter, Affiliation Date © 2011 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, on behalf of the WIDA Consortium www. wida. us
 SECURE & CONFIDENTIAL DO NOT POST THESE MATERIALS TO PUBLIC WEBSITES OR FORUMS. Contains secure and confidential information. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 2
SECURE & CONFIDENTIAL DO NOT POST THESE MATERIALS TO PUBLIC WEBSITES OR FORUMS. Contains secure and confidential information. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 2
 Training Objectives To train test administrators to administer the Kindergarten ACCESS for ELLs and WIDA MODEL for Kindergarten Tests. To understand the organization, layout, and scripting of the tests. To learn the procedures for administering and reliably scoring the tests. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 3
Training Objectives To train test administrators to administer the Kindergarten ACCESS for ELLs and WIDA MODEL for Kindergarten Tests. To understand the organization, layout, and scripting of the tests. To learn the procedures for administering and reliably scoring the tests. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 3
 Purpose of the Kindergarten Tests Assesses students’ academic English language proficiency. Academic language is the vocabulary, grammatical structures and discourse required in learning the academic content of school subjects; aspects of language strongly associated with literacy development and achievement. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 4
Purpose of the Kindergarten Tests Assesses students’ academic English language proficiency. Academic language is the vocabulary, grammatical structures and discourse required in learning the academic content of school subjects; aspects of language strongly associated with literacy development and achievement. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 4
 Orientation to the Pre. K-K ELP Standards WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 5
Orientation to the Pre. K-K ELP Standards WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 5
 The WIDA ELP Standards Standard 1 – Social & Instructional Language (SIL) English language learners communicate for social and instructional purposes in the school setting. Standard 2 – Language of Language Arts (Lo. LA) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Language Arts. Standard 3 – Language of Mathematics (Lo. MA) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Math. Standard 4 – Language of Science (Lo. SC) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Science. Standard 5 – Language of Social Studies (Lo. SS) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Social Studies. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 6
The WIDA ELP Standards Standard 1 – Social & Instructional Language (SIL) English language learners communicate for social and instructional purposes in the school setting. Standard 2 – Language of Language Arts (Lo. LA) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Language Arts. Standard 3 – Language of Mathematics (Lo. MA) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Math. Standard 4 – Language of Science (Lo. SC) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Science. Standard 5 – Language of Social Studies (Lo. SS) English language learners communicate information, ideas and concepts necessary for academic success in the content area of Social Studies. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 6
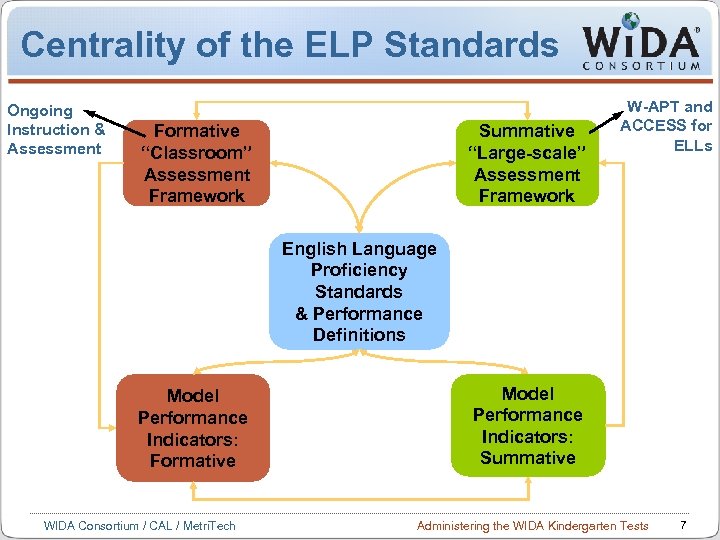 Centrality of the ELP Standards Ongoing Instruction & Assessment Formative “Classroom” Assessment Framework Summative “Large-scale” Assessment Framework W-APT and ACCESS for ELLs English Language Proficiency Standards & Performance Definitions Model Performance Indicators: Formative WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Model Performance Indicators: Summative Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 7
Centrality of the ELP Standards Ongoing Instruction & Assessment Formative “Classroom” Assessment Framework Summative “Large-scale” Assessment Framework W-APT and ACCESS for ELLs English Language Proficiency Standards & Performance Definitions Model Performance Indicators: Formative WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Model Performance Indicators: Summative Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 7
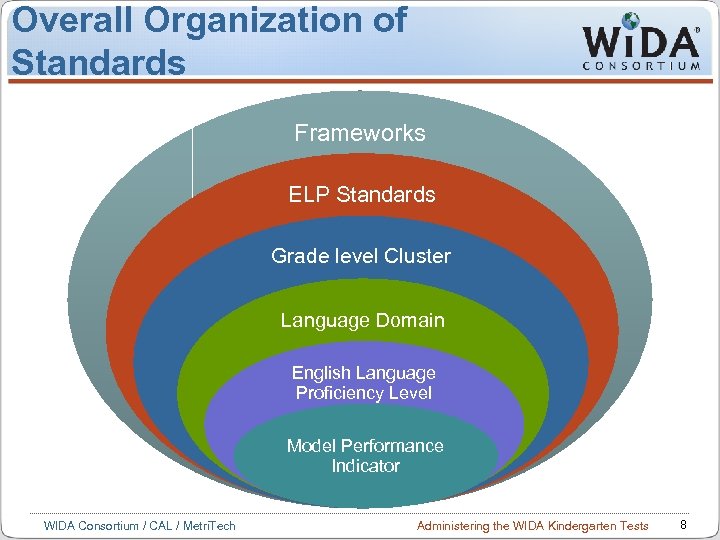 Overall Organization of Standards Frameworks ELP Standards Grade level Cluster Grade Level Clusters (5) Language Domain English Language Proficiency Level Model Performance Indicator WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 8
Overall Organization of Standards Frameworks ELP Standards Grade level Cluster Grade Level Clusters (5) Language Domain English Language Proficiency Level Model Performance Indicator WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 8
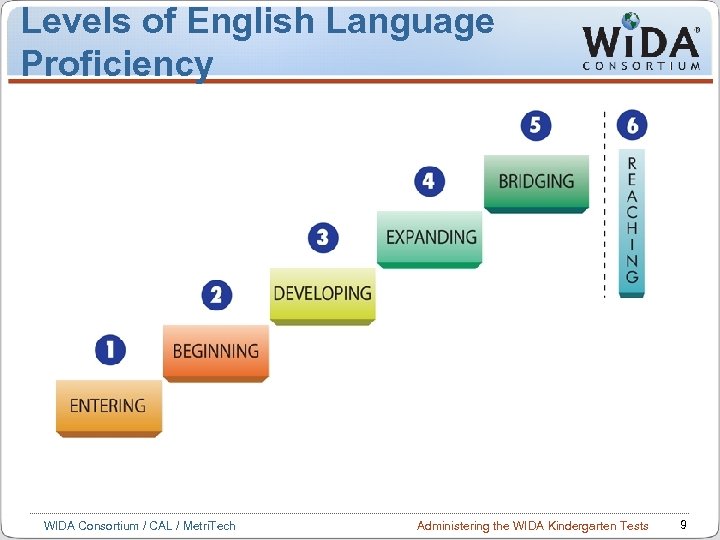 Levels of English Language Proficiency WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 9
Levels of English Language Proficiency WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 9
 Criteria for Performance Definitions Linguistic Complexity: Expectations of the quantity and organization of the student’s verbal response Vocabulary Usage: Expectations of the student’s use of appropriate vocabulary for grade level and proficiency level; refers to language quality Language Control: Expectations of the student’s control of English grammar, word choice in context, and the English sound system; refers to language quality WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 10
Criteria for Performance Definitions Linguistic Complexity: Expectations of the quantity and organization of the student’s verbal response Vocabulary Usage: Expectations of the student’s use of appropriate vocabulary for grade level and proficiency level; refers to language quality Language Control: Expectations of the student’s control of English grammar, word choice in context, and the English sound system; refers to language quality WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 10
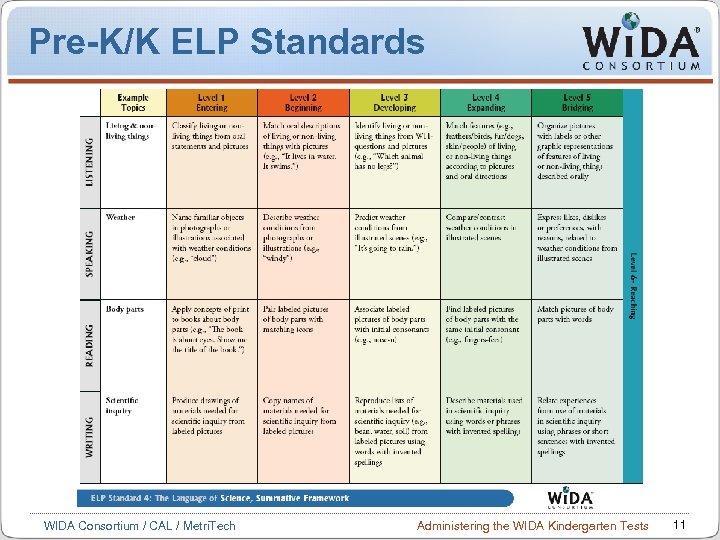 Pre-K/K ELP Standards WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 11
Pre-K/K ELP Standards WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 11
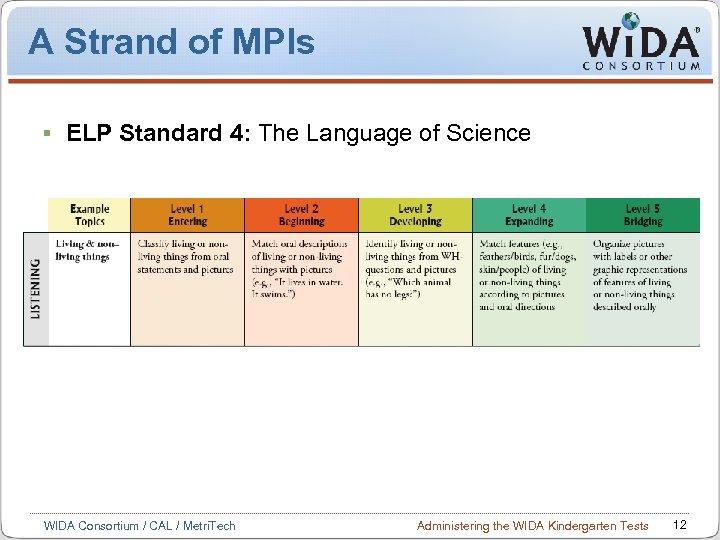 A Strand of MPIs ELP Standard 4: The Language of Science WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 12
A Strand of MPIs ELP Standard 4: The Language of Science WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 12
 MPI WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 13
MPI WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 13
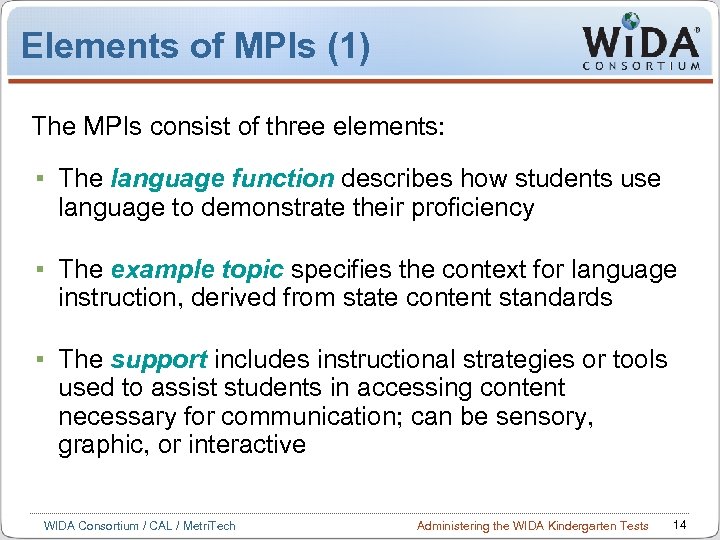 Elements of MPIs (1) The MPIs consist of three elements: The language function describes how students use language to demonstrate their proficiency The example topic specifies the context for language instruction, derived from state content standards The support includes instructional strategies or tools used to assist students in accessing content necessary for communication; can be sensory, graphic, or interactive WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 14
Elements of MPIs (1) The MPIs consist of three elements: The language function describes how students use language to demonstrate their proficiency The example topic specifies the context for language instruction, derived from state content standards The support includes instructional strategies or tools used to assist students in accessing content necessary for communication; can be sensory, graphic, or interactive WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 14
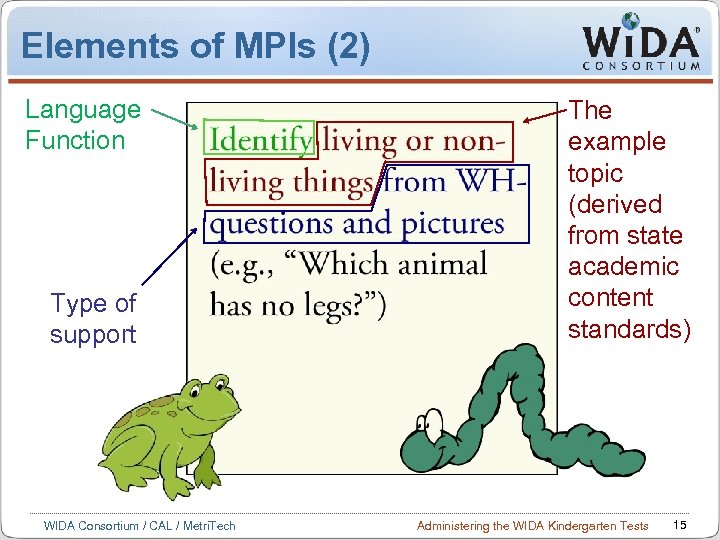 Elements of MPIs (2) Language Function Type of support WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech The example topic (derived from state academic content standards) Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 15
Elements of MPIs (2) Language Function Type of support WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech The example topic (derived from state academic content standards) Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 15
 Kindergarten Test Design and Administration WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 16
Kindergarten Test Design and Administration WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 16
 Kindergarten Test Design Aligned to Pre. K-K Standards The test is thematically integrated within two stories: A narrative story An expository story All domains (listening, speaking, reading, writing) are tested within each story. All domains are individually administered and adaptive so the student will start sections at appropriate levels and stop at his or her “ceiling. ” All components are scored by the Test Administrator (TA) during test administration. In its entirety, the test takes an average of 45 minutes. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 17
Kindergarten Test Design Aligned to Pre. K-K Standards The test is thematically integrated within two stories: A narrative story An expository story All domains (listening, speaking, reading, writing) are tested within each story. All domains are individually administered and adaptive so the student will start sections at appropriate levels and stop at his or her “ceiling. ” All components are scored by the Test Administrator (TA) during test administration. In its entirety, the test takes an average of 45 minutes. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 17
 Unique Features of the Tests Manipulatives Cards Student Activity Board Thematic Test questions center around two themes. All four domains are tested in each theme. Interactive Writing Experience The student has an opportunity to produce whatever he/she is able. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 18
Unique Features of the Tests Manipulatives Cards Student Activity Board Thematic Test questions center around two themes. All four domains are tested in each theme. Interactive Writing Experience The student has an opportunity to produce whatever he/she is able. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 18
 Narrative vs. Expository Narrative: Appropriate graphics Main characters are animals Description Rhyme, Rhythm Reminiscent of quality children’s literature 3 rd person Fictional WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Expository: Time sequence Non-fiction Involves "doing“ or “how to” Realistic or believable actions with people as main characters Story sequence between steps, logical organization Relate to events in student’s life Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 19
Narrative vs. Expository Narrative: Appropriate graphics Main characters are animals Description Rhyme, Rhythm Reminiscent of quality children’s literature 3 rd person Fictional WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Expository: Time sequence Non-fiction Involves "doing“ or “how to” Realistic or believable actions with people as main characters Story sequence between steps, logical organization Relate to events in student’s life Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 19
 Sample Theme Folder Cards Theme Graphic Items WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 20
Sample Theme Folder Cards Theme Graphic Items WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 20
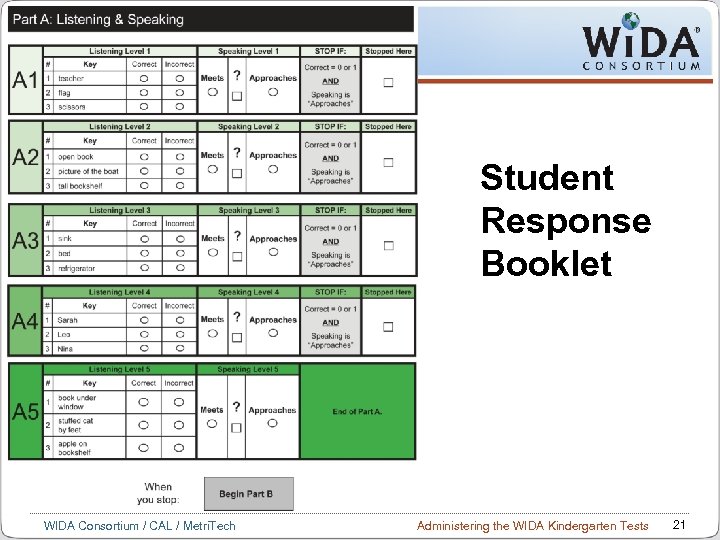 Student Response Booklet WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 21
Student Response Booklet WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 21
 Test Structure The test administrator (TA) reads the Narrative storybook, then administers: A. Listening & Speaking Tests (together) B. Writing Experience C. Reading Test The TA will then administer the following sections using the Expository activity board and cards: D. Listening & Speaking Tests (together) E. Writing Experience (starting point is based on Writing Experience score from Part B) F. Reading Test (starting point based on Reading score from Part C) WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 22
Test Structure The test administrator (TA) reads the Narrative storybook, then administers: A. Listening & Speaking Tests (together) B. Writing Experience C. Reading Test The TA will then administer the following sections using the Expository activity board and cards: D. Listening & Speaking Tests (together) E. Writing Experience (starting point is based on Writing Experience score from Part B) F. Reading Test (starting point based on Reading score from Part C) WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 22
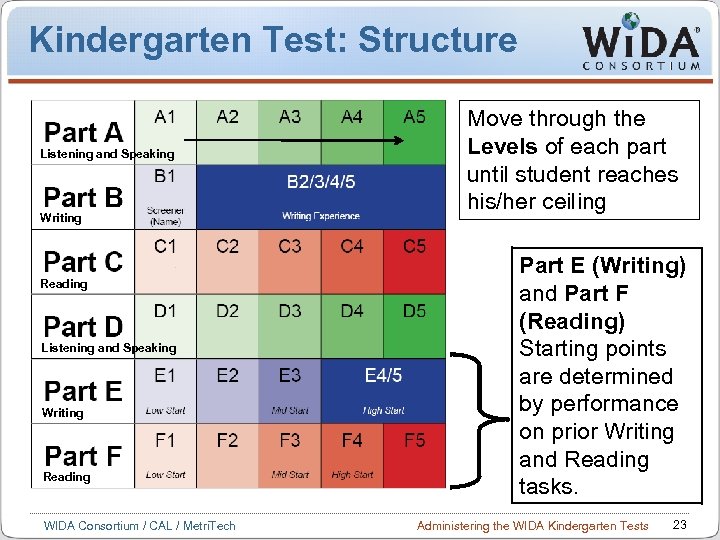 Kindergarten Test: Structure Listening and Speaking Writing Reading WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Move through the Levels of each part until student reaches his/her ceiling Part E (Writing) and Part F (Reading) Starting points are determined by performance on prior Writing and Reading tasks. Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 23
Kindergarten Test: Structure Listening and Speaking Writing Reading WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Move through the Levels of each part until student reaches his/her ceiling Part E (Writing) and Part F (Reading) Starting points are determined by performance on prior Writing and Reading tasks. Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 23
 Testing Materials (1 of 2) The Kindergarten Student Story Booklet contains: Pictures and story for the Narrative section of the test (resembling authentic children’s literature) Graphic organizers related to designated sections of the test Student Story Booklet Kindergarten Student Response Booklet contains: Answer key for Listening & Reading items Space to record and tally student responses Criteria for moving on/winding down Student writing and teacher transcription of student writing WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Student Response Booklet Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 24
Testing Materials (1 of 2) The Kindergarten Student Story Booklet contains: Pictures and story for the Narrative section of the test (resembling authentic children’s literature) Graphic organizers related to designated sections of the test Student Story Booklet Kindergarten Student Response Booklet contains: Answer key for Listening & Reading items Space to record and tally student responses Criteria for moving on/winding down Student writing and teacher transcription of student writing WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Student Response Booklet Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 24
 Testing Materials (2 of 2) Kindergarten Test Administrator Script contains: Moving on/winding down script Expect boxes to assist with scoring students’ speaking responses Kindergarten Student Activity Board Kindergarten Cards & Card Pouch Booklet Cards and Card Pouch Booklet WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Test Administrator Script Student Activity Board Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 25
Testing Materials (2 of 2) Kindergarten Test Administrator Script contains: Moving on/winding down script Expect boxes to assist with scoring students’ speaking responses Kindergarten Student Activity Board Kindergarten Cards & Card Pouch Booklet Cards and Card Pouch Booklet WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Test Administrator Script Student Activity Board Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 25
 General Test Administration Procedures Follow the script EXACTLY. Read aloud everything in black bold and blue bold print. Student responses must be recorded and scored IMMEDIATELY after each level is complete (e. g. after A 3). You must administer and score all items in any one level of a Part before making a determination about whether to continue to the next level or to stop that Part. Kindergarteners may need breaks during the test administration. Stretch breaks may be taken between each section of the test (e. g. after Listening/Speaking, before Writing) The test may be administered in two sessions with a break of no more than 2 school days between Parts C (Narrative) & D (Expository) WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 26
General Test Administration Procedures Follow the script EXACTLY. Read aloud everything in black bold and blue bold print. Student responses must be recorded and scored IMMEDIATELY after each level is complete (e. g. after A 3). You must administer and score all items in any one level of a Part before making a determination about whether to continue to the next level or to stop that Part. Kindergarteners may need breaks during the test administration. Stretch breaks may be taken between each section of the test (e. g. after Listening/Speaking, before Writing) The test may be administered in two sessions with a break of no more than 2 school days between Parts C (Narrative) & D (Expository) WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 26
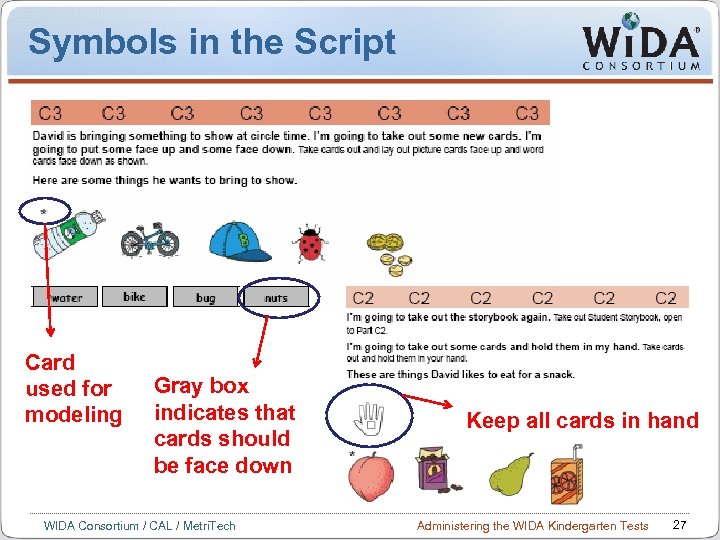 Symbols in the Script Card used for modeling Gray box indicates that cards should be face down WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Keep all cards in hand Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 27
Symbols in the Script Card used for modeling Gray box indicates that cards should be face down WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Keep all cards in hand Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 27
 Preparing for Test Administration Familiarize yourself with the Test Administrator Script for each portion of the Kindergarten Test prior to administering the test. It is recommended to practice with a colleague before you administer to a student. You will need 2 sharpened pencils: one for you and one for the student. Testing should occur in a quiet room. Administer the test to the student using rectangular (preferable) or circular table. Place yourself at a right angle to the student, rather than across from or next to the student. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 28
Preparing for Test Administration Familiarize yourself with the Test Administrator Script for each portion of the Kindergarten Test prior to administering the test. It is recommended to practice with a colleague before you administer to a student. You will need 2 sharpened pencils: one for you and one for the student. Testing should occur in a quiet room. Administer the test to the student using rectangular (preferable) or circular table. Place yourself at a right angle to the student, rather than across from or next to the student. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 28
 About Accommodations Remember, test accommodations are only available to students with disabilities (IEP or 504 Plan in place). Accommodations can vary by state, so check with your state department for list of approved accommodations. The Test Administration Manual contains definitions to explain how to use the accommodations, and coding information for the accommodations section. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 29
About Accommodations Remember, test accommodations are only available to students with disabilities (IEP or 504 Plan in place). Accommodations can vary by state, so check with your state department for list of approved accommodations. The Test Administration Manual contains definitions to explain how to use the accommodations, and coding information for the accommodations section. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 29
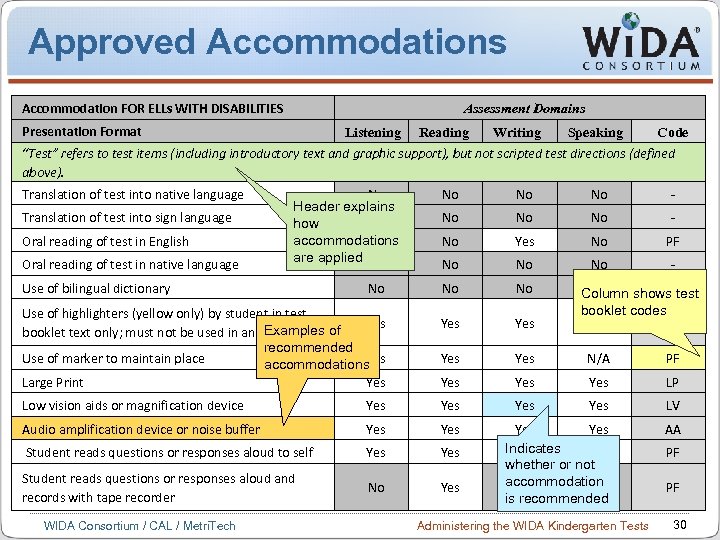 Approved Accommodations Accommodation FOR ELLs WITH DISABILITIES Assessment Domains Presentation Format Listening Reading Writing Speaking Code “Test” refers to test items (including introductory text and graphic support), but not scripted test directions (defined above). Translation of test into native language Translation of test into sign language Oral reading of test in English Oral reading of test in native language No Header explains No how accommodations No are applied No Use of bilingual dictionary No Use of highlighters (yellow only) by student in test Yes Examples booklet text only; must not be used in answer area of recommended Use of marker to maintain place Yes accommodations Large Print Yes No No No - No Yes No PF No No No - No No Yes Yes N/A PF Yes Yes LP Yes LV Yes Indicates Yes N/A whether or not accommodation No No is recommended AA Low vision aids or magnification device Yes Audio amplification device or noise buffer Yes Student reads questions or responses aloud to self Yes Student reads questions or responses aloud and records with tape recorder No Yes WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech No Column shows- test booklet codes N/A - Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests PF PF 30
Approved Accommodations Accommodation FOR ELLs WITH DISABILITIES Assessment Domains Presentation Format Listening Reading Writing Speaking Code “Test” refers to test items (including introductory text and graphic support), but not scripted test directions (defined above). Translation of test into native language Translation of test into sign language Oral reading of test in English Oral reading of test in native language No Header explains No how accommodations No are applied No Use of bilingual dictionary No Use of highlighters (yellow only) by student in test Yes Examples booklet text only; must not be used in answer area of recommended Use of marker to maintain place Yes accommodations Large Print Yes No No No - No Yes No PF No No No - No No Yes Yes N/A PF Yes Yes LP Yes LV Yes Indicates Yes N/A whether or not accommodation No No is recommended AA Low vision aids or magnification device Yes Audio amplification device or noise buffer Yes Student reads questions or responses aloud to self Yes Student reads questions or responses aloud and records with tape recorder No Yes WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech No Column shows- test booklet codes N/A - Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests PF PF 30
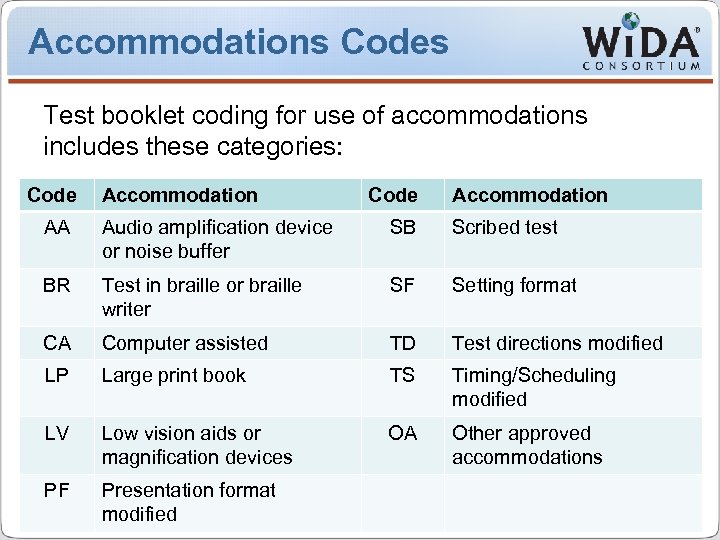 Accommodations Codes Test booklet coding for use of accommodations includes these categories: Code Accommodation AA Audio amplification device or noise buffer SB Scribed test BR Test in braille or braille writer SF Setting format CA Computer assisted TD Test directions modified LP Large print book TS Timing/Scheduling modified LV Low vision aids or magnification devices OA Other approved accommodations PF Presentation format modified WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 31
Accommodations Codes Test booklet coding for use of accommodations includes these categories: Code Accommodation AA Audio amplification device or noise buffer SB Scribed test BR Test in braille or braille writer SF Setting format CA Computer assisted TD Test directions modified LP Large print book TS Timing/Scheduling modified LV Low vision aids or magnification devices OA Other approved accommodations PF Presentation format modified WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 31
 Parts A ― C: Narrative Administration Information WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 32
Parts A ― C: Narrative Administration Information WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 32
 Part A: Listening & Speaking Format: Both domains are administered together by level. The Listening items for one level are administered, then the Speaking items for that same level are administered. Directions: Read the entire narrative story first, then go to the beginning of Part A (level A 1) to administer Listening and Speaking. Move through the levels, A 1 to A 5, based on student’s responses. Guidelines: Follow the Test Administration Script exactly, including pauses. Keep the test going at a steady pace. Scoring: After the student answers all items in a level, complete the score sheet in the Student Response Booklet. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 33
Part A: Listening & Speaking Format: Both domains are administered together by level. The Listening items for one level are administered, then the Speaking items for that same level are administered. Directions: Read the entire narrative story first, then go to the beginning of Part A (level A 1) to administer Listening and Speaking. Move through the levels, A 1 to A 5, based on student’s responses. Guidelines: Follow the Test Administration Script exactly, including pauses. Keep the test going at a steady pace. Scoring: After the student answers all items in a level, complete the score sheet in the Student Response Booklet. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 33
 Listening Items Listening items prompt the student to point to something in a picture, or point to and/or move a card. Do NOT read a Listening item more than one time. * Scoring: Listening items are marked correct or incorrect. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 34
Listening Items Listening items prompt the student to point to something in a picture, or point to and/or move a card. Do NOT read a Listening item more than one time. * Scoring: Listening items are marked correct or incorrect. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 34
 Speaking Items Speaking items prompt the student to talk about the pictures and the story. Scoring: There is guidance as to what to look for in a student response, found in the “Expect” box. Follow these guidelines to determine if the student meets or does not meet the task-level expectations. NOTE: These are based on the WIDA Speaking Rubric; Refer to the rubric if you have questions. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 35
Speaking Items Speaking items prompt the student to talk about the pictures and the story. Scoring: There is guidance as to what to look for in a student response, found in the “Expect” box. Follow these guidelines to determine if the student meets or does not meet the task-level expectations. NOTE: These are based on the WIDA Speaking Rubric; Refer to the rubric if you have questions. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 35
 Task Level Expectations Every task is based on a set of expectations for what the response should look like. The TA rates each task holistically, considering the response to all questions in the task. Scoring expectations are based on: Linguistic Complexity: Expectations of the quantity and organization of the student’s verbal response Vocabulary Usage: Expectations of the student’s use of appropriate vocabulary for grade level and proficiency level; refers to language quality Language Control: Expectations of the student’s control of English grammar, word choice in context, and the English sound system; refers to language quality WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 36
Task Level Expectations Every task is based on a set of expectations for what the response should look like. The TA rates each task holistically, considering the response to all questions in the task. Scoring expectations are based on: Linguistic Complexity: Expectations of the quantity and organization of the student’s verbal response Vocabulary Usage: Expectations of the student’s use of appropriate vocabulary for grade level and proficiency level; refers to language quality Language Control: Expectations of the student’s control of English grammar, word choice in context, and the English sound system; refers to language quality WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 36
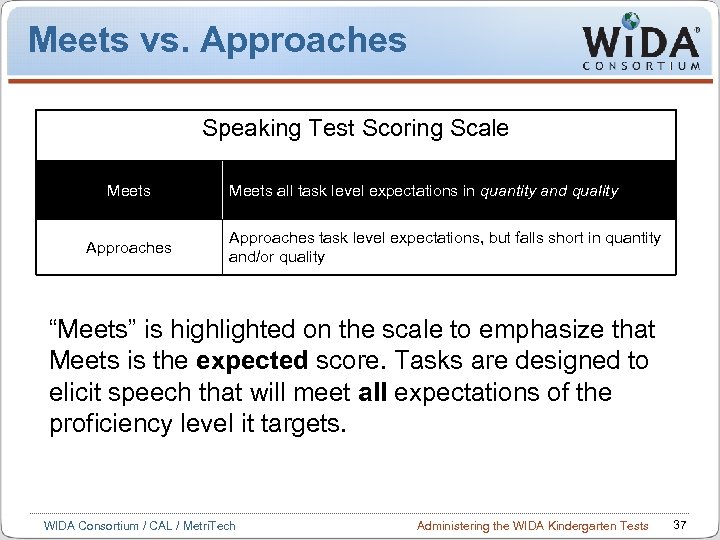 Meets vs. Approaches Speaking Test Scoring Scale Meets Approaches Meets all task level expectations in quantity and quality Approaches task level expectations, but falls short in quantity and/or quality “Meets” is highlighted on the scale to emphasize that Meets is the expected score. Tasks are designed to elicit speech that will meet all expectations of the proficiency level it targets. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 37
Meets vs. Approaches Speaking Test Scoring Scale Meets Approaches Meets all task level expectations in quantity and quality Approaches task level expectations, but falls short in quantity and/or quality “Meets” is highlighted on the scale to emphasize that Meets is the expected score. Tasks are designed to elicit speech that will meet all expectations of the proficiency level it targets. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 37
 Scoring Rules The TA must score the item immediately after the student responds to the last question in a task. If unsure whether to score a response Meets or Approaches, the “? ” (question mark) box can be marked. Then administer the next task. If the response to the next task scores Meets, go back and rate the previous task (the one with ? marked) Meets. If the response to that next task scores Approaches, go back and rate the previous task Approaches. Note: The last task on a Part may not be scored with a “? ”. The rating represents the student’s performance on the complete task, not on individual questions within the task. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 38
Scoring Rules The TA must score the item immediately after the student responds to the last question in a task. If unsure whether to score a response Meets or Approaches, the “? ” (question mark) box can be marked. Then administer the next task. If the response to the next task scores Meets, go back and rate the previous task (the one with ? marked) Meets. If the response to that next task scores Approaches, go back and rate the previous task Approaches. Note: The last task on a Part may not be scored with a “? ”. The rating represents the student’s performance on the complete task, not on individual questions within the task. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 38
 Speaking Rubric WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 39
Speaking Rubric WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 39
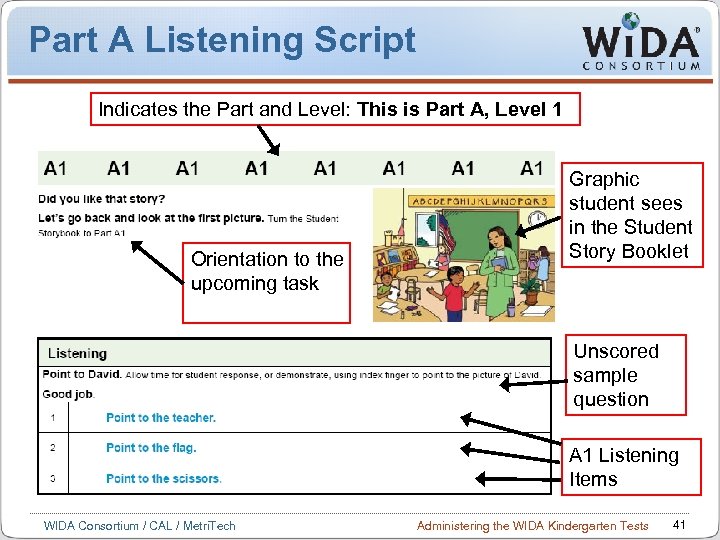 Part A Listening Script Indicates the Part and Level: This is Part A, Level 1 Orientation to the upcoming task Graphic student sees in the Student Story Booklet Unscored sample question A 1 Listening Items WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 41
Part A Listening Script Indicates the Part and Level: This is Part A, Level 1 Orientation to the upcoming task Graphic student sees in the Student Story Booklet Unscored sample question A 1 Listening Items WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 41
 Part A Speaking Script A 1 Speaking Items What to look for in student response WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 42
Part A Speaking Script A 1 Speaking Items What to look for in student response WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 42
 Part A: Recording Answers 1) Fill in the correct or incorrect bubble for each level. 2) Fill in Meets, Approaches, or ? . WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech 3) Determine if you are to move on in Part A, or go to Part B. 4) Stopped Here: fill in if this is the last level administered. Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 43
Part A: Recording Answers 1) Fill in the correct or incorrect bubble for each level. 2) Fill in Meets, Approaches, or ? . WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech 3) Determine if you are to move on in Part A, or go to Part B. 4) Stopped Here: fill in if this is the last level administered. Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 43
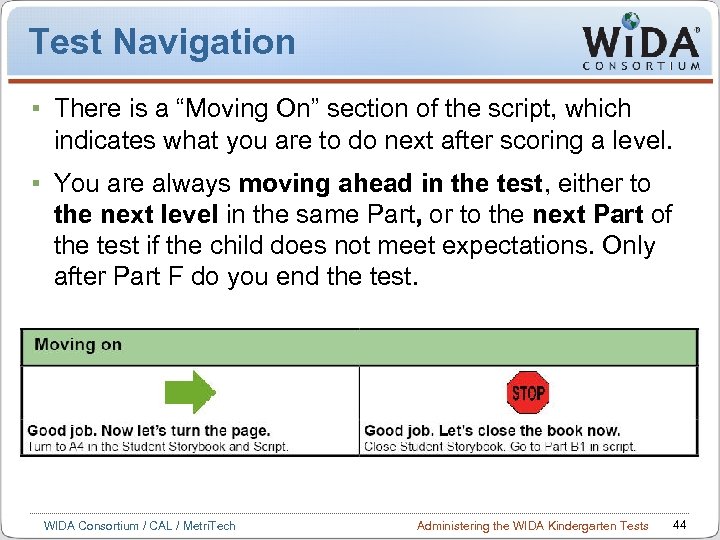 Test Navigation There is a “Moving On” section of the script, which indicates what you are to do next after scoring a level. You are always moving ahead in the test, either to the next level in the same Part, or to the next Part of the test if the child does not meet expectations. Only after Part F do you end the test. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 44
Test Navigation There is a “Moving On” section of the script, which indicates what you are to do next after scoring a level. You are always moving ahead in the test, either to the next level in the same Part, or to the next Part of the test if the child does not meet expectations. Only after Part F do you end the test. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 44
 Part B: Writing Experience Format: There are two tasks in this Part of the Writing Test, assessing five levels. First, the student writes his/her name as a screening task. If done successfully, the student proceeds to the Writing Experience. In the Writing Experience, the script prompts the student to talk about something from the story, then write it. If the student is struggling, there are prompts to scaffold the student to write words and sounds. Scoring: Based on the Pre. K/K Writing Rubric WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 45
Part B: Writing Experience Format: There are two tasks in this Part of the Writing Test, assessing five levels. First, the student writes his/her name as a screening task. If done successfully, the student proceeds to the Writing Experience. In the Writing Experience, the script prompts the student to talk about something from the story, then write it. If the student is struggling, there are prompts to scaffold the student to write words and sounds. Scoring: Based on the Pre. K/K Writing Rubric WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 45
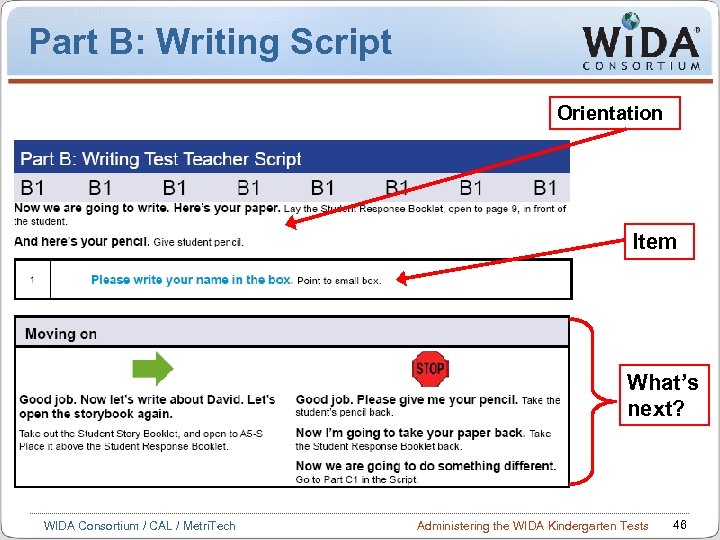 Part B: Writing Script Orientation Item What’s next? WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 46
Part B: Writing Script Orientation Item What’s next? WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 46
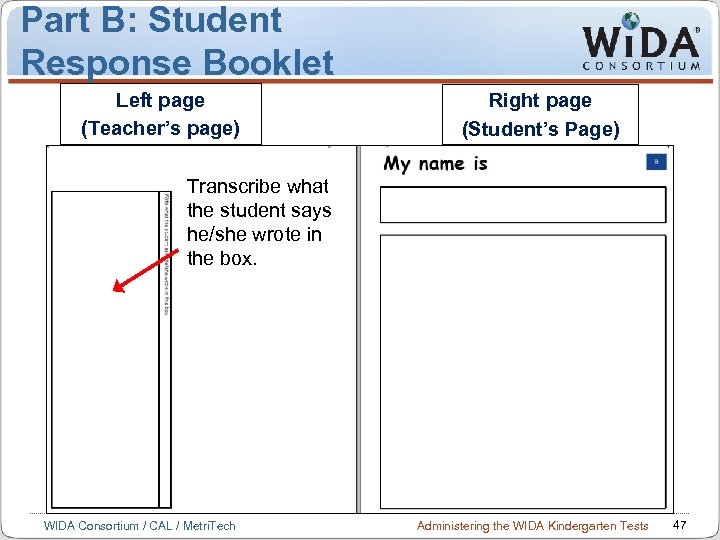 Part B: Student Response Booklet Left page (Teacher’s page) Right page (Student’s Page) Transcribe what the student says he/she wrote in the box. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 47
Part B: Student Response Booklet Left page (Teacher’s page) Right page (Student’s Page) Transcribe what the student says he/she wrote in the box. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 47
 Scoring in Writing The student writes in the Student Response Booklet. After the student writes, the TA transcribes what the student says he/she wrote. Score the writing as “High, ” “Mid, ” or “Low” immediately and check off the box at the bottom of Part B in the Student Response Booklet. Assign the writing a score of 1 -6 using the Writing Rubric after the student completes the entire test. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 48
Scoring in Writing The student writes in the Student Response Booklet. After the student writes, the TA transcribes what the student says he/she wrote. Score the writing as “High, ” “Mid, ” or “Low” immediately and check off the box at the bottom of Part B in the Student Response Booklet. Assign the writing a score of 1 -6 using the Writing Rubric after the student completes the entire test. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 48
 High, Mid, Low The Expect box for writing contains the criteria to determine the starting point in Part E (Writing). WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 49
High, Mid, Low The Expect box for writing contains the criteria to determine the starting point in Part E (Writing). WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 49
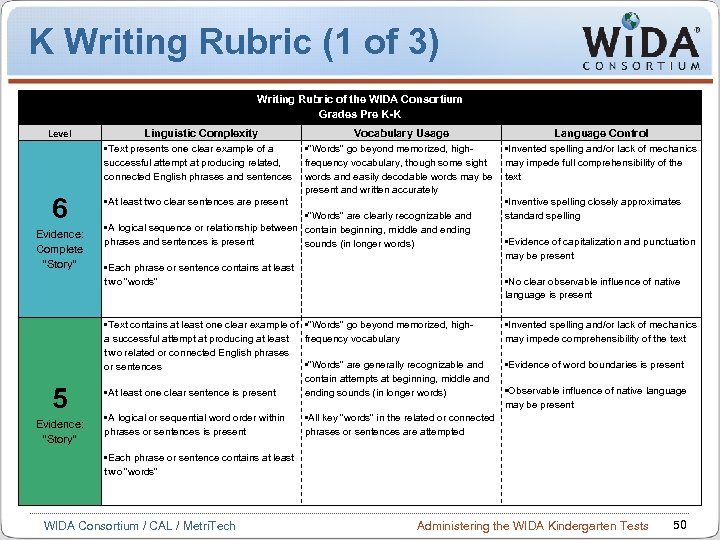 K Writing Rubric (1 of 3) Writing Rubric of the WIDA Consortium Grades Pre K-K Level Linguistic Complexity • Text presents one clear example of a successful attempt at producing related, connected English phrases and sentences 6 • At least two clear sentences are present Evidence: Complete “Story” 5 Evidence: “Story” Vocabulary Usage • “Words” go beyond memorized, highfrequency vocabulary, though some sight words and easily decodable words may be present and written accurately • “Words” are clearly recognizable and • A logical sequence or relationship between contain beginning, middle and ending phrases and sentences is present sounds (in longer words) • Each phrase or sentence contains at least two “words” • Inventive spelling closely approximates standard spelling • Evidence of capitalization and punctuation may be present • No clear observable influence of native language is present • Text contains at least one clear example of • “Words” go beyond memorized, higha successful attempt at producing at least frequency vocabulary two related or connected English phrases • “Words” are generally recognizable and or sentences contain attempts at beginning, middle and • At least one clear sentence is present ending sounds (in longer words) • A logical or sequential word order within phrases or sentences is present Language Control • Invented spelling and/or lack of mechanics may impede full comprehensibility of the text • Invented spelling and/or lack of mechanics may impede comprehensibility of the text • Evidence of word boundaries is present • Observable influence of native language may be present • All key “words” in the related or connected phrases or sentences are attempted • Each phrase or sentence contains at least two “words” WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 50
K Writing Rubric (1 of 3) Writing Rubric of the WIDA Consortium Grades Pre K-K Level Linguistic Complexity • Text presents one clear example of a successful attempt at producing related, connected English phrases and sentences 6 • At least two clear sentences are present Evidence: Complete “Story” 5 Evidence: “Story” Vocabulary Usage • “Words” go beyond memorized, highfrequency vocabulary, though some sight words and easily decodable words may be present and written accurately • “Words” are clearly recognizable and • A logical sequence or relationship between contain beginning, middle and ending phrases and sentences is present sounds (in longer words) • Each phrase or sentence contains at least two “words” • Inventive spelling closely approximates standard spelling • Evidence of capitalization and punctuation may be present • No clear observable influence of native language is present • Text contains at least one clear example of • “Words” go beyond memorized, higha successful attempt at producing at least frequency vocabulary two related or connected English phrases • “Words” are generally recognizable and or sentences contain attempts at beginning, middle and • At least one clear sentence is present ending sounds (in longer words) • A logical or sequential word order within phrases or sentences is present Language Control • Invented spelling and/or lack of mechanics may impede full comprehensibility of the text • Invented spelling and/or lack of mechanics may impede comprehensibility of the text • Evidence of word boundaries is present • Observable influence of native language may be present • All key “words” in the related or connected phrases or sentences are attempted • Each phrase or sentence contains at least two “words” WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 50
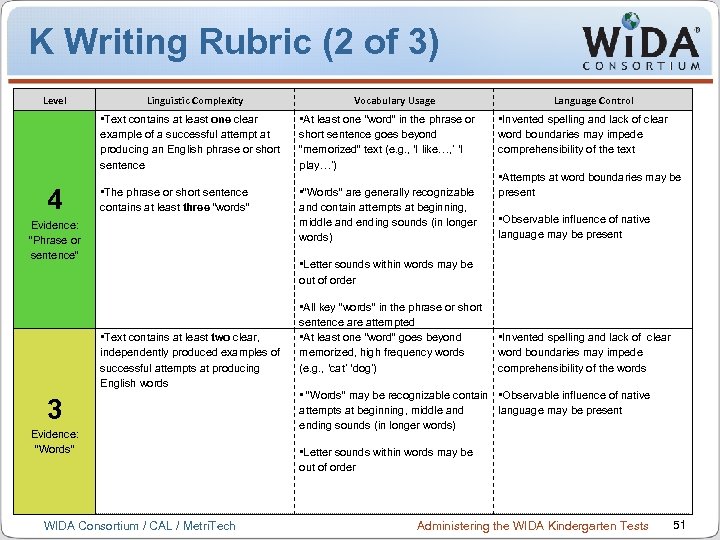 K Writing Rubric (2 of 3) Level Linguistic Complexity Vocabulary Usage • Text contains at least one clear example of a successful attempt at producing an English phrase or short sentence 4 • At least one “word” in the phrase or short sentence goes beyond “memorized” text (e. g. , ‘I like…, ’ ‘I play…’) • The phrase or short sentence contains at least three “words” • “Words” are generally recognizable and contain attempts at beginning, middle and ending sounds (in longer words) Evidence: “Phrase or sentence” Language Control • Invented spelling and lack of clear word boundaries may impede comprehensibility of the text • Attempts at word boundaries may be present • Observable influence of native language may be present • Letter sounds within words may be out of order • Text contains at least two clear, independently produced examples of successful attempts at producing English words 3 Evidence: “Words” WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech • All key “words” in the phrase or short sentence are attempted • At least one “word” goes beyond memorized, high frequency words (e. g. , ‘cat’ ‘dog’) • Invented spelling and lack of clear word boundaries may impede comprehensibility of the words • “Words” may be recognizable contain • Observable influence of native attempts at beginning, middle and language may be present ending sounds (in longer words) • Letter sounds within words may be out of order Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 51
K Writing Rubric (2 of 3) Level Linguistic Complexity Vocabulary Usage • Text contains at least one clear example of a successful attempt at producing an English phrase or short sentence 4 • At least one “word” in the phrase or short sentence goes beyond “memorized” text (e. g. , ‘I like…, ’ ‘I play…’) • The phrase or short sentence contains at least three “words” • “Words” are generally recognizable and contain attempts at beginning, middle and ending sounds (in longer words) Evidence: “Phrase or sentence” Language Control • Invented spelling and lack of clear word boundaries may impede comprehensibility of the text • Attempts at word boundaries may be present • Observable influence of native language may be present • Letter sounds within words may be out of order • Text contains at least two clear, independently produced examples of successful attempts at producing English words 3 Evidence: “Words” WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech • All key “words” in the phrase or short sentence are attempted • At least one “word” goes beyond memorized, high frequency words (e. g. , ‘cat’ ‘dog’) • Invented spelling and lack of clear word boundaries may impede comprehensibility of the words • “Words” may be recognizable contain • Observable influence of native attempts at beginning, middle and language may be present ending sounds (in longer words) • Letter sounds within words may be out of order Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 51
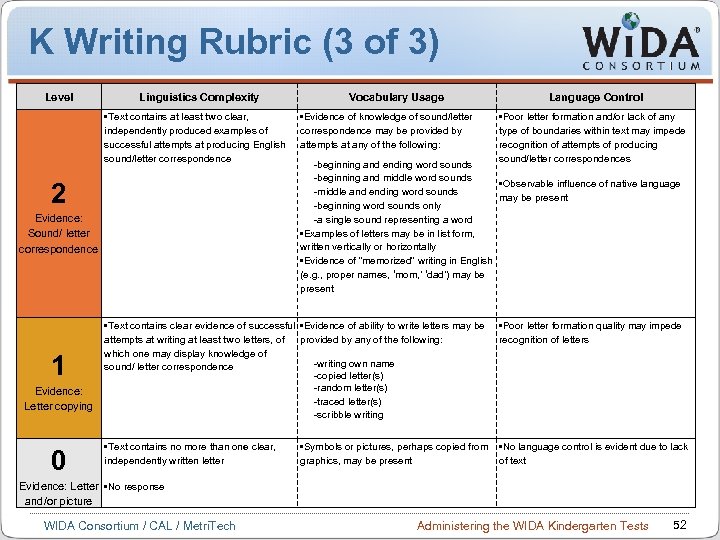 K Writing Rubric (3 of 3) Level Linguistics Complexity • Text contains at least two clear, independently produced examples of successful attempts at producing English sound/letter correspondence 2 Evidence: Sound/ letter correspondence 1 Evidence: Letter copying 0 Vocabulary Usage • Evidence of knowledge of sound/letter correspondence may be provided by attempts at any of the following: Language Control • Poor letter formation and/or lack of any type of boundaries within text may impede recognition of attempts of producing sound/letter correspondences -beginning and ending word sounds -beginning and middle word sounds • Observable influence of native language -middle and ending word sounds may be present -beginning word sounds only -a single sound representing a word • Examples of letters may be in list form, written vertically or horizontally • Evidence of “memorized” writing in English (e. g. , proper names, ‘mom, ’ ‘dad’) may be present • Text contains clear evidence of successful • Evidence of ability to write letters may be attempts at writing at least two letters, of provided by any of the following: which one may display knowledge of -writing own name sound/ letter correspondence -copied letter(s) -random letter(s) -traced letter(s) -scribble writing • Poor letter formation quality may impede recognition of letters • Text contains no more than one clear, independently written letter • No language control is evident due to lack of text • Symbols or pictures, perhaps copied from graphics, may be present Evidence: Letter • No response and/or picture WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 52
K Writing Rubric (3 of 3) Level Linguistics Complexity • Text contains at least two clear, independently produced examples of successful attempts at producing English sound/letter correspondence 2 Evidence: Sound/ letter correspondence 1 Evidence: Letter copying 0 Vocabulary Usage • Evidence of knowledge of sound/letter correspondence may be provided by attempts at any of the following: Language Control • Poor letter formation and/or lack of any type of boundaries within text may impede recognition of attempts of producing sound/letter correspondences -beginning and ending word sounds -beginning and middle word sounds • Observable influence of native language -middle and ending word sounds may be present -beginning word sounds only -a single sound representing a word • Examples of letters may be in list form, written vertically or horizontally • Evidence of “memorized” writing in English (e. g. , proper names, ‘mom, ’ ‘dad’) may be present • Text contains clear evidence of successful • Evidence of ability to write letters may be attempts at writing at least two letters, of provided by any of the following: which one may display knowledge of -writing own name sound/ letter correspondence -copied letter(s) -random letter(s) -traced letter(s) -scribble writing • Poor letter formation quality may impede recognition of letters • Text contains no more than one clear, independently written letter • No language control is evident due to lack of text • Symbols or pictures, perhaps copied from graphics, may be present Evidence: Letter • No response and/or picture WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 52
 Part C: Reading Format: There are five levels of tasks on the Reading Test. Tasks include matching cards, categorizing pictures, and pointing to a picture. Some of the initial tasks assess pre-literacy skills. Scoring: Reading items are each scored correct or incorrect. Based on how many tasks the student correctly completed, score the student’s performance as “High, ” “Mid, ” or “Low” and record in Part F in the Student Response Booklet. This will determine the starting point in the next Part of the Reading test. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 54
Part C: Reading Format: There are five levels of tasks on the Reading Test. Tasks include matching cards, categorizing pictures, and pointing to a picture. Some of the initial tasks assess pre-literacy skills. Scoring: Reading items are each scored correct or incorrect. Based on how many tasks the student correctly completed, score the student’s performance as “High, ” “Mid, ” or “Low” and record in Part F in the Student Response Booklet. This will determine the starting point in the next Part of the Reading test. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 54
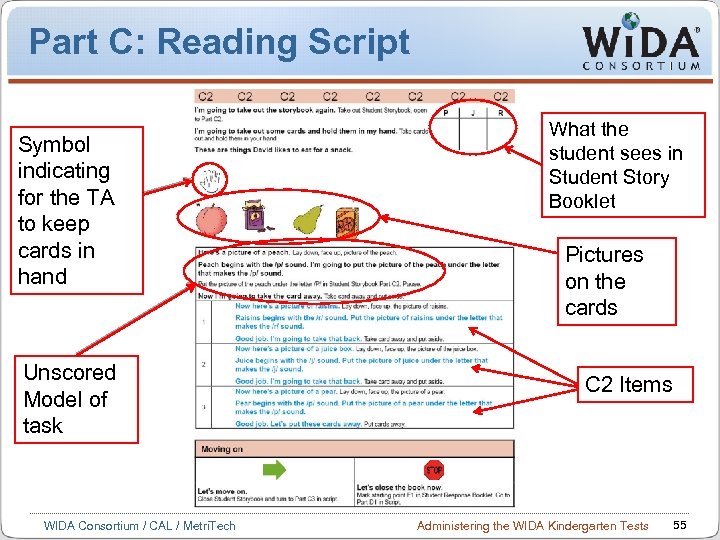 Part C: Reading Script Symbol indicating for the TA to keep cards in hand Unscored Model of task WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech What the student sees in Student Story Booklet Pictures on the cards C 2 Items Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 55
Part C: Reading Script Symbol indicating for the TA to keep cards in hand Unscored Model of task WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech What the student sees in Student Story Booklet Pictures on the cards C 2 Items Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 55
 Part C: Recording Answers Fill in the correct or incorrect bubble for each question. Determine if you will move on to the next Level within Part C, or go to Part D. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Stopped Here: fill in if this is the last level administered. Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 56
Part C: Recording Answers Fill in the correct or incorrect bubble for each question. Determine if you will move on to the next Level within Part C, or go to Part D. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Stopped Here: fill in if this is the last level administered. Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 56
 Parts D — F Expository Administration Directions WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 57
Parts D — F Expository Administration Directions WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 57
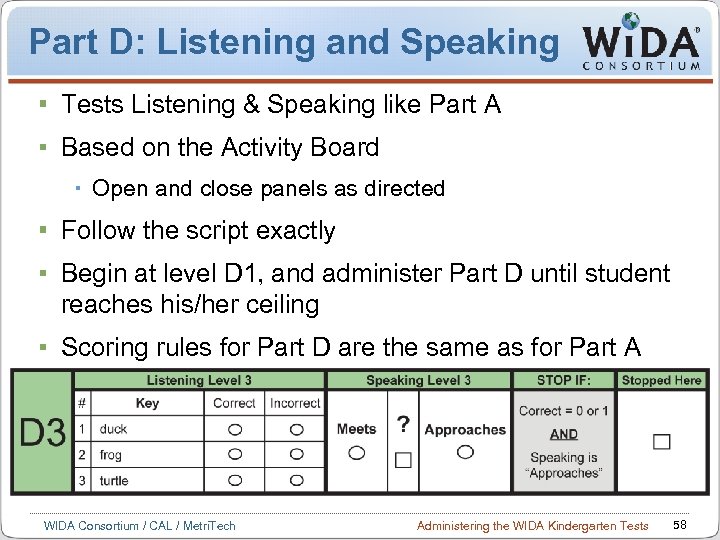 Part D: Listening and Speaking Tests Listening & Speaking like Part A Based on the Activity Board Open and close panels as directed Follow the script exactly Begin at level D 1, and administer Part D until student reaches his/her ceiling Scoring rules for Part D are the same as for Part A WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 58
Part D: Listening and Speaking Tests Listening & Speaking like Part A Based on the Activity Board Open and close panels as directed Follow the script exactly Begin at level D 1, and administer Part D until student reaches his/her ceiling Scoring rules for Part D are the same as for Part A WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 58
 Activity Board WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 59
Activity Board WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 59
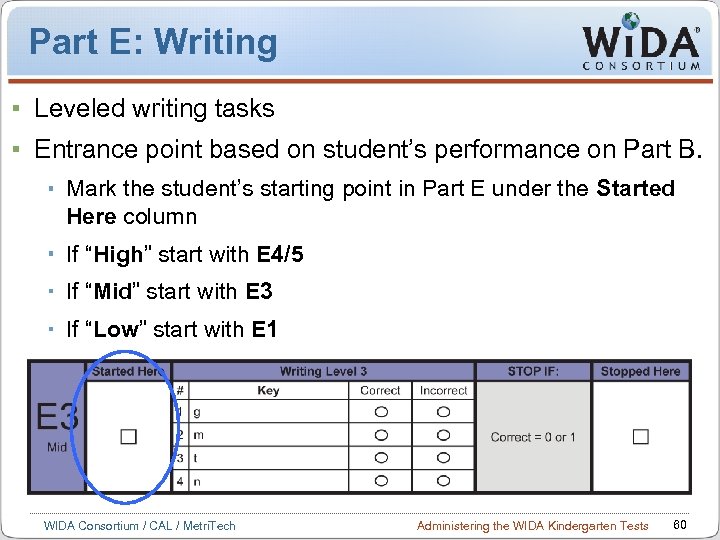 Part E: Writing Leveled writing tasks Entrance point based on student’s performance on Part B. Mark the student’s starting point in Part E under the Started Here column If “High” start with E 4/5 If “Mid” start with E 3 If “Low” start with E 1 WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 60
Part E: Writing Leveled writing tasks Entrance point based on student’s performance on Part B. Mark the student’s starting point in Part E under the Started Here column If “High” start with E 4/5 If “Mid” start with E 3 If “Low” start with E 1 WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 60
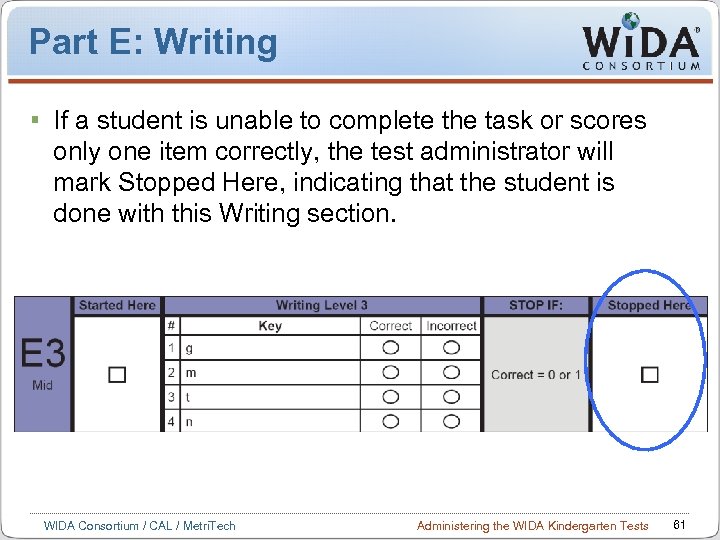 Part E: Writing If a student is unable to complete the task or scores only one item correctly, the test administrator will mark Stopped Here, indicating that the student is done with this Writing section. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 61
Part E: Writing If a student is unable to complete the task or scores only one item correctly, the test administrator will mark Stopped Here, indicating that the student is done with this Writing section. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 61
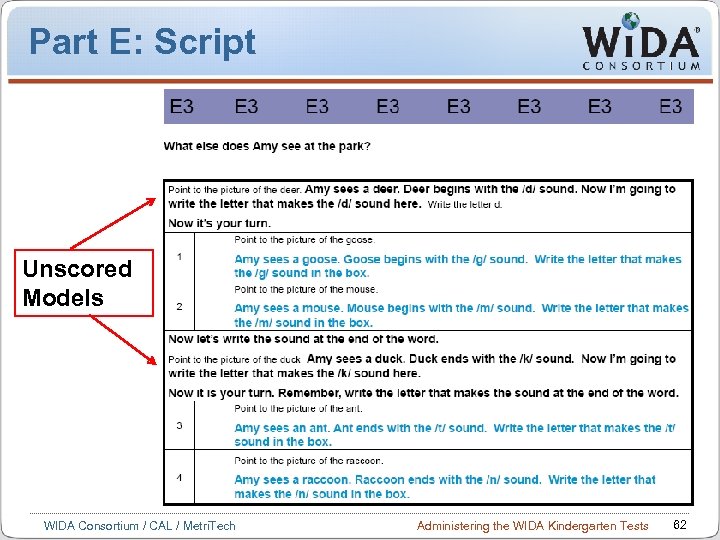 Part E: Script Unscored Models WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 62
Part E: Script Unscored Models WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 62
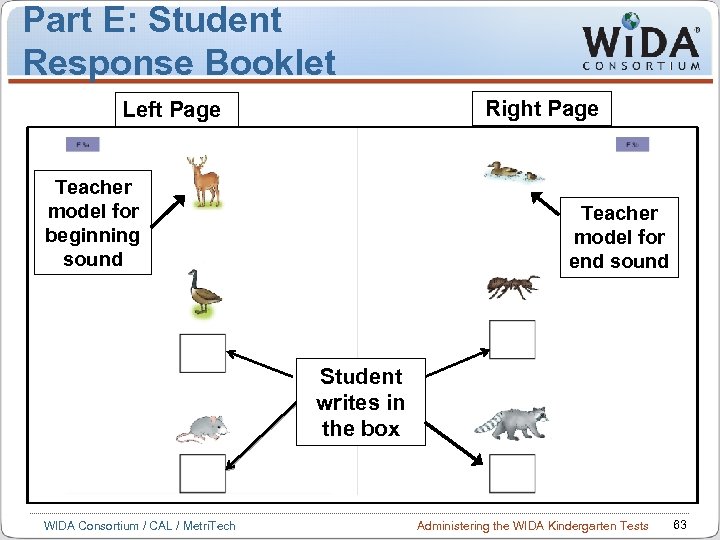 Part E: Student Response Booklet Right Page Left Page Teacher model for beginning sound Teacher model for end sound Student writes in the box WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 63
Part E: Student Response Booklet Right Page Left Page Teacher model for beginning sound Teacher model for end sound Student writes in the box WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 63
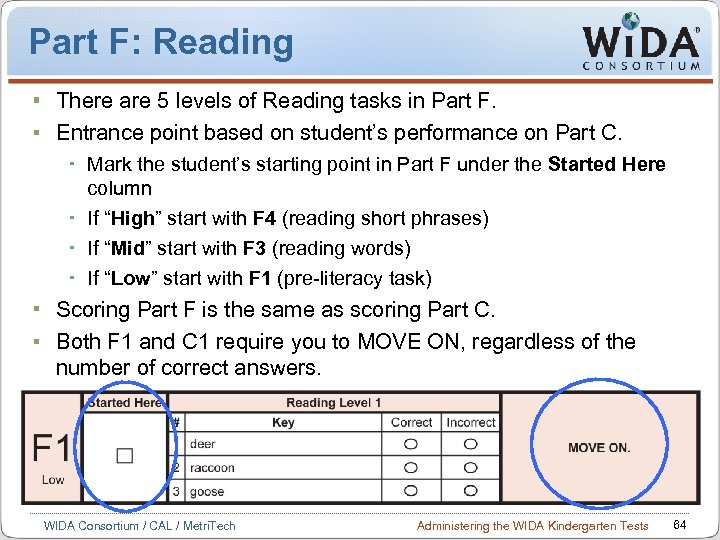 Part F: Reading There are 5 levels of Reading tasks in Part F. Entrance point based on student’s performance on Part C. Mark the student’s starting point in Part F under the Started Here column If “High” start with F 4 (reading short phrases) If “Mid” start with F 3 (reading words) If “Low” start with F 1 (pre-literacy task) Scoring Part F is the same as scoring Part C. Both F 1 and C 1 require you to MOVE ON, regardless of the number of correct answers. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 64
Part F: Reading There are 5 levels of Reading tasks in Part F. Entrance point based on student’s performance on Part C. Mark the student’s starting point in Part F under the Started Here column If “High” start with F 4 (reading short phrases) If “Mid” start with F 3 (reading words) If “Low” start with F 1 (pre-literacy task) Scoring Part F is the same as scoring Part C. Both F 1 and C 1 require you to MOVE ON, regardless of the number of correct answers. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 64
 Positive Reinforcement Be sure you end the test with something the student can do so that students leave with a positive feeling about the experience. In Listening Parts: If the student clearly does not understand the listening task, you may repeat the model. If the student still doesn’t understand, continue modeling with the other items, but score them as incorrect. In Speaking Parts: If the student says “I don’t know” you may assist him/her, but mark the answer “Approaches. ” In Writing Parts: If the student cannot write sentences, prompt him/her to write single words or letters. In Reading Parts: If the student can’t read words or sentences encourage him/her to identify a sound or a picture he/she recognizes. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 65
Positive Reinforcement Be sure you end the test with something the student can do so that students leave with a positive feeling about the experience. In Listening Parts: If the student clearly does not understand the listening task, you may repeat the model. If the student still doesn’t understand, continue modeling with the other items, but score them as incorrect. In Speaking Parts: If the student says “I don’t know” you may assist him/her, but mark the answer “Approaches. ” In Writing Parts: If the student cannot write sentences, prompt him/her to write single words or letters. In Reading Parts: If the student can’t read words or sentences encourage him/her to identify a sound or a picture he/she recognizes. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 65
 What are some challenges of administering a test like this to Kindergarten age students? WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 66
What are some challenges of administering a test like this to Kindergarten age students? WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 66
 Challenge: Behavior of Kindergarteners Kindergarten students are easily distracted Extra effort should be made to ensure the testing area is quiet and away from student traffic. Although TAs should be ready to redirect students to the task, the scripts will include advice for extra prompting. Kindergarten students need more stretch breaks: this should be at the discretion of the TA when he/she senses fatigue or distraction. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 67
Challenge: Behavior of Kindergarteners Kindergarten students are easily distracted Extra effort should be made to ensure the testing area is quiet and away from student traffic. Although TAs should be ready to redirect students to the task, the scripts will include advice for extra prompting. Kindergarten students need more stretch breaks: this should be at the discretion of the TA when he/she senses fatigue or distraction. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 67
 Challenge: Literacy of Young Learners All Kindergarteners are developing literacy skills; the test will therefore include some pre-reading and prewriting tasks. Additionally, at this developmental level, writing and reading skills are very intertwined, yet NCLB requires testing these as discrete skills. The existing WIDA Writing Rubric has been modified for the Kindergarten level to reflect rules for “inventive spelling” and task level expectations. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 68
Challenge: Literacy of Young Learners All Kindergarteners are developing literacy skills; the test will therefore include some pre-reading and prewriting tasks. Additionally, at this developmental level, writing and reading skills are very intertwined, yet NCLB requires testing these as discrete skills. The existing WIDA Writing Rubric has been modified for the Kindergarten level to reflect rules for “inventive spelling” and task level expectations. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 68
 Challenge: Maximizing Student Performance Take time before test administration to establish rapport with the student. Experience with young students is recommended for TAs for the Kindergarten test. Make extra effort to put the student at ease: Small talk on the way to the testing area Say, “We’re going to play some games/read a book” Establish age/birthday Talk about what they were doing in class, what they had for lunch, who is in their family, their favorite food, etc. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 69
Challenge: Maximizing Student Performance Take time before test administration to establish rapport with the student. Experience with young students is recommended for TAs for the Kindergarten test. Make extra effort to put the student at ease: Small talk on the way to the testing area Say, “We’re going to play some games/read a book” Establish age/birthday Talk about what they were doing in class, what they had for lunch, who is in their family, their favorite food, etc. WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 69
 Challenge: Training Test Administrators Given the requirements of the scoring and the quantity of materials used in the test, sufficient training must be made available to test administrators. Additional training resources: Kindergarten Test Administration Training Video Complete Test Administration Scoring and adaptivity instructions Online Training Course at www. wida. us Speaking sound files Scored writing samples Kindergarten Test Administrator Manual Face-to-face training in your state or district Practice giving a test to a colleague WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 70
Challenge: Training Test Administrators Given the requirements of the scoring and the quantity of materials used in the test, sufficient training must be made available to test administrators. Additional training resources: Kindergarten Test Administration Training Video Complete Test Administration Scoring and adaptivity instructions Online Training Course at www. wida. us Speaking sound files Scored writing samples Kindergarten Test Administrator Manual Face-to-face training in your state or district Practice giving a test to a colleague WIDA Consortium / CAL / Metri. Tech Administering the WIDA Kindergarten Tests 70
 Questions or Comments? For more information, please contact the WIDA Help Desk: 1 -866 -276 -7735 or help@wida. us World Class Instructional Design and Assessment, www. wida. us Center for Applied Linguistics, www. cal. org Metri. Tech, Inc. , www. metritech. com © 2011 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, on behalf of the WIDA Consortium www. wida. us
Questions or Comments? For more information, please contact the WIDA Help Desk: 1 -866 -276 -7735 or help@wida. us World Class Instructional Design and Assessment, www. wida. us Center for Applied Linguistics, www. cal. org Metri. Tech, Inc. , www. metritech. com © 2011 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, on behalf of the WIDA Consortium www. wida. us


