ea2b8bb29e70212b70f2788da73f80c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Address Register The Danish experience Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk)

What is an address register? An address register is a systematized collection of addresses: All street names etc. are represented in code structures to ensure unique-ness Example 1. Kochar Street Yervand, Hrachya, etc. (or in different cities!) Example 2. Kochar or Qochar (different spelling) Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 2

Address Register - Why? Why is – Statistics Denmark – Government bodies, regions, municipalities – The private sector pleased with the Danish Address Register? The answer is: 1) The address register is centrally managed and generally accepted by all users 2) The address register connects information • • data sources add value to each other it saves costs it drives digital public administration it reduces burden on businesses and households Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 3

The background 1 The first step • Tax collection • Carry out population censuses • Carry out housing censuses What you need is to know • where to get in touch with people! • what to be taxed! And: • where people live to count them correct • how their living conditions are Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 4

The background 2 Censuses • Censuses regulary since 1787 and every fifth year from 1900 • National population register established 1924 – each family with shared living had a register card – name, address (change of address), day of birth (day of dead), gender, etc. – sufficient information to write out poll cards (one of the most important purposes) • National population register transformed to EDP 1968 (responsible: the municipalities) – rationalize – addresses systematized – contents • dwelling register (all real dwellings, but also caravans if they are used as a dwelling) • address register Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 5

The background 3 Address register The address register in the national population register includes: – all roads all over Denmark • also roads planned and roads where building is only in the planning phase The content is: • municipality code • road code (unambiguous within each municipality) • road name (long 40 characters, short 20 characters) – if a continuous road has more than one name it has also to have more than one road code • areas/districts – bounded by municipality code, road code, number of house and letter of house Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 6

The background 4 Examples of areas/districts • Post-district – Includes information about postcode and postdistrict-name • • Election-district Church-district/parish-district School-district Social-district Urban renewal district Evacuation-district Etc. Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 7

The background 5 Usage • Actually the address register and the connection to persons has made it possible to make geografic data processing without geografic codes (x, y coordinates) • Used for population forecasts, various plannings etc. (Denmark as such, regions and municipalities) • The addresses have been used by the private sector – Private enterprises might validate their customer register against the official addresses Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 8

Building and dwelling register 1 • Population and housing censuses are expensive and people are asked the same questions again and again – 1970: 2 mill. Euro (~ 14 mill. Euro today) – date of birth, name, address etc. (already in the Central Person Register from 1968) – education, work etc. – all about the dwelling and building • Use of informtion about dwellings and buildings – Housing census (every year – and up to date) – Building census (every year – and up to date) – Valuation of property – Tax assessment • Coordinated by Register of Property (updated by the municipalities) Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 9
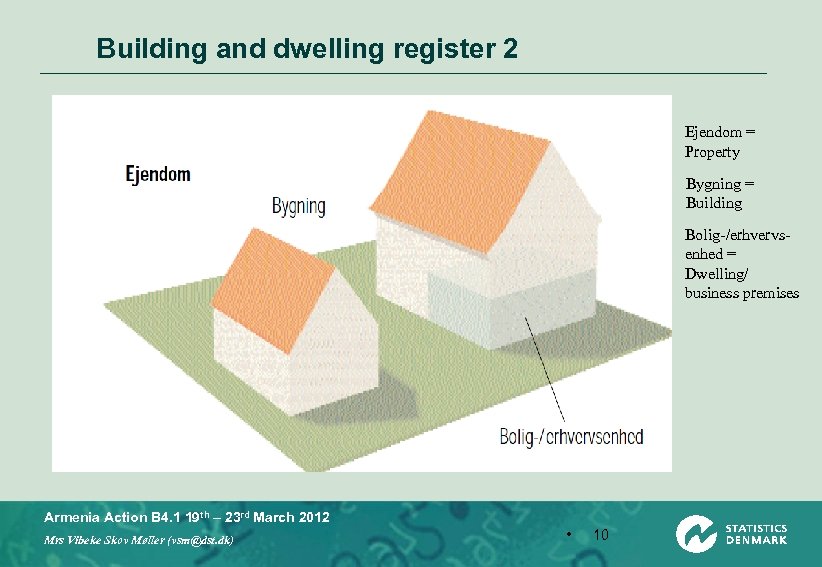
Building and dwelling register 2 Ejendom = Property Bygning = Building Bolig-/erhvervsenhed = Dwelling/ business premises Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 10

Building and dwelling register 3 • Identification - building – Municipality code – Property number – Building number • Identification – dwelling/business premises – municipality code – road code – number of house – letter of house – floor – site/door-number • Building address equal one of the addresses for the dwelling/business premises without floor and site/door-number Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 11

Central Administrative Business Register • Tax authorities and Customs authorities – Used to have separate registers and identification numbers from 1967 -1990 – Statistics Denmark used information about owner and addresses to make its own Statistical Business Register • The Danish Commerce and Companies Agency – Had its own register and own identification number up to 1999 • Central Administrative Business Register established 1999 – – – Units (Legal units and Local Kind of Activity Units) Addresses – using the Address register in the national population register Name Kind of activity Legal form Owner identification if a person Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 12
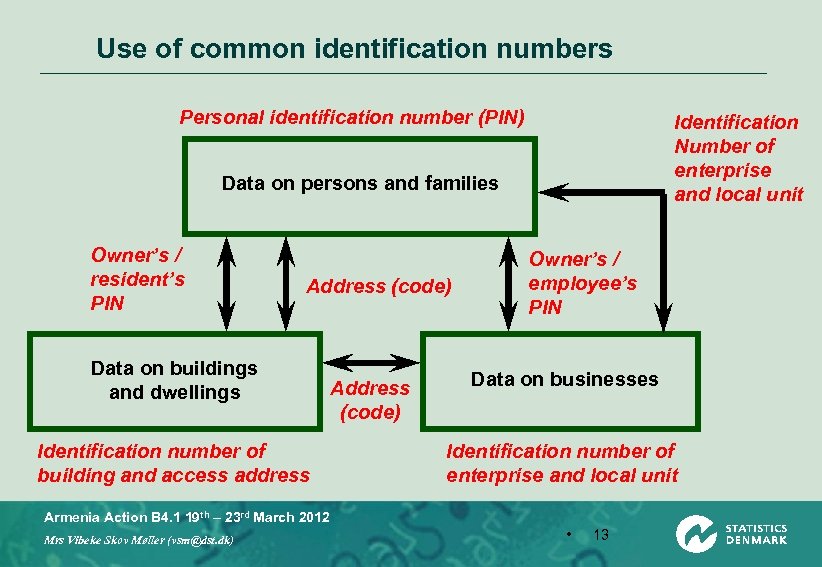
Use of common identification numbers Personal identification number (PIN) Identification Number of enterprise and local unit Data on persons and families Owner’s / resident’s PIN Address (code) Data on buildings and dwellings Identification number of building and access address Address (code) Owner’s / employee’s PIN Data on businesses Identification number of enterprise and local unit Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 13

Land registry 1. Information on areas (lands) 2. Land registration map 3. Information on ownership and restrictions Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 14
Land registry Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 15
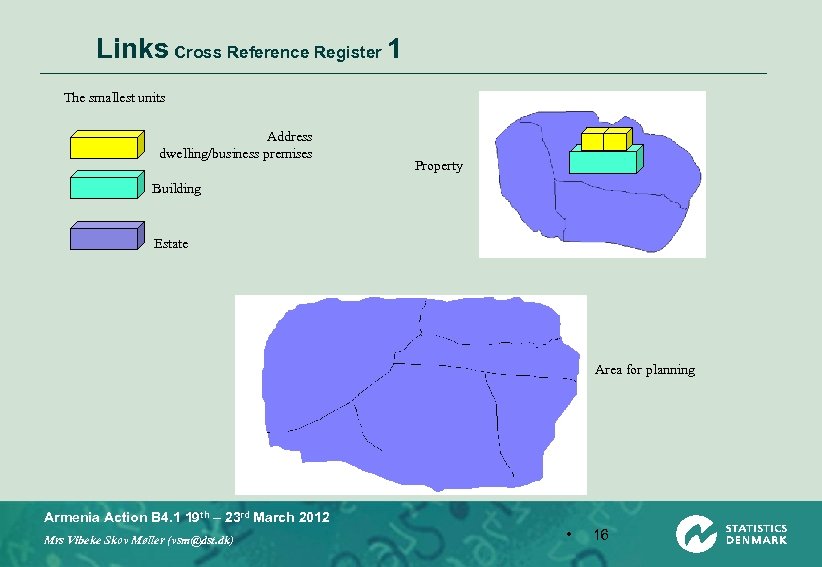
Links Cross Reference Register 1 The smallest units Address dwelling/business premises Property Building Estate Area for planning Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 16
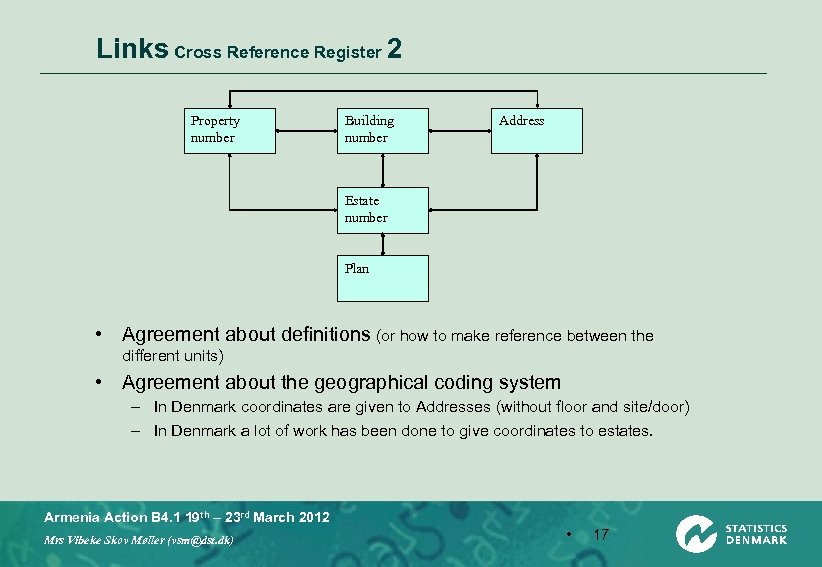
Links Cross Reference Register 2 Property number Building number Address Estate number Plan • Agreement about definitions (or how to make reference between the different units) • Agreement about the geographical coding system – In Denmark coordinates are given to Addresses (without floor and site/door) – In Denmark a lot of work has been done to give coordinates to estates. Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 17

Other registers that use the address register • State Register of sales and tax assessments – the registration of the value of sales of properties gives information about the normally value of properties and is used to set the norm value • Register of owners of wires, pipes and other similar constructions – The owners have to mark interest areas – Actors for digging such as contractors shall investigate the register and ask the owners where their constructions are placed with a view to avoiding damages • Register of explanation – reasons why a tax assessment for a given property has to differ from the norm (it could be because it is very near a lovely forest or a noisy windmill) • Etc. Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 18

Increased application 1 Public sector • Register legal rights to real property • Subdivision according to the Real Property Formation Act • Planning according to the Planning law complex – – – urban and rural areas environmental protection industrial and commercial development bus routes schools and day-care centres • Consideration of building and development application • Collecting utility charges • Observe rules – Building regulations – Plan laws • Analysis Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 19

Increased application 2 Private sector • Lawyers – for instance in disputes about properties – rectification of an agreement about sale of a house • • Banks and institutes granting mortgage credits Insurance companies Architects Building contractors • Logistics planning • Start a sales drive on the basic of bought statistics of for instance the level of education in different districts • Analysis Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 20

How to start? • Intensive communication between all interested parties (during the whole process of establishing and use) • Agree on benefits (but do not forget the costs) • Let one institution take the leadership – prepare strategy and plan – what will be most important – is any information already available (Codes for Marz, Region, Road, Building) – carry out test cases – agree on principles – agree on definitions Armenia Action B 4. 1 19 th – 23 rd March 2012 Mrs Vibeke Skov Møller (vsm@dst. dk) • 21
ea2b8bb29e70212b70f2788da73f80c6.ppt