a03861160e8de9cee12899fcb670d342.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues l Helena Lenihan (University of Limerick) l Mark Hart (Kingston University, UK) Research and the Knowledge Based Society Measuring the Link European conference on good practice in evaluation and indicators May 24 th 2004, NUI Galway 1 Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

Key issue: ‘How’ to evaluate l l l 2 Increased impetus to evaluate industrial policy interventions For decades, significant resources have been allocated by the Irish government re: various types and measures of industrial policy interventions Changes have taken place without insights of evaluation Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

l l 3 Without reference to many of factors at work w. r. t. financial assistance: exploring the counterfactual (deadweight and displacement) Some assessment of additional impact Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

Key findings from Irish experience 2 development agencies - Shannon Development (Lenihan 1999; 2001; 2004) - Enterprise Ireland (Lenihan et al. , 2003; Hart and Lenihan 2004)-Investor and consumer of research l Reflect on key methodological issues l 4 Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

Defining deadweight - Focus on ‘partial degrees’ of deadweight l l l 5 Evaluating the Effects of Shannon Development (SD)Industrial Support 1995 ‘Self assessment approach’ Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

l l l 6 Degree to which projects would have gone ahead anyway without assistance from SD in 1995. Also incorporated other ‘indicators’ of deadweight into the study. Adoption of direct and indirect questions to assess deadweight-considered imperative. Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues
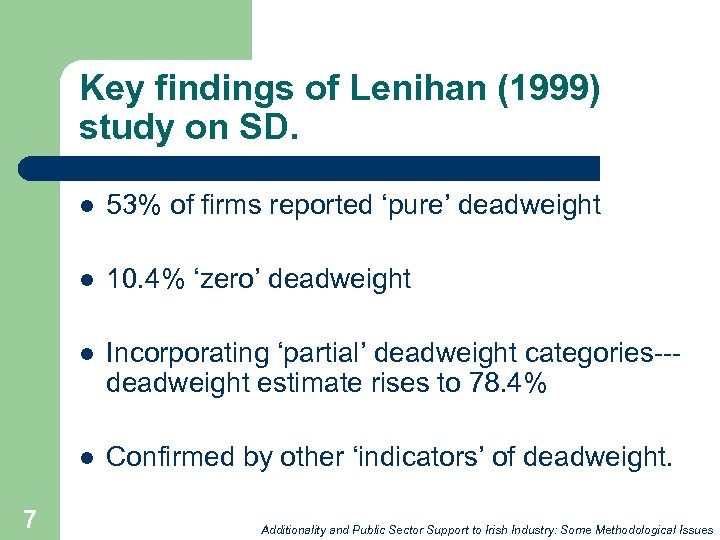
Key findings of Lenihan (1999) study on SD. l l 10. 4% ‘zero’ deadweight l Incorporating ‘partial’ deadweight categories--deadweight estimate rises to 78. 4% l 7 53% of firms reported ‘pure’ deadweight Confirmed by other ‘indicators’ of deadweight. Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues
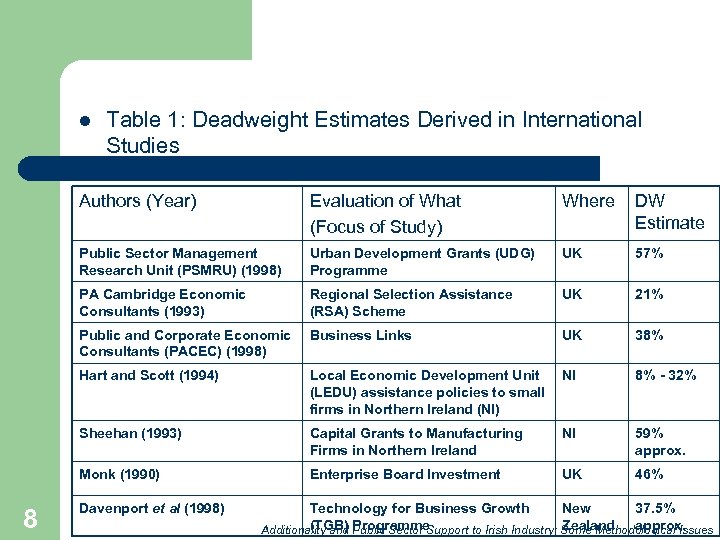
l Table 1: Deadweight Estimates Derived in International Studies Authors (Year) Where DW Estimate Public Sector Management Research Unit (PSMRU) (1998) Urban Development Grants (UDG) Programme UK 57% PA Cambridge Economic Consultants (1993) Regional Selection Assistance (RSA) Scheme UK 21% Public and Corporate Economic Consultants (PACEC) (1998) Business Links UK 38% Hart and Scott (1994) Local Economic Development Unit (LEDU) assistance policies to small firms in Northern Ireland (NI) NI 8% - 32% Sheehan (1993) Capital Grants to Manufacturing Firms in Northern Ireland NI 59% approx. Monk (1990) 8 Evaluation of What (Focus of Study) Enterprise Board Investment UK 46% Davenport et al (1998) Technology for Business Growth New 37. 5% (TGB) Programme Zealand approx. Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues
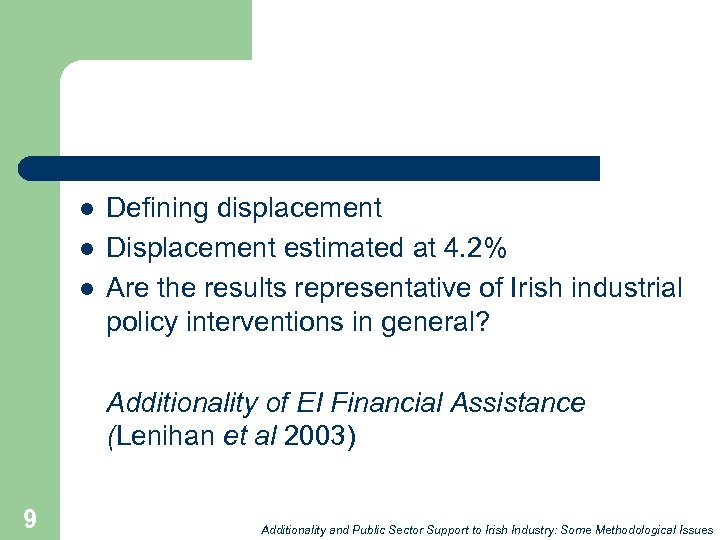
l l l Defining displacement Displacement estimated at 4. 2% Are the results representative of Irish industrial policy interventions in general? Additionality of EI Financial Assistance (Lenihan et al 2003) 9 Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues
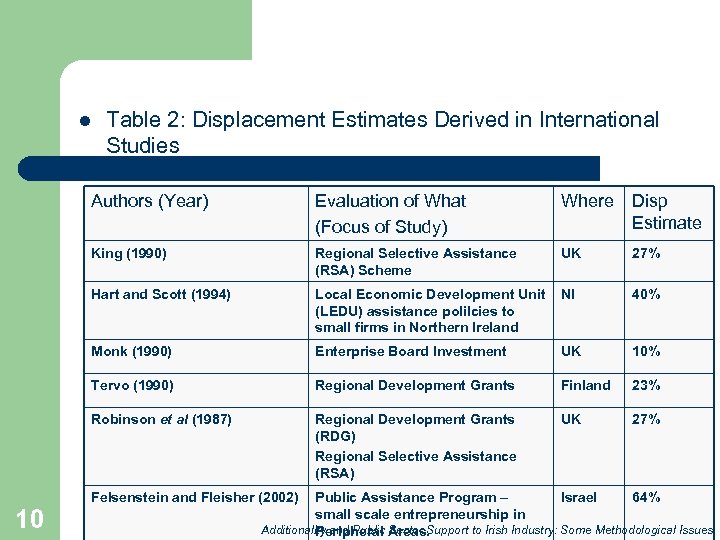
l Table 2: Displacement Estimates Derived in International Studies Authors (Year) Where Disp Estimate King (1990) Regional Selective Assistance (RSA) Scheme UK 27% Hart and Scott (1994) Local Economic Development Unit (LEDU) assistance polilcies to small firms in Northern Ireland NI 40% Monk (1990) Enterprise Board Investment UK 10% Tervo (1990) Regional Development Grants Finland 23% Robinson et al (1987) 10 Evaluation of What (Focus of Study) Regional Development Grants (RDG) Regional Selective Assistance (RSA) UK 27% Felsenstein and Fleisher (2002) Public Assistance Program – Israel 64% small scale entrepreneurship in Additionality and Public Areas. Peripheral Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

Key findings from EI study (Lenihan et al 2003) l l 11 Deadweight between 46. 2% and 55. 8% Displacement estimates between 4. 4% to 12. 2% Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues
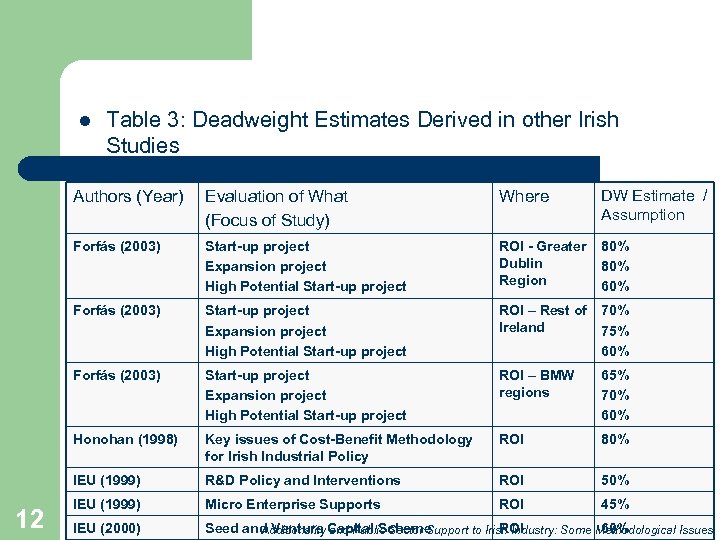
l Table 3: Deadweight Estimates Derived in other Irish Studies Authors (Year) Where DW Estimate / Assumption Forfás (2003) Start-up project Expansion project High Potential Start-up project ROI - Greater Dublin Region 80% 60% Forfás (2003) Start-up project Expansion project High Potential Start-up project ROI – Rest of Ireland 70% 75% 60% Forfás (2003) Start-up project Expansion project High Potential Start-up project ROI – BMW regions 65% 70% 60% Honohan (1998) Key issues of Cost-Benefit Methodology for Irish Industrial Policy ROI 80% IEU (1999) 12 Evaluation of What (Focus of Study) R&D Policy and Interventions ROI 50% IEU (1999) Micro Enterprise Supports ROI 45% IEU (2000) Seed and Venture Capital Scheme ROI 60% Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues
Explaining Deadweight Estimates l No longer sufficient to merely derive estimates of deadweight and displacement and to discuss their consequences (Lenihan 2004). l Focus on specific firm characteristics that influence these estimates. Logit (predictive) regression model for deadweight. l 13 Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

l l 14 Do certain characteristics of grant-aided firms increase the likelihood of deadweight? Useful for policymakers in terms of providing an ex-ante appraisal/evaluation template. Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

Key challenges and opportunities facing the Irish evaluation community Indirect benefits (positive externalities) associated with financial assistance to firms. v Role of EI as evidence of due dilligence and its importance in financial leverage -Deadweight estimate adjusted downwards by between 3 and 7 percentage points. v Benefits of being part of EI international network l Account for fact that some financial assistance is repayable- complicates deadweight estimates. l 15 Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

Best-practice internationally l l 16 Econometric treatment models (e. g. 2 -step Heckman models) which account for ‘selection’ and ‘assistance’ effects Methodological minimum standards: full scale longitudinal set of case studies; control group analysis; selection and assistance modelling; predictive modelling. Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues

Conclusion l l l 17 Importance of accounting for deadweight and displacement. Financial assistance more amenable to evaluation. Methodological approaches and lessons are transferrable. Rigorous, structured but at same time userfriendly approaches. No single best evaluation framework in same way there is no single best economic policy instrument. Additionality and Public Sector Support to Irish Industry: Some Methodological Issues
a03861160e8de9cee12899fcb670d342.ppt