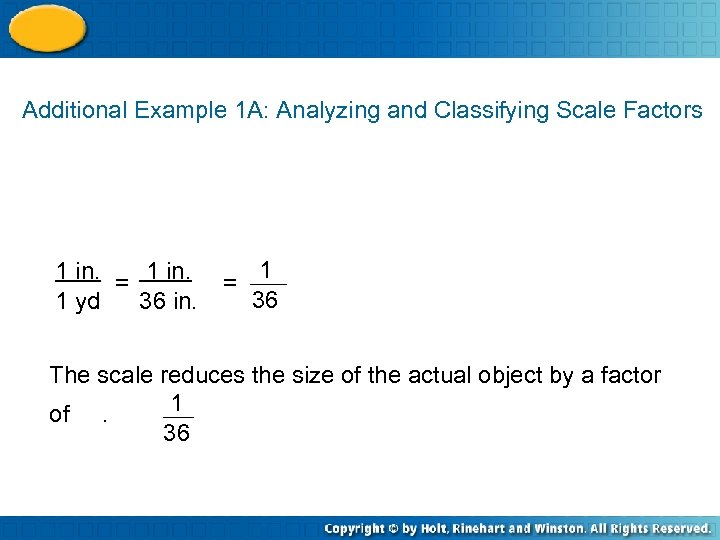
 Additional Example 1 A: Analyzing and Classifying Scale Factors 1 in. = 1 in. 1 yd 36 in. = 1 36 The scale reduces the size of the actual object by a factor 1 of. 36
Additional Example 1 A: Analyzing and Classifying Scale Factors 1 in. = 1 in. 1 yd 36 in. = 1 36 The scale reduces the size of the actual object by a factor 1 of. 36
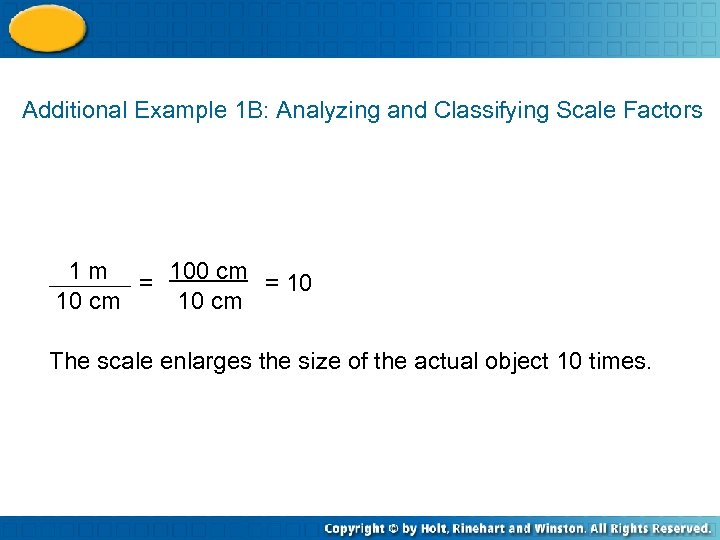 Additional Example 1 B: Analyzing and Classifying Scale Factors 1 m = 100 cm = 10 10 cm The scale enlarges the size of the actual object 10 times.
Additional Example 1 B: Analyzing and Classifying Scale Factors 1 m = 100 cm = 10 10 cm The scale enlarges the size of the actual object 10 times.
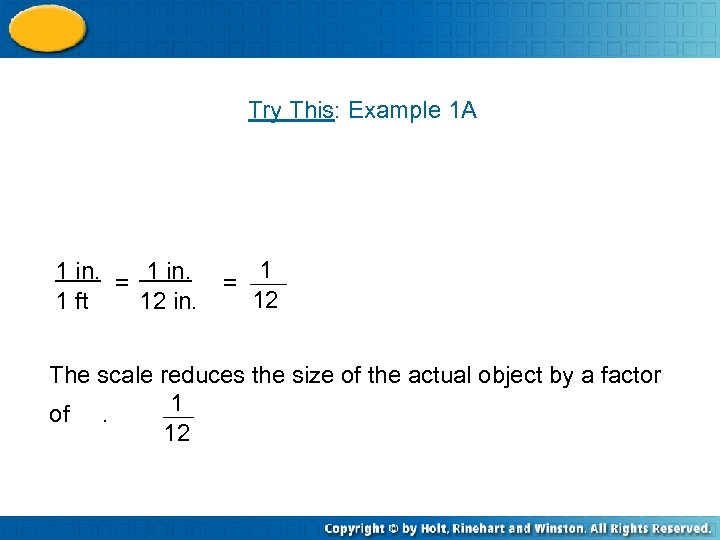 Try This: Example 1 A 1 in. = 1 in. 1 ft 12 in. = 1 12 The scale reduces the size of the actual object by a factor 1 of. 12
Try This: Example 1 A 1 in. = 1 in. 1 ft 12 in. = 1 12 The scale reduces the size of the actual object by a factor 1 of. 12
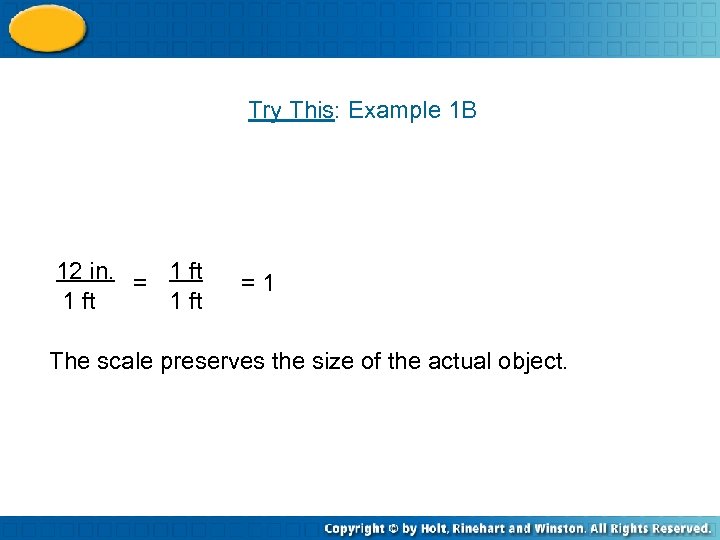 Try This: Example 1 B 12 in. = 1 ft =1 The scale preserves the size of the actual object.
Try This: Example 1 B 12 in. = 1 ft =1 The scale preserves the size of the actual object.
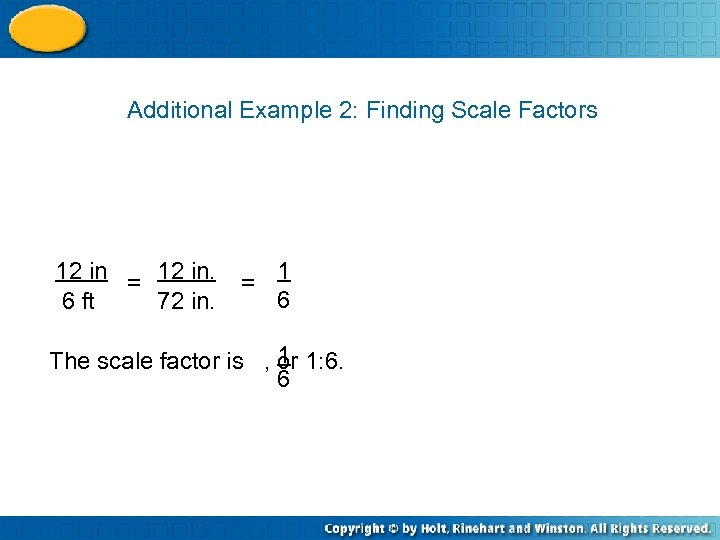 Additional Example 2: Finding Scale Factors 12 in = 12 in. 6 ft 72 in. = 1 6 1 The scale factor is , or 1: 6. 6
Additional Example 2: Finding Scale Factors 12 in = 12 in. 6 ft 72 in. = 1 6 1 The scale factor is , or 1: 6. 6
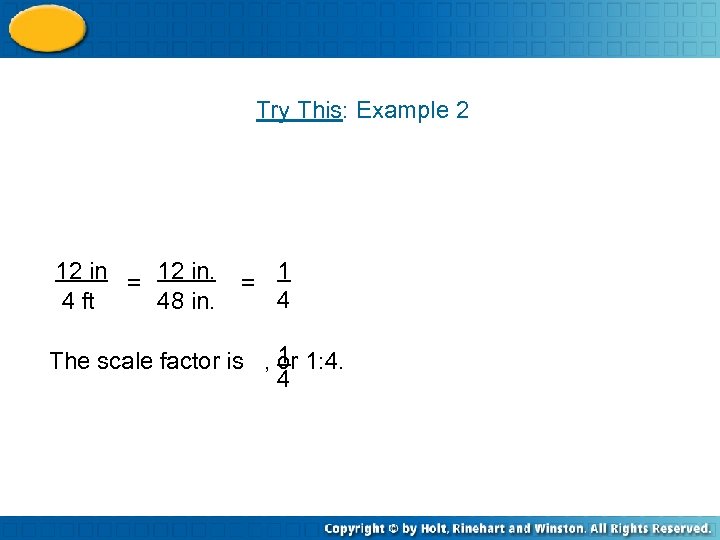 Try This: Example 2 12 in = 12 in. 4 ft 48 in. = 1 4 1 The scale factor is , or 1: 4. 4
Try This: Example 2 12 in = 12 in. 4 ft 48 in. = 1 4 1 The scale factor is , or 1: 4. 4
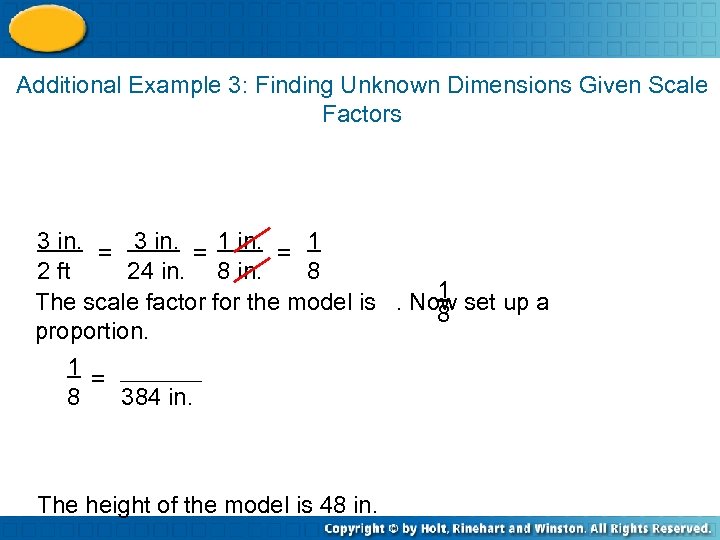 Additional Example 3: Finding Unknown Dimensions Given Scale Factors 3 in. = 1 2 ft 24 in. 8 1 The scale factor for the model is. Now set up a 8 proportion. 1 = 8 384 in. The height of the model is 48 in.
Additional Example 3: Finding Unknown Dimensions Given Scale Factors 3 in. = 1 2 ft 24 in. 8 1 The scale factor for the model is. Now set up a 8 proportion. 1 = 8 384 in. The height of the model is 48 in.
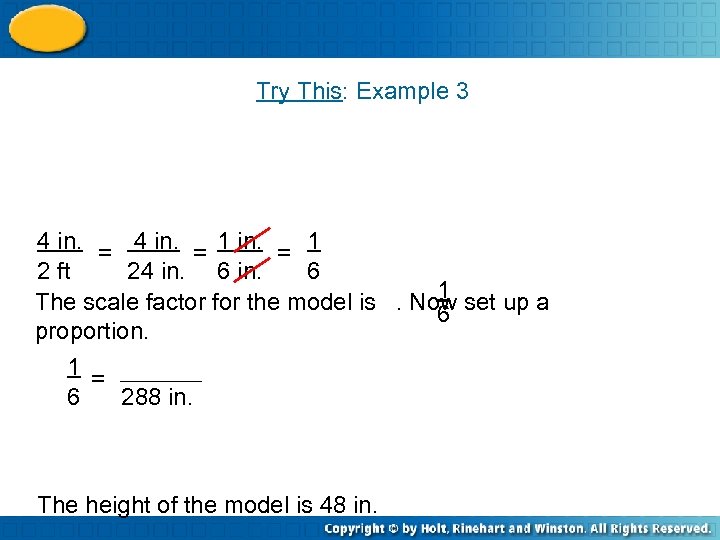 Try This: Example 3 4 in. = 1 2 ft 24 in. 6 1 The scale factor for the model is. Now set up a 6 proportion. 1 = 6 288 in. The height of the model is 48 in.
Try This: Example 3 4 in. = 1 2 ft 24 in. 6 1 The scale factor for the model is. Now set up a 6 proportion. 1 = 6 288 in. The height of the model is 48 in.
 Additional Example 4: Life Science Application 5 cm 0. 0000001 mm 50 mm = 0. 0000001 mm = 500, 000 The scale factor for the model is 500, 000. This means the model is 500 million times larger than the actual chain.
Additional Example 4: Life Science Application 5 cm 0. 0000001 mm 50 mm = 0. 0000001 mm = 500, 000 The scale factor for the model is 500, 000. This means the model is 500 million times larger than the actual chain.
 Additional Example 4 Continued 500, 000 1 = 20 cm
Additional Example 4 Continued 500, 000 1 = 20 cm
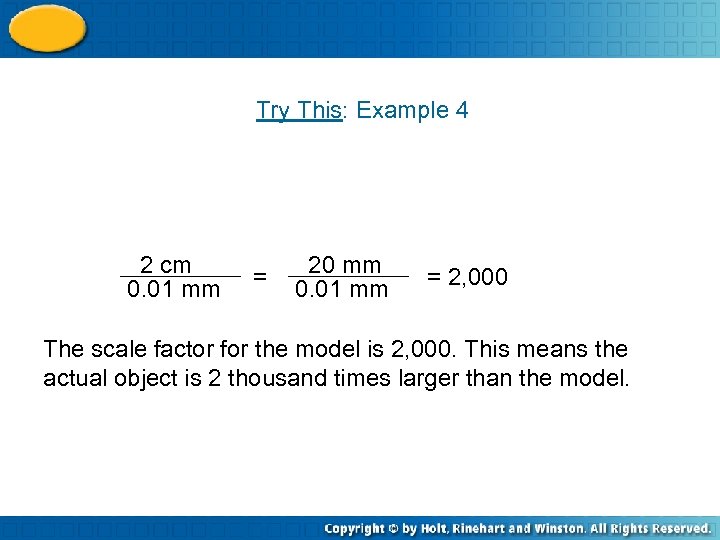 Try This: Example 4 2 cm 0. 01 mm = 20 mm 0. 01 mm = 2, 000 The scale factor for the model is 2, 000. This means the actual object is 2 thousand times larger than the model.
Try This: Example 4 2 cm 0. 01 mm = 20 mm 0. 01 mm = 2, 000 The scale factor for the model is 2, 000. This means the actual object is 2 thousand times larger than the model.
 Try This: Example 4 Continued 2, 000 = 30 cm 1 The length of the actual object is 0. 015 cm.
Try This: Example 4 Continued 2, 000 = 30 cm 1 The length of the actual object is 0. 015 cm.
 Lesson Quiz: Part 1 enlarges preserves reduces 1: 144
Lesson Quiz: Part 1 enlarges preserves reduces 1: 144
 Lesson Quiz: Part 2 4. 5 cm
Lesson Quiz: Part 2 4. 5 cm