53f0f755ecdb03c64bd7de0b3b7b8805.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
![Addition and Subtraction Calculating efficiently and accurately [KS 1] Addition and Subtraction Calculating efficiently and accurately [KS 1]](https://present5.com/presentation/53f0f755ecdb03c64bd7de0b3b7b8805/image-1.jpg)
Addition and Subtraction Calculating efficiently and accurately [KS 1]

Objectives l To explore the knowledge, skills and understanding required for children to add, subtract, multiply and divide efficiently and accurately l To explore the progression in recording and (some of) the teaching approaches used
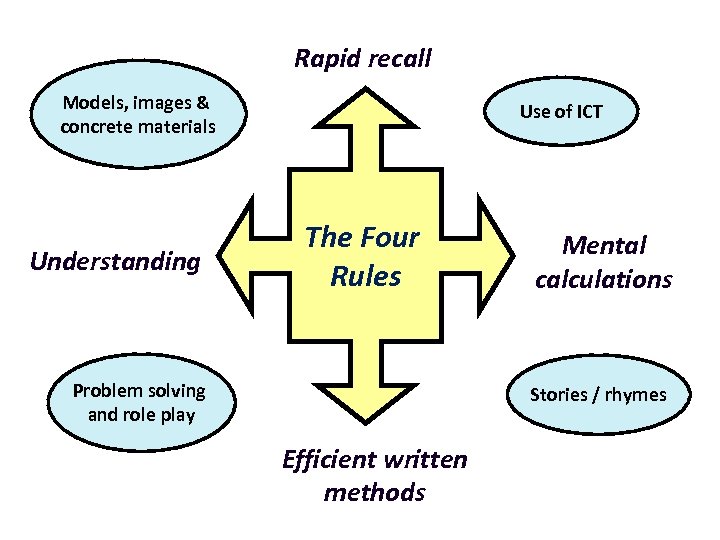
Rapid recall Models, images & concrete materials Understanding Use of ICT The Four Rules Problem solving and role play Mental calculations Stories / rhymes Efficient written methods

Progression for addition and subtraction • Counting • One more / less • Addition as combining two groups, then counting on • Subtraction as take away or difference (eg how many more is … than …? ) • Ten more/less • Recall of addition/subtraction facts to 10, 20 and beyond • Understand that subtraction and addition are inverses

Counting and estimation There are 5 principles of counting: 1. The stable order principle - understanding that the number names must be used in that particular order when counting 2. The one-to-one principle - understanding and ensuring that the next item in a count corresponds to the next number 3. The cardinal principle - knowing that the final number represents the size of the set 4. The abstraction principle - knowing that counting can be applied to any collection, real or imagined 5. The order irrelevance principle - knowing that the order in which the items are counted is not relevant to the total value
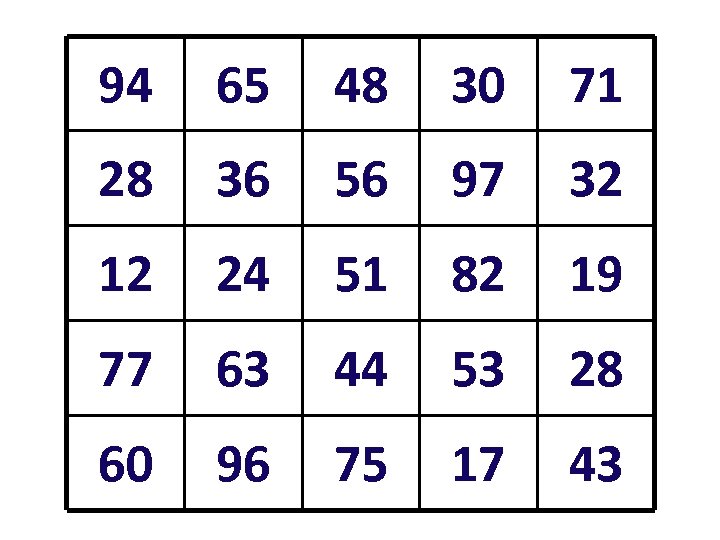
94 65 48 30 71 28 36 56 97 32 12 24 51 82 19 77 63 44 53 28 60 96 75 17 43
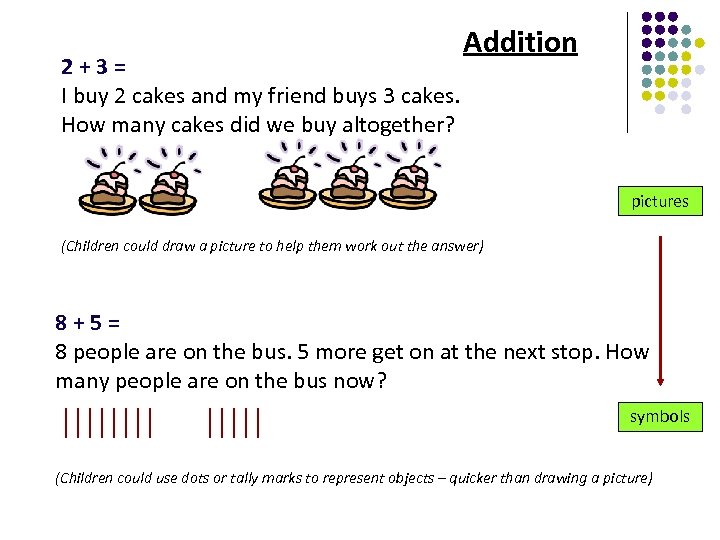
2+3= I buy 2 cakes and my friend buys 3 cakes. How many cakes did we buy altogether? Addition pictures (Children could draw a picture to help them work out the answer) 8 + 5 = 8 people are on the bus. 5 more get on at the next stop. How many people are on the bus now? symbols (Children could use dots or tally marks to represent objects – quicker than drawing a picture)
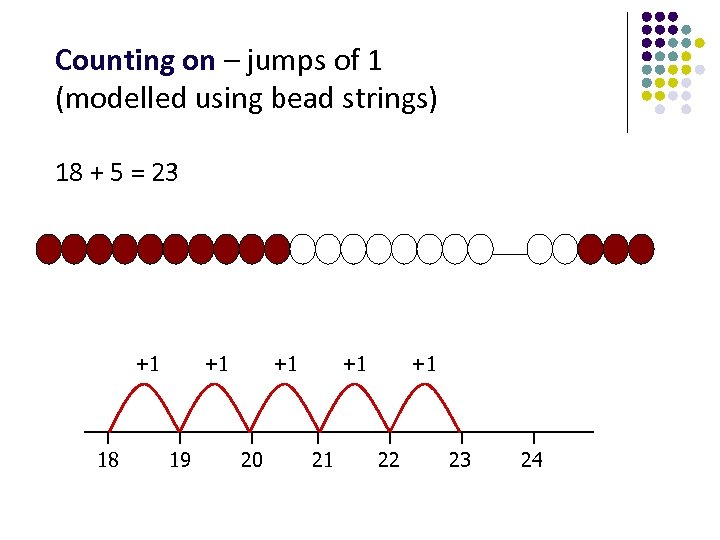
Counting on – jumps of 1 (modelled using bead strings) 18 + 5 = 23 +1 18 +1 19 +1 20 +1 21 +1 22 23 24
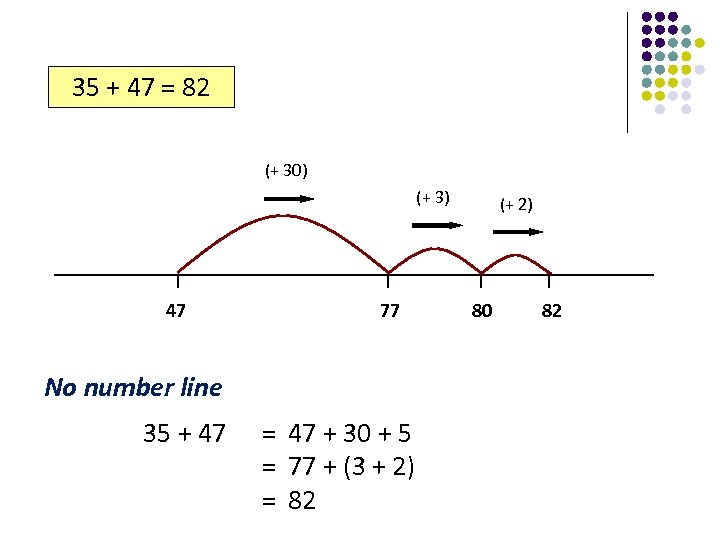
35 + 47 = 82 (+ 30) (+ 3) 47 77 No number line 35 + 47 = 47 + 30 + 5 = 77 + (3 + 2) = 82 (+ 2) 80 82

Addition by partitioning 374 + 248 300 + 200 = 500 70 + 40 = 110 4 + 8 = 12 622
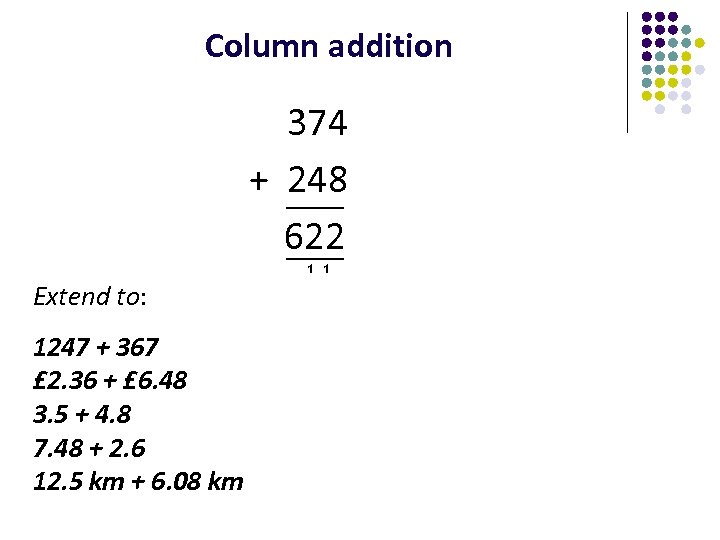
Column addition 374 + 248 622 1 1 Extend to: 1247 + 367 £ 2. 36 + £ 6. 48 3. 5 + 4. 8 7. 48 + 2. 6 12. 5 km + 6. 08 km
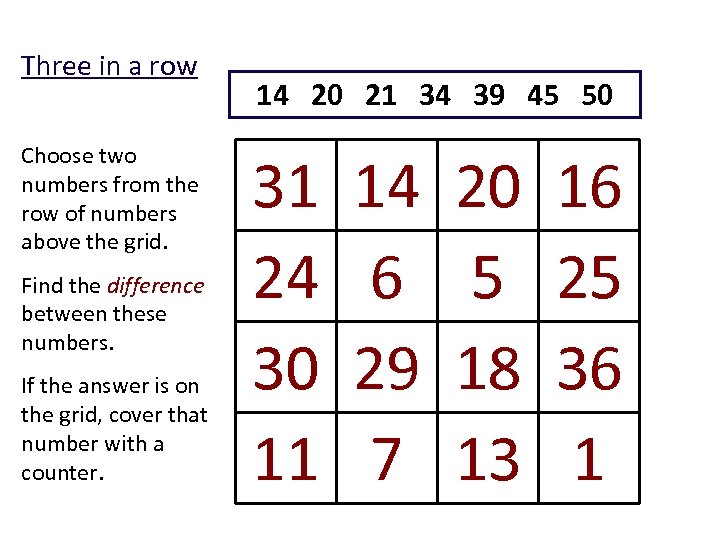
Three in a row Choose two numbers from the row of numbers above the grid. Find the difference between these numbers. If the answer is on the grid, cover that number with a counter. 14 20 21 34 39 45 50 31 24 30 11 14 6 29 7 20 5 18 13 16 25 36 1
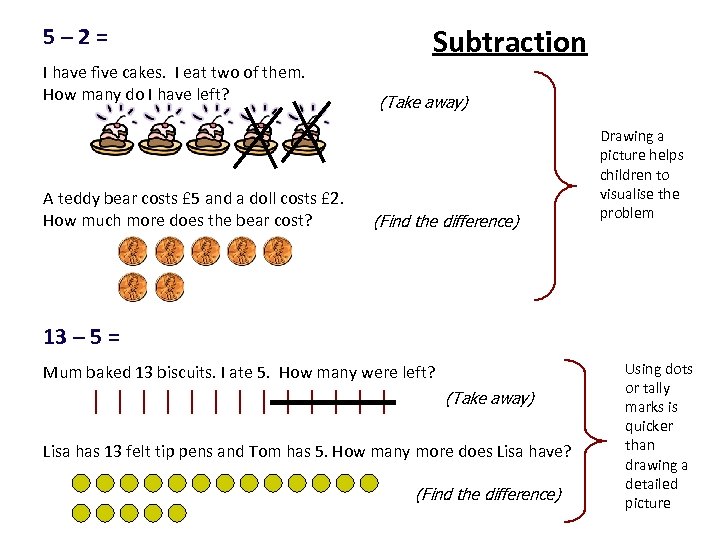
5– 2= Subtraction I have five cakes. I eat two of them. How many do I have left? (Take away) Drawing a picture helps children to visualise the A teddy bear costs £ 5 and a doll costs £ 2. problem How much more does the bear cost? (Find the difference) 13 – 5 = Mum baked 13 biscuits. I ate 5. How many were left? (Take away) Lisa has 13 felt tip pens and Tom has 5. How many more does Lisa have? (Find the difference) Using dots or tally marks is quicker than drawing a detailed picture
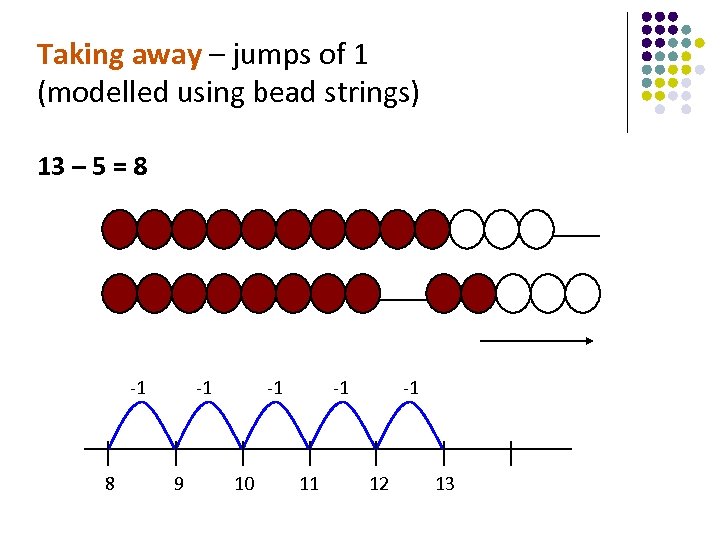
Taking away – jumps of 1 (modelled using bead strings) 13 – 5 = 8 -1 -1 -1 8 9 10 11 12 13
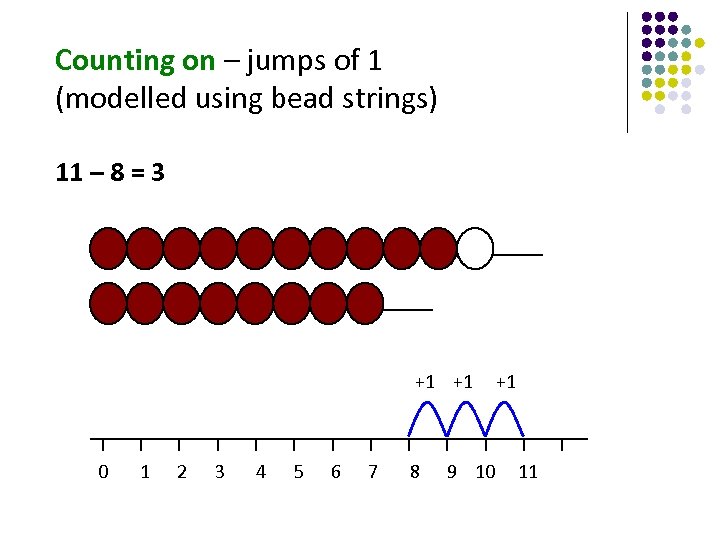
Counting on – jumps of 1 (modelled using bead strings) 11 – 8 = 3 +1 +1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
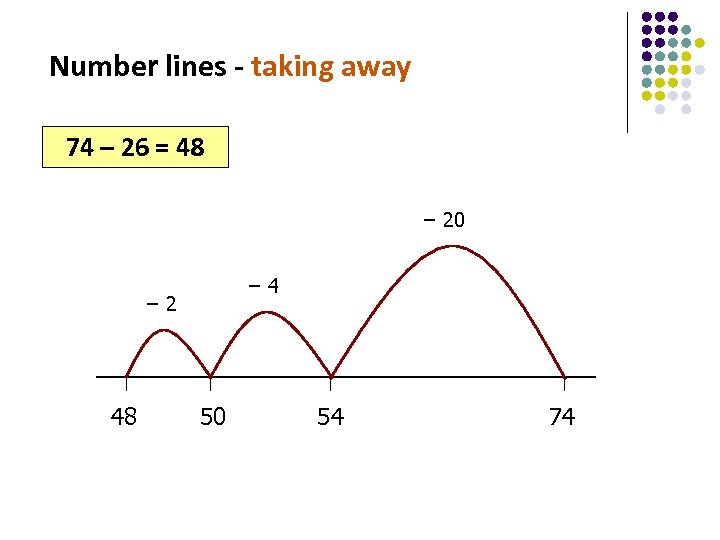
Number lines - taking away 74 – 26 = 48 − 20 − 4 − 2 48 50 54 74
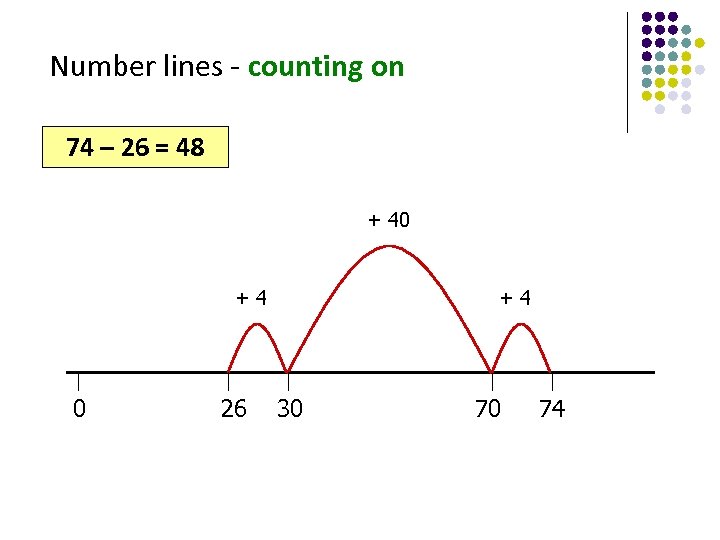
Number lines - counting on 74 – 26 = 48 + 40 +4 0 26 +4 30 70 74

Subtraction by partitioning 754 - 186 754 – 100 = 654 – 80 = 574 – 6 = 568
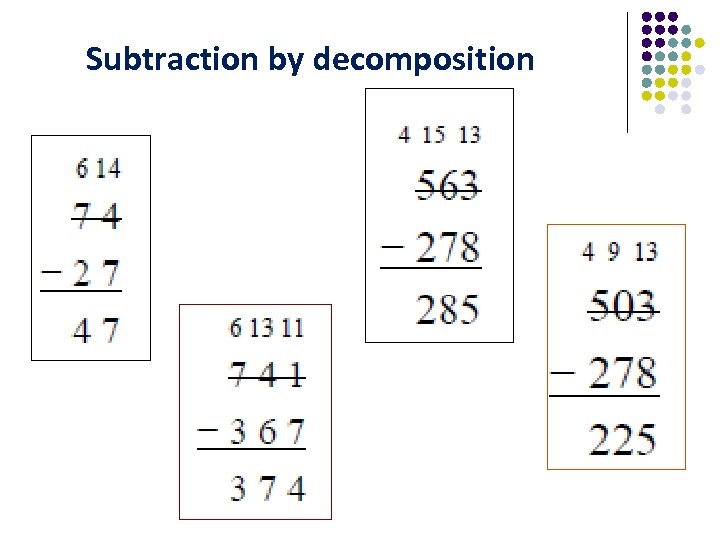
Subtraction by decomposition
53f0f755ecdb03c64bd7de0b3b7b8805.ppt