69af85bb6e176ce5dd0773b378314132.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

Adding Your Own IP to the OPB Bus This material exempt per Department of Commerce license exception TSU

Objectives After completing this module, you will be able to: • Understand basic OPB bus transactions • Differentiate between free and evaluation-based IP delivered in EDK • Identify the requirements for integrating your IP • List the steps involved in importing peripherals when using the wizard • Identify the limitations of creating peripherals with the wizard 2

Outline • OPB Bus • XPS Directory Structure • File Creation: MPD, PAO, BBD • IP Delivery in EDK • Creating/Importing Peripheral Wizard 3
Overview • The peripherals are connected to the microprocessor by using the data and address buses • Xilinx has implemented IBM's Core. Connect bus architecture • On-chip Peripheral Bus (OPB) version 2. 1 of the Core. Connect architecture is designed for easy connection of on-chip peripheral devices • Any custom peripheral that connects to the OPB bus must do the following: – Meet the principles of the OPB protocol – Meet the requirements of the Platform Generator • This allows you to take advantage of the simple automated flow that generates the system-level architecture
Features • Platform Generator supports the following features for OPB peripherals, and it is a subset of the OPB v 2. 1 features – Fully synchronous single-clock edge – 32 -bit address bus, 32 -bit data bus – Single-cycle transfer of data between the OPB master and the – – OPB slave Supports master byte enables Supports slave timeout suppress Supports slave retry No three-state drivers required • Note that the dynamic bus sizing feature is not supported in OPB v 2. 1
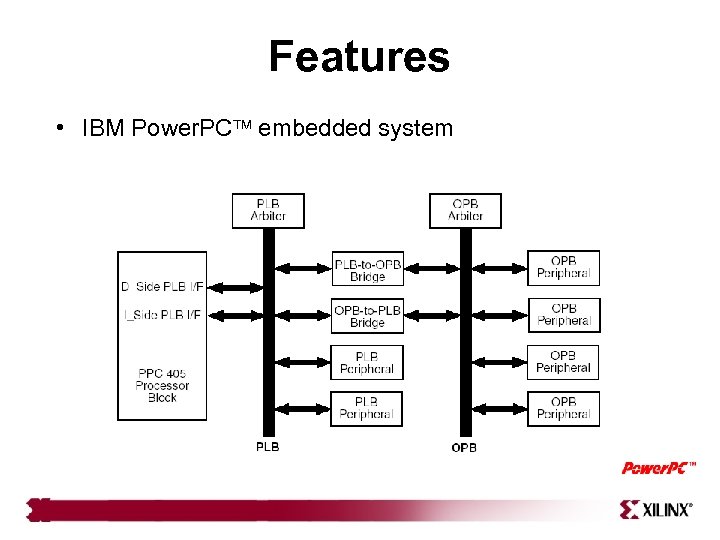
Features • IBM Power. PC embedded system
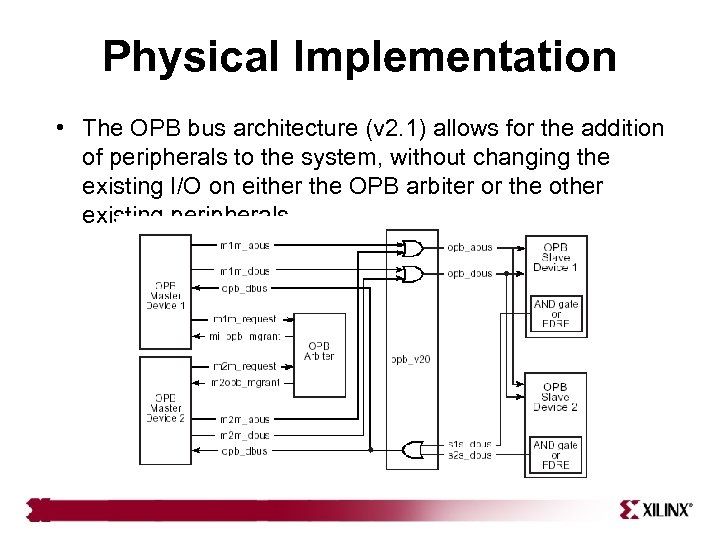
Physical Implementation • The OPB bus architecture (v 2. 1) allows for the addition of peripherals to the system, without changing the existing I/O on either the OPB arbiter or the other existing peripherals
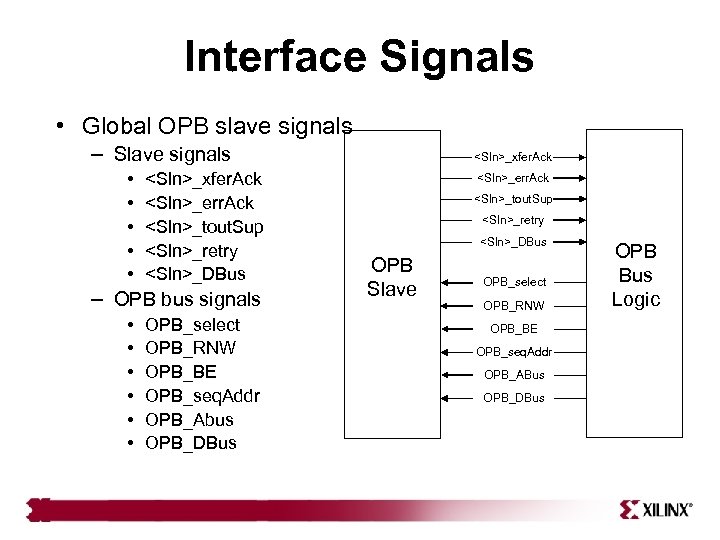
Interface Signals • Global OPB slave signals – Slave signals • <Sln>_xfer. Ack • <Sln>_err. Ack • <Sln>_tout. Sup • <Sln>_retry • <Sln>_DBus – OPB bus signals • OPB_select • OPB_RNW • OPB_BE • OPB_seq. Addr • OPB_Abus • OPB_DBus <Sln>_xfer. Ack <Sln>_err. Ack <Sln>_tout. Sup <Sln>_retry <Sln>_DBus OPB Slave OPB_select OPB_RNW OPB_BE OPB_seq. Addr OPB_ABus OPB_DBus OPB Bus Logic
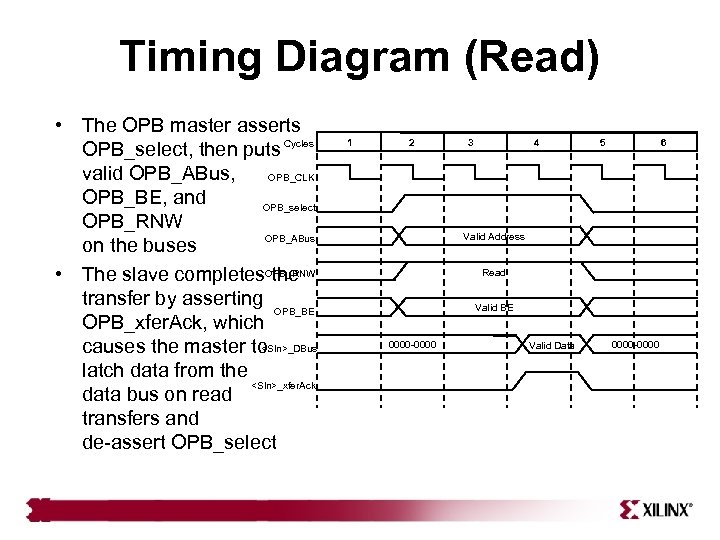
Timing Diagram (Read) • The OPB master asserts OPB_select, then puts Cycles valid OPB_ABus, OPB_CLK OPB_BE, and OPB_select OPB_RNW OPB_ABus on the buses • The slave completes. OPB_RNW the transfer by asserting OPB_BE OPB_xfer. Ack, which <Sln>_DBus causes the master to latch data from the <Sln>_xfer. Ack data bus on read transfers and de-assert OPB_select 1 2 3 4 5 6 Valid Address Read Valid BE 0000 -0000 Valid Data 0000 -0000
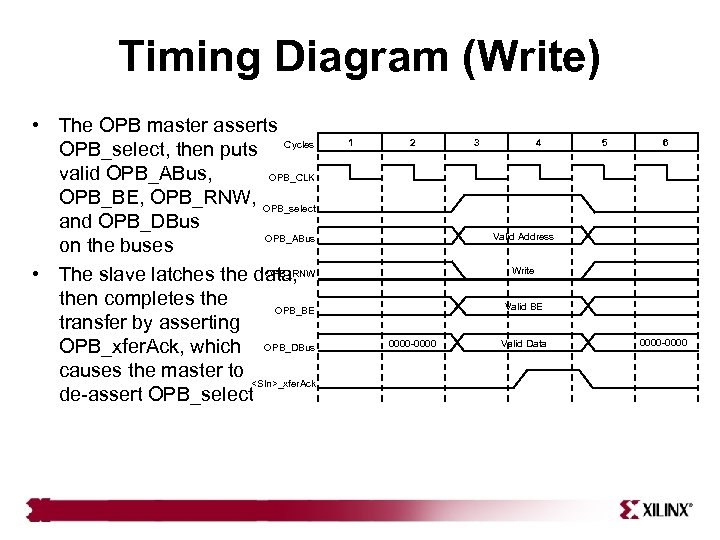
Timing Diagram (Write) • The OPB master asserts OPB_select, then puts Cycles valid OPB_ABus, OPB_CLK OPB_BE, OPB_RNW, OPB_select and OPB_DBus OPB_ABus on the buses OPB_RNW • The slave latches the data, then completes the OPB_BE transfer by asserting OPB_xfer. Ack, which OPB_DBus causes the master to <Sln>_xfer. Ack de-assert OPB_select 1 2 3 4 5 6 Valid Address Write Valid BE 0000 -0000 Valid Data 0000 -0000
Outline • OPB Bus • XPS Directory Structure • File Creation: MPD, PAO, BBD • IP Delivery in EDK • Creating/Importing Peripheral Wizard 11
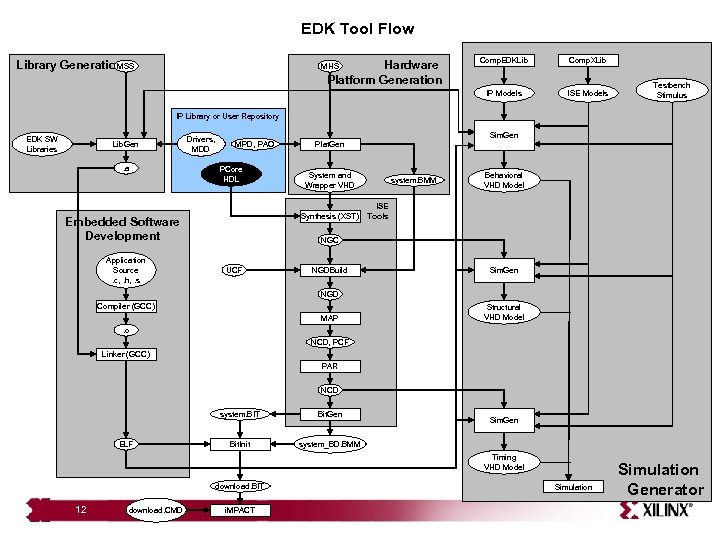
EDK Tool Flow Hardware Platform Generation MHS Comp. EDKLib Comp. XLib IP Models MSS Library Generation ISE Models Testbench Stimulus IP Library or User Repository EDK SW Libraries Lib. Gen. a Drivers, MDD Sim. Gen MPD, PAO PCore HDL System and Wrapper VHD Synthesis (XST) Embedded Software Development Application Source. c, . h, . s Plat. Gen system. BMM Behavioral VHD Model ISE Tools NGC UCF NGDBuild Sim. Gen NGD Compiler (GCC) MAP Structural VHD Model . o NCD, PCF Linker (GCC) PAR NCD system. BIT ELF Bit. Gen Bit. Init system_BD. BMM Sim. Gen Timing VHD Model download. BIT 12 download. CMD i. MPACT Simulation Generator
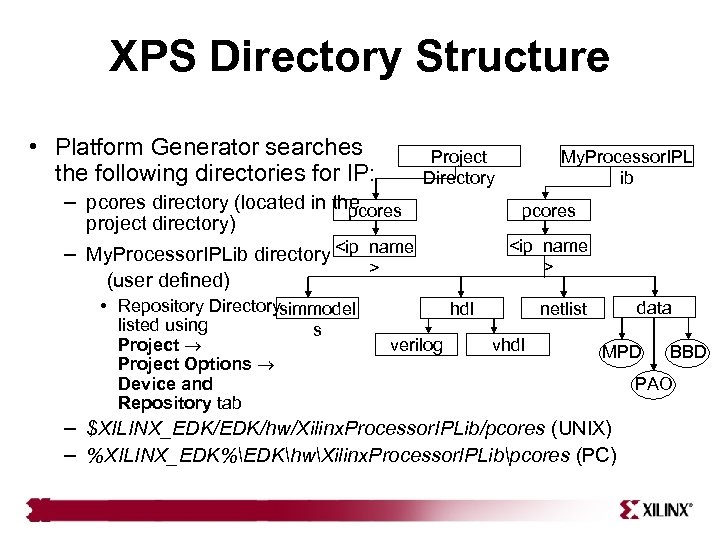
XPS Directory Structure • Platform Generator searches Project Directory the following directories for IP: – pcores directory (located in the pcores project directory) <ip_name > – My. Processor. IPLib directory <ip_name (user defined) • Repository Directorysimmodel listed using Project Options Device and Repository tab s My. Processor. IPL ib > hdl verilog data netlist vhdl MPD – $XILINX_EDK/hw/Xilinx. Processor. IPLib/pcores (UNIX) – %XILINX_EDK%EDKhwXilinx. Processor. IPLibpcores (PC) BBD PAO
Outline • OPB Bus • OPB User Core • • 14 Templates XPS Directory Structure File Creation: MPD, PAO, BBD IP Delivery in EDK Creating/Importing Peripheral Wizard
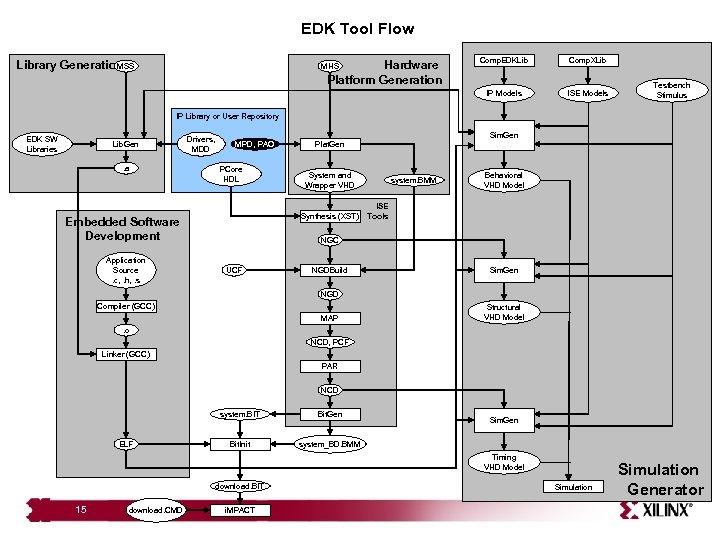
EDK Tool Flow Hardware Platform Generation MHS Comp. EDKLib Comp. XLib IP Models MSS Library Generation ISE Models Testbench Stimulus IP Library or User Repository EDK SW Libraries Lib. Gen. a Drivers, MDD Sim. Gen MPD, PAO PCore HDL System and Wrapper VHD Synthesis (XST) Embedded Software Development Application Source. c, . h, . s Plat. Gen system. BMM Behavioral VHD Model ISE Tools NGC UCF NGDBuild Sim. Gen NGD Compiler (GCC) MAP Structural VHD Model . o NCD, PCF Linker (GCC) PAR NCD system. BIT ELF Bit. Gen Bit. Init system_BD. BMM Sim. Gen Timing VHD Model download. BIT 15 download. CMD i. MPACT Simulation Generator
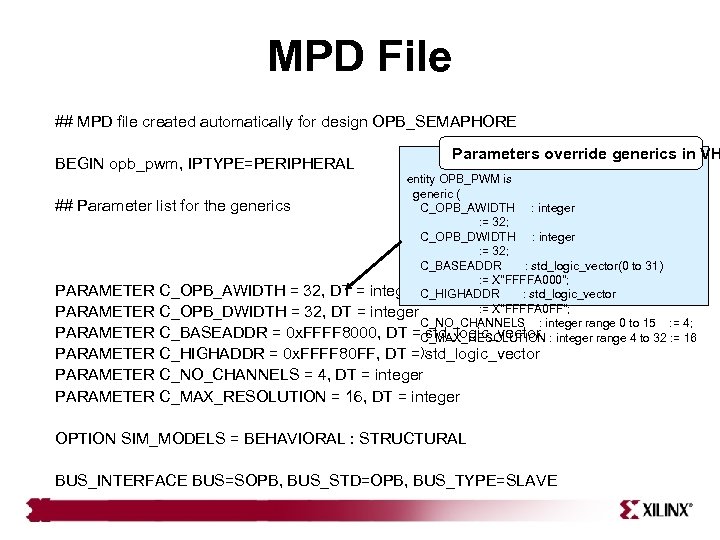
MPD File ## MPD file created automatically for design OPB_SEMAPHORE BEGIN opb_pwm, IPTYPE=PERIPHERAL Parameters override generics in VH entity OPB_PWM is generic ( ## Parameter list for the generics C_OPB_AWIDTH : integer : = 32; C_OPB_DWIDTH : integer : = 32; C_BASEADDR : std_logic_vector(0 to 31) : = X"FFFFA 000"; PARAMETER C_OPB_AWIDTH = 32, DT = integer C_HIGHADDR : std_logic_vector : = X"FFFFA 0 FF"; PARAMETER C_OPB_DWIDTH = 32, DT = integer C_NO_CHANNELS : integer range 0 to 15 : = 4; PARAMETER C_BASEADDR = 0 x. FFFF 8000, DT =C_MAX_RESOLUTION : integer range 4 to 32 : = 16 std_logic_vector PARAMETER C_HIGHADDR = 0 x. FFFF 80 FF, DT =); std_logic_vector PARAMETER C_NO_CHANNELS = 4, DT = integer PARAMETER C_MAX_RESOLUTION = 16, DT = integer OPTION SIM_MODELS = BEHAVIORAL : STRUCTURAL BUS_INTERFACE BUS=SOPB, BUS_STD=OPB, BUS_TYPE=SLAVE
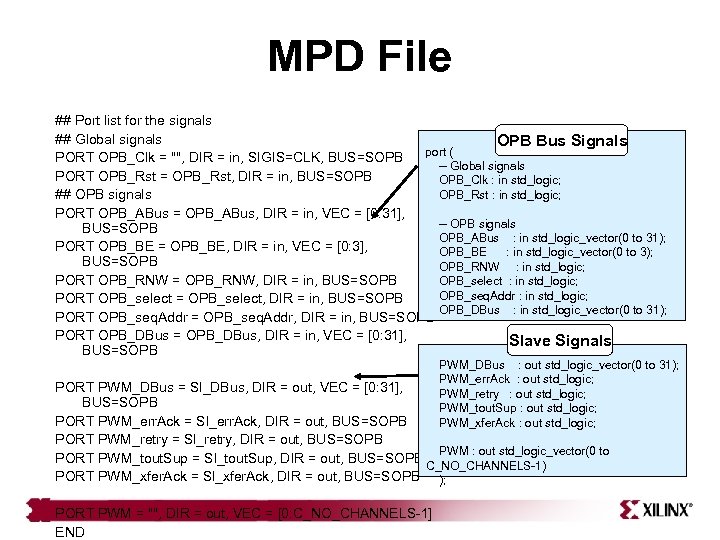
MPD File ## Port list for the signals ## Global signals OPB Bus Signals port ( PORT OPB_Clk = "", DIR = in, SIGIS=CLK, BUS=SOPB -- Global signals PORT OPB_Rst = OPB_Rst, DIR = in, BUS=SOPB OPB_Clk : in std_logic; OPB_Rst : in std_logic; ## OPB signals PORT OPB_ABus = OPB_ABus, DIR = in, VEC = [0: 31], -- OPB signals BUS=SOPB OPB_ABus : in std_logic_vector(0 to 31); PORT OPB_BE = OPB_BE, DIR = in, VEC = [0: 3], OPB_BE : in std_logic_vector(0 to 3); BUS=SOPB OPB_RNW : in std_logic; PORT OPB_RNW = OPB_RNW, DIR = in, BUS=SOPB OPB_select : in std_logic; OPB_seq. Addr : in std_logic; PORT OPB_select = OPB_select, DIR = in, BUS=SOPB OPB_DBus : in std_logic_vector(0 to 31); PORT OPB_seq. Addr = OPB_seq. Addr, DIR = in, BUS=SOPB PORT OPB_DBus = OPB_DBus, DIR = in, VEC = [0: 31], Slave Signals BUS=SOPB PWM_DBus : out std_logic_vector(0 to 31); PWM_err. Ack : out std_logic; PWM_retry : out std_logic; PWM_tout. Sup : out std_logic; PWM_xfer. Ack : out std_logic; PORT PWM_DBus = Sl_DBus, DIR = out, VEC = [0: 31], BUS=SOPB PORT PWM_err. Ack = Sl_err. Ack, DIR = out, BUS=SOPB PORT PWM_retry = Sl_retry, DIR = out, BUS=SOPB PWM : out std_logic_vector(0 to PORT PWM_tout. Sup = Sl_tout. Sup, DIR = out, BUS=SOPB C_NO_CHANNELS-1) PORT PWM_xfer. Ack = Sl_xfer. Ack, DIR = out, BUS=SOPB ); PORT PWM = "", DIR = out, VEC = [0: C_NO_CHANNELS-1] END
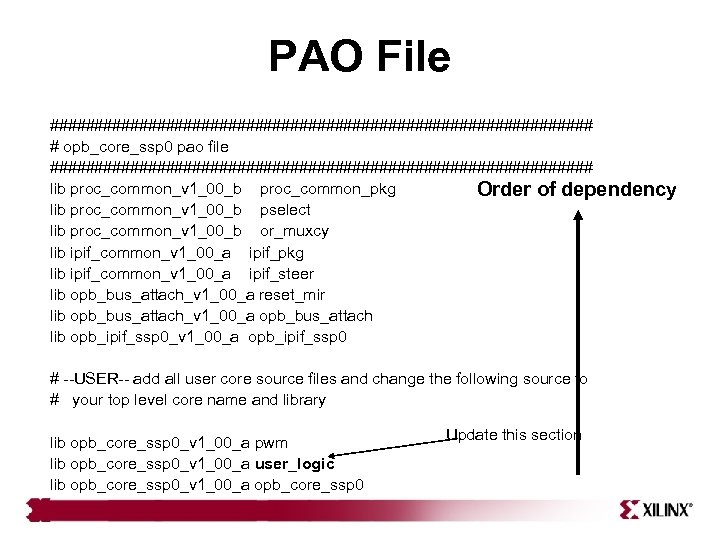
PAO File ############################### # opb_core_ssp 0 pao file ############################### lib proc_common_v 1_00_b proc_common_pkg Order of dependency lib proc_common_v 1_00_b pselect lib proc_common_v 1_00_b or_muxcy lib ipif_common_v 1_00_a ipif_pkg lib ipif_common_v 1_00_a ipif_steer lib opb_bus_attach_v 1_00_a reset_mir lib opb_bus_attach_v 1_00_a opb_bus_attach lib opb_ipif_ssp 0_v 1_00_a opb_ipif_ssp 0 # --USER-- add all user core source files and change the following source to # your top level core name and library lib opb_core_ssp 0_v 1_00_a pwm lib opb_core_ssp 0_v 1_00_a user_logic lib opb_core_ssp 0_v 1_00_a opb_core_ssp 0 Update this section
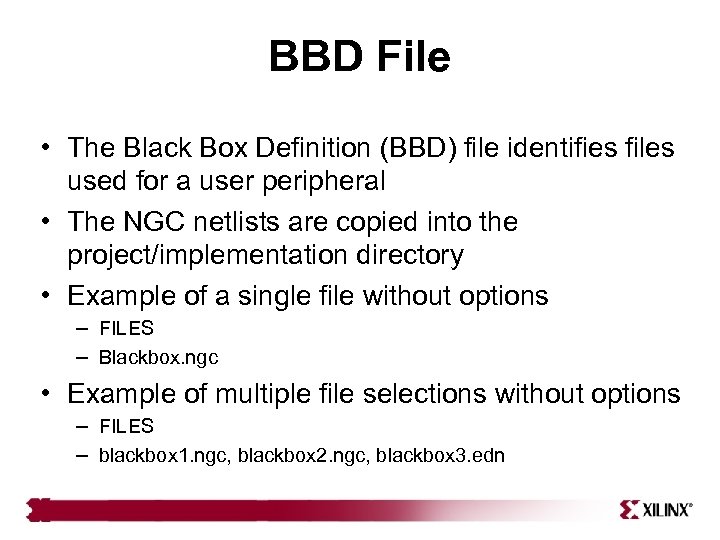
BBD File • The Black Box Definition (BBD) file identifies files used for a user peripheral • The NGC netlists are copied into the project/implementation directory • Example of a single file without options – FILES – Blackbox. ngc • Example of multiple file selections without options – FILES – blackbox 1. ngc, blackbox 2. ngc, blackbox 3. edn
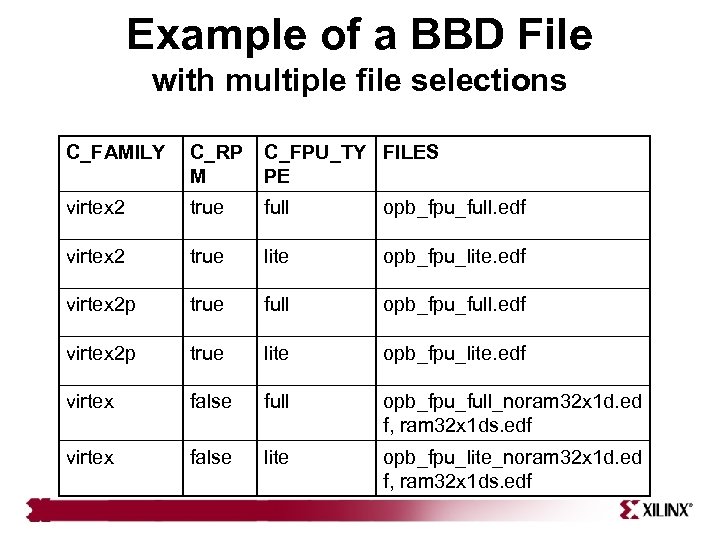
Example of a BBD File with multiple file selections C_FAMILY C_RP M C_FPU_TY FILES PE virtex 2 true full opb_fpu_full. edf virtex 2 true lite opb_fpu_lite. edf virtex 2 p true full opb_fpu_full. edf virtex 2 p true lite opb_fpu_lite. edf virtex false full opb_fpu_full_noram 32 x 1 d. ed f, ram 32 x 1 ds. edf virtex false lite opb_fpu_lite_noram 32 x 1 d. ed f, ram 32 x 1 ds. edf
File Usage • There are two ways to integrate your own IP into XPS – As a blackbox • Synthesized with XST or a third-party synthesis tool • Requires MPD and BBD – As HDL • Synthesized with the rest of the processor system • Uses XST • Requires MPD and PAO
Outline • OPB Bus • OPB User Core • • 22 Templates XPS Directory Structure File Creation: MPD, PAO, BBD IP Delivery in EDK Creating/Importing Peripheral Wizard
IP Peripherals • Xilinx has created a wide variety of IP cores: – Bus infrastructure cores • PLB 2 OPB bridge • PLB – Memory interface cores • PLB block RAM • PLB Double Data Rate (DDR) Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) controller – Peripherals • OPB Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) • Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) – User core template • OPB slave attachment • OPB master attachment
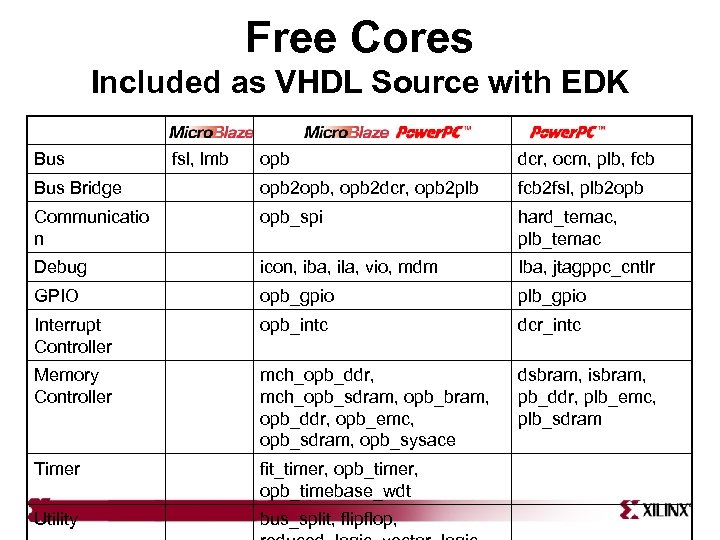
Free Cores Included as VHDL Source with EDK Bus fsl, lmb opb dcr, ocm, plb, fcb Bus Bridge opb 2 opb, opb 2 dcr, opb 2 plb fcb 2 fsl, plb 2 opb Communicatio n opb_spi hard_temac, plb_temac Debug icon, iba, ila, vio, mdm Iba, jtagppc_cntlr GPIO opb_gpio plb_gpio Interrupt Controller opb_intc dcr_intc Memory Controller mch_opb_ddr, mch_opb_sdram, opb_bram, opb_ddr, opb_emc, opb_sdram, opb_sysace dsbram, isbram, pb_ddr, plb_emc, plb_sdram Timer fit_timer, opb_timebase_wdt Utility bus_split, flipflop,
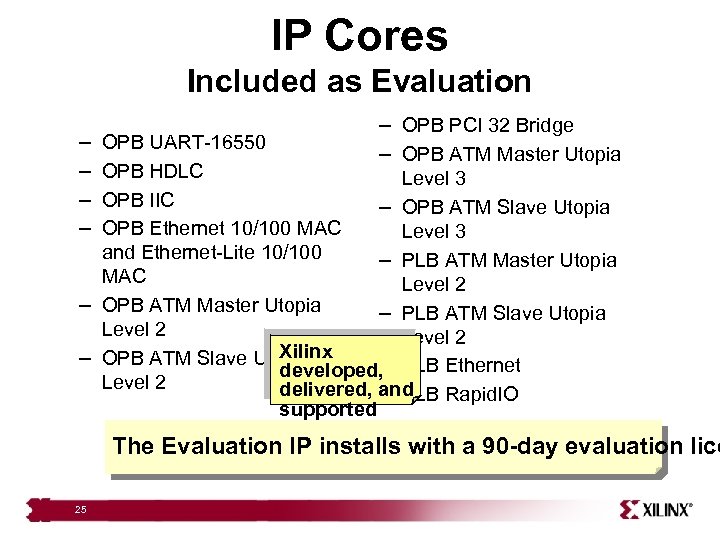
IP Cores Included as Evaluation – – – OPB PCI 32 Bridge – OPB ATM Master Utopia OPB UART-16550 OPB HDLC Level 3 OPB IIC – OPB ATM Slave Utopia OPB Ethernet 10/100 MAC Level 3 and Ethernet-Lite 10/100 – PLB ATM Master Utopia MAC Level 2 – OPB ATM Master Utopia – PLB ATM Slave Utopia Level 2 Xilinx – OPB ATM Slave Utopia – developed, PLB Ethernet Level 2 delivered, and – PLB Rapid. IO supported The Evaluation IP installs with a 90 -day evaluation lice 25
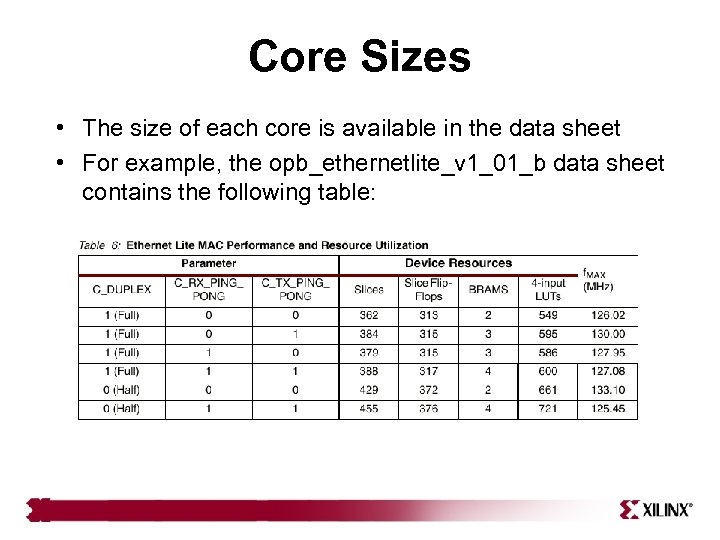
Core Sizes • The size of each core is available in the data sheet • For example, the opb_ethernetlite_v 1_01_b data sheet contains the following table:
Processor System Size • The Processor IP Calculator is an online tool that helps you easily estimate the processor IP core size usage • www. support. xilinx. com/i pcenter/processor_centr al/ppcip/calc. htm • Try it out!!
Outline • OPB Bus • OPB User Core • • 28 Templates XPS Directory Structure File Creation: MPD, PAO, BBD IP Delivery in EDK Create/Import Peripheral Wizard

Create/Import Peripheral Wizard • The wizard helps you create your own peripheral and then import it into your design • The wizard will generate the necessary core description files into the user selected directory • You can start the wizard after creating a new project or opening an existing project in XPS • The user peripheral can be imported directly through the wizard by skipping the creation option – Ensure that the peripheral complies with Xilinx 29 implementation of the IBM Core. Connect Bus Standard

Starting the IP Wizard The Create and Import Peripheral Wizard can be started after creating a project and using Hardware Create or Import Peripheral … or opening an existing project or using Start Programs Xilinx Platform Studio 8. 2 i Accessories Create and Import Peripheral Wizard 30

Creating a Peripheral 1 Select Create Peripheral flow 2 Select the target directory – project directory or user repository The project directory assigned as the target directory will allow the peripheral to be available to the project without importing it. User repository will allow multiple projects to access the same peripheral by importing it in a project 31
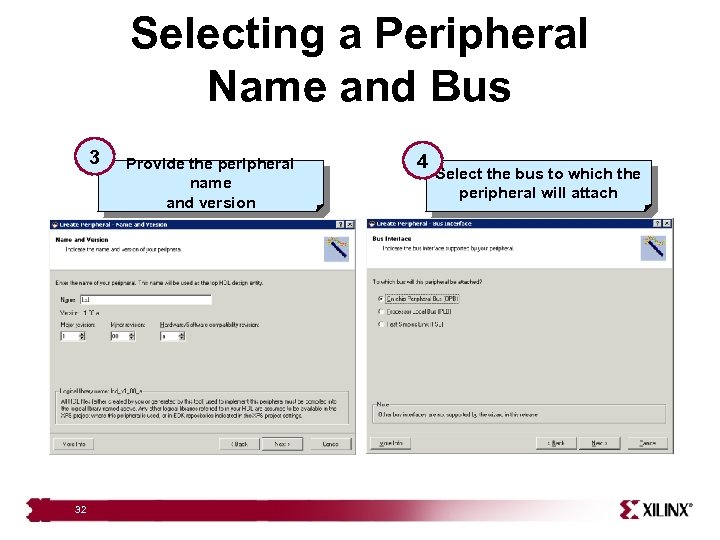
Selecting a Peripheral Name and Bus 3 32 Provide the peripheral name and version 4 Select the bus to which the peripheral will attach
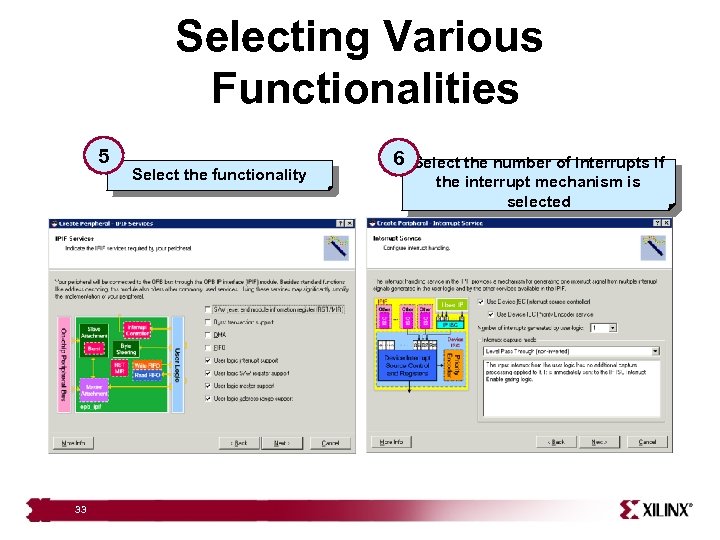
Selecting Various Functionalities 5 33 Select the functionality 6 Select the number of interrupts if the interrupt mechanism is selected
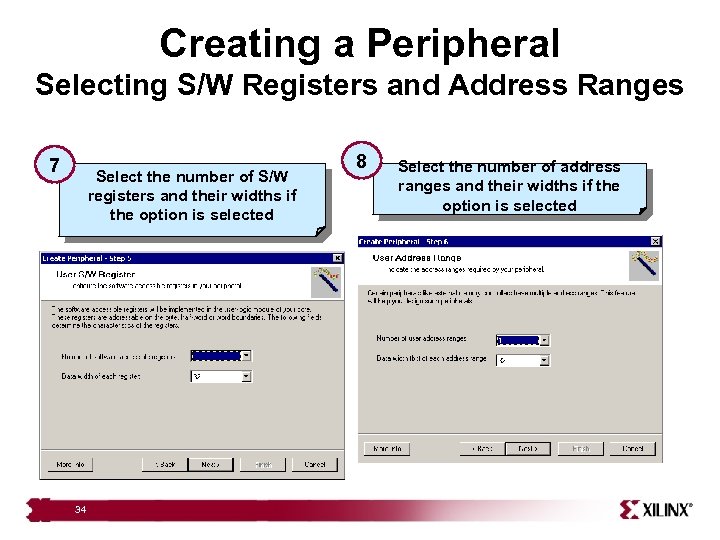
Creating a Peripheral Selecting S/W Registers and Address Ranges 7 Select the number of S/W registers and their widths if the option is selected 34 8 Select the number of address ranges and their widths if the option is selected
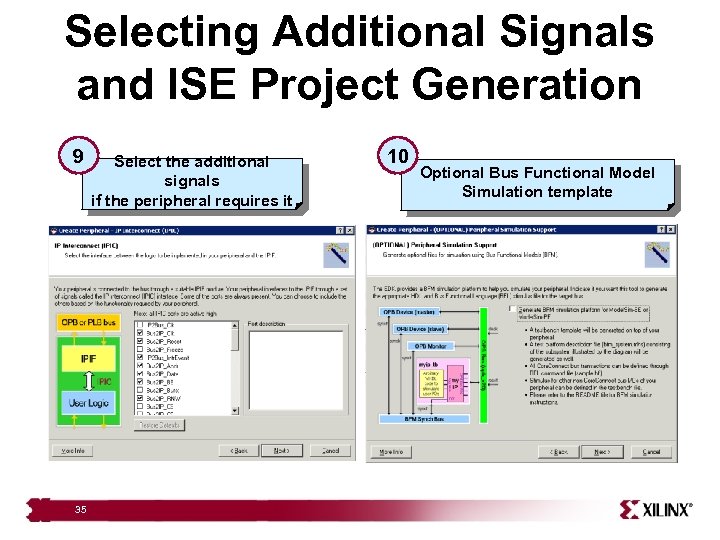
Selecting Additional Signals and ISE Project Generation 9 35 Select the additional signals if the peripheral requires it 10 Optional Bus Functional Model Simulation template

Selecting Additional Signals and ISE Project Generation 11 Optional Implementation Tools support 12 Finish Since the project directory was assigned as the target directory the peripheral will appear in the IP Catalog under Project Repository folder 36
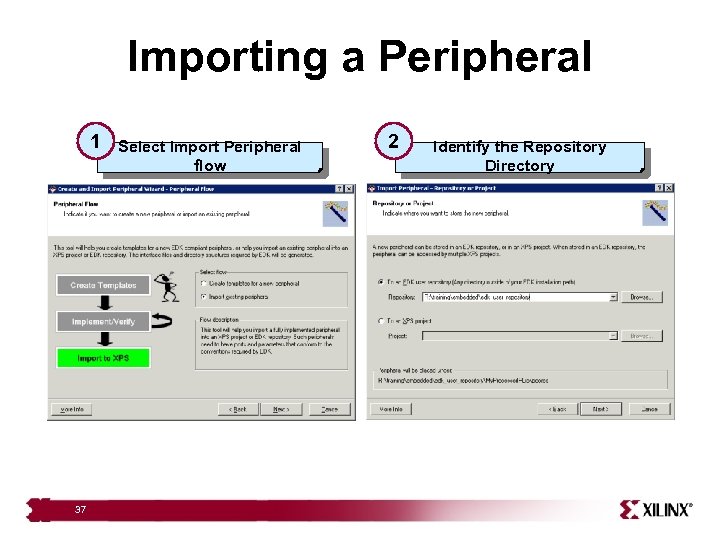
Importing a Peripheral 1 37 Select Import Peripheral flow 2 Identify the Repository Directory
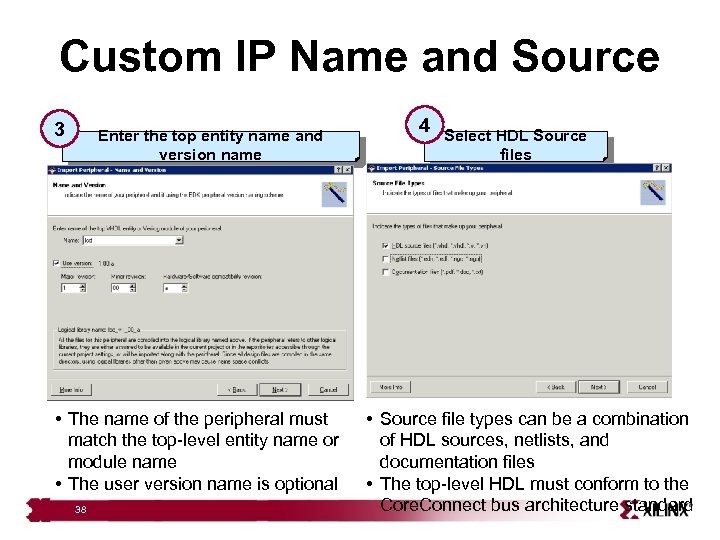
Custom IP Name and Source 3 Enter the top entity name and version name • The name of the peripheral must match the top-level entity name or module name • The user version name is optional 38 4 Select HDL Source files • Source file types can be a combination of HDL sources, netlists, and documentation files • The top-level HDL must conform to the Core. Connect bus architecture standard
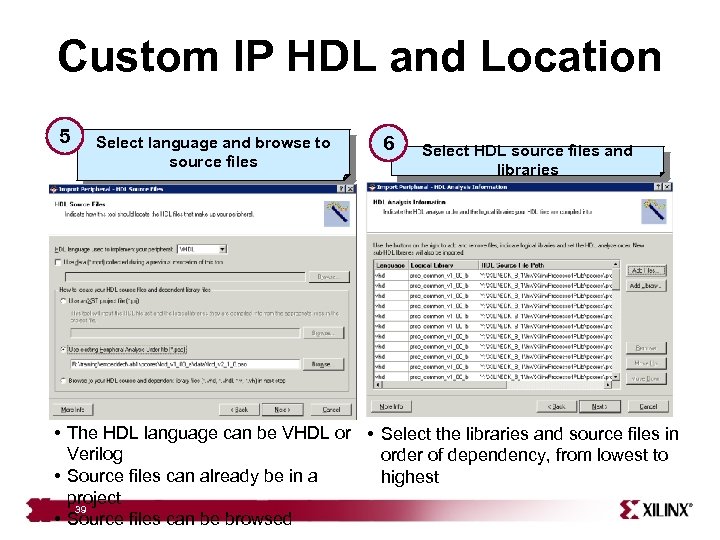
Custom IP HDL and Location 5 Select language and browse to source files 6 Select HDL source files and libraries • The HDL language can be VHDL or • Select the libraries and source files in Verilog order of dependency, from lowest to • Source files can already be in a highest project 39 • Source files can be browsed
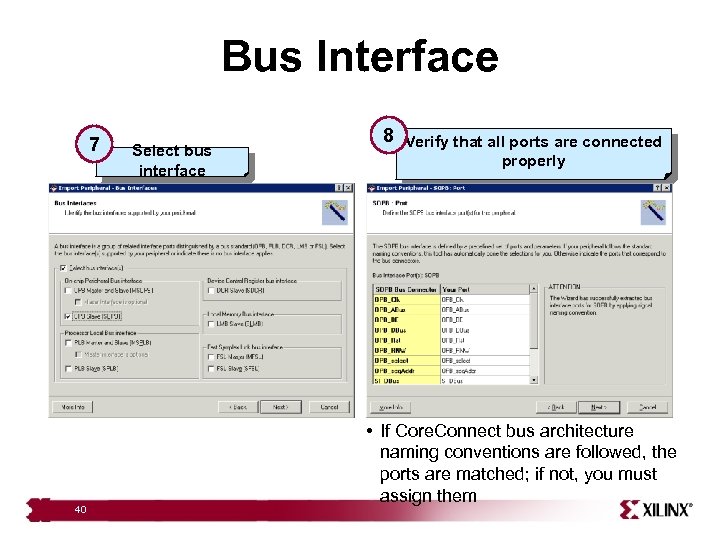
Bus Interface 7 40 Select bus interface 8 Verify that all ports are connected properly • If Core. Connect bus architecture naming conventions are followed, the ports are matched; if not, you must assign them

Interrupt Source 9 41 Verify the bus information 10 Select source and any type of interrupt • Select interrupting signal source, type (level versus edge), and polarity • This will be presented only if interrupt present
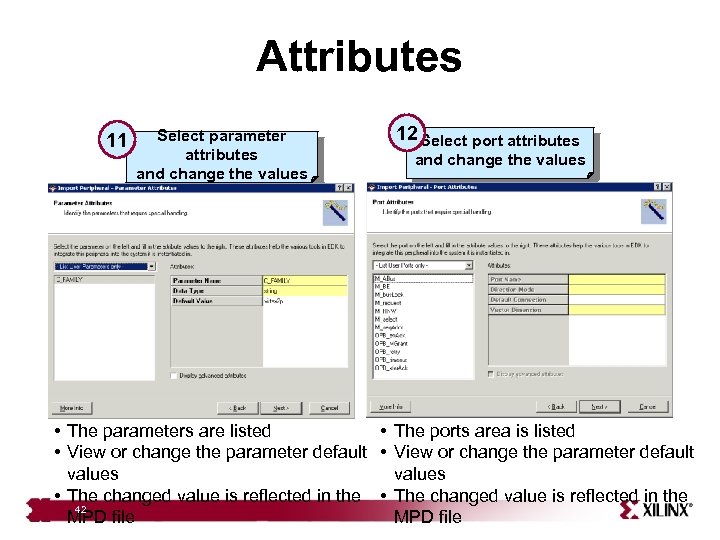
Attributes 11 Select parameter attributes and change the values 12 Select port attributes and change the values • The parameters are listed • The ports area is listed • View or change the parameter default values • The changed value is reflected in the 42 MPD file

Generating Custom IP • If the netlist and documentation files were selected earlier, the corresponding GUI displays, requesting their locations • If not, the Finished GUI displays • If the save box is checked, the previously generated files will also be saved The peripheral will appear under the Peripheral or Project Repository folder in the IP Catalog 43

Review Questions • What is the process for creating a peripheral of custom IP in XPS? • What is the process for importing a piece of custom IP into XPS? • If you are using a third-party synthesis tool to compile your IP, what files are required to integrate that IP into XPS? 45

Answers • What is the process for creating a peripheral of custom IP in XPS? – – – – – 46 Start the Create and Import Wizard tool from XPS Select the Create templates for a new peripheral option Identify the destination directory location Select the bus interface Select functionality and any interrupts Define any software registers and address ranges Add additional signals which the peripheral may be using Generate the files Add user logic in user_logic. vhd

Answers • What is the process for incorporating a piece of custom IP into XPS – Develop your custom IP by using any combination of HDL, netlist, or libraries • Make sure that the top-level file conforms to Core. Connect requirements – Start the Importing IP Wizard tool from XPS – Identify location of libraries, netlists, and source files in the order of dependency – Select the bus interface – Select the source and type of the interrupt, if any • If you are using a third-party synthesis tool to compile your IP, what files are required to integrate that IP into XPS? 47 – MPD and BBD

Where Can I Learn More? • Tool documentation – Platform Specification Format Reference Manual – Processor IP Reference Guide – Embedded System Tools Guide Create/Import Peripheral Wizard – Embedded System Tools Guide Microprocessor Peripheral Description – Embedded System Tools Guide Peripheral Analyze Order – Xilinx Drivers • Support website – EDK Home Page: support. xilinx. com/edk
69af85bb6e176ce5dd0773b378314132.ppt