5337ac64d1a203e28dbda6b359e5072a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Adding Value to the Data Warehouse: Utilizing OLAP Technology and Analytical Applications January 16, 2003 Mark Max, Managing Partner All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Adding Value to the Data Warehouse: Utilizing OLAP Technology and Analytical Applications January 16, 2003 Mark Max, Managing Partner All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Mark Max Bio email: mmax@istrategyconsulting. com • B. S. Accounting & M. S. Business – University of Maryland • University of Maryland, Instructor • 20 years Consulting, Corporate, Software Vendor Work Experience • Started i. Strategy Consulting in 1999 – Maryland based consulting firm specializing in Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing – Principals have been working in BI for 15+ years – Experience in BI/DW for higher education – Launching new DW/Analytical Application for Higher Education in Q 1 2003
Mark Max Bio email: mmax@istrategyconsulting. com • B. S. Accounting & M. S. Business – University of Maryland • University of Maryland, Instructor • 20 years Consulting, Corporate, Software Vendor Work Experience • Started i. Strategy Consulting in 1999 – Maryland based consulting firm specializing in Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing – Principals have been working in BI for 15+ years – Experience in BI/DW for higher education – Launching new DW/Analytical Application for Higher Education in Q 1 2003
 Discussion Points 1. Information Delivery Challenges 2. Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence Technology 3. Higher Education Analytical Application Framework 4. Demonstration 5. Q&A All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Discussion Points 1. Information Delivery Challenges 2. Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence Technology 3. Higher Education Analytical Application Framework 4. Demonstration 5. Q&A All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Shift Towards Information Based Management – High Visibility Areas • • • Recruiting Effectiveness Retention Enrollment Funnel Student Demographics Course Planning Resource Management Outcomes Management Compliance Reporting Early Intervention Key Performance Indicators All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Shift Towards Information Based Management – High Visibility Areas • • • Recruiting Effectiveness Retention Enrollment Funnel Student Demographics Course Planning Resource Management Outcomes Management Compliance Reporting Early Intervention Key Performance Indicators All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Emerging Strategies in in Higher Education Strategic Enrollment Management (SEM) “Strategic Enrollment Management is a comprehensive process designed to achieve and maintain the optimum recruitment, retention, and graduation rates of students where ‘optimum’ is defined within the academic context of the institution”. Strategic Planning Engine (SPE) “The heart of the Strategic Planning Engine links strategic decision making with organizational key performance indicators (KPI's). ” from Michael G. Dolence & Associates These processes require information! All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Emerging Strategies in in Higher Education Strategic Enrollment Management (SEM) “Strategic Enrollment Management is a comprehensive process designed to achieve and maintain the optimum recruitment, retention, and graduation rates of students where ‘optimum’ is defined within the academic context of the institution”. Strategic Planning Engine (SPE) “The heart of the Strategic Planning Engine links strategic decision making with organizational key performance indicators (KPI's). ” from Michael G. Dolence & Associates These processes require information! All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Typical Reporting Challenges • Financials • Housing/ Judicial Human Resources • Student Admin • • Recruiting Alumni All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting • No central repository of official information – many non-integrated systems and databases Databases are structured for transaction processing, audit trail and operational needs; they are not organized for ease of reporting! Lack of standardized metrics and information rules (e. g. , how is retention % calculated? ) Some information needs require data from multiple systems (e. g. , Cost per Student) Many informal databases and spreadsheets used by individuals for reporting, analysis, external reporting No standardized tools for reporting and analysis
Typical Reporting Challenges • Financials • Housing/ Judicial Human Resources • Student Admin • • Recruiting Alumni All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting • No central repository of official information – many non-integrated systems and databases Databases are structured for transaction processing, audit trail and operational needs; they are not organized for ease of reporting! Lack of standardized metrics and information rules (e. g. , how is retention % calculated? ) Some information needs require data from multiple systems (e. g. , Cost per Student) Many informal databases and spreadsheets used by individuals for reporting, analysis, external reporting No standardized tools for reporting and analysis
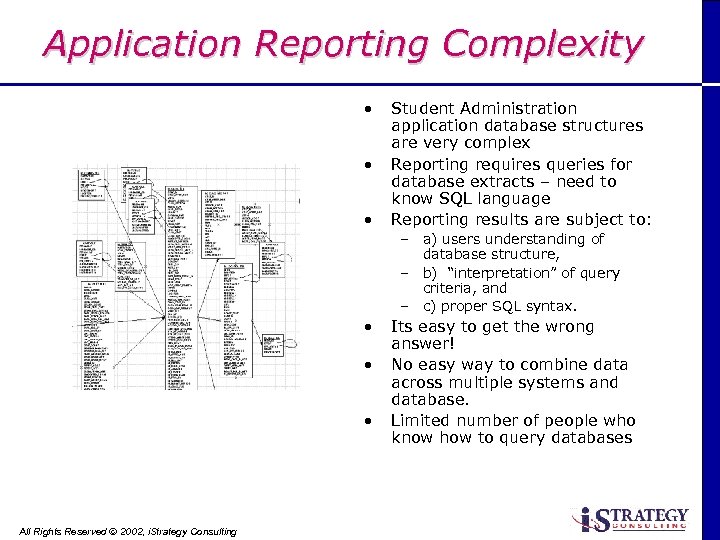 Application Reporting Complexity • • • Student Administration application database structures are very complex Reporting requires queries for database extracts – need to know SQL language Reporting results are subject to: – a) users understanding of database structure, – b) “interpretation” of query criteria, and – c) proper SQL syntax. • • • All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Its easy to get the wrong answer! No easy way to combine data across multiple systems and database. Limited number of people who know how to query databases
Application Reporting Complexity • • • Student Administration application database structures are very complex Reporting requires queries for database extracts – need to know SQL language Reporting results are subject to: – a) users understanding of database structure, – b) “interpretation” of query criteria, and – c) proper SQL syntax. • • • All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Its easy to get the wrong answer! No easy way to combine data across multiple systems and database. Limited number of people who know how to query databases
 The Impact • No ability for self service access to information – users are totally dependent upon others to produce information • Time consuming, manually intensive process to produce reports • Different people produce reports with the same information but have different results – What is the real answer? – How do you know the information is correct? • Have to repeat the same time consuming process each time you want a report • No time available for analysis because of the extensive time required to produce information All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
The Impact • No ability for self service access to information – users are totally dependent upon others to produce information • Time consuming, manually intensive process to produce reports • Different people produce reports with the same information but have different results – What is the real answer? – How do you know the information is correct? • Have to repeat the same time consuming process each time you want a report • No time available for analysis because of the extensive time required to produce information All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
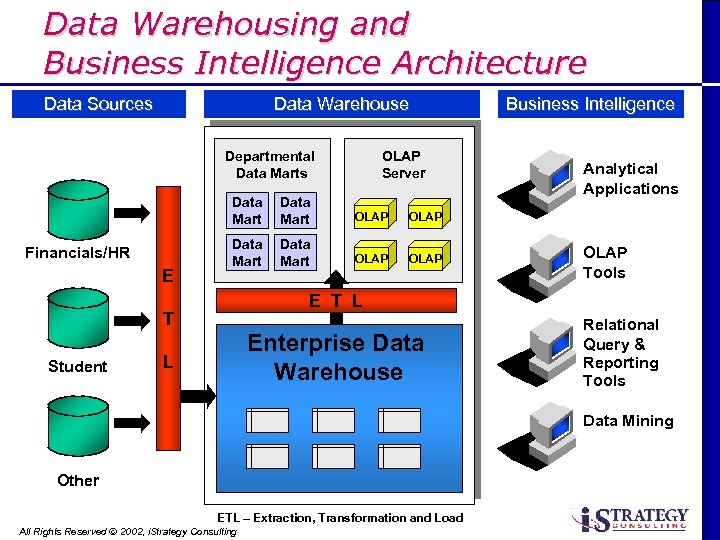 Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence Architecture Data Sources Data Warehouse Business Intelligence Data/Application Servers Departmental Data Marts OLAP Server Data Mart Financials/HR E Data Mart OLAP OLAP Tools E T L T Student Analytical Applications Enterprise Data Warehouse L Relational Query & Reporting Tools Data Mining Other ETL – Extraction, Transformation and Load All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence Architecture Data Sources Data Warehouse Business Intelligence Data/Application Servers Departmental Data Marts OLAP Server Data Mart Financials/HR E Data Mart OLAP OLAP Tools E T L T Student Analytical Applications Enterprise Data Warehouse L Relational Query & Reporting Tools Data Mining Other ETL – Extraction, Transformation and Load All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 2002 Higher Education ERP Survey • 39% of institutions surveyed have implemented or are in the process of implementing a Data Warehouse • 37% of institutions surveyed plan to implement a Data Warehouse within the next three years, with almost 1/3 of the projects beginning in 2003 Source: The Promise and Performance of Enterprise Systems, 2002 ECARS Research Study by Dr. Robert Kvavik (500 Institutions surveyed) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
2002 Higher Education ERP Survey • 39% of institutions surveyed have implemented or are in the process of implementing a Data Warehouse • 37% of institutions surveyed plan to implement a Data Warehouse within the next three years, with almost 1/3 of the projects beginning in 2003 Source: The Promise and Performance of Enterprise Systems, 2002 ECARS Research Study by Dr. Robert Kvavik (500 Institutions surveyed) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Recipe for Failure • Start by looking for application data to source a DW • Move as much transactional data as possible into a “warehouse database” • Purchase a relational reporting or query tool • Send users to training -- This approach rarely works! -- All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Recipe for Failure • Start by looking for application data to source a DW • Move as much transactional data as possible into a “warehouse database” • Purchase a relational reporting or query tool • Send users to training -- This approach rarely works! -- All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Big Difference between Data vs. Information vs. Knowledge • Data – raw facts that have been collected, processed, stored, but not organized to convey meaning. • Information – a collection of data organized in a manner to be meaningful to a recipient. • Knowledge – information combined with understanding, experience, accumulated learning, and expertise relevant to a problem, decision, or process. Data Transformation, Derivation and Aggregation are necessary, along with a self service access capability! All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Big Difference between Data vs. Information vs. Knowledge • Data – raw facts that have been collected, processed, stored, but not organized to convey meaning. • Information – a collection of data organized in a manner to be meaningful to a recipient. • Knowledge – information combined with understanding, experience, accumulated learning, and expertise relevant to a problem, decision, or process. Data Transformation, Derivation and Aggregation are necessary, along with a self service access capability! All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 DW Casual User vs. Power User • Different audiences with different: – – – Information needs Analytical capabilities Technical aptitudes Level of insight into application data Time constraints • 80% – 90% of information consumers are casual users ØNeed to consider both in technology decisions All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
DW Casual User vs. Power User • Different audiences with different: – – – Information needs Analytical capabilities Technical aptitudes Level of insight into application data Time constraints • 80% – 90% of information consumers are casual users ØNeed to consider both in technology decisions All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Confusing BI Product Space • 25 to 50 legitimate vendors; many overlapping products that may appear similar but are fundamentally different • Reporting vs. Analytics – there’s a big difference! • Relational vs. OLAP Technology – MOLAP vs. ROLAP vs. HOLAP – Multidimensional Presentation vs. OLAP engine • Products/Vendors: Front-end only vs. Back-end only vs. Both • Open vs. Proprietary platforms • Web vs. Client Server – HTML vs. Rich web client (JAVA, Active-X) • Open component architecture vs. self contained products – Portal integration Conclusions Ø There’s no magic product that does it all! Ø Understand your user base, information needs and objectives before selecting BI technology All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Confusing BI Product Space • 25 to 50 legitimate vendors; many overlapping products that may appear similar but are fundamentally different • Reporting vs. Analytics – there’s a big difference! • Relational vs. OLAP Technology – MOLAP vs. ROLAP vs. HOLAP – Multidimensional Presentation vs. OLAP engine • Products/Vendors: Front-end only vs. Back-end only vs. Both • Open vs. Proprietary platforms • Web vs. Client Server – HTML vs. Rich web client (JAVA, Active-X) • Open component architecture vs. self contained products – Portal integration Conclusions Ø There’s no magic product that does it all! Ø Understand your user base, information needs and objectives before selecting BI technology All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Why OLAP Technology? • Multi-dimensional presentation is the natural orientation for business information and analysis – Intuitive and easy to use – Hides user from underlying relational data model • OLAP Technology is very fast – Most reports run within 1 -3 seconds – Speed advantage substantial in highly aggregated reports such as multi-year trends – Without OLAP, the burden is on the developer to build the aggregation • Enables calculations that are impractical using relational technology – e. g. , moving averages, prior period % change • Produces consistent information – Pre-calculated results – Not subject to unexpected SQL query behavior All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Why OLAP Technology? • Multi-dimensional presentation is the natural orientation for business information and analysis – Intuitive and easy to use – Hides user from underlying relational data model • OLAP Technology is very fast – Most reports run within 1 -3 seconds – Speed advantage substantial in highly aggregated reports such as multi-year trends – Without OLAP, the burden is on the developer to build the aggregation • Enables calculations that are impractical using relational technology – e. g. , moving averages, prior period % change • Produces consistent information – Pre-calculated results – Not subject to unexpected SQL query behavior All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Aggregation Management: Relational Summary Tables Scenario • Fact table with four dimensions • Each dimension has four levels in its hierarchy (e. g. , Time: Section, Course, Subject, All) • How many summary fact tables are required to support every combination of dimension level? 255 • If you don’t build 255, how many should you build and which ones? • What if you have a 20 dimensional Student Term Fact Table? • OLAP Technology makes aggregation management very easy! All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Aggregation Management: Relational Summary Tables Scenario • Fact table with four dimensions • Each dimension has four levels in its hierarchy (e. g. , Time: Section, Course, Subject, All) • How many summary fact tables are required to support every combination of dimension level? 255 • If you don’t build 255, how many should you build and which ones? • What if you have a 20 dimensional Student Term Fact Table? • OLAP Technology makes aggregation management very easy! All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Why an Analytical Application? (vs. Reporting Tools) • Casual Users – majority of information users (80 – 90 %) are casual users who will have difficulty mastering a reporting tool. An Analytical Application will be much easier to use and be more highly utilized • Hide Database Complexity – most reporting tools require the user to understand the reporting database content and relationships. An analytical application enables casual users to get information without understanding the underlying database and functionality of reporting tools • Guided Analysis – an application framework provides the opportunity to guide users through an analytical process and better leverage the metrics and analytical capabilities inherent in the solution • Personalization – provide users with the ability to personalize their content and interface • Embed Customized Analytical Functionality – enables customized application functionality to be integrated with reporting (e. g. , Student Peer Group Analysis) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Why an Analytical Application? (vs. Reporting Tools) • Casual Users – majority of information users (80 – 90 %) are casual users who will have difficulty mastering a reporting tool. An Analytical Application will be much easier to use and be more highly utilized • Hide Database Complexity – most reporting tools require the user to understand the reporting database content and relationships. An analytical application enables casual users to get information without understanding the underlying database and functionality of reporting tools • Guided Analysis – an application framework provides the opportunity to guide users through an analytical process and better leverage the metrics and analytical capabilities inherent in the solution • Personalization – provide users with the ability to personalize their content and interface • Embed Customized Analytical Functionality – enables customized application functionality to be integrated with reporting (e. g. , Student Peer Group Analysis) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 What the experts are saying! “. . . most decision support software is gathering dust on office bookshelves” “Whether you build and/or buy, the key is to … deliver a robust analytic application that delivers the information and analysis that business users need. ” Wayne Eckerson, Director of Education and Research for The Data Warehousing Institute (TDWI) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
What the experts are saying! “. . . most decision support software is gathering dust on office bookshelves” “Whether you build and/or buy, the key is to … deliver a robust analytic application that delivers the information and analysis that business users need. ” Wayne Eckerson, Director of Education and Research for The Data Warehousing Institute (TDWI) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Analytical Application for Higher Education • Information Scope – Serve a broad audience: institutional research, management reporting, compliance reporting, operational analysis – Span complete student lifecycle: admissions, enrollment, course activity, graduation – Address key objectives: recruiting effectiveness, retention, student achievement, course curriculum and schedule • Provide self service access to information: – Intuitive and easy to use (the basics are simple) – Minimal training required – Easy to deploy • Functionality: – – – Interactive standard reports and charts, Guided Analysis, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), Personalized Dashboard (KPIs and Charts) Ad hoc analysis, “Actionable” analytical tools (e. g. , support early intervention through student risk analysis, student peer group analysis) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Analytical Application for Higher Education • Information Scope – Serve a broad audience: institutional research, management reporting, compliance reporting, operational analysis – Span complete student lifecycle: admissions, enrollment, course activity, graduation – Address key objectives: recruiting effectiveness, retention, student achievement, course curriculum and schedule • Provide self service access to information: – Intuitive and easy to use (the basics are simple) – Minimal training required – Easy to deploy • Functionality: – – – Interactive standard reports and charts, Guided Analysis, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), Personalized Dashboard (KPIs and Charts) Ad hoc analysis, “Actionable” analytical tools (e. g. , support early intervention through student risk analysis, student peer group analysis) All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
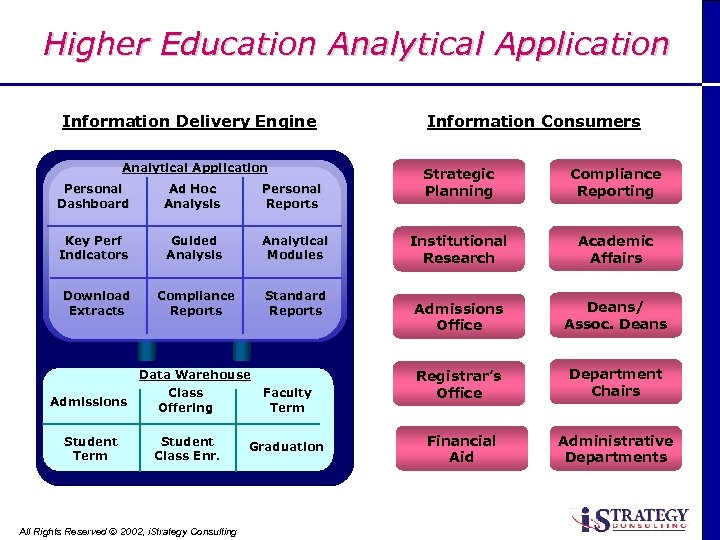 Higher Education Analytical Application Information Delivery Engine Analytical Application Personal Dashboard Ad Hoc Analysis Personal Reports Key Perf Indicators Guided Analysis Analytical Modules Download Extracts Compliance Reports Standard Reports Admissions Student Term Data Warehouse Class Offering Student Class Enr. All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Faculty Term Graduation Information Consumers Strategic Planning Compliance Reporting Institutional Research Academic Affairs Admissions Office Deans/ Assoc. Deans Registrar’s Office Department Chairs Financial Aid Administrative Departments
Higher Education Analytical Application Information Delivery Engine Analytical Application Personal Dashboard Ad Hoc Analysis Personal Reports Key Perf Indicators Guided Analysis Analytical Modules Download Extracts Compliance Reports Standard Reports Admissions Student Term Data Warehouse Class Offering Student Class Enr. All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Faculty Term Graduation Information Consumers Strategic Planning Compliance Reporting Institutional Research Academic Affairs Admissions Office Deans/ Assoc. Deans Registrar’s Office Department Chairs Financial Aid Administrative Departments
 Demonstration Background Information All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Demonstration Background Information All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Student Administration Information Categories 1. Admissions 2. Student Demographics 3. Enrollment Trends 4. Retention 5. Class Offering and Utilization 6. Student Class Enrollment 7. Student Performance 8. Student Risk Analysis 9. Student Peer Group Analysis 10. Graduation 11. Faculty Information All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Student Administration Information Categories 1. Admissions 2. Student Demographics 3. Enrollment Trends 4. Retention 5. Class Offering and Utilization 6. Student Class Enrollment 7. Student Performance 8. Student Risk Analysis 9. Student Peer Group Analysis 10. Graduation 11. Faculty Information All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
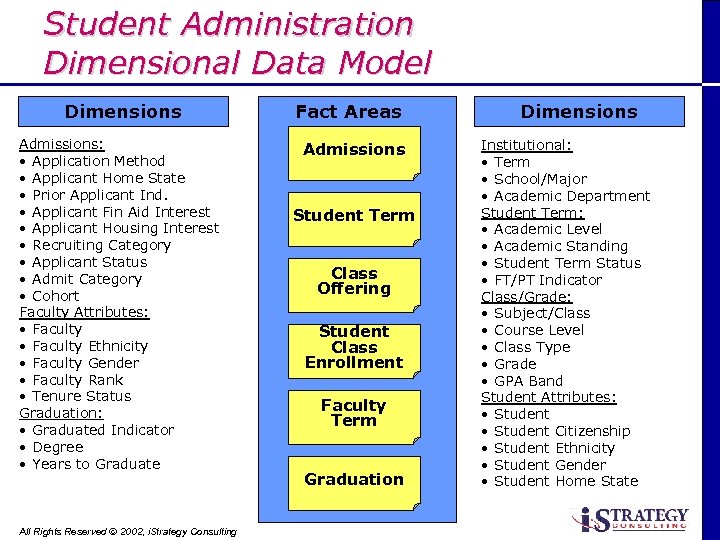 Student Administration Dimensional Data Model Dimensions Admissions: • Application Method • Applicant Home State • Prior Applicant Ind. • Applicant Fin Aid Interest • Applicant Housing Interest • Recruiting Category • Applicant Status • Admit Category • Cohort Faculty Attributes: • Faculty Ethnicity • Faculty Gender • Faculty Rank • Tenure Status Graduation: • Graduated Indicator • Degree • Years to Graduate All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Fact Areas Admissions Student Term Class Offering Student Class Enrollment Faculty Term Graduation Dimensions Institutional: • Term • School/Major • Academic Department Student Term: • Academic Level • Academic Standing • Student Term Status • FT/PT Indicator Class/Grade: • Subject/Class • Course Level • Class Type • Grade • GPA Band Student Attributes: • Student Citizenship • Student Ethnicity • Student Gender • Student Home State
Student Administration Dimensional Data Model Dimensions Admissions: • Application Method • Applicant Home State • Prior Applicant Ind. • Applicant Fin Aid Interest • Applicant Housing Interest • Recruiting Category • Applicant Status • Admit Category • Cohort Faculty Attributes: • Faculty Ethnicity • Faculty Gender • Faculty Rank • Tenure Status Graduation: • Graduated Indicator • Degree • Years to Graduate All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Fact Areas Admissions Student Term Class Offering Student Class Enrollment Faculty Term Graduation Dimensions Institutional: • Term • School/Major • Academic Department Student Term: • Academic Level • Academic Standing • Student Term Status • FT/PT Indicator Class/Grade: • Subject/Class • Course Level • Class Type • Grade • GPA Band Student Attributes: • Student Citizenship • Student Ethnicity • Student Gender • Student Home State
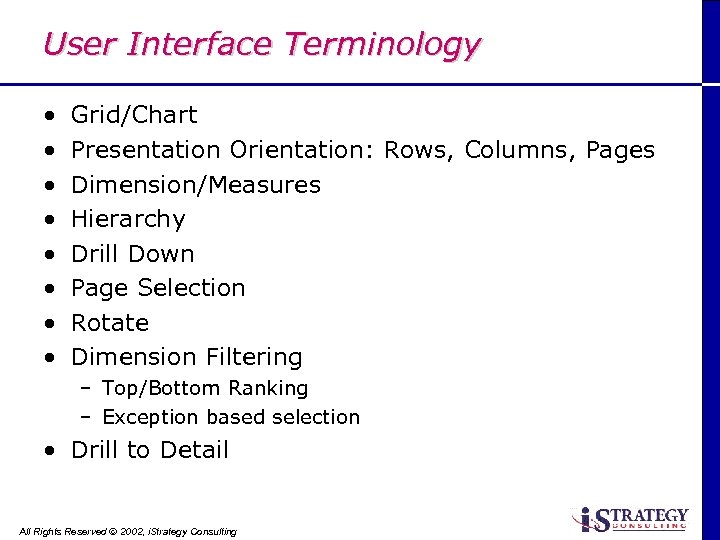 User Interface Terminology • • Grid/Chart Presentation Orientation: Rows, Columns, Pages Dimension/Measures Hierarchy Drill Down Page Selection Rotate Dimension Filtering – Top/Bottom Ranking – Exception based selection • Drill to Detail All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
User Interface Terminology • • Grid/Chart Presentation Orientation: Rows, Columns, Pages Dimension/Measures Hierarchy Drill Down Page Selection Rotate Dimension Filtering – Top/Bottom Ranking – Exception based selection • Drill to Detail All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
 Application Demonstration All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Application Demonstration All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
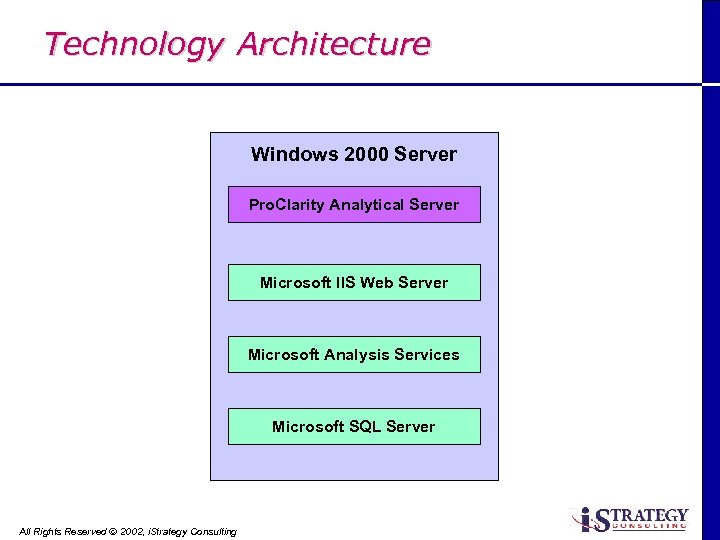 Technology Architecture Windows 2000 Server Pro. Clarity Analytical Server Microsoft IIS Web Server Microsoft Analysis Services Microsoft SQL Server All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Technology Architecture Windows 2000 Server Pro. Clarity Analytical Server Microsoft IIS Web Server Microsoft Analysis Services Microsoft SQL Server All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
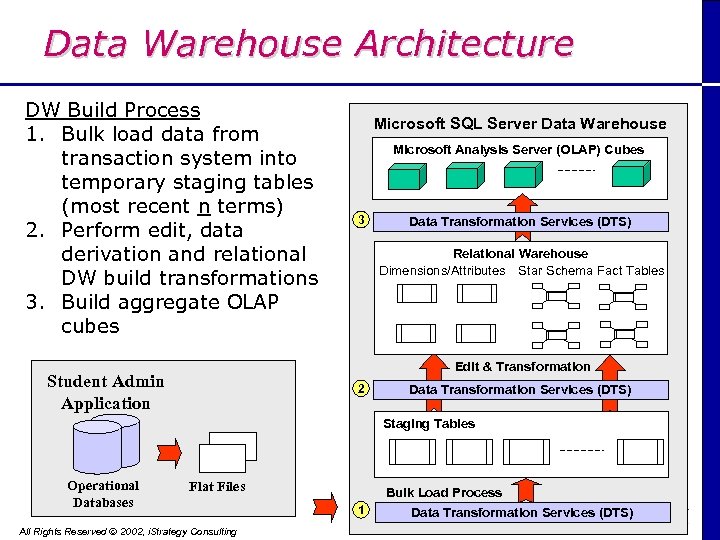 Data Warehouse Architecture DW Build Process 1. Bulk load data from transaction system into temporary staging tables (most recent n terms) 2. Perform edit, data derivation and relational DW build transformations 3. Build aggregate OLAP cubes Microsoft SQL Server Data Warehouse Microsoft Analysis Server (OLAP) Cubes 3 Data Transformation Services (DTS) Relational Warehouse Dimensions/Attributes Star Schema Fact Tables Edit & Transformation Student Admin Application 2 Data Transformation Services (DTS) Staging Tables Operational Databases Flat Files All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Bulk Load Process 1 Data Transformation Services (DTS)
Data Warehouse Architecture DW Build Process 1. Bulk load data from transaction system into temporary staging tables (most recent n terms) 2. Perform edit, data derivation and relational DW build transformations 3. Build aggregate OLAP cubes Microsoft SQL Server Data Warehouse Microsoft Analysis Server (OLAP) Cubes 3 Data Transformation Services (DTS) Relational Warehouse Dimensions/Attributes Star Schema Fact Tables Edit & Transformation Student Admin Application 2 Data Transformation Services (DTS) Staging Tables Operational Databases Flat Files All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting Bulk Load Process 1 Data Transformation Services (DTS)
 Keys to Success • Set reasonable expectations – It’s impossible to address every imaginable information need – It’s better to successfully deliver 80% - 90% of the requirements than to deliver nothing – Continue to expand scope based on needs • Target a quick success story • Ensure that the casual users have an application interface that is: – Simple to use – Fast – Supports analytics as the user skills develop • Design must incorporate transformation of data to a dimensional data model • Provide a good support infrastructure All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting
Keys to Success • Set reasonable expectations – It’s impossible to address every imaginable information need – It’s better to successfully deliver 80% - 90% of the requirements than to deliver nothing – Continue to expand scope based on needs • Target a quick success story • Ensure that the casual users have an application interface that is: – Simple to use – Fast – Supports analytics as the user skills develop • Design must incorporate transformation of data to a dimensional data model • Provide a good support infrastructure All Rights Reserved Ó 2002, i. Strategy Consulting


