5e9d1c8658afd25403bb6cb08dcdaeb6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Adaptive Support using Cognitive Models of Trust Robbert-Jan Beun (UU), Jurriaan van Diggelen (TNO), Mark Hoogendoorn (VU), Syed Waqar Jaffry (VU), Peter-Paul van Maanen (TNO), Francien Wisse (UU)

Overview of talk • • Introduction and motivation Adaptive support based on cognitive models of trust General methodology Part I: Validation and verification of trust models • Independent vs. relative trust model • Method • Results • Conclusions • Part II: Evaluation of adaptive support based on trust models • Reliance support by advising vs. adaptive autonomy • Method • Results • Conclusions • General discussion AI Seminar October 2010

Introduction and motivation • Trends in military / homeland security / incident management / … : • More complex situations • More different situations • More information • Reduced manning / less human assistance • Less experience • Less specific training possible • Increased computer intelligence • … • Challenge: Human error in the appropriate reliance on information from humans and computers is evident • Possible solution: Let support systems take into account human limitations in reliance decision making: Trust-aware adaptive systems AI Seminar October 2010
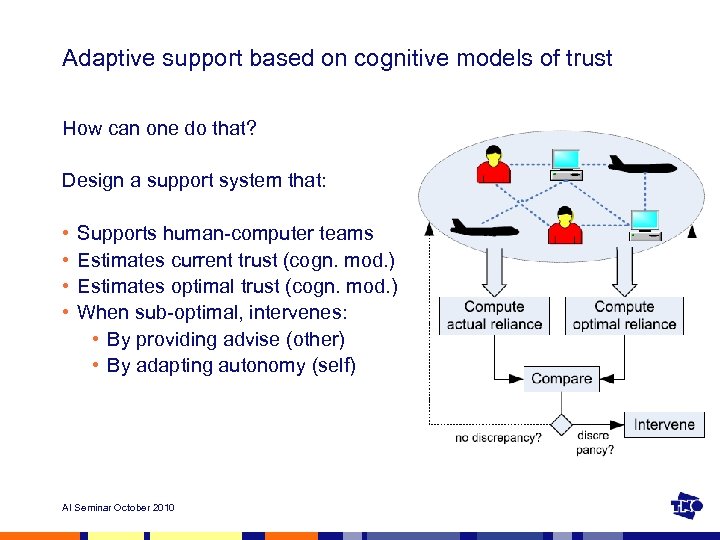
Adaptive support based on cognitive models of trust How can one do that? Design a support system that: • • Supports human-computer teams Estimates current trust (cogn. mod. ) Estimates optimal trust (cogn. mod. ) When sub-optimal, intervenes: • By providing advise (other) • By adapting autonomy (self) AI Seminar October 2010
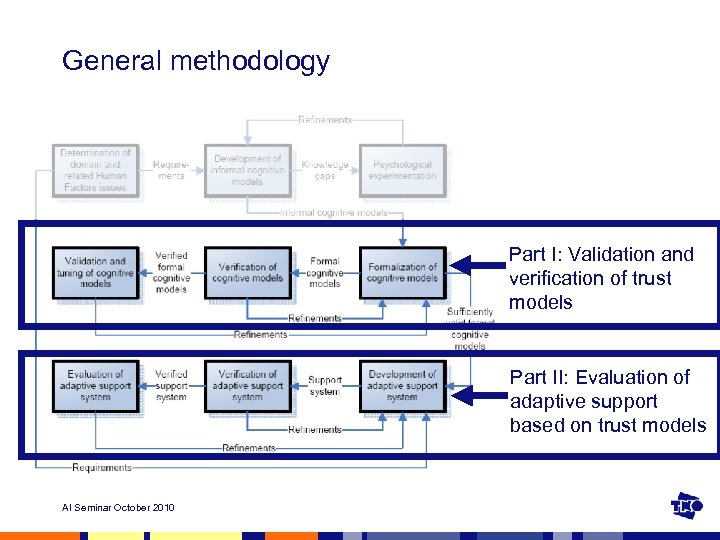
General methodology Part I: Validation and verification of trust models Part II: Evaluation of adaptive support based on trust models AI Seminar October 2010

Part I: Validation and verification of trust models AI Seminar October 2010
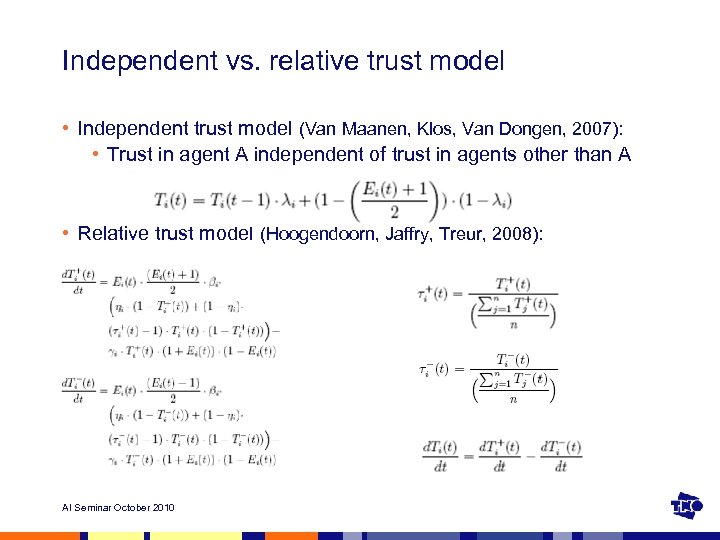
Independent vs. relative trust model • Independent trust model (Van Maanen, Klos, Van Dongen, 2007): • Trust in agent A independent of trust in agents other than A • Relative trust model (Hoogendoorn, Jaffry, Treur, 2008): AI Seminar October 2010
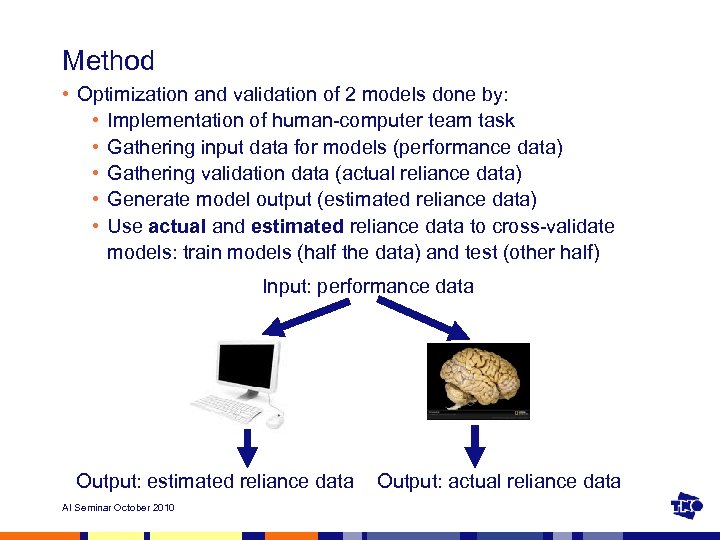
Method • Optimization and validation of 2 models done by: • Implementation of human-computer team task • Gathering input data for models (performance data) • Gathering validation data (actual reliance data) • Generate model output (estimated reliance data) • Use actual and estimated reliance data to cross-validate models: train models (half the data) and test (other half) Input: performance data Output: estimated reliance data AI Seminar October 2010 Output: actual reliance data
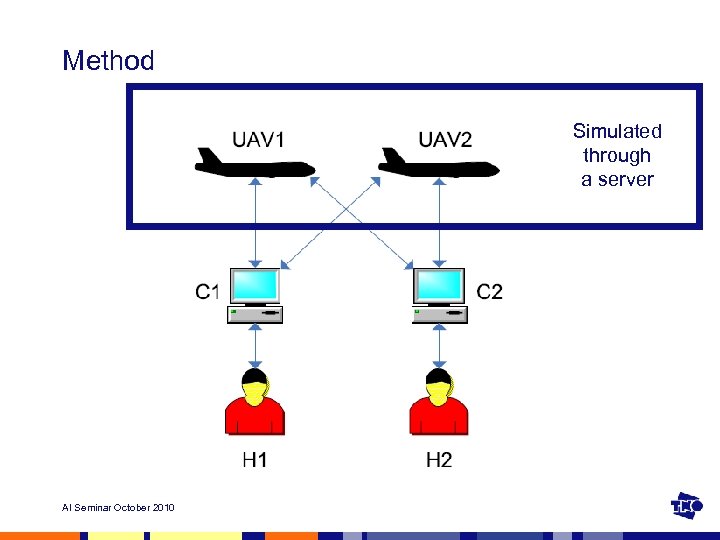
Method Simulated through a server AI Seminar October 2010
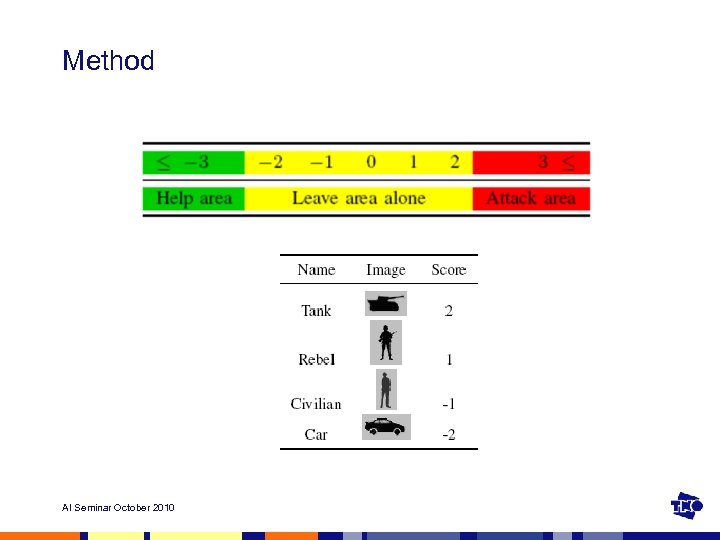
Method AI Seminar October 2010
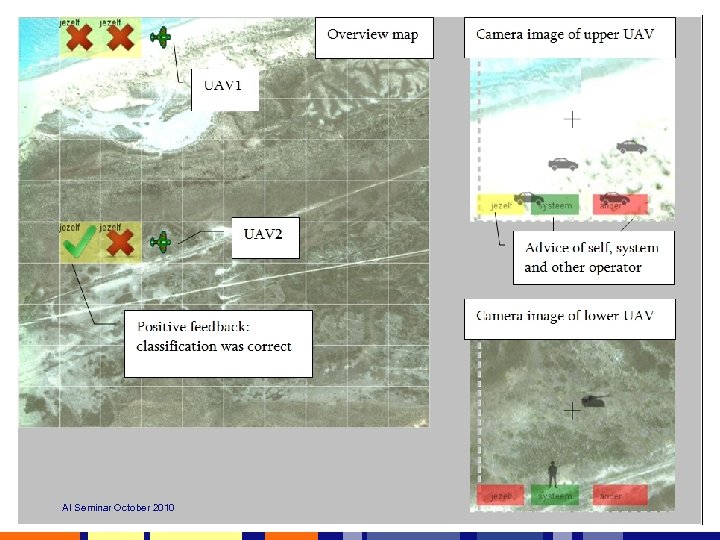
AI Seminar October 2010
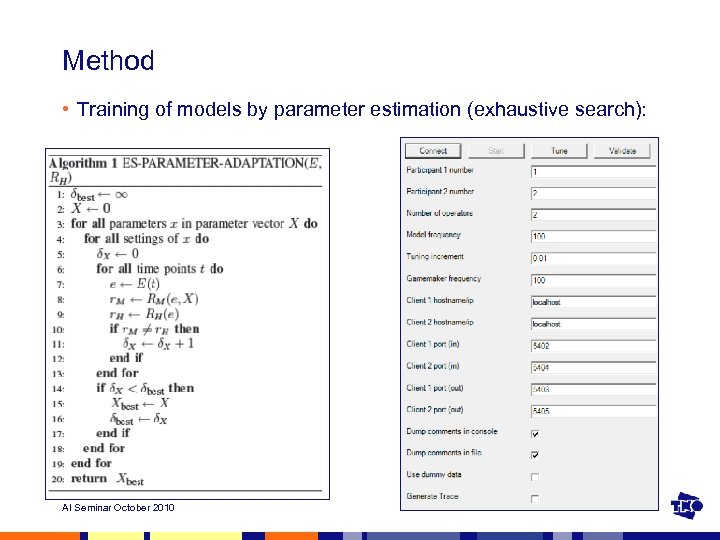
Method • Training of models by parameter estimation (exhaustive search): AI Seminar October 2010
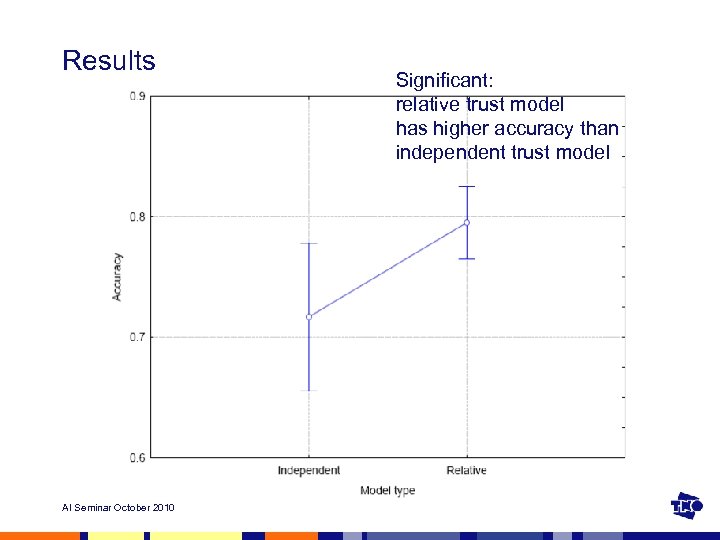
Results AI Seminar October 2010 Significant: relative trust model has higher accuracy than independent trust model

Conclusions • Trust models were optimized an attempt was made to see what model structure is best for the specific task • The relative trust model improves reliance decision estimation over the independent trust model • Future research could focus on: • improved models and • model verification and validation techniques • and for other domains/tasks AI Seminar October 2010

Part II: Evaluation of adaptive support based on trust models AI Seminar October 2010
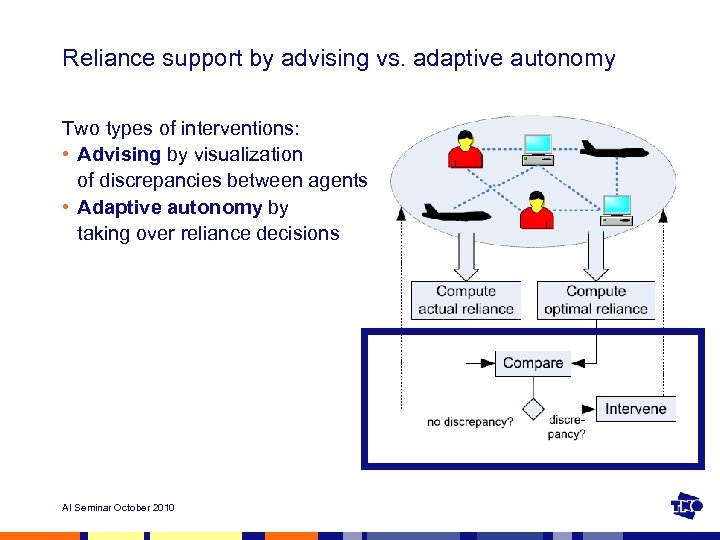
Reliance support by advising vs. adaptive autonomy Two types of interventions: • Advising by visualization of discrepancies between agents • Adaptive autonomy by taking over reliance decisions AI Seminar October 2010

Method Evaluation of 2 adaptive support types done by: • Usage of same task as previously explained • Calculate appropriateness (alpha) of trust in self, system and other: t^d(t) = estimated trust, t^p(t) = desired trust • Per agent, when above or below a certain (-)threshold, advise: • In total, when above or below a certain (-)threshold, adapt autonomy: • Calculate performances: • For no support (NS), advising (GS), adaptive autonomy (AA) AI Seminar October 2010
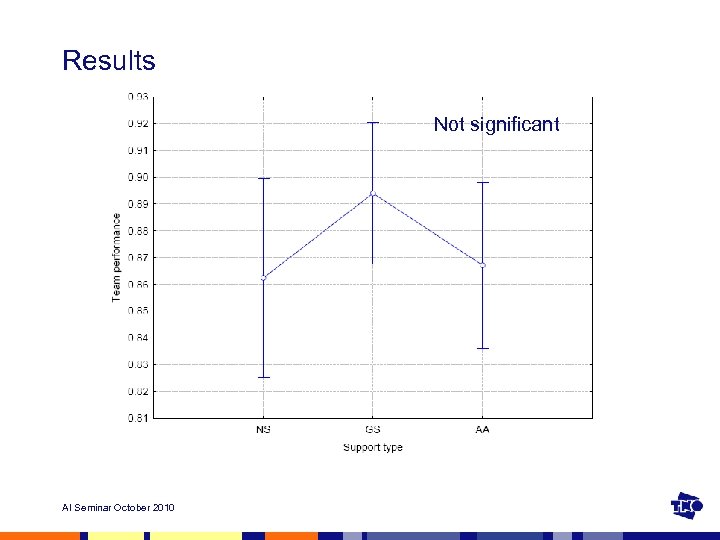
Results Not significant AI Seminar October 2010
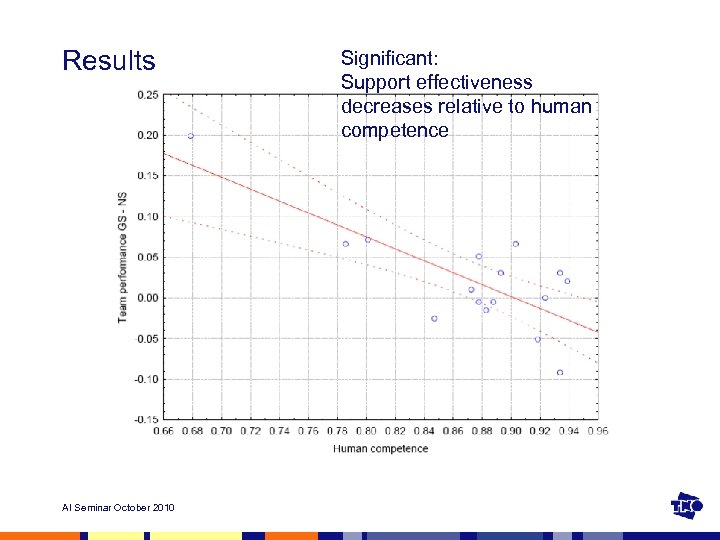
Results AI Seminar October 2010 Significant: Support effectiveness decreases relative to human competence
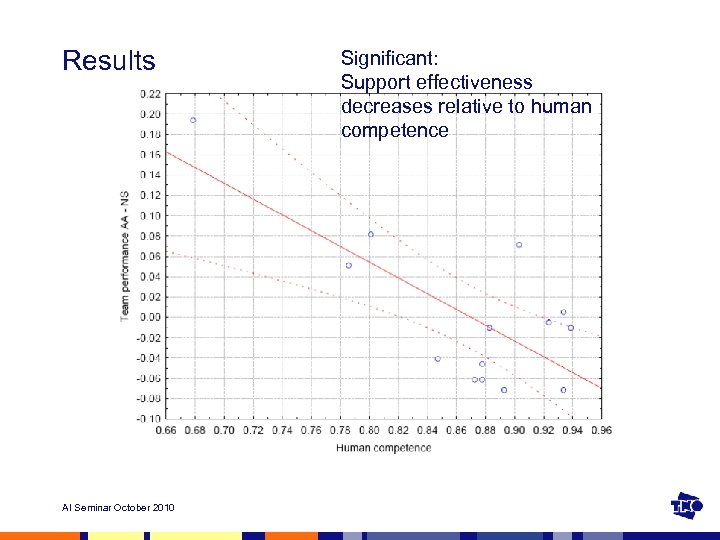
Results AI Seminar October 2010 Significant: Support effectiveness decreases relative to human competence
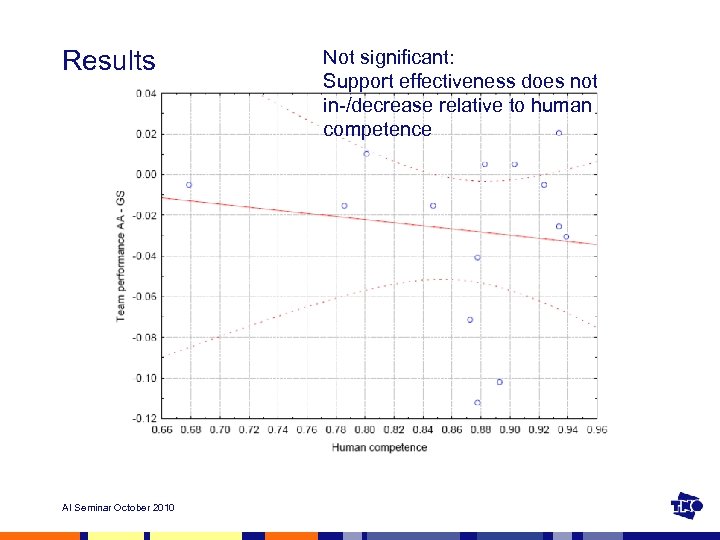
Results AI Seminar October 2010 Not significant: Support effectiveness does not in-/decrease relative to human competence
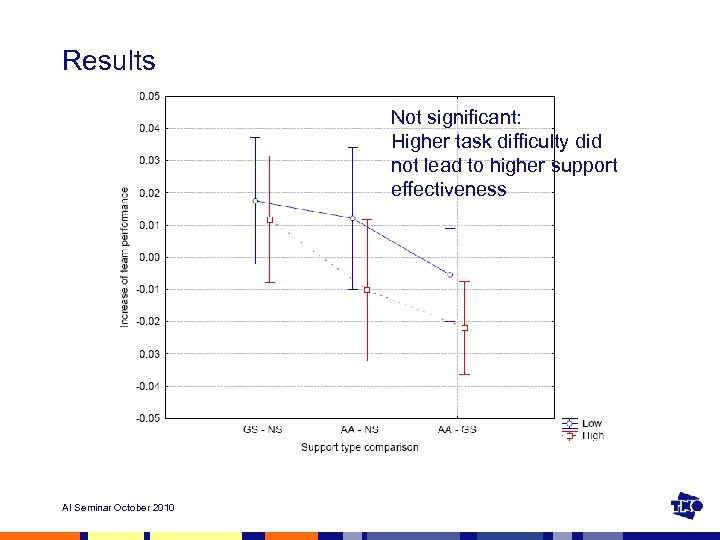
Results Not significant: Higher task difficulty did not lead to higher support effectiveness AI Seminar October 2010
Results • Finally: GS was more satisfactory than AA (significant) AI Seminar October 2010
Conclusions • Proof of concept: It is indeed possible to implement adaptive support using cognitive optimized and validated models of trust • Results show no significant effect of the support types for the current task • Future work: • Effect of validity on the effectiveness of support • Effect of intrusiveness of support • Improvements of satisfaction and acceptance of support • Improvement of reliance decisions of system (in case of adaptive autonomy) • Other domains, tasks, support types AI Seminar October 2010

General discussion Questions that can be raised: • Can the proposed methodology be used for the development of adaptive support using cognitive models? • Are there other cognitive models that can be used? • How would machines that take over tasks or manipulate the human mind be perceived by humans? Are they accepted? • What would future human-aware machines be like? Would they augment the human mind, cooperating with humans, or would they be better of without humans? AI Seminar October 2010
5e9d1c8658afd25403bb6cb08dcdaeb6.ppt