b5a8c4de20b384b40f6b020692566ee4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66
 Adaptive Multi-sensor Integrated Security System (AMISS) August 1998
Adaptive Multi-sensor Integrated Security System (AMISS) August 1998
 AMISS Agenda • • AMISS Overview Source Detection and Location Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Multi-sensor Data Fusion Shape Recognition and Identification Reasoning/Data Mining Remote Operation AMISS Integrated Exercise Los Alamos National Laboratory 2
AMISS Agenda • • AMISS Overview Source Detection and Location Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Multi-sensor Data Fusion Shape Recognition and Identification Reasoning/Data Mining Remote Operation AMISS Integrated Exercise Los Alamos National Laboratory 2
 AMISS Vision Develop and demonstrate state-of-science adaptive technology to determine potential threats and anomalous situations and ascertain appropriate action to increase facility security, safeguards, and safety. Los Alamos National Laboratory 3
AMISS Vision Develop and demonstrate state-of-science adaptive technology to determine potential threats and anomalous situations and ascertain appropriate action to increase facility security, safeguards, and safety. Los Alamos National Laboratory 3
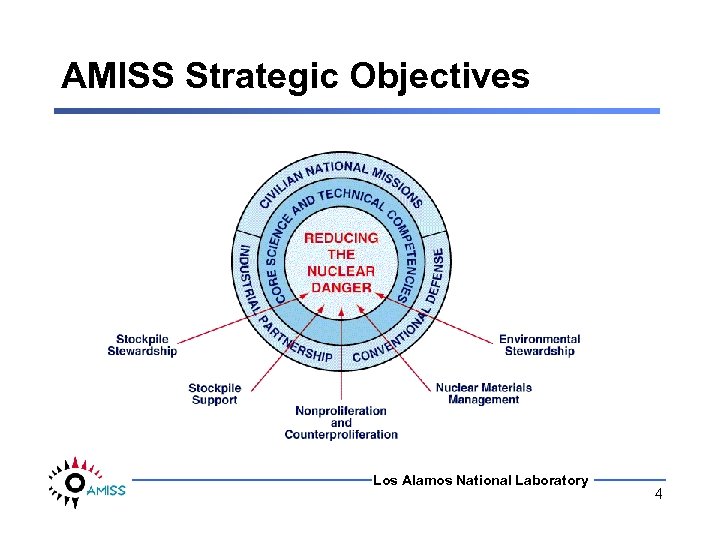 AMISS Strategic Objectives Los Alamos National Laboratory 4
AMISS Strategic Objectives Los Alamos National Laboratory 4
 AMISS Strategic Objectives • • • Provide continuous, adaptive real-time detection and categorization of all activity Assist security personnel Enhance material movement monitoring Reconstruct threatening events Ensure compliance Los Alamos National Laboratory 5
AMISS Strategic Objectives • • • Provide continuous, adaptive real-time detection and categorization of all activity Assist security personnel Enhance material movement monitoring Reconstruct threatening events Ensure compliance Los Alamos National Laboratory 5
 AMISS Tactics • • • Develop test bed Learn correct/acceptable facility operating conditions and detect unusual behavior Build techniques for active facility Build portable capabilities Provide feedback to security personnel Los Alamos National Laboratory 6
AMISS Tactics • • • Develop test bed Learn correct/acceptable facility operating conditions and detect unusual behavior Build techniques for active facility Build portable capabilities Provide feedback to security personnel Los Alamos National Laboratory 6
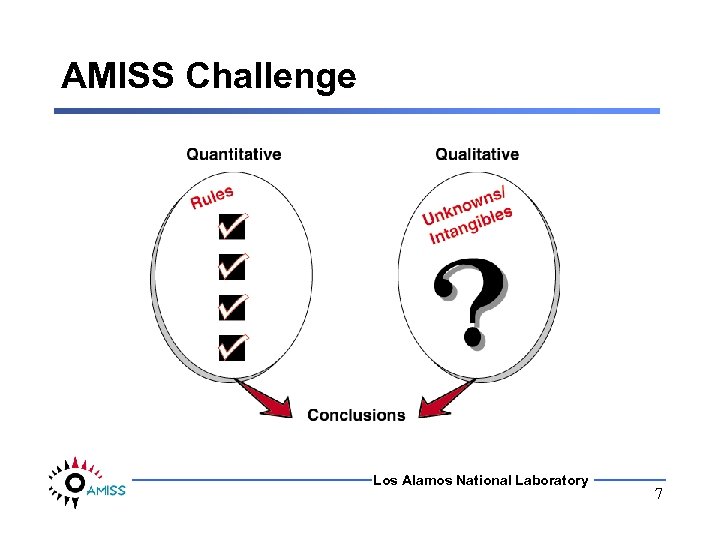 AMISS Challenge Los Alamos National Laboratory 7
AMISS Challenge Los Alamos National Laboratory 7
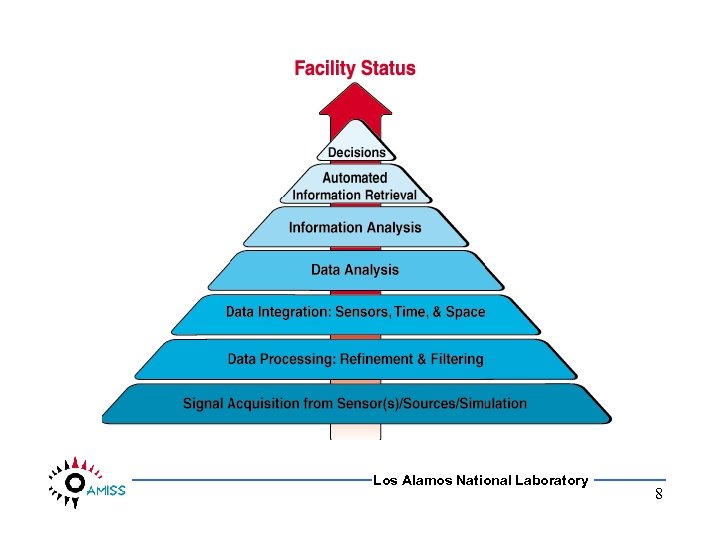 Los Alamos National Laboratory 8
Los Alamos National Laboratory 8
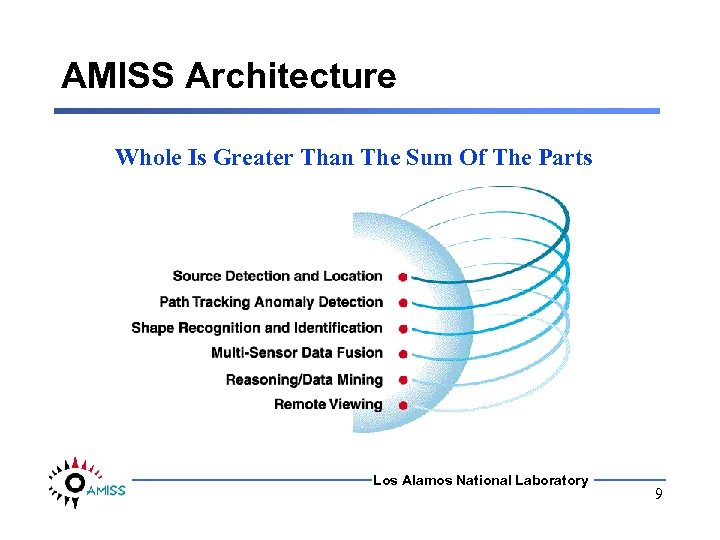 AMISS Architecture Whole Is Greater Than The Sum Of The Parts Los Alamos National Laboratory 9
AMISS Architecture Whole Is Greater Than The Sum Of The Parts Los Alamos National Laboratory 9
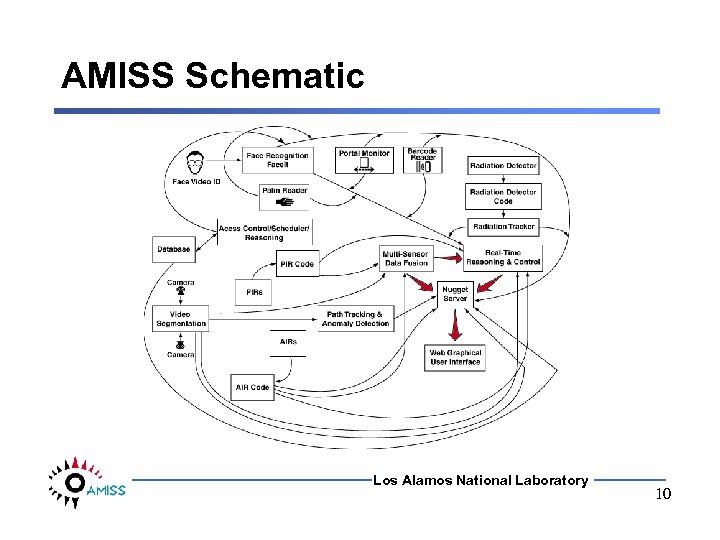 AMISS Schematic Los Alamos National Laboratory 10
AMISS Schematic Los Alamos National Laboratory 10
 AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 11
AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 11
 Source Detection And Location • Long-term vision – Detect, identify, and locate multiple sources and track movement and activity • Initial goal – Detect and locate single moving source in a room Los Alamos National Laboratory 12
Source Detection And Location • Long-term vision – Detect, identify, and locate multiple sources and track movement and activity • Initial goal – Detect and locate single moving source in a room Los Alamos National Laboratory 12
 Source Location Problem • • • Detector gives imperfect information Source moves around room Inconsistent signals (candle flickers) Background changes Detectors are non-directional Shielding or occlusions Los Alamos National Laboratory 13
Source Location Problem • • • Detector gives imperfect information Source moves around room Inconsistent signals (candle flickers) Background changes Detectors are non-directional Shielding or occlusions Los Alamos National Laboratory 13
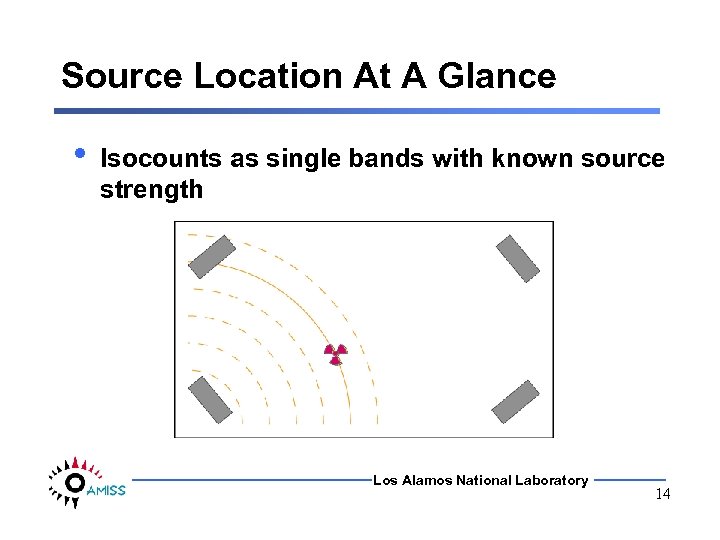 Source Location At A Glance • Isocounts as single bands with known source strength Los Alamos National Laboratory 14
Source Location At A Glance • Isocounts as single bands with known source strength Los Alamos National Laboratory 14
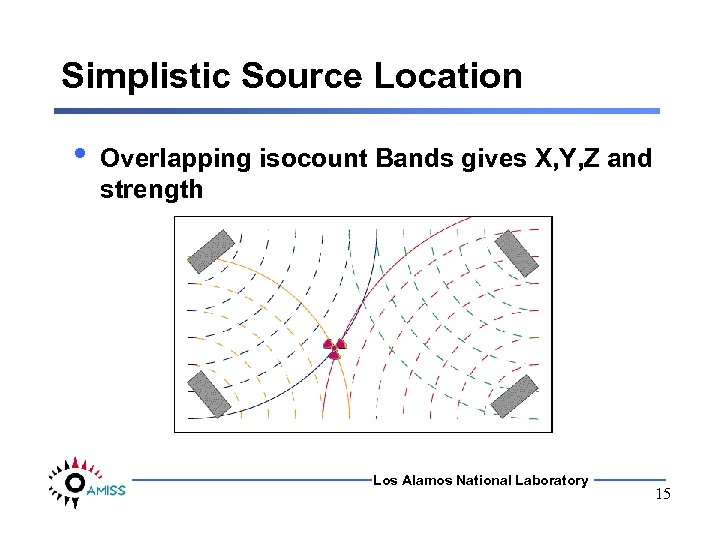 Simplistic Source Location • Overlapping isocount Bands gives X, Y, Z and strength Los Alamos National Laboratory 15
Simplistic Source Location • Overlapping isocount Bands gives X, Y, Z and strength Los Alamos National Laboratory 15
 Source Location Solution • • Estimate X, Y, Z background levels Radiation detection model for rectangular detector and spherical source Optimization algorithm – Kalman Filter – Constrained optimization Elements of uncertainty – – Counting statistics Occlusion, shielding Varying background Directional detectors Los Alamos National Laboratory 16
Source Location Solution • • Estimate X, Y, Z background levels Radiation detection model for rectangular detector and spherical source Optimization algorithm – Kalman Filter – Constrained optimization Elements of uncertainty – – Counting statistics Occlusion, shielding Varying background Directional detectors Los Alamos National Laboratory 16
 Source Location Future • • • Improve Location Accuracy with known source strength Locate Multiple Sources Deduce multiple source strength Deduce Nuclear Signatures Decrease uncertainties – Location – Source Strength – Source Material Los Alamos National Laboratory 17
Source Location Future • • • Improve Location Accuracy with known source strength Locate Multiple Sources Deduce multiple source strength Deduce Nuclear Signatures Decrease uncertainties – Location – Source Strength – Source Material Los Alamos National Laboratory 17
 AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 18
AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 18
 Path Tracking Anomaly Detection • Automated process using data collection to locate individual movement to detect and determine anomalous behavior patterns Los Alamos National Laboratory 19
Path Tracking Anomaly Detection • Automated process using data collection to locate individual movement to detect and determine anomalous behavior patterns Los Alamos National Laboratory 19
 Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Current Technology • • Unsupervised neural network Clusters spatial-temporal patterns Learns individual behavior Defines normal behavior – X, Y locations in sequence – Broader patterns Los Alamos National Laboratory 20
Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Current Technology • • Unsupervised neural network Clusters spatial-temporal patterns Learns individual behavior Defines normal behavior – X, Y locations in sequence – Broader patterns Los Alamos National Laboratory 20
 Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Los Alamos National Laboratory 21
Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Los Alamos National Laboratory 21
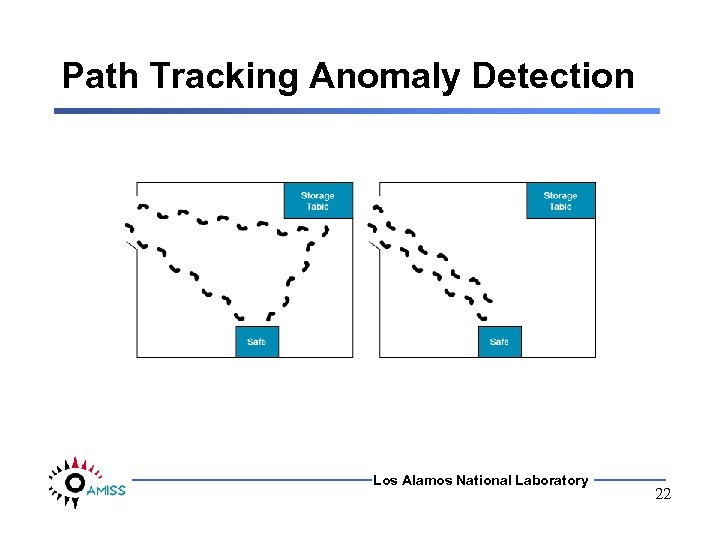 Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Los Alamos National Laboratory 22
Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Los Alamos National Laboratory 22
 Path Tracking Anomaly Detection AMISS Innovative Technology • • • Determine anomalies from examples of normal behavior - more secure Real-time Provide explanation facility Learns quickly Customized by changing sensitivity parameters Los Alamos National Laboratory 23
Path Tracking Anomaly Detection AMISS Innovative Technology • • • Determine anomalies from examples of normal behavior - more secure Real-time Provide explanation facility Learns quickly Customized by changing sensitivity parameters Los Alamos National Laboratory 23
 Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Future • Facility Security – – • Identify number of people in a room Identify open doors Examine time Determine expected behavior – Expand to larger areas Other domains – Verification of dismantlement activities – Assist IAEA inspections – Ensure unattended monitoring Los Alamos National Laboratory 24
Path Tracking Anomaly Detection Future • Facility Security – – • Identify number of people in a room Identify open doors Examine time Determine expected behavior – Expand to larger areas Other domains – Verification of dismantlement activities – Assist IAEA inspections – Ensure unattended monitoring Los Alamos National Laboratory 24
 AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 25
AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 25
 Multi-sensor Data Fusion • Combining multi-sensor data to provide more accurate, descriptive, and useful information for higher-level reasoning and display Los Alamos National Laboratory 26
Multi-sensor Data Fusion • Combining multi-sensor data to provide more accurate, descriptive, and useful information for higher-level reasoning and display Los Alamos National Laboratory 26
 Multi-sensor Data Fusion Challenges • Different sensor characteristics – – – Different data collected Various accuracy Various reliability Different resolutions Varying speed Los Alamos National Laboratory 27
Multi-sensor Data Fusion Challenges • Different sensor characteristics – – – Different data collected Various accuracy Various reliability Different resolutions Varying speed Los Alamos National Laboratory 27
 Multi-sensor Data Fusion Current Research • • • Uses proven graph theory technique, including edge trimming Robust sensor suite – Handle sensor failure – Redundancy for level of assurance Fuse active and passive infrared and video to identify and locate personnel Experimental code complete Evaluation phase starting Los Alamos National Laboratory 28
Multi-sensor Data Fusion Current Research • • • Uses proven graph theory technique, including edge trimming Robust sensor suite – Handle sensor failure – Redundancy for level of assurance Fuse active and passive infrared and video to identify and locate personnel Experimental code complete Evaluation phase starting Los Alamos National Laboratory 28
 Multi-sensor Data Fusion Future • • Integrate into AMISS Research other methodologies Add new sensor types Framework for future development Los Alamos National Laboratory 29
Multi-sensor Data Fusion Future • • Integrate into AMISS Research other methodologies Add new sensor types Framework for future development Los Alamos National Laboratory 29
 AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 30
AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 30
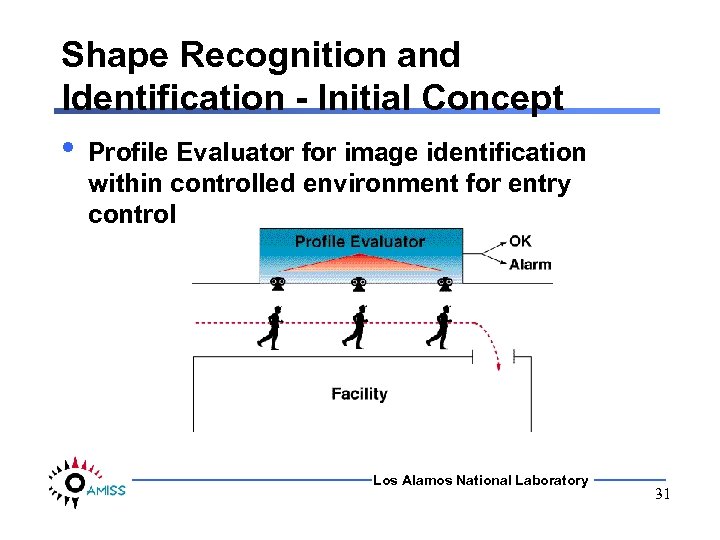 Shape Recognition and Identification - Initial Concept • Profile Evaluator for image identification within controlled environment for entry control Los Alamos National Laboratory 31
Shape Recognition and Identification - Initial Concept • Profile Evaluator for image identification within controlled environment for entry control Los Alamos National Laboratory 31
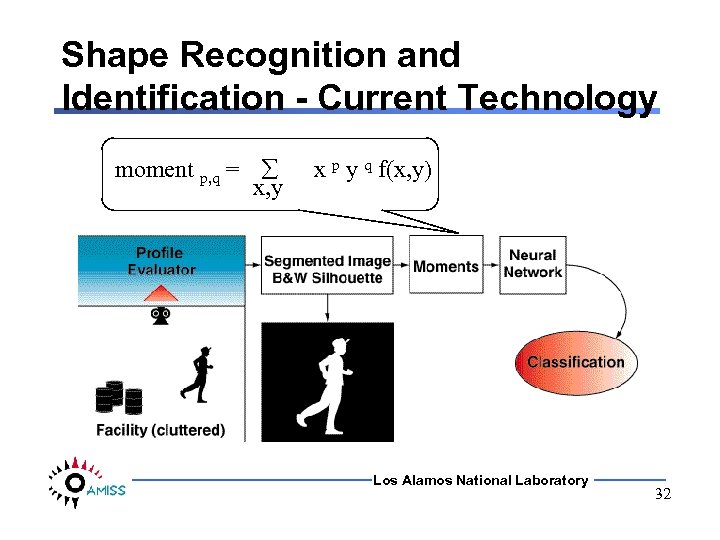 Shape Recognition and Identification - Current Technology moment p, q = x, y x p y q f(x, y) Los Alamos National Laboratory 32
Shape Recognition and Identification - Current Technology moment p, q = x, y x p y q f(x, y) Los Alamos National Laboratory 32
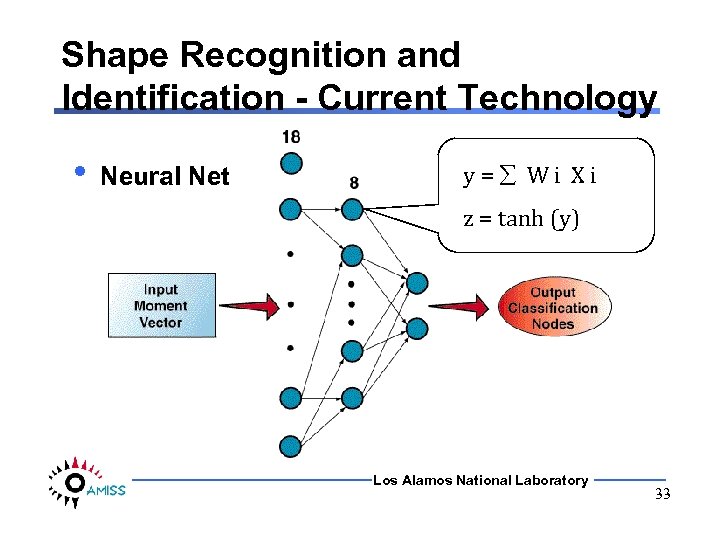 Shape Recognition and Identification - Current Technology • Neural Net y= Wi Xi z = tanh (y) Los Alamos National Laboratory 33
Shape Recognition and Identification - Current Technology • Neural Net y= Wi Xi z = tanh (y) Los Alamos National Laboratory 33
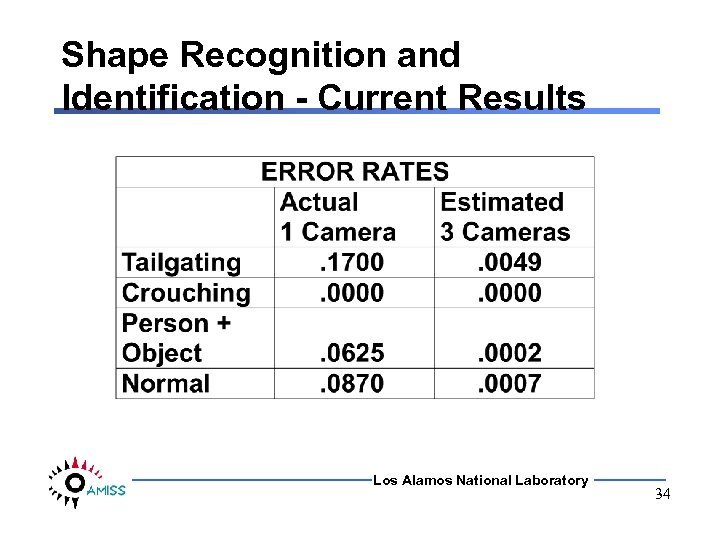 Shape Recognition and Identification - Current Results Los Alamos National Laboratory 34
Shape Recognition and Identification - Current Results Los Alamos National Laboratory 34
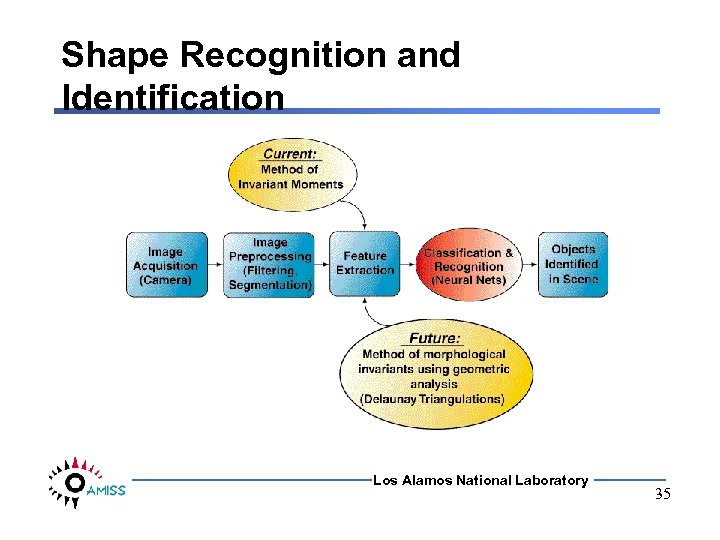 Shape Recognition and Identification Los Alamos National Laboratory 35
Shape Recognition and Identification Los Alamos National Laboratory 35
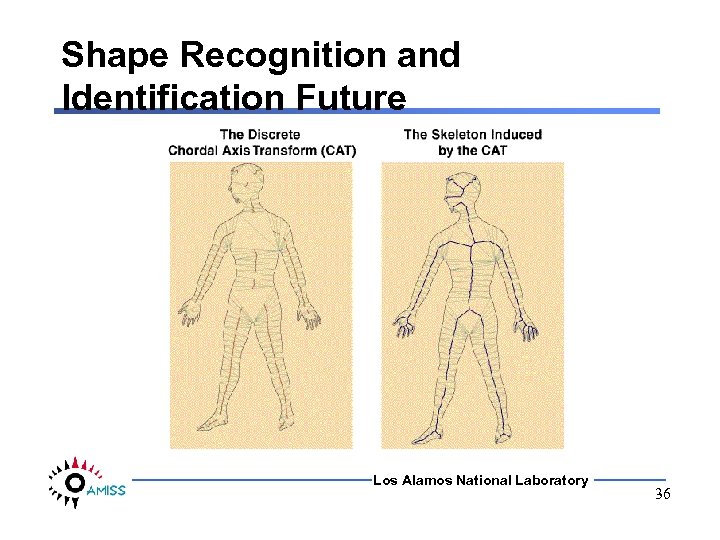 Shape Recognition and Identification Future Los Alamos National Laboratory 36
Shape Recognition and Identification Future Los Alamos National Laboratory 36
 Shape Recognition and Identification - Future • Detect and identify a complete inventory of objects in a scene – New Feature Extraction - Image Understanding – Better hardware – Post processing classification Los Alamos National Laboratory 37
Shape Recognition and Identification - Future • Detect and identify a complete inventory of objects in a scene – New Feature Extraction - Image Understanding – Better hardware – Post processing classification Los Alamos National Laboratory 37
 AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 38
AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 38
 Reasoning/Data Mining • ADaptive Virtual Integrating sen. SOR (ADVISOR) • Provide continuous, integrated facility status reasoned from real-time and historical data and human input. Los Alamos National Laboratory 39
Reasoning/Data Mining • ADaptive Virtual Integrating sen. SOR (ADVISOR) • Provide continuous, integrated facility status reasoned from real-time and historical data and human input. Los Alamos National Laboratory 39
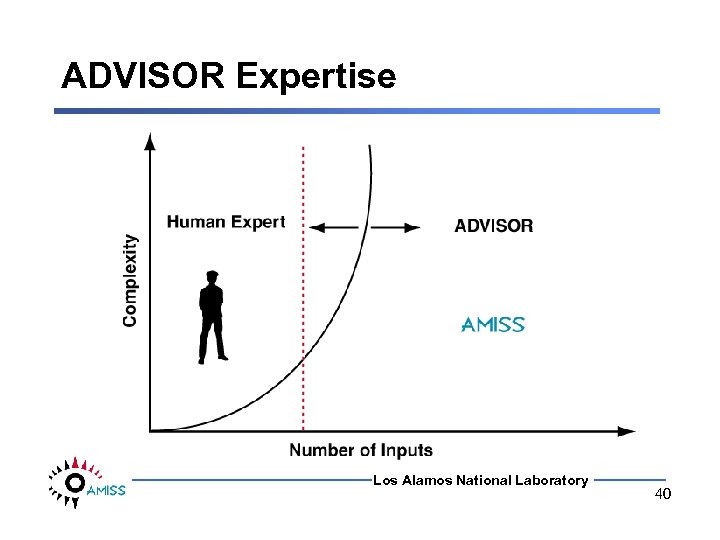 ADVISOR Expertise Los Alamos National Laboratory 40
ADVISOR Expertise Los Alamos National Laboratory 40
 ADVISOR Benefits • • Provides continuous real-time detection of procedure violations and anomalies Reduce information overload and tedious data analysis Consistent rule interpretation and application Continuous information integration Continuity of knowledge Provides detailed explanation capability Active role, advisory role or combination Los Alamos National Laboratory 41
ADVISOR Benefits • • Provides continuous real-time detection of procedure violations and anomalies Reduce information overload and tedious data analysis Consistent rule interpretation and application Continuous information integration Continuity of knowledge Provides detailed explanation capability Active role, advisory role or combination Los Alamos National Laboratory 41
 ADVISOR Objectives • • Knowledge engineering to obtain human expert experience Integrate policies and procedures Dynamic adaptation Learn normal facility status Los Alamos National Laboratory 42
ADVISOR Objectives • • Knowledge engineering to obtain human expert experience Integrate policies and procedures Dynamic adaptation Learn normal facility status Los Alamos National Laboratory 42
 ADVISOR Components • • • Real-time reasoning and control (current) Data mining Real-time integrated with data mining Los Alamos National Laboratory 43
ADVISOR Components • • • Real-time reasoning and control (current) Data mining Real-time integrated with data mining Los Alamos National Laboratory 43
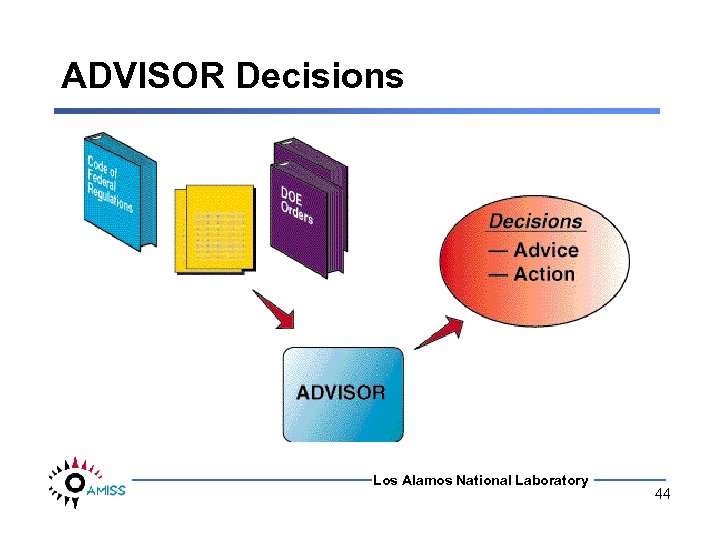 ADVISOR Decisions Los Alamos National Laboratory 44
ADVISOR Decisions Los Alamos National Laboratory 44
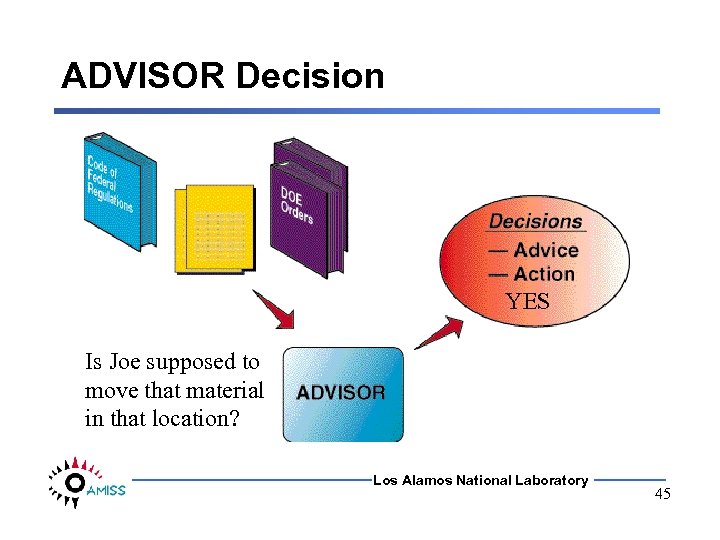 ADVISOR Decision YES Is Joe supposed to move that material in that location? Los Alamos National Laboratory 45
ADVISOR Decision YES Is Joe supposed to move that material in that location? Los Alamos National Laboratory 45
 ADVISOR Future • • • Develop System Health reasoning diagnostics Expand to multiple buildings and facilities Countermeasures (e. g. know when being fooled) New domain applications Develop and integrate data mining Los Alamos National Laboratory 46
ADVISOR Future • • • Develop System Health reasoning diagnostics Expand to multiple buildings and facilities Countermeasures (e. g. know when being fooled) New domain applications Develop and integrate data mining Los Alamos National Laboratory 46
 AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 47
AMISS Architecture Los Alamos National Laboratory 47
 Remote Operation • • World Wide Web (www) – Remote (e. g. global) – Secure (SSL) Remote alarm (e. g. notify guard through pager) Potential to take action immediately Operate several facilities Los Alamos National Laboratory 48
Remote Operation • • World Wide Web (www) – Remote (e. g. global) – Secure (SSL) Remote alarm (e. g. notify guard through pager) Potential to take action immediately Operate several facilities Los Alamos National Laboratory 48
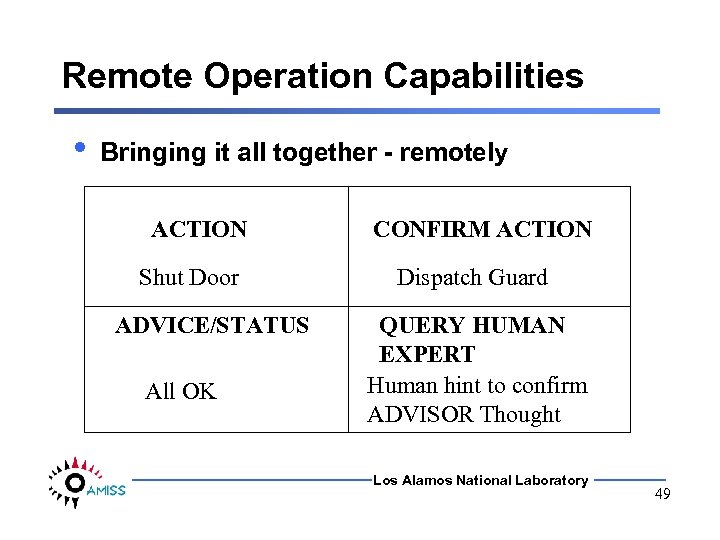 Remote Operation Capabilities • Bringing it all together - remotely ACTION Shut Door ADVICE/STATUS All OK CONFIRM ACTION Dispatch Guard QUERY HUMAN EXPERT Human hint to confirm ADVISOR Thought Los Alamos National Laboratory 49
Remote Operation Capabilities • Bringing it all together - remotely ACTION Shut Door ADVICE/STATUS All OK CONFIRM ACTION Dispatch Guard QUERY HUMAN EXPERT Human hint to confirm ADVISOR Thought Los Alamos National Laboratory 49
 AMISS Los Alamos National Laboratory 50
AMISS Los Alamos National Laboratory 50
 Potential Application Areas • MC&A at DOE Facilities • Treaty Verification • IAEA – Remote (unattended) monitoring – Environmental monitoring – Covert and/or underground facilities • Other – Critical infrastructure – Recent national and international incidents Los Alamos National Laboratory 51
Potential Application Areas • MC&A at DOE Facilities • Treaty Verification • IAEA – Remote (unattended) monitoring – Environmental monitoring – Covert and/or underground facilities • Other – Critical infrastructure – Recent national and international incidents Los Alamos National Laboratory 51
 AMISS Future • • Confidence versus redundancy Aging facilities Robust and hardened Adaptable, portable, scalable Address emerging requirements Define measurable performance measures Further reasoning development Integrate to entire facility Los Alamos National Laboratory 52
AMISS Future • • Confidence versus redundancy Aging facilities Robust and hardened Adaptable, portable, scalable Address emerging requirements Define measurable performance measures Further reasoning development Integrate to entire facility Los Alamos National Laboratory 52
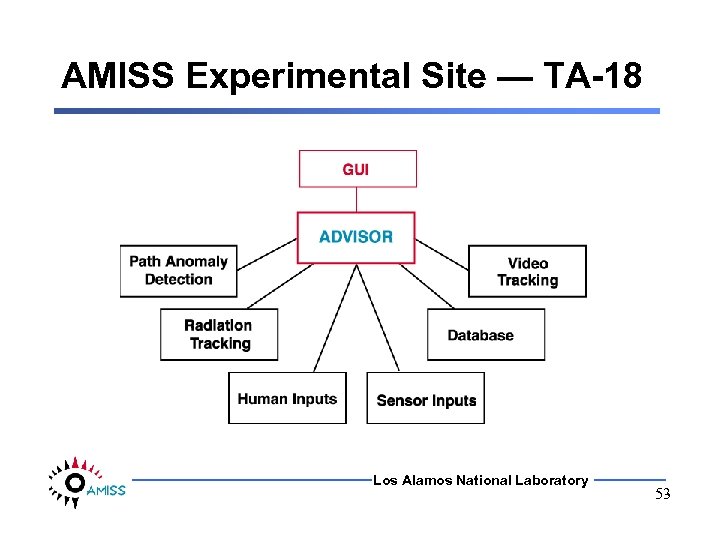 AMISS Experimental Site — TA-18 Los Alamos National Laboratory 53
AMISS Experimental Site — TA-18 Los Alamos National Laboratory 53
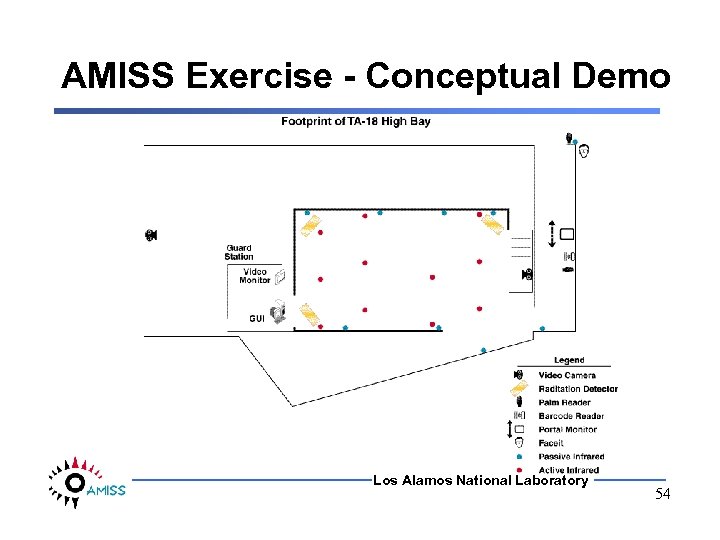 AMISS Exercise - Conceptual Demo Los Alamos National Laboratory 54
AMISS Exercise - Conceptual Demo Los Alamos National Laboratory 54
 AMISS Exercise - A Day In The Life • • • Identify and locate personnel and material Alert unauthorized activities, material shielding, and unauthorized movements Track paths of interest and detect anomalous behaviors Provide real-time facility status decisions based upon all available data sources Provide security personnel with effortless facility status view Los Alamos National Laboratory 55
AMISS Exercise - A Day In The Life • • • Identify and locate personnel and material Alert unauthorized activities, material shielding, and unauthorized movements Track paths of interest and detect anomalous behaviors Provide real-time facility status decisions based upon all available data sources Provide security personnel with effortless facility status view Los Alamos National Laboratory 55
 AMISS Exercise - A Day In The Life 1. Unlock High Bay – Alarm unauthorized entry 2. Security Sweep High Bay – Alert attempted sweep against protocol pattern 3. Experiment Entry Procedures – Alert improper approvals, personnel, materials, or schedule Los Alamos National Laboratory 56
AMISS Exercise - A Day In The Life 1. Unlock High Bay – Alarm unauthorized entry 2. Security Sweep High Bay – Alert attempted sweep against protocol pattern 3. Experiment Entry Procedures – Alert improper approvals, personnel, materials, or schedule Los Alamos National Laboratory 56
 AMISS Exercise - A Day In The Life 4. Perform Experiment – Alert improper procedures with material – Alarm invalid exit while material shielded 5. Experiment Exit Procedures – Alarm unauthorized material removal 6. Secure High Bay Los Alamos National Laboratory 57
AMISS Exercise - A Day In The Life 4. Perform Experiment – Alert improper procedures with material – Alarm invalid exit while material shielded 5. Experiment Exit Procedures – Alarm unauthorized material removal 6. Secure High Bay Los Alamos National Laboratory 57
 AMISS Integrated Exercise Los Alamos National Laboratory 58
AMISS Integrated Exercise Los Alamos National Laboratory 58
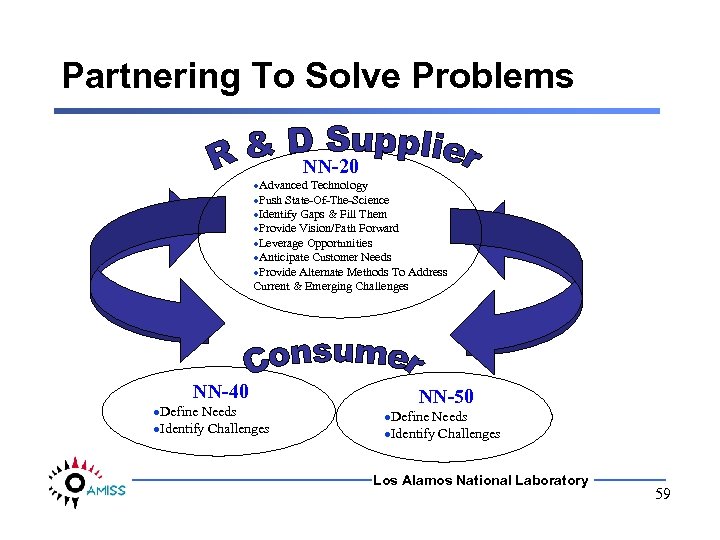 Partnering To Solve Problems NN-20 ·Advanced Technology ·Push State-Of-The-Science ·Identify Gaps & Fill Them ·Provide Vision/Path Forward ·Leverage Opportunities ·Anticipate Customer Needs ·Provide Alternate Methods To Address Current & Emerging Challenges NN-40 ·Define Needs ·Identify Challenges NN-50 ·Define Needs ·Identify Challenges Los Alamos National Laboratory 59
Partnering To Solve Problems NN-20 ·Advanced Technology ·Push State-Of-The-Science ·Identify Gaps & Fill Them ·Provide Vision/Path Forward ·Leverage Opportunities ·Anticipate Customer Needs ·Provide Alternate Methods To Address Current & Emerging Challenges NN-40 ·Define Needs ·Identify Challenges NN-50 ·Define Needs ·Identify Challenges Los Alamos National Laboratory 59
 Differences from Radiation Instrumentation Problems • Instrumentation imperfections – Moving source within integration interval – Sensor sensitivity decreases with angle and distance – Minimal detector technology Los Alamos National Laboratory 60
Differences from Radiation Instrumentation Problems • Instrumentation imperfections – Moving source within integration interval – Sensor sensitivity decreases with angle and distance – Minimal detector technology Los Alamos National Laboratory 60
 Radiation Detection • • Identify “Unusual” background changes Factors in developing “Decision Rules” – – Recognizable source strength Recognition time Time between events Acceptable error rates • • False positive False negative Los Alamos National Laboratory 61
Radiation Detection • • Identify “Unusual” background changes Factors in developing “Decision Rules” – – Recognizable source strength Recognition time Time between events Acceptable error rates • • False positive False negative Los Alamos National Laboratory 61
 Radiation Detectors • Gamma Detector – Gamma hits cause Fluorescence – Light flashes counted Los Alamos National Laboratory 62
Radiation Detectors • Gamma Detector – Gamma hits cause Fluorescence – Light flashes counted Los Alamos National Laboratory 62
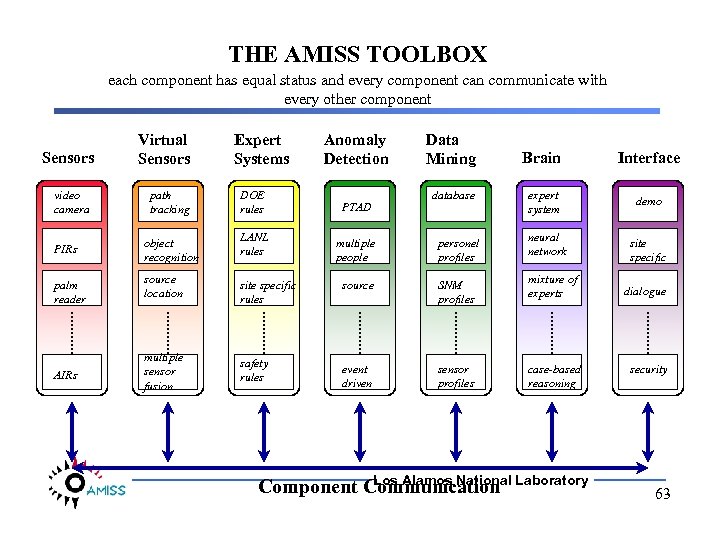 THE AMISS TOOLBOX each component has equal status and every component can communicate with every other component Sensors video camera Virtual Sensors Expert Systems Anomaly Detection Data Mining Brain Interface expert system demo site specific path tracking DOE rules PTAD PIRs object recognition LANL rules multiple people personel profiles neural network palm reader source location site specific rules source SNM profiles mixture of experts AIRs multiple sensor fusion safety rules event driven sensor profiles case-based reasoning database Los Alamos National Component Communication Laboratory dialogue security 63
THE AMISS TOOLBOX each component has equal status and every component can communicate with every other component Sensors video camera Virtual Sensors Expert Systems Anomaly Detection Data Mining Brain Interface expert system demo site specific path tracking DOE rules PTAD PIRs object recognition LANL rules multiple people personel profiles neural network palm reader source location site specific rules source SNM profiles mixture of experts AIRs multiple sensor fusion safety rules event driven sensor profiles case-based reasoning database Los Alamos National Component Communication Laboratory dialogue security 63
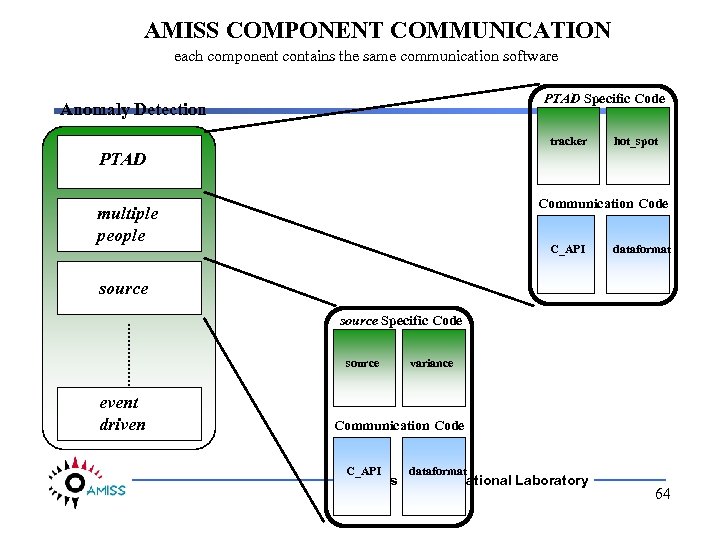 AMISS COMPONENT COMMUNICATION each component contains the same communication software PTAD Specific Code Anomaly Detection tracker hot_spot PTAD Communication Code multiple people C_API dataformat source Specific Code source event driven variance Communication Code C_API dataformat Los Alamos National Laboratory 64
AMISS COMPONENT COMMUNICATION each component contains the same communication software PTAD Specific Code Anomaly Detection tracker hot_spot PTAD Communication Code multiple people C_API dataformat source Specific Code source event driven variance Communication Code C_API dataformat Los Alamos National Laboratory 64
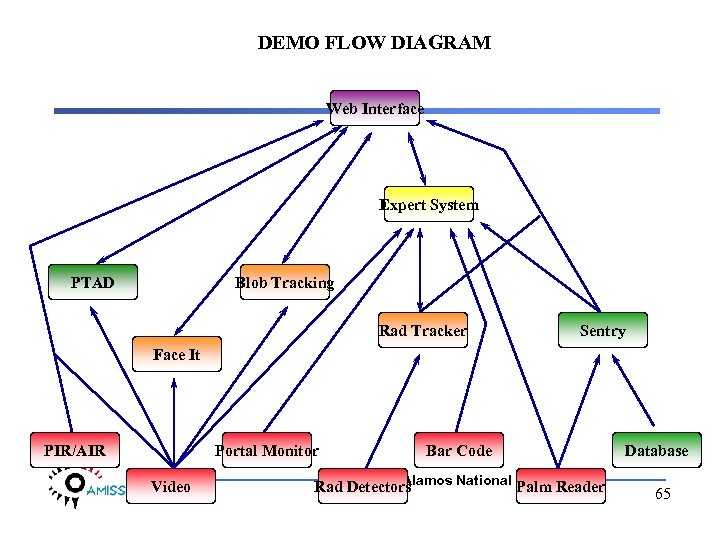 DEMO FLOW DIAGRAM Web Interface Expert System PTAD Blob Tracking Rad Tracker Sentry Face It PIR/AIR Portal Monitor Video Bar Code Los Alamos National Laboratory Rad Detectors Palm Reader Database 65
DEMO FLOW DIAGRAM Web Interface Expert System PTAD Blob Tracking Rad Tracker Sentry Face It PIR/AIR Portal Monitor Video Bar Code Los Alamos National Laboratory Rad Detectors Palm Reader Database 65
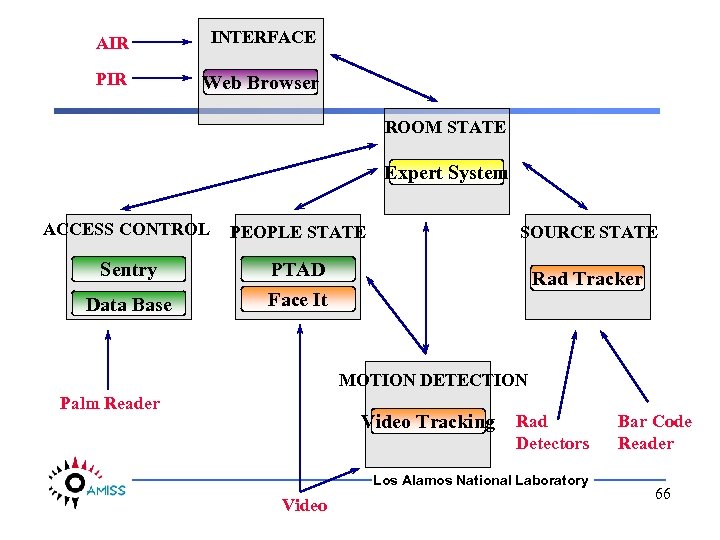 AIR INTERFACE PIR Web Browser ROOM STATE Expert System ACCESS CONTROL PEOPLE STATE SOURCE STATE Sentry PTAD Face It Rad Tracker Data Base MOTION DETECTION Palm Reader Video Tracking Rad Detectors Los Alamos National Laboratory Video Bar Code Reader 66
AIR INTERFACE PIR Web Browser ROOM STATE Expert System ACCESS CONTROL PEOPLE STATE SOURCE STATE Sentry PTAD Face It Rad Tracker Data Base MOTION DETECTION Palm Reader Video Tracking Rad Detectors Los Alamos National Laboratory Video Bar Code Reader 66


